CINVANTI
These highlights do not include all the information needed to use CINVANTI safely and effectively. See full prescribing information for CINVANTI. CINVANTI (aprepitant) injectable emulsion, for intravenous use Initial U.S. Approval: 2003
4c218d3a-a508-4abc-9ed8-a6e8e191d1b4
HUMAN PRESCRIPTION DRUG LABEL
Mar 13, 2024
Heron Therapeutics, Inc.
DUNS: 102099843
Products 1
Detailed information about drug products covered under this FDA approval, including NDC codes, dosage forms, ingredients, and administration routes.
aprepitant
Product Details
FDA regulatory identification and product classification information
FDA Identifiers
Product Classification
Product Specifications
INGREDIENTS (7)
Drug Labeling Information
PACKAGE LABEL.PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL
PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL - 130 mg/18 mL Vial Carton - Not For Sale
NDC 47426-201-01
Rx Only
CINVANTI ®
(aprepitant)
injectable emulsion
130 mg/18 mL
(7.2 mg/mL)
For Intravenous Use Only
Must be refrigerated. Store at
2°C-8°C (36°F-46°F). Do Not Freeze.
1 Sterile Single-Dose Vial
Discard Unused Portion
Not For Sale
HERON
THERAPEUTICS

INDICATIONS & USAGE SECTION
1 INDICATIONS AND USAGE
CINVANTI, in combination with other antiemetic agents, is indicated in adults for the prevention of:
- acute and delayed nausea and vomiting associated with initial and repeat courses of highly emetogenic cancer chemotherapy (HEC) including high-dose cisplatin as a single-dose regimen.
- delayed nausea and vomiting associated with initial and repeat courses of moderately emetogenic cancer chemotherapy (MEC) as a single-dose regimen.
- nausea and vomiting associated with initial and repeat courses of MEC as a 3-day regimen.
Limitations of Use
- CINVANTI has not been studied for the treatment of established nausea and vomiting.
CINVANTI is a substance P/neurokinin-1 (NK1) receptor antagonist, indicated in adults, in combination with other antiemetic agents, for the prevention of:
- acute and delayed nausea and vomiting associated with initial and repeat courses of highly emetogenic cancer chemotherapy (HEC) including high-dose cisplatin as a single-dose regimen. (1)
- delayed nausea and vomiting associated with initial and repeat courses of moderately emetogenic cancer chemotherapy (MEC) as a single-dose regimen. (1)
- nausea and vomiting associated with initial and repeat courses of MEC as a 3-day regimen. (1)
Limitations of Use:
CINVANTI has not been studied for treatment of established nausea and vomiting. (1)
CONTRAINDICATIONS SECTION
4 CONTRAINDICATIONS
CINVANTI is contraindicated in patients:
- who are hypersensitive to any component of the product [see Description (11)]. Hypersensitivity reactions including anaphylaxis have been reported [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2), Adverse Reactions (6.2)].
- taking pimozide. Inhibition of CYP3A4 by aprepitant could result in elevated plasma concentrations of pimozide, which is a CYP3A4 substrate, potentially causing serious or life-threatening reactions, such as QT prolongation, a known adverse reaction of pimozide [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)].
- Known hypersensitivity to any component of this drug. (4, 5.2)
- Concurrent use with pimozide. (4)
WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS SECTION
5 WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS
5.1 Clinically Significant CYP3A4 Drug Interactions
Aprepitant is a substrate, weak-to-moderate (dose-dependent) inhibitor, and an inducer of CYP3A4.
- Use of CINVANTI with other drugs that are CYP3A4 substrates may result in increased plasma concentration of the concomitant drug.
- Use of pimozide with CINVANTI is contraindicated due to the risk of significantly increased plasma concentrations of pimozide, potentially resulting in prolongation of the QT interval, a known adverse reaction of pimozide [see Contraindications (4)].
- Use of CINVANTI with strong or moderate CYP3A4 inhibitors (e.g., ketoconazole, diltiazem) may increase plasma concentrations of aprepitant and result in an increased risk of adverse reactions related to CINVANTI.
- Use of CINVANTI with strong CYP3A4 inducers (e.g., rifampin) may result in a reduction in aprepitant plasma concentrations and decreased efficacy of CINVANTI.
See Table 8 and Table 9 for a listing of potentially significant drug interactions [see Drug Interactions (7.1, 7.2)].
5.2 Hypersensitivity Reactions
Serious hypersensitivity reactions, including anaphylaxis during or soon after administration of CINVANTI have occurred. Symptoms including dyspnea, eye swelling, flushing, pruritus and wheezing have been reported [see Adverse Reactions (6.2)].
Monitor patients during and after administration. If hypersensitivity reactions occur, discontinue CINVANTI and administer appropriate medical therapy. Do not reinitiate CINVANTI in patients who experience these symptoms with previous use.
5.3 Decrease in INR with Concomitant Warfarin
Coadministration of CINVANTI with warfarin, a CYP2C9 substrate, may result in a clinically significant decrease in the International Normalized Ratio (INR) of prothrombin time [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)]. Monitor the INR in patients on chronic warfarin therapy in the 2-week period, particularly at 7 to 10 days, following initiation of CINVANTI with each chemotherapy cycle [see Drug Interactions (7.1)].
5.4 Risk of Reduced Efficacy of Hormonal Contraceptives
Upon coadministration with CINVANTI, the efficacy of hormonal contraceptives may be reduced during administration of and for 28 days following the last dose of CINVANTI [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)]. Advise patients to use effective alternative or back-up methods of non-hormonal contraception during treatment with CINVANTI and for 1 month following administration of CINVANTI or oral aprepitant, whichever is administered last [see Drug Interactions (7.1), Use in Specific Populations (8.3)].
- CYP3A4 Interactions: Aprepitant is a substrate, weak-to-moderate (dose-dependent) inhibitor and an inducer of CYP3A4; see Full Prescribing Information for recommendations regarding contraindications, risk of adverse reactions, and dosage adjustment of CINVANTI and concomitant drugs. (4, 5.1, 7.1, 7.2)
- Hypersensitivity Reactions (including anaphylaxis): May occur during or soon after administration. If symptoms occur, discontinue CINVANTI and do not reinitiate it. (4, 5.2)
- Warfarin (a CYP2C9 substrate): Risk of decreased INR of prothrombin time; monitor INR in 2–week period, particularly at 7 to 10 days, following initiation of CINVANTI. (5.3, 7.1)
- Hormonal Contraceptives: Efficacy of contraceptives may be reduced during and for 28 days following administration of aprepitant. Use effective alternative or back-up methods of non-hormonal contraception. (5.4, 7.1, 8.3)
ADVERSE REACTIONS SECTION
6 ADVERSE REACTIONS
The following clinically significant adverse reactions are described elsewhere in the labeling:
- Hypersensitivity Reactions [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2)]
6.1 Clinical Trials Experience
Because clinical trials are conducted under widely varying conditions, adverse reaction rates observed in the clinical trials of a drug cannot be directly compared to rates in the clinical trials of another drug and may not reflect the rates observed in clinical practice.
The safety of CINVANTI was evaluated as a single-dose in healthy subjects and established from adequate and well-controlled studies of intravenous fosaprepitant and/or oral aprepitant [see Clinical Studies (14)]. Adverse reactions observed in these adequate and well-controlled studies are described below.
Safety of CINVANTI
A total of 200 healthy subjects received a single 130 mg dose of CINVANTI as a 30-minute infusion. Adverse reactions reported in at least 2% of subjects were headache (3%) and fatigue (2%). The safety profile of CINVANTI in 50 healthy subjects who received a single 2-minute injection was similar to that seen with a 30-minute infusion.
