Olumiant
These highlights do not include all the information needed to use OLUMIANT safely and effectively. See full prescribing information for OLUMIANT. OLUMIANT (baricitinib) tablets, for oral useInitial U.S. Approval: 2018
866e9f35-9035-4581-a4b1-75a621ab55cf
HUMAN PRESCRIPTION DRUG LABEL
Mar 20, 2023
Eli Lilly and Company
DUNS: 006421325
Products 3
Detailed information about drug products covered under this FDA approval, including NDC codes, dosage forms, ingredients, and administration routes.
baricitinib
Product Details
FDA regulatory identification and product classification information
FDA Identifiers
Product Classification
Product Specifications
INGREDIENTS (11)
baricitinib
Product Details
FDA regulatory identification and product classification information
FDA Identifiers
Product Classification
Product Specifications
INGREDIENTS (11)
baricitinib
Product Details
FDA regulatory identification and product classification information
FDA Identifiers
Product Classification
Product Specifications
INGREDIENTS (11)
Drug Labeling Information
PACKAGE LABEL.PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL
PACKAGE LABEL – OLUMIANT 4 mg 30ct Bottle
Rx Only
Always Dispense with Medication Guide
NDC 0002-4479-30
Olumiant®
(baricitinib) tablets
4 mg
30 tablets
Lilly

DRUG INTERACTIONS SECTION
7 DRUG INTERACTIONS
7.1 Strong OAT3 Inhibitors
Baricitinib exposure is increased when OLUMIANT is co-administered with strong OAT3 inhibitors (such as probenecid), hence the dosage of baricitinib should be reduced by half the recommended dose [see Dosage and Administration (2.2, 2.3) and Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)].
7.2 Other JAK Inhibitors or Biologic DMARDs
OLUMIANT has not been studied in combination with other JAK inhibitors or with biologic DMARDs [see Indications and Usage (1.1, 1.2)].
In patients taking strong Organic Anion Transporter 3 (OAT3) inhibitors (e.g., probenecid) the recommended dosage should be reduced. (2.7, 7.1)
RECENT MAJOR CHANGES SECTION
RECENT MAJOR CHANGES
|
Boxed Warning |
05/2022 |
|
Indications and Usage, COVID-19 (1.2) |
05/2022 |
|
Indications and Usage, Alopecia Areata (1.3) |
06/2022 |
|
Dosage and Administration (2.1, 2.2, 2.3, 2.8) |
05/2022 |
|
Dosage and Administration (2.4, 2.5, 2.6, 2.7) |
06/2022 |
|
Warnings and Precautions (5.1, 5.2, 5.3, 5.4, 5.5) |
12/2021 |
|
Warnings and Precautions (5.8) |
05/2022 |
USE IN SPECIFIC POPULATIONS SECTION
8 USE IN SPECIFIC POPULATIONS
8.1 Pregnancy
Risk Summary
Based on the findings from animal reproduction studies, OLUMIANT may cause fetal harm during pregnancy. Available data from clinical trials and postmarketing case reports with OLUMIANT exposure in pregnancy are insufficient to inform a drug-associated risk for major birth defects, miscarriage, or other adverse maternal or fetal outcomes. There are no human data on chronic baricitinib exposure throughout pregnancy. There are risks to the mother and the fetus associated with rheumatoid arthritis in pregnancy (see Clinical Considerations). Consider the risks and benefits with chronic use of OLUMIANT during pregnancy.
In animal embryo-fetal development studies, oral baricitinib administration to pregnant rats and rabbits at exposures equal to and greater than approximately 11 and 46 times the maximum recommended human dose (MRHD) of 4 mg/day, respectively, resulted in reduced fetal body weights, increased embryolethality (rabbits only), and dose-related increases in skeletal malformations. No developmental toxicity was observed in pregnant rats and rabbits treated with oral baricitinib during organogenesis at approximately 2 and 7 times the exposure at the MRHD, respectively. In a pre- and post-natal development study in pregnant female rats, oral baricitinib administration at exposures approximately 24 times the MRHD resulted in reduction in pup viability (increased incidence of stillborn pups and early neonatal deaths), decreased fetal birth weight, reduced fetal body weight gain, decreased cytotoxic T cells on post-natal day (PND) 35 with evidence of recovery by PND 65, and developmental delays that might be attributable to decreased body weight gain. No developmental toxicity was observed at an exposure approximately 5 times the exposure at the MRHD (see Data).
The background risks of major birth defects and miscarriage for the indicated population(s) are unknown. All pregnancies have a background risk of birth defect, loss, or other adverse outcomes. In the U.S. general population, the estimated background risk of major birth defects and miscarriage in clinically recognized pregnancies is 2-4% and 15-20%, respectively.
Report pregnancies to Eli Lilly and Company at 1-800-LillyRx (1-800-545-5979).
Clinical Considerations
Disease-Associated Maternal and/or Embryo/Fetal Risk
Published data suggest that increased disease activity is associated with the risk of developing adverse pregnancy outcomes in women with rheumatoid arthritis. Adverse pregnancy outcomes include preterm delivery (before 37 weeks of gestation), low birth weight (less than 2500 g) infants, and small for gestational age at birth.
Data
Animal Data
In an embryofetal development study in pregnant rats, dosed orally during the period of organogenesis from gestation days 6 to 17, baricitinib was teratogenic (skeletal malformations that consisted of bent limb bones and rib anomalies) at exposures equal to or greater than approximately 11 times the MRHD (on an AUC basis at maternal oral doses of 10 mg/kg/day and higher). No developmental toxicity was observed in rats at an exposure approximately 2 times the MRHD (on an AUC basis at a maternal oral dose of 2 mg/kg/day).
In an embryofetal development study in pregnant rabbits, dosed orally during the period of organogenesis from gestation days 7 to 20, embryolethality, decreased fetal body weights, and skeletal malformations (rib anomalies) were observed in the presence of maternal toxicity at an exposure approximately 46 times the MRHD (on an AUC basis at a maternal oral dose of 30 mg/kg/day). Embryolethality consisted of increased post-implantation loss that was due to elevated incidences of both early and late resorptions. No developmental toxicity was observed in rabbits at an exposure approximately 7 times the MRHD (on an AUC basis at a maternal oral dose of 10 mg/kg/day).
In a pre- and post-natal development study in pregnant female rats dosed orally from gestation day 6 through lactation day 20, adverse findings observed in pups included decreased survival from birth to post-natal day 4 (due to increased stillbirths and early neonatal deaths), decreased birth weight, decreased body weight gain during the pre-weaning phase, increased incidence of malrotated forelimbs during the pre-weaning phase, and decreased cytotoxic T cells on PND 35 with recovery by PND 65 at exposures approximately 24 times the MRHD (on an AUC basis at a maternal oral dose of 25 mg/kg/day). Developmental delays (that may be secondary to decreased body weight gain) were observed in males and females at exposures approximately 24 times the MRHD (on an AUC basis at a maternal oral dose of 25 mg/kg/day). These findings included decreased forelimb and hindlimb grip strengths, and delayed mean age of sexual maturity. No developmental toxicity was observed in rats at an exposure approximately 5 times the MRHD (on an AUC basis at a maternal oral dose of 5 mg/kg/day).