Single-Dose Intravenous Fosaprepitant -- HEC
In an active-controlled clinical study in patients receiving HEC, safety was evaluated for 1143 patients receiving a single intravenous dose of fosaprepitant, a prodrug of aprepitant, compared to 1169 patients receiving a 3-day regimen of oral aprepitant [see Clinical Studies (14.1)]. When administered intravenously, fosaprepitant is converted to aprepitant within 30 minutes. The safety profile was generally similar to that seen in prior HEC studies with a 3-day regimen of oral aprepitant. However, infusion-site reactions occurred at a higher incidence in patients in the intravenous fosaprepitant group (3%) compared to those in the oral aprepitant group (0.5%). The reported infusion-site reactions included: infusion-site erythema, infusion-site pruritus, infusion-site pain, infusion-site induration and infusion-site thrombophlebitis.
Adverse reactions associated with oral aprepitant may also be expected to occur with CINVANTI. See the full prescribing information for oral aprepitant for complete safety information.
Single-Dose Intravenous Fosaprepitant -- MEC
In an active-controlled clinical trial in patients receiving MEC, safety was evaluated in 504 patients receiving a single dose of intravenous fosaprepitant in combination with ondansetron and dexamethasone (intravenous fosaprepitant regimen) compared to 497 patients receiving ondansetron and dexamethasone alone (standard therapy). The most common adverse reactions are listed in Table 5.
Table 5. Most Common Adverse Reactions in Patients Receiving MEC*|
Intravenous fosaprepitant, ondansetron, and dexamethasone† |
Ondansetron and dexamethasone‡ | |
|---|---|---|
| ||
|
Fatigue |
15% |
13% |
|
Diarrhea |
13% |
11% |
|
Neutropenia |
8% |
7% |
|
Asthenia |
4% |
3% |
|
Anemia |
3% |
2% |
|
Peripheral Neuropathy |
3% |
2% |
|
Leukopenia |
2% |
1% |
|
Dyspepsia |
2% |
1% |
|
Urinary Tract Infection |
2% |
1% |
|
Pain In Extremity |
2% |
1% |
Infusion-site reactions were reported in 2.2% of patients treated with the intravenous fosaprepitant regimen compared to 0.6% of patients treated with standard therapy. The infusion-site reactions included: infusion-site pain (1.2%, 0.4%), injection-site irritation (0.2%, 0.0%), vessel puncture-site pain (0.2%, 0.0%), and 8 infusion-site thrombophlebitis (0.6%, 0.0%), reported in the intravenous fosaprepitant regimen compared to standard therapy, respectively.
3-Day Oral Aprepitant -- MEC
In 2 active-controlled clinical trials in patients receiving MEC, 868 patients were treated with a 3-day oral aprepitant regimen during Cycle 1 of chemotherapy and 686 of these patients continued into extensions for up to 4 cycles of chemotherapy. In both studies, oral aprepitant was given in combination with ondansetron and dexamethasone (oral aprepitant regimen) and was compared to ondansetron and dexamethasone alone (standard therapy) [see Clinical Studies (14.2)].
In the combined analysis of Cycle 1 data for these 2 studies, adverse reactions were reported in approximately 14% of patients treated with the aprepitant regimen compared with approximately 15% of patients treated with standard therapy. Treatment was discontinued due to adverse reactions in 0.7% of patients treated with the aprepitant regimen compared with 0.2% of patients treated with standard therapy.
The most common adverse reactions reported in patients treated with the oral aprepitant regimen with an incidence of at least 1% and greater than standard therapy are listed in Table 6.
Table 6. Adverse Reactions (≥ 1%) in Patients Receiving MEC with a Greater Incidence in the Oral 3-Day Aprepitant Regimen Relative to Standard Therapy|
Oral Aprepitant Regimen |
Standard Therapy | |
|---|---|---|
|
Fatigue |
1.4 |
0.9 |
|
Eructation |
1.0 |
0.1 |
A listing of adverse reactions reported in less than 1% in patients treated with the oral aprepitant regimen that occurred at an incidence greater than in patients treated with standard therapy are presented in the Less Common Adverse Reactions subsection below.
Less Common Adverse Reactions
Adverse reactions reported in studies in patients treated with the 3-day oral aprepitant regimen with an incidence < 1% and greater than standard therapy are listed in Table 7.
Table 7. Adverse Reactions (incidence < 1%) in Patients Observed in Studies with a Greater Incidence in the Oral Aprepitant Regimen Relative to Standard Therapy|
Infection and infestations |
candidiasis, staphylococcal infection |
|
Blood and the lymphatic system disorders |
anemia, febrile neutropenia |
|
Metabolism and nutrition disorders |
weight gain, polydipsia |
|
Psychiatric disorders |
disorientation, euphoria, anxiety |
|
Nervous system disorders |
dizziness, dream abnormality, cognitive disorder, lethargy, somnolence |
|
Eye disorders |
conjunctivitis |
|
Ear and labyrinth disorders |
tinnitus |
|
Cardiac disorders |
bradycardia, cardiovascular disorder, palpitations |
|
Vascular disorders |
hot flush, flushing |
|
Respiratory, thoracic and mediastinal disorders |
pharyngitis, sneezing, cough, postnasal drip, throat irritation |
|
Gastrointestinal disorders |
nausea, acid reflux, dysgeusia, epigastric discomfort, obstipation, gastroesophageal reflux disease, perforating duodenal ulcer, vomiting, abdominal pain, dry mouth, abdominal distension, feces hard, neutropenic colitis, flatulence, stomatitis |
|
Skin and subcutaneous tissue disorders |
rash, acne, photosensitivity, hyperhidrosis, oily skin, pruritus, skin lesion |
|
Musculoskeletal and connective tissue disorders |
muscle cramp, myalgia, muscular weakness |
|
Renal and urinary disorders |
polyuria, dysuria, pollakiuria |
|
General disorders and administration site condition |
edema, chest discomfort, malaise, thirst, chills, gait disturbance |
|
Investigations |
alkaline phosphatase increased, hyperglycemia, microscopic hematuria, hyponatremia, weight decreased, neutrophil count decreased |
In another chemotherapy-induced nausea and vomiting study, Stevens-Johnson syndrome was reported as a serious adverse reaction in a patient receiving aprepitant with cancer chemotherapy.
The adverse experience profiles in the Multiple-Cycle extensions of HEC and MEC studies for up to 6 cycles of chemotherapy were similar to that observed in Cycle 1.
6.2 Postmarketing Experience
The following adverse reactions have been identified during post-approval use of intravenous fosaprepitant and/or intravenous or oral aprepitant. Because these reactions are reported voluntarily from a population of uncertain size, it is not always possible to reliably estimate their frequency or establish a causal relationship to drug exposure.
Skin and subcutaneous tissue disorders: pruritus, rash, urticaria, Stevens- Johnson syndrome/toxic epidermal necrolysis [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2)].
Immune system disorders: hypersensitivity reactions including anaphylaxis and anaphylactic shock [see Contraindications (4), Warnings and Precautions (5.2)].
Nervous system disorders: ifosfamide-induced neurotoxicity reported after aprepitant and ifosfamide coadministration.
Most common adverse reactions are:
- Single-dose fosaprepitant with MEC (≥2%): fatigue, diarrhea, neutropenia, asthenia, anemia, peripheral neuropathy, leukopenia, dyspepsia, urinary tract infection, pain in extremity. (6.1)
- 3-day oral aprepitant with MEC (≥1% and greater than standard therapy): fatigue and eructation. (6.1)
- Single-dose fosaprepitant with HEC: generally similar to 3-day oral aprepitant. In addition, infusion site reactions (3%) occurred. (6.1)
- Single-dose CINVANTI (≥2%): headache and fatigue. (6.1)
**To report SUSPECTED ADVERSE REACTIONS, contact Heron Therapeutics, Inc. at 1-844-437-6611 andwww.CINVANTI.com or FDA at 1-800-FDA-1088 or **www.fda.gov/medwatch
DRUG INTERACTIONS SECTION
7 DRUG INTERACTIONS
7.1 Effect of Aprepitant on the Pharmacokinetics of Other Drugs
Aprepitant is a substrate, weak-to-moderate (dose-dependent) inhibitor, and an inducer of CYP3A4. Aprepitant is also an inducer of CYP2C9 [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)].