8.2 Lactation
Risk Summary
No information is available on the presence of OLUMIANT in human milk, the effects of the drug on the breastfed infant, or the effects of the drug on milk production. Baricitinib is present in the milk of lactating rats (see Data). Because of the potential for serious adverse reactions in nursing infants advise women not to breastfeed during treatment with OLUMIANT and for 4 days after the last dose (approximately 5 to 6 elimination half-lives).
Data
A single oral dose of 25 mg/kg radiolabeled baricitinib was administered to lactating female Sprague-Dawley rats on post-partum day 13. Drug exposure was approximately 45-fold greater in milk than in plasma based on AUC0-t values.
8.3 Females and Males of Reproductive Potential
Contraception
Based on animal studies, OLUMIANT may cause fetal harm when administered during pregnancy [see Use in Specific Populations (8.1)]. Consider pregnancy planning and prevention for females of reproductive potential.
8.4 Pediatric Use
The safety and effectiveness of OLUMIANT in pediatric patients have not been established.
8.5 Geriatric Use
Of the 3100 patients treated in the rheumatoid arthritis clinical trials, a total of 537 patients were 65 years of age and older, including 71 patients 75 years of age and older. Of the 2558 patients treated in the COVID-19 clinical trials, a total of 791 were 65 years of age and older, including 295 patients 75 years and older. No overall differences in safety or effectiveness were observed between these subjects and younger subjects, and other reported clinical experience has not identified differences in responses between the elderly and younger patients, but greater sensitivity of some older individuals cannot be ruled out [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)].
Of the 1200 patients in the alopecia areata clinical trials, a total of 29 patients were 65 years of age or older. The number of patients aged 65 years and older was not sufficient to determine whether they respond differently from younger patients.
OLUMIANT is known to be substantially excreted by the kidney, and the risk of adverse reactions to this drug may be greater in patients with impaired renal function. Because geriatric patients are more likely to have decreased renal function, care should be taken in dose selection, and it may be useful to monitor renal function [see Dosage and Administration (2.6)].
8.6 Hepatic Impairment
No dose adjustment is necessary in patients with mild or moderate hepatic impairment.
The use of OLUMIANT has not been studied in patients with rheumatoid arthritis or alopecia areata and severe hepatic impairment and is therefore not recommended. OLUMIANT has not been studied in patients with COVID-19 and severe hepatic impairment. OLUMIANT should only be used in patients with COVID-19 and severe hepatic impairment if the potential benefit outweighs the potential risk [see Dosage and Administration (2.6) and Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)].
8.7 Renal Impairment
Renal function was found to significantly affect baricitinib exposure.
Rheumatoid Arthritis and Alopecia Areata - The recommended dosage of OLUMIANT in patients with moderate renal impairment (estimated glomerular filtration rate (GFR) between 30 and <60 mL/min/1.73 m2) should be reduced by half the recommended dose. OLUMIANT is not recommended for use in patients with rheumatoid arthritis or alopecia areata and severe renal impairment (estimated GFR of less than 30 mL/min/1.73 m2) [see Dosage and Administration (2.6) and Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)].
COVID-19 - The recommended dosage of OLUMIANT in patients with moderate renal impairment (estimated GFR between 30 and <60 mL/min/1.732) or severe renal impairment (estimated GFR between 15 and <30 mL/min/1.73 m2) is 2 mg once daily and 1 mg once daily, respectively. OLUMIANT is not recommended for use in patients who are on dialysis, have end-stage renal disease (ESRD), or with estimated GFR of <15 mL/min/1.73 m2 [see Dosage and Administration (2.6) and Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)].
- Hepatic Impairment: Not recommended in patients with RA or AA and severe hepatic impairment. OLUMIANT has not been studied in patients with COVID-19 and severe hepatic impairment. (2.5, 8.6)
- Renal Impairment: Not recommended in COVID-19 patients with eGFR <15 mL/min/1.73m2, who are on dialysis, have ESRD, or acute kidney injury. OLUMIANT is not recommend in patients with RA or AA with eGFR <30 mL/min/1.73m2. (2.6, 8.7)
- Pregnancy: Based on animal data, may cause fetal harm. (8.1, 8.3)
- Lactation: Advise not to breastfeed. (8.2)
DESCRIPTION SECTION
11 DESCRIPTION
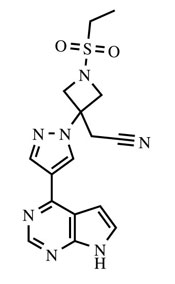
OLUMIANT (baricitinib) is a Janus kinase (JAK) inhibitor with the chemical name {1-(ethylsulfonyl)-3-[4-(7H-pyrrolo[2,3-d]pyrimidin-4-yl)-1H-pyrazol-1-yl]azetidin-3-yl}acetonitrile. Baricitinib has an empirical formula of C16H17N7O2S and a molecular weight of 371.42. Baricitinib has the following structural formula:
OLUMIANT tablets contain a recessed area on each face of the tablet surface and are available for oral administration as debossed, film-coated tablets. The 1 mg tablet is very light pink, round, debossed with “Lilly” on one side and “1” on the other. The 2 mg tablet is light pink, oblong, debossed with “Lilly” on one side and “2” on the other. The 4 mg tablet is medium pink, round, debossed with “Lilly” on one side and “4” on the other.
Each tablet contains 1, 2, or 4 mg of baricitinib and the following inactive ingredients: croscarmellose sodium, ferric oxide, lecithin (soya), magnesium stearate, mannitol, microcrystalline cellulose, polyethylene glycol, polyvinyl alcohol, talc and titanium dioxide.
NONCLINICAL TOXICOLOGY SECTION
13 NONCLINICAL TOXICOLOGY
13.1 Carcinogenesis, Mutagenesis, Impairment of Fertility
The carcinogenic potential of baricitinib was evaluated in Sprague-Dawley rats and Tg.rasH2 mice. No evidence of tumorigenicity was observed in male or female rats that received baricitinib for 91 to 94 weeks at oral doses up to 8 or 25 mg/kg/day, respectively (approximately 7 and 30 times the MRHD on an AUC basis). No evidence of tumorigenicity was observed in Tg.rasH2 mice that received baricitinib for 26 weeks at oral doses up to 300 and 150 mg/kg/day in male and female mice, respectively.
Baricitinib tested negative in the following genotoxicity assays: the in vitro bacterial mutagenicity assay (Ames assay), in vitro chromosome aberration assay in human peripheral blood lymphocytes, and in vivo rat bone marrow micronucleus assay.