Some substrates of CYP3A4 are contraindicated with CINVANTI [see Contraindications (4)]. Dosage adjustment of some CYP3A4 and CYP2C9 substrates may be warranted, as shown in Table 8.
Table 8. Effects of Aprepitant on the Pharmacokinetics of Other Drugs|
CYP3A4 Substrates | |
|
Pimozide | |
|
Clinical Impact |
Increased pimozide exposure. |
|
Intervention |
CINVANTI is contraindicated [see Contraindications (4)]. |
|
Benzodiazepines | |
|
Clinical Impact |
Increased exposure to midazolam or other benzodiazepines metabolized via CYP3A4 (alprazolam, triazolam) may increase the risk of adverse reactions [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)]. |
|
Intervention |
Monitor for benzodiazepine-related adverse reactions. |
|
Dexamethasone | |
|
Clinical Impact |
Increased dexamethasone exposure [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)]. |
|
Intervention |
Reduce the dose of oral dexamethasone by approximately 50% [see Dosage and Administration (2.1)]. |
|
Methylprednisolone | |
|
Clinical Impact |
Increased methylprednisolone exposure [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)]. |
|
Intervention |
Reduce the dose of oral methylprednisolone by approximately 50% on Days 1 and
2 for patients receiving HEC and on Day 1 for patients receiving MEC. |
|
Chemotherapeutic Agents that are Metabolized by CYP3A4 | |
|
Clinical Impact |
Increased exposure of the chemotherapeutic agent may increase the risk of adverse reactions [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)]. |
|
Intervention |
Vinblastine, vincristine, or ifosfamide or other chemotherapeutic agents
Etoposide, vinorelbine, paclitaxel, and docetaxel
|
|
Hormonal Contraceptives | |
|
Clinical Impact |
Decreased hormonal exposure during administration of and for 28 days after administration of the last dose of aprepitant [see Warnings and Precautions (5.4), Use in Specific Populations (8.3), and Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)]. |
|
Intervention |
Effective alternative or back-up methods of contraception (such as condoms or spermicides) should be used during treatment with CINVANTI and for 1 month following administration of CINVANTI or oral aprepitant, whichever is administered last. |
|
Examples |
birth control pills, skin patches, implants, and certain IUDs |
|
CYP2C9 Substrates | |
|
Warfarin | |
|
Clinical Impact |
Decreased warfarin exposure and decreased prothrombin time (INR) [see Warnings and Precautions (5.3), Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)]. |
|
Intervention |
In patients on chronic warfarin therapy, monitor the prothrombin time (INR) in the 2-week period, particularly at 7 to 10 days, following administration of CINVANTI with each chemotherapy cycle. |
|
Other Antiemetic Agents | |
|
5-HT3 Antagonists | |
|
Clinical Impact |
No change in the exposure of the 5-HT3 antagonist [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)]. |
|
Intervention |
No dosage adjustment needed. |
|
Examples |
ondansetron, granisetron, dolasetron |
7.2 Effect of Other Drugs on the Pharmacokinetics of Aprepitant
Aprepitant is a CYP3A4 substrate [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)]. Co- administration of CINVANTI with drugs that are inhibitors or inducers of CYP3A4 may result in increased or decreased plasma concentrations of aprepitant, respectively, as shown in Table 9.
Table 9. Effects of Other Drugs on Pharmacokinetics of Aprepitant|
Moderate to Strong CYP3A4 Inhibitors | |
|
Clinical Impact |
Significantly increased exposure of aprepitant may increase the risk of adverse reactions associated with CINVANTI [see Adverse Reactions (6.1) and Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)]. |
|
Intervention |
Avoid concomitant use of CINVANTI. |
|
Examples |
Moderate inhibitor: |
|
Strong CYP3A4 Inducers | |
|
Clinical Impact |
Substantially decreased exposure of aprepitant in patients chronically taking a strong CYP3A4 inducer may decrease the efficacy of CINVANTI [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)]. |
|
Intervention |
Avoid concomitant use of CINVANTI. |
|
Examples |
rifampin, carbamazepine, phenytoin |
See full prescribing information for a list of clinically significant drug interactions. (4, 5.1, 5.3, 5.4, 7.1, 7.2)
DOSAGE & ADMINISTRATION SECTION
2 DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
2.1 Prevention of Nausea and Vomiting Associated with HEC and MEC
The recommended dosages in adults of CINVANTI, dexamethasone, and a 5-HT3 antagonist for the prevention of nausea and vomiting associated with administration of HEC or MEC are shown in Table 1, Table 2 and Table 3 respectively. Administer CINVANTI intravenously either by injection over a two (2) minute period or by infusion over a thirty (30) minute period on Day 1, completing the injection or infusion approximately 30 minutes prior to chemotherapy.
Table 1. Recommended Dosage of CINVANTI for the Prevention of Nausea and Vomiting Associated with HEC (Single-Dose Regimen)|
Agent |
Day 1 |
Day 2 |
Day 3 |
Day 4 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ||||
|
CINVANTI |
130 mg intravenously |
None |
None |
None |
|
Dexamethasone* |
12 mg orally |
8 mg orally |
8 mg orally |
8 mg orally |
|
5-HT3 antagonist |
See selected 5-HT3 antagonist prescribing information for recommended dosage |
None |
None |
None |
|
Agent |
Day 1 |
|---|---|
| |
|
CINVANTI |
130 mg intravenously |
|
Dexamethasone* |
12 mg orally |
|
5-HT3 antagonist |
See selected 5-HT3 antagonist prescribing information for recommended dosage |
|
Agent |
Day 1 |
Day 2 |
Day 3 |
|---|---|---|---|
| |||
|
CINVANTI |
100 mg intravenously |
None |
None |
|
Oral Aprepitant |
None |
80 mg orally |
80 mg orally |
|
Dexamethasone* |
12 mg orally |
None |
None |
|
5-HT3 antagonist |
See selected 5-HT3 antagonist prescribing information for recommended dosage |
None |
None |
2.2 Preparation of CINVANTI for Administration
Intravenous Injection over a period of 2 minutes
For intravenous injection over a period of 2 minutes, administer 130 mg of CINVANTI as part of a HEC or MEC regimen or 100 mg as part of a MEC regimen as a single dose on Day 1.
Aseptically withdraw18 mL for the 130 mg dose or14 mL for the 100 mg dose from the vial. Do not dilute.
The infusion line should be flushed with normal saline before and after administration of CINVANTI.
Intravenous Infusion over a period of 30 minutes
Table 4 includes preparation instructions for CINVANTI for HEC or MEC as a 130 mg single-dose regimen, and for MEC as a 100 mg single-dose followed by 2 days of oral aprepitant as a 3-day regimen. Differences in preparation for each dose are displayed as bolded text.
Table 4. Preparation Instructions for CINVANTI Intravenous Infusion|
Note: The differences in preparation for each recommended dosage of CINVANTI are displayed in bolded text (see Table 1 for HEC Regimen and Table 2 for MEC Regimen). | |
| |
|
Step 1 |
Aseptically withdraw18 mL for the 130 mg dose or14 mL for the 100 mg dose from the vial and transfer it into an infusion bag* filled with100 mL of 0.9% Sodium Chloride Injection, USP or 5% Dextrose for Injection, USP. |
|
Step 2 |
Gently invert the bag 4 to 5 times. Avoid shaking. |
|
Step 3 |
Before administration, inspect the bag for particulate matter and discoloration. Discard the bag if particulate and/or discoloration are observed. |
Caution: Do not mix CINVANTI with solutions for which physical and chemical compatibility have not been established.