Fertility (achievement of pregnancy) was reduced in male and female rats that received baricitinib at oral doses of 50 and 100 mg/kg/day respectively (approximately 62 and 93 times the MRHD in males and females, respectively, on an AUC basis) based upon findings that 7 of 19 (36.8%) drug-treated females with evidence of mating were not gravid compared to 1 of 19 (5.3%) control females. It could not be determined from the study design if these findings were attributable to toxicities in one sex or both. Fertility was unaffected in male and female rats at oral doses of 15 mg/kg and 25 mg/kg, respectively (approximately 13 and 26 times the MRHD on an AUC basis). However, maintenance of pregnancy was adversely affected at these doses based upon findings of increased post-implantation losses (early resorptions) and decreased numbers of mean viable embryos per litter. The number of viable embryos was unaffected in female rats that received baricitinib at an oral dose of 5 mg/kg/day and were mated to males that received the same dose (approximately 6 times the MRHD on an AUC basis). Reproductive performance was unaffected in male and female rats that received baricitinib at oral doses up to 50 and 100 mg/kg/day respectively (approximately 62 and 93 times the MRHD in males and females, respectively, on an AUC basis).
CLINICAL STUDIES SECTION
14 CLINICAL STUDIES
14.1 Rheumatoid Arthritis
The OLUMIANT clinical development program included two dose-ranging trials and four confirmatory phase 3 trials in patients with rheumatoid arthritis (RA). Although other doses have been studied, the recommended dosage of OLUMIANT is 2 mg once daily.
Dose-Ranging Studies
The dose-ranging studies RA-1 (NCT01185353) and RA-2 (NCT01469013) included a 12-week randomized comparison of baricitinib 1, 2, 4, and 8 mg orally once daily versus placebo in 301 and 145 patients, respectively.
The results from the dose-ranging studies are shown in Table 11. In dose- ranging Study RA-1, the observed ACR response was similar for baricitinib 1 and 2 mg daily and for baricitinib 4 and 8 mg daily, with the highest response for baricitinib 8 mg daily. In dose-ranging Study RA-2, there was not a clear trend of dose response, with similar response rates for 1 mg and 4 mg and 2 mg and 8 mg.
Table 11: Proportion of Patients with ACR20 Response at Week 12 in Dose-Ranging RA Studies|
% ACR20 Responders | |||||
|
Dose-Ranging Study |
Placebo |
Baricitinib |
Baricitinib |
Baricitinib |
Baricitinib |
|
RA-1 (N=301) |
41 |
57 |
54 |
75 |
78 |
|
RA-2 (N=145) |
31 |
67 |
83 |
67 |
88 |
Confirmatory Studies
The efficacy and safety of OLUMIANT 2 mg once daily was assessed in two confirmatory phase 3 trials. These trials were randomized, double-blind, multicenter studies in patients with active rheumatoid arthritis diagnosed according to American College of Rheumatology (ACR)/European League Against Rheumatism 2010 criteria. Patients over 18 years of age were eligible if at least 6 tender and 6 swollen joints were present at baseline. The two studies (Studies RA-3 and RA-4) evaluated OLUMIANT 2 mg and baricitinib 4 mg.
Study RA-3 (NCT01721057) was a 24-week trial in 684 patients with moderately to severely active rheumatoid arthritis who had an inadequate response or intolerance to conventional DMARDs (cDMARDs). Patients received OLUMIANT 2 mg or 4 mg once daily or placebo added to existing background cDMARD treatment. From Week 16, non-responding patients could be rescued to receive baricitinib 4 mg once daily. The primary endpoint was the proportion of patients who achieved an ACR20 response at Week 12.
Study RA-4 (NCT01721044) was a 24-week trial in 527 patients with moderately to severely active rheumatoid arthritis who had an inadequate response or intolerance to 1 or more TNF inhibitor therapies with or without other biologic DMARDs (TNFi-IR). Patients received OLUMIANT 2 mg or baricitinib 4 mg once daily or placebo added to background cDMARD treatment. From Week 16, non- responding patients could be rescued to receive baricitinib 4 mg once daily. The primary endpoint was the proportion of patients who achieved an ACR20 response at Week 12.
Clinical Response
The percentages of OLUMIANT-treated patients achieving ACR20, ACR50, and ACR70 responses, and Disease Activity Score (DAS28-CRP) <2.6 in Studies RA-3 and RA-4 are shown in Table 8.
Patients treated with OLUMIANT had higher rates of ACR response and DAS28-CRP <2.6 versus placebo-treated patients at Week 12 (Studies RA-3 and RA-4) (Table 12).
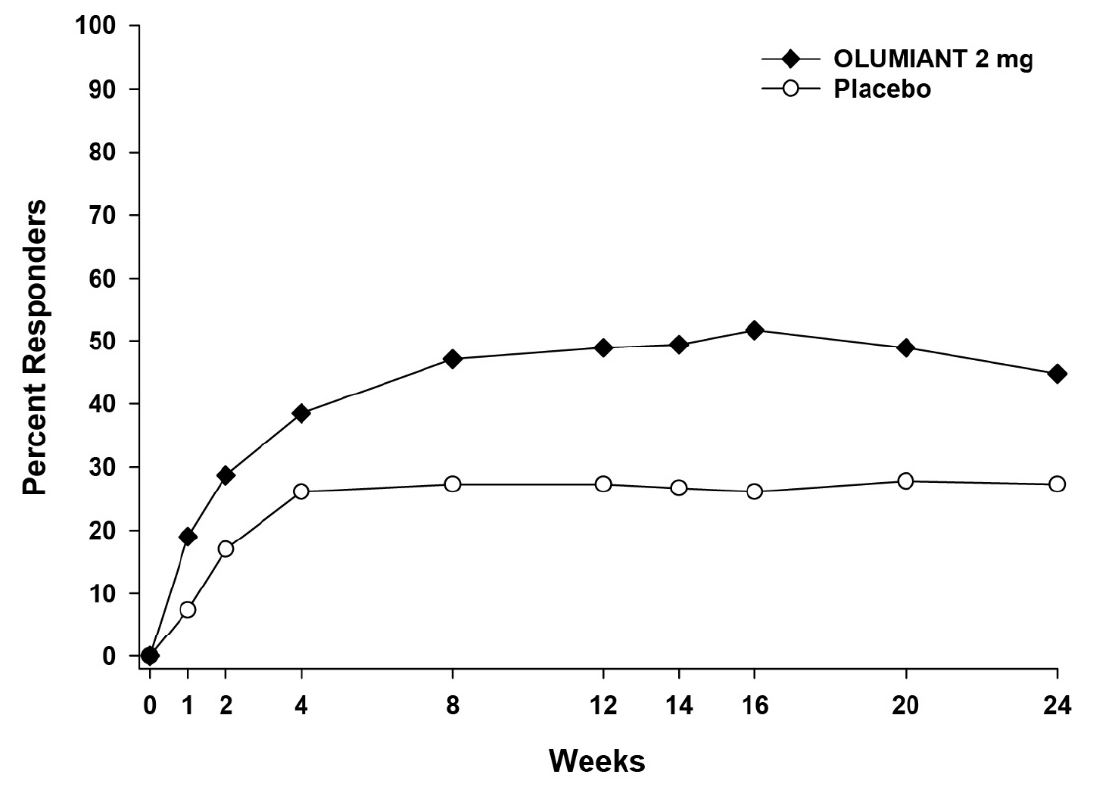
In Study RA-4, higher ACR20 response rates (Figure 4) were observed as early as 1 week with OLUMIANT 2 mg versus placebo.
In Study RA-4, the proportions of patients achieving DAS28-CRP <2.6 who had at least 3 active joints at the end of Week 24 were 18.2% and 10.5%, in the placebo and OLUMIANT 2 mg arms, respectively.
Table 12: Clinical Response in RA Studies RA-3 and RA-4a|
a Patients who were rescued or discontinued treatment were considered as non- responders in the analyses. | ||||
|
b 95% confidence interval for the difference (∆) in response rate between OLUMIANT treatment and placebo (Study RA-3, Study RA-4). | ||||
|
Percent of Patients | ||||
|
cDMARD-IR |
TNFi-IR | |||
|
Study RA-3 |
Study RA-4 | |||
|
Placebo + cDMARDs |
OLUMIANT **∆ (95% CI)**b |
Placebo + cDMARDs |
OLUMIANT **∆ (95% CI)**b | |
|
N |
228 |
229 |
176 |
174 |
|
ACR 20 | ||||
|
Week 12 |
39 |
66 |
27 |
49 |
|
Week 24 |
42 |
61 |
27 |
45 |
|
ACR 50 | ||||
|
Week 12 |
13 |
34 |
8 |
20 |
|
Week 24 |
21 |
41 |
13 |
23 |
|
ACR 70 | ||||
|
Week 12 |
3 |
18 |
2 |
13 |
|
Week 24 |
8 |
25 |
3 |
13 |
|
DAS28-CRP<2.6 | ||||
|
Week 12 |
9 |
26 |
4 |
11 |
|
Week 24 |
11 |
31 |
6 |
11 |
The effects of OLUMIANT treatment on the components of the ACR response criteria for Studies RA-3 and RA-4 are shown in Table 13.
Table 13: Components of ACR Response at Week 12 in RA Studies RA-3 and RA-4a|
a Data shown are mean (standard deviation). | ||||
|
b Visual analog scale: 0=best, 100=worst. | ||||
|
c Health Assessment Questionnaire–Disability Index: 0=best, 3=worst; 20 questions; 8 categories: dressing and grooming, arising, eating, walking, hygiene, reach, grip, and activities. | ||||
|
cDMARD-IR |
TNFi-IR | |||
|
Study RA-3 |
Study RA-4 | |||
|
Placebo |
OLUMIANT |
Placebo |
OLUMIANT | |
|
N |
228 |
229 |
176 |
174 |
|
Number of Tender Joints (0-68) | ||||
|
Baseline |
24 (15) |
24 (14) |
28 (16) |
31 (16) |
|
Week 12 |
15 (14) |
11 (13) |
20 (16) |
19 (18) |
|
Number of Swollen Joints (0-66) | ||||
|
Baseline |
13 (7) |
14 (9) |
17 (11) |
19 (12) |
|
Week 12 |
8 (8) |
5 (6) |
12 (10) |
10 (12) |
|
Pain****b | ||||
|
Baseline |
57 (23) |
60 (21) |
65 (19) |
62 (22) |
|
Week 12 |
43 (24) |
34 (25) |
55 (25) |
46 (28) |
|
Patient Global Assessment****b | ||||
|
Baseline |
60 (21) |
62 (20) |
66 (19) |
67 (19) |
|
Week 12 |
44 (23) |
36 (25) |
56 (25) |
46 (26) |
|
Physician Global Assessment****b | ||||
|
Baseline |
62 (17) |
64 (17) |
67 (19) |
67 (17) |
|
Week 12 |
41 (24) |
33 (22) |
50 (26) |
36 (24) |
|
**Disability Index (HAQ-DI)**c | ||||
|
Baseline |
1.50 (0.60) |
1.51 (0.62) |
1.78 (0.57) |
1.71 (0.55) |
|
Week 12 |
1.17 (0.62) |
0.96 (0.69) |
1.59 (0.68) |
1.31 (0.72) |
|
hsCRP (mg/L) | ||||
|
Baseline |
17.7 (20.4) |
18.2 (21.5) |
20.6 (25.3) |
19.9 (22.5) |
|
Week 12 |
17.2 (19.3) |
8.6 (14.6) |
19.9 (23.0) |
13.5 (20.1) |
Figure 4: Percent of RA Patients Achieving ACR20 in Study RA-4
Physical Function Response
Improvement in physical function was measured by the Health Assessment Questionnaire-Disability Index (HAQ-DI). Patients receiving OLUMIANT 2 mg demonstrated greater improvement from baseline in physical functioning compared to placebo at Week 24. The mean difference (95% CI) from placebo in HAQ-DI change from baseline at Week 24 was -0.24 (-0.35, -0.14) in Study RA-3 and -0.23 (-0.35, -0.12) in Study RA-4.
Other Health Related Outcomes
General health status was assessed by the Short Form health survey (SF-36). In Studies RA-3 and RA-4, compared to placebo, patients treated with OLUMIANT 2 mg demonstrated greater improvement from baseline in the physical component summary (PCS) score and the physical function, role physical, bodily pain, vitality, and general health domains at Week 12, with no consistent improvements in the mental component summary (MCS) scores or the role emotional, mental health, and social functioning domains.
14.2 COVID-19
The efficacy and safety of baricitinib were assessed in 2 Phase 3, randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled clinical trials:
- COVID I (NCT04401579), which evaluated the combination of baricitinib 4 mg + remdesivir compared to placebo + remdesivir.
- COVID II (NCT04421027), which evaluated baricitinib 4 mg compared to placebo. Patients could remain on background therapy, as defined per local guidelines. An additional exploratory sub-study in patients requiring invasive mechanical ventilation or ECMO at baseline was also conducted under this protocol and analyzed separately.
COVID I
A randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled clinical trial (NCT04401579) of hospitalized adults with confirmed SARS-CoV-2 infection compared treatment with baricitinib plus remdesivir (n = 515) with placebo plus remdesivir (n = 518). Patients had to have laboratory-confirmed SARS-CoV-2 infection as well as at least one of the following to be enrolled in the trial: radiographic infiltrates by imaging, SpO2 ≤94% on room air, a requirement for supplemental oxygen, or a requirement for mechanical ventilation or ECMO. Patients treated with the combination received the following regimen:
- Baricitinib 4 mg once daily (orally) for up to 14 days or until hospital discharge, whichever came first
- Remdesivir 200 mg on Day 1 and 100 mg once daily (via intravenous infusion) on subsequent days for a total treatment duration of 10 days or until hospital discharge
In this study prophylaxis for venous thromboembolic event (VTEs) was recommended for all patients unless a major contraindication was noted.
For the overall population (N = 1033 patients) at randomization, mean age was 55 years (with 30% of patients aged 65 or older); 63% of patients were male, 51% were Hispanic or Latino, 48% were White, 15% were Black or African American, and 10% were Asian; 14% did not require supplemental oxygen, 55% required supplemental oxygen, 21% required non-invasive ventilation or high- flow oxygen, and 11% required invasive mechanical ventilation or ECMO. The most common comorbidities were obesity (56%), hypertension (52%), and type 2 diabetes (37%). Demographics and disease characteristics were balanced across the combination group and the placebo group.