In-Use Storage Conditions for CINVANTI in Acceptable Intravenous Diluents
Diluted CINVANTI solution is stable at ambient room temperature for up to 6 hours in 0.9% Sodium Chloride Injection, USP or 12 hours in 5% Dextrose Injection, USP or up to 72 hours if stored under refrigeration in 0.9% Sodium Chloride Injection, USP or in 5% Dextrose Injection, USP.
2.3 Compatibilities
CINVANTI is compatible with 0.9% Sodium Chloride Injection, USP or 5% Dextrose Injection, USP.
2.4 Incompatibilities
CINVANTI is incompatible with any solutions containing divalent cations (e.g. calcium, magnesium), including Lactated Ringer's Solution and Hartmann's Solution.
Recommended Dosage (2.1):
- Administer CINVANTI intravenously as an injection over 2 minutes or an infusion over 30 minutes; complete the injection or infusion approximately 30 minutes prior to chemotherapy.
- HEC and MEC (Single-Dose Regimen): The recommended dosage in adults is 130 mg on Day 1.
- MEC (3-Day Regimen): The recommended dosage in adults is 100 mg on Day 1. Aprepitant capsules (80 mg) are given orally on Days 2 and 3.
- CINVANTI is part of a regimen that includes a corticosteroid and a 5-HT3 antagonist.
Preparation:
- See the full prescribing information for instructions. (2.2)
DOSAGE FORMS & STRENGTHS SECTION
3 DOSAGE FORMS AND STRENGTHS
Injectable emulsion: 130 mg/18 mL (7.2 mg/mL) aprepitant as an opaque, off- white to amber emulsion, in single-dose vial
Injectable emulsion: 130 mg/18 mL (7.2 mg/mL) aprepitant in single-dose vial (3)
USE IN SPECIFIC POPULATIONS SECTION
8 USE IN SPECIFIC POPULATIONS
8.1 Pregnancy
Risk Summary
There are no available data on CINVANTI use in pregnant women to inform a drug-associated risk of adverse developmental outcomes. Avoid use of CINVANTI in pregnant women due to the alcohol content (see Clinical Considerations). In animal reproduction studies, no adverse developmental effects were observed in rats or rabbits exposed during the period of organogenesis to systemic drug concentrations (area under the plasma-concentration time curve [AUC]) of aprepitant approximately equivalent to the exposure at the recommended human dose (RHD) of CINVANTI 130 mg (see Data).
The estimated background risk of major birth defects and miscarriage for the indicated populations is unknown. All pregnancies have a background risk of birth defect, loss, or other adverse outcomes. In the U.S. general population, the estimated background risk of major birth defects and miscarriage in clinically recognized pregnancies is 2 to 4% and 15 to 20%, respectively.
Clinical Considerations
Fetal/Neonatal adverse reactions
CINVANTI contains alcohol. Published studies have demonstrated that alcohol is associated with fetal harm including central nervous system abnormalities, behavioral disorders, and impaired intellectual development. There is no safe level of alcohol exposure in pregnancy; therefore, avoid use of CINVANTI in pregnant women.
Data
Animal Data
In embryofetal development studies in rats and rabbits, aprepitant was administered during the period of organogenesis at oral doses up to 1000 mg/kg twice daily (rats) and up to the maximum tolerated dose of 25 mg/kg/day (rabbits). No embryofetal lethality or malformations were observed at any dose level in either species. The exposures (AUC) in pregnant rats at 1000 mg/kg twice daily and in pregnant rabbits at 125 mg/kg/day were approximately equivalent to the exposure at the RHD of CINVANTI 130 mg. Aprepitant crosses the placenta in rats and rabbits.
8.2 Lactation
Risk Summary
There are no data on the presence of aprepitant in human milk, the effects on the breastfed infant, or the effects on milk production. Aprepitant is present in rat milk. The developmental and health benefits of breastfeeding should be considered along with the mother's clinical need for CINVANTI and any potential adverse effects on the breastfed infant from CINVANTI or from the underlying maternal condition.
8.3 Females and Males of Reproductive Potential
Contraception
Upon administration of CINVANTI, the efficacy of hormonal contraceptives may be reduced. Advise females of reproductive potential using hormonal contraceptives to use an effective alternative or back-up non-hormonal contraceptive (such as condoms or spermicides) during treatment with CINVANTI and for 1 month following the last dose of CINVANTI or oral aprepitant, whichever is administered last [see Warnings and Precautions (5.4), Drug Interactions (7.1), Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)].
8.4 Pediatric Use
The safety and effectiveness of CINVANTI have not been established in pediatric patients.
8.5 Geriatric Use
Of the 1649 adult cancer patients treated with intravenous fosaprepitant in HEC and MEC clinical studies, 27% were aged 65 and over, while 5% were aged 75 and over. Other reported clinical experience with fosaprepitant and/or oral aprepitant has not identified differences in responses between elderly and younger patients. In general, use caution when dosing elderly patients as they have a greater frequency of decreased hepatic, renal or cardiac function and concomitant disease or other drug therapy [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)].
8.6 Hepatic Impairment
The pharmacokinetics of aprepitant in patients with mild and moderate hepatic impairment were similar to those of healthy subjects with normal hepatic function. No dosage adjustment is necessary for patients with mild to moderate hepatic impairment (Child-Pugh score 5 to 9). There are no clinical or pharmacokinetic data in patients with severe hepatic impairment (Child-Pugh score greater than 9). Therefore, additional monitoring for adverse reactions in these patients may be warranted when CINVANTI is administered [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)].
Pregnancy: May cause fetal harm. (8.1)
OVERDOSAGE SECTION
10 OVERDOSAGE
There is no specific information on the treatment of overdosage with aprepitant.
In the event of overdose, CINVANTI should be discontinued and general supportive treatment and monitoring should be provided. Because of the antiemetic activity of CINVANTI, drug-induced emesis may not be effective in cases of CINVANTI overdosage.
Aprepitant is not removed by hemodialysis.
DESCRIPTION SECTION
11 DESCRIPTION
CINVANTI injectable emulsion contains the active ingredient, aprepitant. Aprepitant is a substance P/neurokinin 1 (NK1) receptor antagonist, an antiemetic agent, chemically described as 5-[[(2R,3S)-2-[(1R)-1-[3,5-bis(trifluoromethyl)phenyl]ethoxy]-3-(4-fluorophenyl)-4-morpholinyl]methyl]-1,2-dihydro-3H-1,2,4-triazol-3-one.
Its empirical formula is C23H21F7N4O3, and its structural formula is:
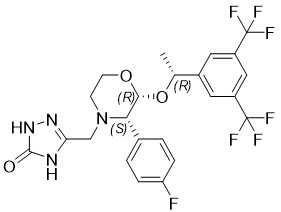
Aprepitant is a white to off-white crystalline solid, with a molecular weight of 534.43. It is practically insoluble in water. Aprepitant is sparingly soluble in ethanol and isopropyl acetate and slightly soluble in acetonitrile.
CINVANTI (aprepitant) injectable emulsion is a sterile, opaque, off-white to amber liquid in a single-dose vial for intravenous use. Each vial contains 130 mg aprepitant in 18 mL of emulsion. The emulsion also contains the following inactive ingredients: egg lecithin (2602 mg), dehydrated alcohol (513 mg), sodium oleate (87 mg), soybean oil (1734 mg), sucrose (973 mg), and water for injection (12142 mg).
HOW SUPPLIED SECTION
16 HOW SUPPLIED/STORAGE AND HANDLING
CINVANTI injectable emulsion is supplied as an opaque, off-white to amber emulsion in a single-dose glass vial containing 130 mg/18 mL (7.2 mg/mL) aprepitant:
|
NDC 47426-201-01 |
1 single-dose vial per carton |
Storage
CINVANTI injectable emulsion vials must be refrigerated, store at 2°C-8°C (36°F-46°F).
CINVANTI injectable emulsion vials can remain at room temperature up to 60 days.
Do not freeze.
SPL UNCLASSIFIED SECTION
Manufactured for: Heron Therapeutics, Inc., San Diego, CA 92121, USA
Patent: https://herontx.com/patents/
CINVANTI® is a registered trademark of Heron Therapeutics, Inc.
Copyright © 2017-2024Heron Therapeutics, Inc.
All rights reserved.
SPL PATIENT PACKAGE INSERT SECTION
|
PATIENT INFORMATION | ||
|---|---|---|
|
This Patient Information has been approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration |
Revised: September 2023 | |
|
What is CINVANTI?
| ||
|
Do not receive CINVANTI if you:
| ||
|
Before receiving CINVANTI, tell your healthcare provider about all of your medical conditions, including if you:
Tell your healthcare provider about all the medicines you take, including
prescription and over-the- counter medicines, vitamins, and herbal
supplements. | ||
|
How will I receive CINVANTI?
| ||
|
What are the possible side effects of CINVANTI? ***Serious allergic reactions.**Serious allergic reactions can happen during your CINVANTI infusion. Tell your healthcare provider or nurse right away if you get any of these symptoms during or soon after your infusion: * trouble breathing or swallowing, shortness of breath or wheezing * swelling of your eyes, face, tongue, or throat * flushing or redness of your face or skin * hives, rash, itching * dizziness, a rapid or weak heartbeat, or you feel faint The most common side effects of CINVANTI include: | ||
|
| |
|
Infusion-site side effects with CINVANTI may include: pain, hardening,
redness or itching at the site of infusion. Swelling (inflammation) of a vein
caused by a blood clot can also happen at the infusion site. Tell your
healthcare provider if you get any infusion-site side effects. | ||
|
General information about the safe and effective use of CINVANTI. | ||
|
What are the ingredients in CINVANTI? Copyright © 2017-2023Heron Therapeutics, Inc. All rights reserved. |
CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY SECTION
12 CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY
12.1 Mechanism of Action
Aprepitant is a selective high-affinity antagonist of human substance P/neurokinin 1 (NK1) receptors. Aprepitant has little or no affinity for serotonin (5-HT3), dopamine, and corticosteroid receptors. Aprepitant has been shown in animal models to inhibit emesis induced by cytotoxic chemotherapeutic agents, such as cisplatin, via central actions. Animal and human Positron Emission Tomography (PET) studies with aprepitant have shown that it crosses the blood brain barrier and occupies brain NK1 receptors. Animal and human studies show that aprepitant augments the antiemetic activity of the 5-HT3-receptor antagonist ondansetron and the corticosteroid dexamethasone and inhibits both the acute and delayed phases of cisplatin-induced emesis.
12.2 Pharmacodynamics
Cardiac Electrophysiology
In a randomized, double-blind, positive-controlled, thorough QTc study, a single 200 mg intravenous dose of fosaprepitant, a prodrug of aprepitant, had no effect on the QTc interval. In a cross-study comparison, maximum aprepitant concentrations (Cmax) after a single 200 mg dose of fosaprepitant were 1.04- and 1.5-fold higher than that achieved with CINVANTI 130 mg dose and 100 mg dose given as a 30-minute infusion, respectively.
12.3 Pharmacokinetics
Pharmacokinetic parameters following administration of a single intravenous 130 mg dose of CINVANTI administered as a 2-minute injection or 100 mg or 130 mg dose of CINVANTI administered as a 30-minute infusion to healthy subjects are summarized in Table 10.
Table 10. Aprepitant Pharmacokinetic Parameters (Mean (± Standard Deviation)) After Single Dose Intravenous Administration of CINVANTI|
CINVANTI 130 mg |
CINVANTI 130 mg |
CINVANTI 100 mg | |
|---|---|---|---|
|
AUC0-72hr (mcg∙hr/mL) |
45.6 (± 15.5) |
43.9 (± 12.7) |
27.8 (± 6.5) |
|
Cmax (mcg/mL) |
13.9 (±3.8) |
6.1 (± 1.5) |
4.3 (± 1.2) |
Distribution
Aprepitant is greater than 99% bound to plasma proteins. The mean apparent volume of distribution at steady state (Vdss) was approximately 70 L in humans.
Aprepitant crosses the blood brain barrier in humans [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.1)].
Elimination
Metabolism
Aprepitant undergoes extensive metabolism. In vitro studies using human liver microsomes indicate that aprepitant is metabolized primarily by CYP3A4 with minor metabolism by CYP1A2 and CYP2C19. Metabolism is largely via oxidation at the morpholine ring and its side chains. No metabolism by CYP2D6, CYP2C9, or CYP2E1 was detected.
In healthy young adults, aprepitant accounts for approximately 24% of the radioactivity in plasma over 72 hours following a single oral 300 mg dose of [14C]-aprepitant, indicating a substantial presence of metabolites in the plasma. Seven metabolites of aprepitant, which are only weakly active, have been identified in human plasma.
Excretion
Aprepitant is eliminated primarily by metabolism; aprepitant is not renally excreted. The apparent terminal half-life ranged from approximately 9 to 13 hours.
Specific Populations
Geriatric Patients
Following oral administration of a single 125 mg dose of aprepitant on Day 1 and 80 mg once daily on Days 2 through 5, the AUC0-24hr of aprepitant was 21% higher on Day 1 and 36% higher on Day 5 in elderly (65 years and older) relative to younger adults. The Cmax was 10% higher on Day 1 and 24% higher on Day 5 in elderly relative to younger adults. These differences are not considered clinically meaningful [see Use in Specific Populations (8.5)].
Male and Female Patients
Following oral administration of a single dose of aprepitant ranging from 40 mg to 375 mg, the AUC0-24hr and Cmax are 9% and 17% higher in females as compared with males. The half-life of aprepitant is 25% lower in females as compared with males and Tmax occurs at approximately the same time. These differences are not considered clinically meaningful.
Racial or Ethnic Groups
Following oral administration of a single dose of aprepitant, ranging from 40 mg to 375 mg, the AUC0-24hr and Cmax are approximately 27% and 19% higher in Hispanics as compared with Caucasians. The AUC0-24hr and Cmax were 74% and 47% higher in Asians as compared to Caucasians. There was no difference in AUC0-24hr or Cmax between Caucasians and Blacks. These differences are not considered clinically meaningful.
Patients with Renal Impairment
A single 240 mg oral dose of aprepitant was administered to patients with severe renal impairment (creatinine clearance less than 30 mL/min/1.73 m2 as measured by 24-hour urinary creatinine clearance) and to patients with end stage renal disease (ESRD) requiring hemodialysis.
In patients with severe renal impairment, the AUC0-∞ of total aprepitant (unbound and protein bound) decreased by 21% and Cmax decreased by 32%, relative to healthy subjects (creatinine clearance greater than 80 mL/min estimated by Cockcroft-Gault method). In patients with ESRD undergoing hemodialysis, the AUC0-∞ of total aprepitant decreased by 42% and Cmax decreased by 32%. Due to modest decreases in protein binding of aprepitant in patients with renal disease, the AUC of pharmacologically active unbound drug was not significantly affected in patients with renal impairment compared with healthy subjects. Hemodialysis conducted 4 or 48 hours after dosing had no significant effect on the pharmacokinetics of aprepitant; less than 0.2% of the dose was recovered in the dialysate.