The primary endpoint, for the intent to treat population, was time to recovery within 29 days after randomization. Recovery was defined as being discharged from the hospital without limitations on activities, being discharged from the hospital with limitations on activities and/or requiring home oxygen or hospitalized but not requiring supplemental oxygen and no longer requiring medical care. The key secondary endpoint was clinical status on Day 15 assessed on an 8-point ordinal scale (OS) consisting of the following categories:
- Not hospitalized, no limitations on activities [OS-1];
- Not hospitalized, limitation on activities and/or requiring home oxygen [OS-2];
- Hospitalized, not requiring supplemental oxygen - no longer requires ongoing medical care [OS-3];
- Hospitalized, not requiring supplemental oxygen - requiring ongoing medical care (COVID-19 related or otherwise) [OS 4];
- Hospitalized, requiring supplemental oxygen [OS 5];
- Hospitalized, on non-invasive ventilation or high-flow oxygen devices [OS 6];
- Hospitalized, on invasive mechanical ventilation or ECMO [OS 7]; and
- Death [OS 8]
For the overall population, the median time to recovery (defined as discharged from hospital or hospitalized but not requiring supplemental oxygen or ongoing medical care) was 7 days for baricitinib + remdesivir compared to 8 days for placebo + remdesivir [hazard ratio: 1.16 (95% CI 1.01, 1.33); p = 0.035].
Patients assigned to baricitinib + remdesivir were more likely to have a better clinical status (according to an 8-point ordinal scale) at Day 15 compared to patients assigned to placebo + remdesivir [odds ratio: 1.26 (95% CI 1.01, 1.57); p = 0.044].
The proportion of patients who died or progressed to non-invasive ventilation/high-flow oxygen or invasive mechanical ventilation by Day 29 was lower in baricitinib + remdesivir (23%) compared to placebo + remdesivir (28%) [odds ratio: 0.74 (95% CI 0.56, 0.99); p = 0.039]. Patients who required non- invasive ventilation/high-flow oxygen or invasive mechanical ventilation (including ECMO) at baseline needed to worsen by at least 1 point on an 8-point ordinal scale to progress.
The proportion of patients who died by Day 29 was 4.7% (24/515) for baricitinib + remdesivir compared to 7.1% (37/518) for placebo + remdesivir [Kaplan Meier estimated difference in Day 29 probability of mortality: -2.6% (95% CI: -5.8%, 0.5%); hazard ratio = 0.65 (95% CI: 0.39, 1.09)].
COVID II
A randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled clinical trial (NCT04421027) of hospitalized adults with confirmed SARS-CoV-2 infection compared treatment with baricitinib 4mg once daily (n = 764) with placebo (n = 761) for 14 days or hospital discharge, whichever came first. Patients could remain on background standard of care, as defined per local guidelines, including antimalarials, antivirals, corticosteroids, and/or azithromycin. In this study prophylaxis for venous thromboembolic event (VTE) was required for all patients unless contraindicated.
The most frequently used therapies at baseline were:
- corticosteroids (79% of patients, mostly dexamethasone)
- remdesivir (19% of patients)
Patients had to have laboratory-confirmed SARS-CoV-2 infection, at least one instance of elevation in at least one inflammatory marker above the upper limit of normal according to local laboratory ranges (CRP, D-dimer, LDH, ferritin), and at least one of the following to be enrolled in the trial: radiographic infiltrates by imaging, SpO2 <94% on room air, evidence of active COVID infection (with clinical symptoms including any of the following: fever, vomiting, diarrhea, dry cough, tachypnea defined as respiratory rate >24 breaths/min) or requirement for supplemental oxygen.
For the overall population (N = 1525 patients) at randomization, mean age was 58 years (with 33% of patients aged 65 or older); 63% of patients were male, 60% were White, 5% were Black or African American, 11% were Asian; 12% did not require supplemental oxygen (OS 4), 63% required supplemental oxygen (OS 5), 24% required non-invasive ventilation or high-flow oxygen (OS 6). The most common comorbidities were hypertension (48%), obesity (33%), and type 2 diabetes (29%). Demographics and disease characteristics were balanced across the baricitinib and placebo groups.
The primary endpoint was the proportion of patients who died or progressed to non-invasive ventilation/high-flow oxygen or invasive mechanical ventilation within the first 28-days of the study. Patients who required non-invasive ventilation/high-flow oxygen at baseline needed to worsen by at least 1 point on an 8-point OS to progress (refer to the description of COVID I for the definition of the 8-point OS). A key secondary endpoint was all-cause mortality by Day 28.
The estimated proportion of patients who died or progressed to non-invasive ventilation/high-flow oxygen or invasive mechanical ventilation was lower in patients treated with baricitinib (27.8%) compared to placebo (30.5%), but this effect was not statistically significant [odds ratio: 0.85 (95% CI 0.67, 1.08); p = 0.180].
The proportion of patients who died by Day 28 was 8.1% (62/764) for baricitinib compared to 13.3% (101/761) for placebo [estimated difference in Day 28 probability of mortality = -4.9% (95% CI: -8.0%, -1.9%); hazard ratio = 0.56 (95% CI: 0.41, 0.77)].
COVID II Exploratory Sub-Study
In a separate group of patients requiring invasive mechanical ventilation or ECMO at baseline and enrolled in an addendum to COVID II, a pre-specified exploratory analysis showed that the proportion who died by Day 28 was 39.2% (20/51) for baricitinib compared to 58.0% (29/50) for placebo [estimated difference in Day 28 risk of mortality = -18.8% (95% CI: -36.3%, 0.6%); hazard ratio = 0.54 (95% CI: 0.31, 0.96)].
14.3 Alopecia Areata
Two randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trials [Trials AA-1 (NCT03570749) and AA-2 (NCT03899259)] enrolled a total of 1200 patients, with alopecia areata (AA), who had at least 50% scalp hair loss as measured by the Severity of Alopecia Tool (SALT) for more than 6 months. The trials enrolled males 18 to 60 years of age and females 18 to 70 years of age. Among the patients enrolled, 61% were female, 2% were 65 years of age or older, and 52% were White, 36% were Asian, and 8% were Black. At baseline, 53% of patients had at least 95% scalp hair loss, 34% had their current episode lasting at least 4 years, 69% had significant gaps in eyebrow hair or no notable eyebrow hair, and 58% had significant gaps in eyelashes or no notable eyelashes.
In the Phase 3 portion of Trial AA-1 and in Trial AA-2, patients received OLUMIANT 2 mg, OLUMIANT 4 mg, or placebo once daily.
Both trials assessed the proportion of patients who achieved at least 80% scalp hair coverage (SALT score of ≤20) at Week 36 as the primary endpoint. Other outcomes at Week 36 included the proportion of patients who achieved at least 90% scalp hair coverage (SALT score of ≤10), patients with Scalp Hair Assessment PRO™ score of 0 or 1 with at least 2-point reduction on the 5-point scale, and assessments of eyebrow and eyelash hair loss.