Patients with Hepatic Impairment
Following administration of a single 125 mg oral dose of aprepitant on Day 1 and 80 mg once daily on Days 2 and 3 to patients with mild hepatic impairment (Child-Pugh score 5 to 6), the AUC0-24hr of aprepitant was 11% lower on Day 1 and 36% lower on Day 3, as compared with healthy subjects given the same regimen. In patients with moderate hepatic impairment (Child-Pugh score 7 to 9), the AUC0-24hr of aprepitant was 10% higher on Day 1 and 18% higher on Day 3, as compared with healthy subjects given the same regimen. These differences in AUC0-24hr are not considered clinically meaningful. There are no clinical or pharmacokinetic data in patients with severe hepatic impairment (Child-Pugh score greater than 9) [see Use in Specific Populations (8.6)].
Body Mass Index (BMI)
For every 5 kg/m2 increase in BMI AUC0-24hr and Cmax of aprepitant decrease by 9% and 10%. BMI of subjects in the analysis ranged from 18 kg/m2 to 36 kg/m2. This change is not considered clinically meaningful.
Drug Interactions Studies
Aprepitant is a substrate, and a weak-to-moderate (dose-dependent) inhibitor of CYP3A4. Aprepitant is also an inducer of CYP3A4, and CYP2C9. Aprepitant is unlikely to interact with drugs that are substrates for the P-glycoprotein transporter.
Effects of Fosaprepitant/Aprepitant on the Pharmacokinetics of Other Drugs
CYP3A4 Substrates:
Midazolam: Fosaprepitant 150 mg (corresponding to CINVANTI 130 mg) administered as a single intravenous dose on Day 1 increased the AUC0-∞ of midazolam by approximately 1.8-fold on Day 1 and had no effect on Day 4 when midazolam was coadministered as a single oral dose of 2 mg on Days 1 and 4.
Corticosteroids:
Dexamethasone: Fosaprepitant administered as a single 150 mg (corresponding to CINVANTI 130 mg) intravenous dose on Day 1 increased the AUC0-24hr of dexamethasone, administered as a single 8 mg oral dose on Days 1, 2, and Day 3, by approximately 2-fold on Days 1 and 2 [see Dosage and Administration (2.1), Drug Interactions (7.1)].
Methylprednisolone: When oral aprepitant as a 3-day regimen (125 mg/80 mg/80 mg) was administered with intravenous methylprednisolone 125 mg on Day 1 and oral methylprednisolone 40 mg on Days 2 and 3, the AUC of methylprednisolone was increased by 1.34-fold on Day 1 and by 2.5-fold on Day 3 [see Drug Interactions (7.1)].
Chemotherapeutic agents:
Docetaxel: In a pharmacokinetic study, oral aprepitant administered as a 3-day regimen (125 mg/80 mg/80 mg) did not influence the pharmacokinetics of docetaxel [see Drug Interactions (7.1)].
Vinorelbine: In a pharmacokinetic study, oral aprepitant administered as a 3-day regimen (125 mg/80 mg/80 mg) did not influence the pharmacokinetics of vinorelbine to a clinically significant degree [see Drug Interactions (7.1)].
CYP2C9 substrates (Warfarin, Tolbutamide):
Warfarin: A single 125 mg dose of oral aprepitant was administered on Day 1 and 80 mg/day on Days 2 and 3 to subjects who were stabilized on chronic warfarin therapy. Although there was no effect of oral aprepitant on the plasma AUC of R(+) or S(-) warfarin determined on Day 3, there was a 34% decrease in S(-) warfarin trough concentration accompanied by a 14% decrease in the prothrombin time (reported as International Normalized Ratio or INR) 5 days after completion of dosing with oral aprepitant [see Drug Interactions (7.1)].
Tolbutamide: Oral aprepitant, when given as 125 mg on Day 1 and 80 mg/day on Days 2 and 3, decreased the AUC of tolbutamide by 23% on Day 4, 28% on Day 8, and 15% on Day 15, when a single dose of tolbutamide 500 mg was administered prior to the administration of the 3-day regimen of oral aprepitant and on Days 4, 8, and 15. This effect was not considered clinically important.
Other Drugs:
Oral contraceptives: When oral aprepitant was administered as a 3-day regimen (125 mg/80 mg/80 mg) with ondansetron and dexamethasone, and coadministered with an oral contraceptive containing ethinyl estradiol and norethindrone, the trough concentrations of both ethinyl estradiol and norethindrone were reduced by as much as 64% for 3 weeks post-treatment [see Drug Interactions (7.1)].
P-glycoprotein substrates: Aprepitant is unlikely to interact with drugs that are substrates for the P-glycoprotein transporter, as demonstrated by the lack of interaction of oral aprepitant with digoxin in a clinical drug interaction study.
5-HT3 antagonists: In clinical drug interaction studies, aprepitant did not have clinically important effects on the pharmacokinetics of ondansetron, granisetron, or hydrodolasetron (the active metabolite of dolasetron).
Effect of Other Drugs on the Pharmacokinetics of Fosaprepitant/Aprepitant
Rifampin: When a single 375 mg dose of oral aprepitant was administered on Day 9 of a 14-day regimen of 600 mg/day of rifampin, a strong CYP3A4 inducer, the AUC of aprepitant decreased approximately 11-fold and the mean terminal half- life decreased approximately 3-fold [see Drug Interactions (7.2)].
Ketoconazole: When a single 125 mg dose of oral aprepitant was administered on Day 5 of a 10-day regimen of 400 mg/day of ketoconazole, a strong CYP3A4 inhibitor, the AUC of aprepitant increased approximately 5-fold and the mean terminal half-life of aprepitant increased approximately 3-fold [see Drug Interactions (7.2)].
Diltiazem: In a study in 10 patients with mild to moderate hypertension, administration of 100 mg of fosaprepitant as an intravenous infusion with 120 mg of diltiazem, a moderate CYP3A4 inhibitor administered three times daily, resulted in a 1.5-fold increase in the aprepitant AUC and a 1.4-fold increase in the diltiazem AUC.
When fosaprepitant was administered with diltiazem, the mean maximum decrease in diastolic blood pressure was significantly greater than that observed with diltiazem alone [24.3 ± 10.2 mm Hg with fosaprepitant versus 15.6 ± 4.1 mm Hg without fosaprepitant]. The mean maximum decrease in systolic blood pressure was also greater after co-administration of diltiazem with fosaprepitant than administration of diltiazem alone [29.5 ± 7.9 mm Hg with fosaprepitant versus 23.8 ± 4.8 mm Hg without fosaprepitant]. Co-administration of fosaprepitant and diltiazem; however, did not result in any additional clinically significant changes in heart rate or PR interval, beyond those changes observed with diltiazem alone [see Drug Interactions (7.2)].
Paroxetine: Coadministration of once daily doses of oral aprepitant 170 mg, with paroxetine 20 mg once daily, resulted in a decrease in AUC by approximately 25% and Cmax by approximately 20% of both aprepitant and paroxetine. This effect was not considered clinically important.
NONCLINICAL TOXICOLOGY SECTION
13 NONCLINICAL TOXICOLOGY
13.1 Carcinogenesis, Mutagenesis, Impairment of Fertility
Carcinogenesis
Carcinogenicity studies were conducted in Sprague-Dawley rats and in CD-1 mice for 2 years. In the rat carcinogenicity studies, animals were treated with oral doses ranging from 0.05 to 1000 mg/kg twice daily. The highest dose produced systemic exposures to aprepitant approximately equivalent to (female rats) or less than (male rats) the human exposure at the CINVANTI RHD of 130 mg. Treatment with aprepitant at doses of 5 to 1000 mg/kg twice daily caused an increase in the incidences of thyroid follicular cell adenomas and carcinomas in male rats. In female rats, it produced hepatocellular adenomas at 5 to1000 mg/kg twice daily and hepatocellular carcinomas and thyroid follicular cell adenomas at 125 to 1000 mg/kg twice daily. In the mouse carcinogenicity studies, the animals were treated with oral doses ranging from 2.5 to 2000 mg/kg/day. The highest dose produced a systemic exposure approximately 2 times the human exposure at the RHD of CINVANTI 130 mg. Treatment with aprepitant produced skin fibrosarcomas at 125 and 500 mg/kg/day doses in male mice.
Mutagenesis
Aprepitant was not genotoxic in the Ames test, the human lymphoblastoid cell (TK6) mutagenesis test, the rat hepatocyte DNA strand break test, the Chinese hamster ovary (CHO) cell chromosome aberration test and the mouse micronucleus test.
Impairment of Fertility
Oral aprepitant did not affect the fertility or general reproductive performance of male or female rats at doses up to the maximum feasible dose of 1000 mg/kg twice daily (providing exposure in male rats lower than the exposure at the RHD of CINVANTI 130 mg and exposure in female rats approximately equivalent to the human exposure).
CLINICAL STUDIES SECTION
14 CLINICAL STUDIES
The safety and efficacy of CINVANTI have been established based on adequate and well-controlled adult studies of a single-dose of intravenous fosaprepitant, a prodrug of aprepitant, and a 3-day regimen of oral aprepitant in chemotherapy-induced nausea and vomiting associated with HEC and MEC, respectively. Below is a description of the results of these adequate and well-controlled studies of fosaprepitant/aprepitant in these conditions.
14.1 Prevention of Nausea and Vomiting Associated with HEC
In a randomized, parallel, double-blind, active-controlled study, 150 mg fosaprepitant as a single intravenous infusion (N = 1147) was compared to a 3-day oral aprepitant regimen (N = 1175) in patients receiving a HEC regimen that included cisplatin (≥70 mg/m2). All patients in both groups received dexamethasone and ondansetron (see Table 11) Patient demographics were similar between the two treatment groups. Of the total 2322 patients, 63% were men, 56% White, 26% Asian, 3% American Indian/Alaska Native, 2% Black, 13% Multi- Racial, and 33% Hispanic/Latino ethnicity. Patient ages ranged from 19 to 86 years of age, with a mean age of 56 years. Other concomitant chemotherapy agents commonly administered were fluorouracil (17%), gemcitabine (16%), paclitaxel (15%), and etoposide (12%).
Table 11. Treatment Regimens in HEC Trial*|
Day 1 |
Day 2 |
Day 3 |
Day 4 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ||||
|
Intravenous Fosaprepitant Regimen | ||||
|
Fosaprepitant |
150 mg intravenously over 20 to 30 minutes approximately 30 minutes prior to chemotherapy |
None |
None |
None |
|
Oral dexamethasone† |
12 mg |
8 mg |
8 mg twice daily |
8 mg twice daily |
|
Ondansetron |
Ondansetron‡ |
None |
None |
None |
|
Oral Aprepitant Regimen | ||||
|
Aprepitant capsules |
125 mg |
80 mg |
80 mg |
None |
|
Oral dexamethasone§ |
12 mg |
8 mg |
8 mg |
8 mg |
|
Ondansetron |
Ondansetron‡ |
None |
None |
None |
The efficacy of a single-dose of intravenous fosaprepitant was evaluated based on the primary and secondary endpoints listed in Table 12 and was shown to be non-inferior to that of the 3-day oral aprepitant regimen with regard to complete response in each of the evaluated phases. The pre-specified non- inferiority margin for complete response in the overall phase was 7%. The pre- specified non-inferiority margin for complete response in the delayed phase was 7.3%. The pre-specified non-inferiority margin for no vomiting in the overall phase was 8.2%.
Table 12. Percent of Patients Receiving HEC Responding by Treatment Group and Phase — Cycle 1|
ENDPOINTS |
Intravenous Fosaprepitant Regimen |
Oral aprepitant Regimen |
Difference† |
|---|---|---|---|
| |||
|
PRIMARY ENDPOINT | |||
|
Complete Response‡ | |||
|
Overall§ |
71.9 |
72.3 |
-0.4 (-4.1, 3.3) |
|
SECONDARY ENDPOINTS | |||
|
Complete Response‡ | |||
|
Delayed phase¶ |
74.3 |
74.2 |
0.1 (-3.5, 3.7) |
|
No Vomiting | |||
|
Overall§ |
72.9 |
74.6 |
-1.7 (-5.3, 2.0) |
14.2 Prevention of Nausea and Vomiting Associated with MEC
Single-Dose Intravenous Fosaprepitant – MEC
In a randomized, parallel, double-blind, active comparator-controlled study, 150 mg fosaprepitant as a single intravenous infusion (N=502) in combination with ondansetron and dexamethasone (intravenous fosaprepitant regimen) was compared with ondansetron and dexamethasone alone (standard therapy) (N=498) (see Table 13) in patients receiving a MEC regimen. Patient demographics were similar between the two treatment groups. Of the total 1,000 patients included in the efficacy analysis, 41% were men, 84% White, 4% Asian, 1% American Indian/Alaska Native, 2% Black, 10% Multi-Racial, and 19% Hispanic/Latino ethnicity. Patient ages ranged from 23 to 88 years of age, with a mean age of 60 years. The most commonly administered MEC chemotherapeutic agents were carboplatin (51%), oxaliplatin (24%), and cyclophosphamide (12%).
Table 13. Treatment Regimens in MEC Trial*|
Day 1 |
Day 2 |
Day 3 | |
|---|---|---|---|
| |||
|
Intravenous Fosaprepitant Regimen | |||
|
Fosaprepitant |
150 mg intravenously over 20 to 30 minutes approximately 30 minutes prior to chemotherapy |
None |
None |
|
Oral Dexamethasone† |
12 mg |
None |
None |
|
Oral Ondansetron‡ |
8 mg for 2 doses |
None |
None |
|
Standard Therapy | |||
|
Oral Dexamethasone |
20 mg |
None |
None |
|
Oral Ondansetron‡ |
8 mg for 2 doses |
8 mg twice daily |
8 mg twice daily |
The primary endpoint was complete response (defined as no vomiting and no rescue therapy) in the delayed phase (25 to 120 hours) of chemotherapy-induced nausea and vomiting. The results by treatment group are shown in Table 14.
Table 14. Percent of Patients Receiving MEC Responding by Treatment Group|
ENDPOINTS |
Intravenous Fosaprepitant Regimen |
Standard Therapy Regimen |
p-Value |
Treatment Difference |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ||||
|
PRIMARY ENDPOINT | ||||
|
Complete Response† | ||||
|
Delayed phase‡ |
78.9 |
68.5 |
<0.001 |
10.4 (5.1, 15.9) |
3-Day Oral Aprepitant -- MEC
In a multicenter, randomized, double-blind, parallel-group, clinical study in breast cancer patients, a 3-day oral aprepitant regimen was compared with a standard of care therapy in patients receiving a MEC regimen that included cyclophosphamide 750 to1500 mg/m2; or cyclophosphamide 500 to1500 mg/m2 and doxorubicin (≤ 60 mg/m2) or epirubicin (≤ 100 mg/m2). Patients (N = 866) were randomized to either the aprepitant regimen (N = 438) or standard therapy (N = 428). The treatment regimens are defined in Table 15.
In this study, the most common chemotherapy combinations were cyclophosphamide plus doxorubicin (61%); and cyclophosphamide plus epirubicin and fluorouracil (22%).
Of the 438 patients who were randomized to receive the oral aprepitant regimen, 99.5% were women. Of these, approximately 80% were White, 8% Black, 8% Asian, 4% Hispanic, and < 1% Other. The aprepitant-treated patients in this clinical study ranged from 25 to 78 years of age, with a mean age of 53 years; 70 patients were 65 years or older, with 12 patients being over 74 years.