Clinical Response
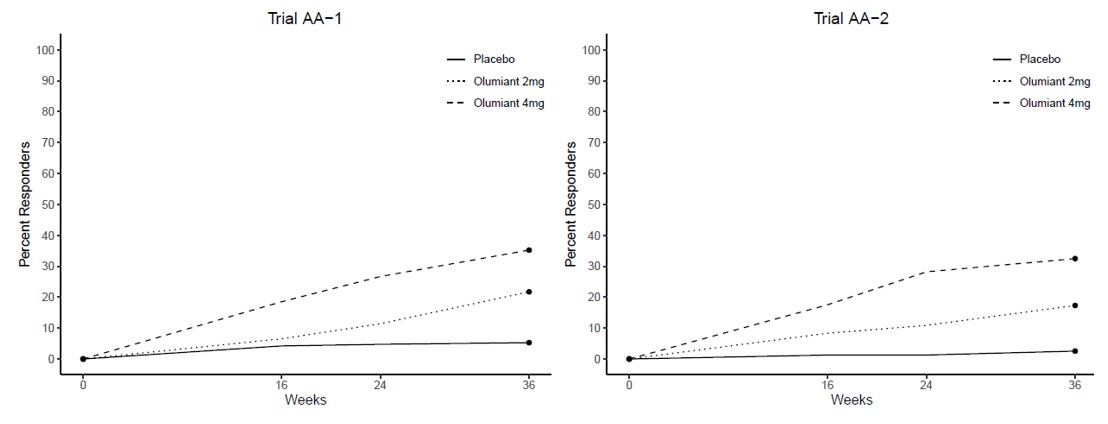
The results of the OLUMIANT trials (AA-1 and AA-2) are provided in Table 14 and Figure 5.
Table 14: Clinical Response at Week 36 in Patients with Severe AA|
a Not statistically significant under the multiplicity control plan | ||||||
|
b Patients evaluated scalp hair coverage on a 5-point scale where 0 = No missing hair (0% of scalp hair missing; full head of hair), 1 = A limited area of scalp hair loss (1% to 20%), 2 = moderate scalp hair loss (21% to 49%), 3 = a large area of scalp hair loss (50% to 94%), and 4 = nearly all or all scalp hair loss (95% to 100%). | ||||||
|
Trial AA-1 |
Trial AA-2 | |||||
|
Placebo |
OLUMIANT |
OLUMIANT |
Placebo |
OLUMIANT |
OLUMIANT | |
|
Number of subjects with at least 50% scalp hair loss at baseline | ||||||
|
N |
189 |
184 |
281 |
156 |
156 |
234 |
|
SALT ≤ 20 |
5% |
22% |
35% |
3% |
17% |
32% |
|
SALT ≤ 10 |
4% |
13% |
26% |
1% |
11% |
24% |
|
Number of subjects reporting Scalp Hair Assessment PRO™ score ≥3 at baseline | ||||||
|
N |
181 |
175 |
275 |
151 |
149 |
215 |
|
Scalp Hair Assessment PRO score of 0 or 1b |
5% |
16% |
33% |
4% |
16% |
34% |
Among patients with substantial eyebrow and eyelash hair loss at baseline, an improvement in eyebrow and eyelash coverage was observed on OLUMIANT 4 mg once daily dosage at Week 36.
Figure 5: Percent of Patients Achieving SALT ≤20
Analyses by age, gender, race, and body weight did not identify differences in response to 36-weeks of treatment with OLUMIANT among these subgroups. SALT ≤20 response rates were higher in all dose groups in patients with baseline SALT 50 to 94 versus SALT 95 to 100. See Table 15.
Table 15: SALT ≤20 at Week 36 by Baseline SALT Severity in AA|
Trials AA-1 and AA-2 | |||
|
Placebo |
OLUMIANT |
OLUMIANT | |
|
50 % to 94% Scalp Hair Loss |
166 |
147 |
248 |
|
95 % to 100% Scalp Hair Loss |
178 |
193 |
267 |
In AA-2, patients who achieved adequate response (SALT ≤20) to OLUMIANT 4 mg once daily at 52 weeks of treatment entered a randomized down-titration period and received OLUMIANT 2 mg once daily or remained on OLUMIANT 4 mg once daily. After an additional 24 weeks of treatment (76 weeks total), 75% (30/40) of patients randomized to OLUMIANT 2 mg once daily maintained response and 98% (41/42) of patients who remained on OLUMIANT 4 mg once daily maintained response.
HOW SUPPLIED SECTION
16 HOW SUPPLIED/STORAGE AND HANDLING
16.1 How Supplied
OLUMIANT for oral administration is available as debossed, film-coated, tablets. Each tablet contains a recessed area on each face of the tablet surface.
|
OLUMIANT Tablets |
1 mg |
2 mg |
4 mg |
|
Color |
Very Light Pink |
Light Pink |
Medium Pink |
|
Shape |
Round |
Oblong |
Round |
|
Identification |
Lilly |
Lilly |
Lilly |
|
1 |
2 |
4 | |
|
NDC Codes | |||
|
Bottle of 30 |
0002-4732-30 |
0002-4182-30 |
0002-4479-30 |
16.2 Storage and Handling
Store at 20°C to 25°C (68°F to 77°F); excursions permitted to 15°C to 30°C (59°F to 86°F) [see USP Controlled Room Temperature].
Keep out of reach of children.
INFORMATION FOR PATIENTS SECTION
17 PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATION
Advise the patient to read the FDA-approved patient labeling (Medication Guide).
Infections
Inform patients that they may be more likely to develop infections when taking OLUMIANT. Instruct patients to tell their healthcare provider if they develop any signs or symptoms of an infection [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)].
Advise patients that the risk of herpes zoster is increased in patients treated with OLUMIANT and some cases can be serious [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)].
Malignancies and Lymphoproliferative Disorders
Inform patients that OLUMIANT may increase their risk of developing lymphomas and other malignancies, including of the skin and that periodic skin examinations should be performed while using OLUMIANT. Instruct patients to inform their healthcare provider if they have ever had any type of cancer [see Warnings and Precautions (5.3)].
Major Adverse Cardiovascular Events
Inform patients that OLUMIANT may increase their risk of major adverse cardiovascular events (MACE) including myocardial infarction, stroke, and cardiovascular death. Instruct all patients, especially current or past smokers or patients with other cardiovascular risk factors, to be alert for the development of signs and symptoms of cardiovascular events [see Warnings and Precautions (5.4)].
Thrombosis
Advise patients that events of DVT and PE have been reported in clinical studies with OLUMIANT. Instruct patients to seek immediate medical attention if they develop any signs or symptoms of a DVT or PE [see Warnings and Precautions (5.5)].
Hypersensitivity Reactions
Advise patients to discontinue OLUMIANT and seek immediate medical attention if they develop any signs and symptoms of serious allergic reactions [see Warnings and Precautions (5.6)].
Gastrointestinal Perforations
Inform patients that gastrointestinal perforations have been reported in clinical trials with OLUMIANT. Instruct patients to seek medical care immediately if they experience new onset of abdominal pain, fever, chills, nausea, or vomiting [see Warnings and Precautions (5.7)].
Laboratory Abnormalities
Inform patients that OLUMIANT may affect certain lab tests, and that blood tests are required before and during OLUMIANT treatment [see Warnings and Precautions (5.8)].
Live Vaccines
Instruct patients to inform the healthcare practitioner that they are taking OLUMIANT prior to a potential vaccination since the use of live vaccine is not recommended [see Warnings and Precautions (5.9)].
Pregnancy
Advise pregnant females and females of reproductive potential of the potential risk to a fetus and to inform their healthcare provider if they are pregnant or intend to become pregnant during treatment with OLUMIANT. Inform patients to report their pregnancy to Eli Lilly and Company at 1-800-LillyRx (1-800-545-5979) [see Use in Specific Populations (8.1, 8.3)].
Lactation
Advise a woman not to breastfeed during treatment with OLUMIANT and for four days after the last dose [see Use in Specific Populations (8.2)].
Literature revised: 06/2022
Marketed by: Lilly USA, LLC, Indianapolis, IN 46285, USA
www.olumiant.com
Copyright © 2018, 2022, Eli Lilly and Company. All rights reserved.
OLM-0007-USPI-20220613
DOSAGE & ADMINISTRATION SECTION
2 DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
2.1 Recommended Evaluations and Immunization Prior to Treatment Initiation
Prior to OLUMIANT treatment initiation, consider performing the following evaluations:
- Active and latent tuberculosis (TB) infection evaluation – OLUMIANT should not be given to patients with active tuberculosis (TB). If latent infection is positive in patients with rheumatoid arthritis or alopecia areata, consider treatment for TB prior to OLUMIANT use [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)].
- Viral hepatitis screening in accordance with clinical guidelines [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)].
- Complete blood count – Assess baseline values and verify whether treatment can be initiated:
-
In patients with rheumatoid arthritis or alopecia areata, OLUMIANT initiation is not recommended in patients with an absolute lymphocyte count (ALC) <500 cells/μl, absolute neutrophil count (ANC) <1000 cells/μl, or hemoglobin level <8 g/dL.
-
In patients with COVID-19, OLUMIANT initiation is not recommended if the ALC is <200 cells/μl or if the ANC is <500 cells/μl.
Monitor complete blood counts during treatment and modify dosage as recommended [see Dosage and Administration (2.5) and Warnings and Precautions (5.7)].
- Baseline hepatic and renal function – Assess baseline values and monitor patients for laboratory changes. Modify dosage based on hepatic and renal impairment, and laboratory abnormalities [see Dosage and Administration (2.5) and Warnings and Precautions (5.7)].
In patients with rheumatoid arthritis or alopecia areata, update immunizations in agreement with current immunization guidelines [see Warnings and Precautions (5.9)].
2.2 Dosage Recommendations in Rheumatoid Arthritis
The recommended dosage of OLUMIANT is 2 mg once daily orally, with or without food [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)]. An alternative administration for patients unable to swallow tablets may be used [see Dosage and Administration (2.8)]. OLUMIANT may be used as monotherapy or in combination with methotrexate or other non-biologic DMARDs.
2.3 Dosage Recommendations in COVID-19
The recommended dosage of OLUMIANT for adults is 4 mg once daily orally, with or without food, for 14 days or until hospital discharge, whichever occurs first. An alternative administration for patients unable to swallow tablets may be used [see Dosage and Administration (2.8)].
2.4 Dosage Recommendations in Alopecia Areata
The recommended dosage of OLUMIANT is 2 mg once daily orally, with or without food. Increase to 4 mg once daily if the response to treatment is not adequate.
For patients with nearly complete or complete scalp hair loss, with or without substantial eyelash or eyebrow hair loss, consider treating with 4 mg once daily, with or without food.
Once patients achieve an adequate response to treatment with 4 mg, decrease the dosage to 2 mg once daily.
2.5 Dosage Modifications Due to Infections, Cytopenias and Anemia
Rheumatoid Arthritis and Alopecia Areata
- Avoid use of OLUMIANT in patients with active, serious or opportunistic infection, including localized infections. If a patient develops a serious infection hold treatment with OLUMIANT until the infection is controlled [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)].
- Dosage modifications for patients with rheumatoid arthritis or alopecia areata and cytopenias or anemia are described in Table 1.
|
Laboratory Analyte |
Laboratory Analyte Value |
Recommendation |
|
Absolute Lymphocyte Count (ALC) |
≥500 cells/μL |
Maintain dosage |
|
<500 cells/μL |
Interrupt OLUMIANT until ALC ≥500 cells/μL | |
|
Absolute Neutrophil Count (ANC) |
≥1000 cells/μL |
Maintain dosage |
|
<1000 cells/μL |
Interrupt OLUMIANT until ANC ≥1000 cells/μL | |
|
Hemoglobin |
≥8 g/dL |
Maintain dosage |
|
<8 g/dL |
Interrupt OLUMIANT until hemoglobin ≥8 g/dL |
COVID-19
- Monitor patients for signs and symptoms of new infections during treatment with OLUMIANT. The risks and benefits of treatment with OLUMIANT in COVID-19 patients with other concurrent infections should be considered [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)].
- Dosage modifications for patients with COVID-19 and cytopenias are described in Table 2.
|
Laboratory Analyte |
Laboratory Analyte Value |
Recommendation |
|
Absolute Lymphocyte Count (ALC) |
≥200 cells/μL |
Maintain dosage |
|
<200 cells/μL |
Interrupt OLUMIANT until ALC ≥200 cells/μL | |
|
Absolute Neutrophil Count (ANC) |
≥500 cells/μL |
Maintain dosage |
|
<500 cells/μL |
Interrupt OLUMIANT until ANC ≥500 cells/μL |
2.6 Dosage Modifications for Patients with Renal Impairment or Hepatic
Impairment
Rheumatoid Arthritis
Renal Impairment
Dosage modifications for patients with rheumatoid arthritis and renal impairment are described in Table 3.
Table 3: Dosage Modifications for Patients with Rheumatoid Arthritis and Renal Impairment|
Renal Impairment Stage |
Estimated Glomerular Filtration Rate (eGFR) |
Recommendation |
|
Mild |
60 – <90 mL/minute/1.73 m2 |
2 mg once daily |
|
Moderate |
30 - <60 mL/min/1.73 m2 |
1 mg once daily |
|
Severe |
<30 mL/minute/1.73 m2 |
Not recommended |
Hepatic Impairment
- OLUMIANT is not recommended for use in patients with severe hepatic impairment.
- Interrupt OLUMIANT, if increases in ALT or AST are observed and drug-induced liver injury (DILI) is suspected, until the diagnosis of DILI is excluded [see Warnings and Precautions (5.8)].
COVID-19
Renal Impairment
- Dosage modifications for patients with COVID-19 and renal impairment are described in Table 4.
|
Renal Impairment Stage |
Estimated Glomerular Filtration Rate (eGFR) |
Recommendation |
|
Mild |
60 - <90 mL/min/1.73m2 |
4 mg once daily |
|
Moderate |
30 - <60 mL/min/1.73m2 |
2 mg once daily |
|
Severe |
15 - <30 mL/min/1.73m2 |
1 mg once daily |
|
End Stage Renal Disease, Patients on Dialysis, or Acute Kidney Injury |
<15 mL/min/1.73m2 |
Not recommended |
Hepatic Impairment
- It is not known if dosage adjustment is needed in patients with COVID-19 and severe hepatic impairment. OLUMIANT should only be used in patients with COVID-19 and severe hepatic impairment if the potential benefit outweighs the potential risk.