Table 15. Treatment Regimens in MEC Trial*|
Day 1 |
Day 2 |
Day 3 | |
|---|---|---|---|
| |||
|
Oral Aprepitant Regimen | |||
|
Aprepitant |
125 mg orally† |
80 mg orally |
80 mg orally |
|
Dexamethasone |
12 mg orally‡ |
None |
None |
|
Ondansetron |
8 mg orally × 2 doses§ |
None |
None |
|
Standard Therapy | |||
|
Dexamethasone |
20 mg orally |
None |
None |
|
Ondansetron |
8 mg orally × 2 doses |
8 mg orally twice daily |
8 mg orally twice daily |
The antiemetic activity of oral aprepitant was evaluated based on the following endpoints in which emetic episodes included vomiting, retching, or dry heaves:
Primary endpoint:
- complete response (defined as no emetic episodes and no use of rescue therapy as recorded in patient diaries) in the overall phase (0 to 120 hours post-chemotherapy)
Other prespecified endpoints:
- no emesis (defined as no emetic episodes regardless of use of rescue therapy)
- no nausea (maximum nausea visual analogue scale [VAS] score < 5 mm on a 0 to 100 mm scale)
- no significant nausea (maximum VAS score < 25 mm on a 0 to 100 mm scale)
- complete protection (defined as no emetic episodes, no use of rescue therapy, and a maximum VAS score < 25 mm on a 0 to 100 mm scale)
- complete response during the acute and delayed phases.
A summary of the key results from this study is shown in Table 16.
Table 16. Percent of Patients Receiving MEC Responding by Treatment Group and Phase – Cycle 1|
ENDPOINTS |
Oral Aprepitant Regimen |
Standard Therapy |
p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| |||
|
PRIMARY ENDPOINT† | |||
|
Complete Response |
51 |
42 |
0.015 |
|
OTHER PRESPECIFIED ENDPOINTS† | |||
|
No Emesis |
76 |
59 |
NS‡ |
|
No Nausea |
33 |
33 |
NS |
|
No Significant Nausea |
61 |
56 |
NS |
|
No Rescue Therapy |
59 |
56 |
NS |
|
Complete Protection |
43 |
37 |
NS |
In this study, a statistically significantly (p = 0.015) higher proportion of patients receiving the oral aprepitant regimen in Cycle 1 had a complete response (primary endpoint) during the overall phase compared with patients receiving standard therapy. The difference between treatment groups was primarily driven by the "No Emesis Endpoint", a principal component of this composite primary endpoint. In addition, a higher proportion of patients receiving the oral aprepitant regimen in Cycle 1 had a complete response during the acute (0 to 24 hours) and delayed (25 to 120 hours) phases compared with patients receiving standard therapy; however, the treatment group differences failed to reach statistical significance, after multiplicity adjustments.
Additional Patient-Reported Outcomes: In this study, in patients receiving MEC, the impact of nausea and vomiting on patients' daily lives was assessed in Cycle 1 using the FLIE. A higher proportion of patients receiving the oral aprepitant regimen reported minimal or no impact on daily life (64% versus 56%). This difference between treatment groups was primarily driven by the "No Vomiting Domain" of this composite endpoint.
Multiple-Cycle Extension: Patients receiving MEC were permitted to continue into the Multiple-Cycle extension of the study for up to 3 additional cycles of chemotherapy. Antiemetic effect for patients receiving the aprepitant regimen is maintained during all cycles.
Oral Aprepitant Postmarketing Trial: In another multicenter, randomized, double-blind, parallel-group, clinical study in 848 cancer patients, the 3-day oral aprepitant regimen (N = 430) was compared with a standard of care therapy (N = 418) in patients receiving a MEC regimen that included any intravenous dose of oxaliplatin, carboplatin, epirubicin, idarubicin, ifosfamide, irinotecan, daunorubicin, doxorubicin; intravenous cyclophosphamide (less than 1500 mg/m2); or intravenous cytarabine (greater than 1 g/m2).
Of the 430 patients who were randomized to receive the oral aprepitant regimen, 76% were women and 24% were men. The distribution by race was 67% White, 6% Black or African American, 11% Asian, and 12% multiracial. Classified by ethnicity, 36% were Hispanic and 64% were non-Hispanic. The aprepitant-treated patients in this clinical study ranged from 22 to 85 years of age, with a mean age of 57 years; approximately 59% of the patients were 55 years or older with 32 patients being over 74 years. Patients receiving the aprepitant regimen were receiving chemotherapy for a variety of tumor types including 50% with breast cancer, 21% with gastrointestinal cancers including colorectal cancer, 13% with lung cancer and 6% with gynecological cancers.
The antiemetic activity of aprepitant was evaluated based on no vomiting (with or without rescue therapy) in the overall period (0 to 120 hours post- chemotherapy) and complete response (defined as no vomiting and no use of rescue therapy) in the overall period.
A summary of the key results from this study is shown in Table 17.
Table 17. Percent of Patients Receiving MEC Responding by Treatment Group for Study 2 – Cycle 1|
ENDPOINTS |
Oral Aprepitant Regimen |
Standard Therapy |
p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| |||
|
No Vomiting Overall |
76 |
62 |
< 0.0001 |
|
Complete Response Overall |
69 |
56 |
0.0003 |
In this study, a statistically significantly higher proportion of patients receiving the oral aprepitant regimen (76%) in Cycle 1 had no vomiting during the overall phase compared with patients receiving standard therapy (62%). In addition, a higher proportion of patients receiving the aprepitant regimen (69%) in Cycle 1 had a complete response in the overall phase (0 to 120 hours) compared with patients receiving standard therapy (56%). In the acute phase (0 to 24 hours following initiation of chemotherapy), a higher proportion of patients receiving aprepitant compared to patients receiving standard therapy were observed to have no vomiting (92% and 84%, respectively) and complete response (89% and 80%, respectively). In the delayed phase (25 to 120 hours following initiation of chemotherapy), a higher proportion of patients receiving aprepitant compared to patients receiving standard therapy were observed to have no vomiting (78% and 67%, respectively) and complete response (71% and 61%, respectively).
In a subgroup analysis by tumor type, a numerically higher proportion of patients receiving aprepitant were observed to have no vomiting and complete response compared to patients receiving standard therapy. For gender, the difference in complete response rates between the aprepitant and standard regimen groups was 14% in females (64.5% and 50.3%, respectively) and 4% in males (82.2% and 78.2%, respectively) during the overall phase. A similar difference for gender was observed for the no vomiting endpoint.
INFORMATION FOR PATIENTS SECTION
17 PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATION
Advise the patient to read the FDA-approved patient labeling (Patient Information).
Hypersensitivity
Advise patients that hypersensitivity reactions, including anaphylaxis, have been reported [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2)]. Advise patients to stop taking CINVANTI and seek immediate medical attention if they experience signs or symptoms of a hypersensitivity reaction, such as hives, rash and itching, skin peeling or sores, or difficulty in breathing or swallowing, or dizziness, rapid or weak heartbeat or feeling faint.
Drug Interactions
Advise patients to discuss all medications they are taking, including other prescription, non- prescription medication or herbal products [see Contraindications (4), Warnings and Precautions (5.1)].
Warfarin: Instruct patients on chronic warfarin therapy to follow instructions from their healthcare provider regarding blood draws to monitor their INR during the 2-week period, particularly at 7 to 10 days, following initiation of CINVANTI with each chemotherapy cycle [see Warnings and Precautions (5.3)].
Hormonal Contraceptives: Advise patients that administration of CINVANTI may reduce the efficacy of hormonal contraceptives. Instruct patients to use effective alternative or back-up methods of non-hormonal contraception (such as condoms or spermicides) during treatment with CINVANTI and for 1 month following administration of CINVANTI or oral aprepitant, whichever is administered last [see Warnings and Precautions (5.4), Use in Specific Populations (8.3)].
Pregnancy
Advise pregnant women of the potential risk to a fetus and to avoid use of CINVANTI during pregnancy [see Use in Specific Populations (8.1)].