- Interrupt OLUMIANT, if increases in ALT or AST are observed and DILI is suspected, until the diagnosis of DILI is excluded [see Warnings and Precautions (5.8)].
Alopecia Areata
Renal Impairment
Dosage modifications for patients with alopecia areata and renal impairment are described in Table 5.
Table 5: Dosage Modifications for Patients with Alopecia Areata and Renal Impairment|
Renal Impairment Stage |
Estimated Glomerular Filtration Rate (eGFR) |
Recommendation | |
|
If the recommended dosage is |
If the recommended dosage is | ||
|
Mild |
60 – <90 mL/minute/1.73 m2 |
Maintain dosage | |
|
Moderate |
30 – <60 mL/min/1.73 m2 |
Reduce to 1 mg once daily |
Reduce to 2 mg once daily |
|
Severe |
<30 mL/minute/1.73 m2 |
Not recommended |
Hepatic Impairment
- OLUMIANT is not recommended for use in patients with severe hepatic impairment.
- Interrupt OLUMIANT, if increases in ALT or AST are observed and DILI is suspected, until the diagnosis of DILI is excluded [see Warnings and Precautions (5.8)].
2.7 Dosage Modifications Due to Drug Interactions
Rheumatoid Arthritis, COVID-19 or Alopecia Areata
The recommended dosage of OLUMIANT in patients taking strong Organic Anion Transporter 3 (OAT3) inhibitors, such as probenecid, are shown in Table 6 [see Drug Interactions (7.1) and Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)].
Table 6: Dosage Modifications when Coadministered with Strong OAT3 Inhibitors in Patients With Rheumatoid Arthritis, COVID-19 or Alopecia Areata|
Concomitant Medication |
Recommendation |
|
Strong OAT3 inhibitors (e.g., probenecid) |
If the recommended dosage is 4 mg once daily, reduce dosage to 2 mg once daily. |
|
If the recommended dosage is 2 mg once daily, reduce dosage to 1 mg once daily. | |
|
If the recommended dosage is 1 mg once daily, consider discontinuing probenecid. |
2.8 Alternative Administration for Patients Unable to Swallow Tablets
For patients who are unable to swallow whole tablets, an alternative mode of administration may be considered:
- Oral dispersion
- Gastrostomy tube (G tube)
- Nasogastric tube (NG tube) or orogastric tube (OG tube)
Intact tablets are not hazardous. Tablets may be crushed to facilitate dispersion. It is not known if powder from the crushed tablets may constitute a reproductive hazard to the preparer. If tablets are crushed, use proper control measures (e.g., ventilated enclosure) or personal protective equipment (i.e., N95 respirator). Dispersed tablets are stable in water for up to 4 hours.
Preparation Instructions for Alternative Administration:
- Oral administration of dispersed tablets in water: For patients who are unable to swallow whole tablets, 1-mg, 2-mg, or 4-mg baricitinib tablet(s), or any combination of tablets necessary to achieve the desired dose up to 4-mg may be placed in a container with approximately 10 mL (5 mL minimum) of room temperature water, dispersed by gently swirling the tablet(s) and immediately taken orally. The container should be rinsed with an additional 10 mL (5 mL minimum) of room temperature water and the entire contents swallowed by the patient (Table 7).
- Administration via G tube: For patients with a G tube, 1-mg, 2-mg, or 4-mg baricitinib tablet(s), or any combination of tablets necessary to achieve the desired dose up to 4-mg may be placed in a container with approximately 15 mL (10 mL minimum) of room temperature water and dispersed with gentle swirling. Ensure the tablet(s) are sufficiently dispersed to allow free passage through the tip of the syringe. Withdraw entire contents from the container into an appropriate syringe and immediately administer through the gastric feeding tube. Rinse container with approximately 15 mL (10 mL minimum) of room temperature water, withdraw the contents into the syringe, and administer through the tube (Table 7).
- Administration via NG or OG tube: For patients with a NG or OG tube, 1-mg, 2-mg, or 4-mg baricitinib tablet(s), or a combination of tablets necessary to achieve the desired dose up to 4-mg may be placed into a container with approximately 30 mL of room temperature water and dispersed with gentle swirling. Ensure the tablet(s) are sufficiently dispersed to allow free passage through the tip of the syringe. Withdraw the entire contents from the container into an appropriate syringe and immediately administer through the enteral feeding tube. To avoid clogging of small diameter tubes (smaller than 12 Fr), the syringe can be held horizontally and shaken during administration. Rinse container with a sufficient amount (minimum of 15 mL) of room temperature water, withdraw the contents into the syringe, and administer through the tube (Table 7).
|
Administration via |
Dispersion Volume |
Container Rinse Volume |
|
Oral dispersion |
10 mL |
10 mL |
|
G tube |
15 mL |
15 mL |
|
NG tube |
30 mL |
15 mL |
3 DOSAGE FORMS AND STRENGTHS
OLUMIANT is available as debossed, film-coated tablets:
- 1 mg tablet contains a recessed area on each face of the tablet surface, is very light pink, round, debossed with “Lilly” on one side and “1” on the other.
- 2 mg tablet contains a recessed area on each face of the tablet surface, is light pink, oblong, debossed with “Lilly” on one side and “2” on the other.
- 4 mg tablet contains a recessed area on each face of the tablet surface, is medium pink, round, debossed with “Lilly” on one side and “4” on the other.
Administration Instructions:
- See the full prescribing information for recommended evaluations and immunizations prior to treatment. (2.1)
- Rheumatoid Arthritis and Alopecia Areata: Avoid initiation or interrupt OLUMIANT in patients with anemia (hemoglobin <8 g/dL), lymphopenia (ALC <500 cells/mm3) or neutropenia (ANC <1000 cells/mm3). (2.1, 2.5, 5.8)
- COVID-19: Avoid initiation or interrupt OLUMIANT in patients with lymphopenia (ALC <200 cells/mm3) or neutropenia (ANC <500 cells/mm3). (2.1, 2.5, 5.8)
Recommended Dosage:
Rheumatoid Arthritis:
- 2 mg once daily. (2.2)
- OLUMIANT may be used as monotherapy or in combination with methotrexate or other non-biologic DMARDs. (2.2)
COVID-19:
- 4 mg once daily for up to 14 days. (2.3)
Alopecia Areata:
- 2 mg once daily. Increase to 4 mg once daily, if the response to treatment is not adequate. (2.4)
- For patients with nearly complete or complete scalp hair loss, with or without substantial eyelash or eyebrow hair loss, consider treating with 4 mg once daily. (2.4)
- Reduce the dose to 2 mg once daily when an adequate response has been achieved. (2.4)
Dosage Modifications in Patients with Renal or Hepatic Impairment, or Cytopenias
- See the full prescribing information for dosage modifications by indication. (2.5, 2.6, 5.8)
