Pomalyst
These highlights do not include all the information needed to use POMALYST safely and effectively. See full prescribing information for POMALYST. POMALYST (pomalidomide) capsules, for oral use Initial U.S. Approval: 2013
2b25ef01-5c9e-11e1-b86c-0800200c9a66
HUMAN PRESCRIPTION DRUG LABEL
Mar 24, 2023
Celgene Corporation
DUNS: 174201137
Products 4
Detailed information about drug products covered under this FDA approval, including NDC codes, dosage forms, ingredients, and administration routes.
pomalidomide
Product Details
FDA regulatory identification and product classification information
FDA Identifiers
Product Classification
Product Specifications
INGREDIENTS (4)
pomalidomide
Product Details
FDA regulatory identification and product classification information
FDA Identifiers
Product Classification
Product Specifications
INGREDIENTS (4)
pomalidomide
Product Details
FDA regulatory identification and product classification information
FDA Identifiers
Product Classification
Product Specifications
INGREDIENTS (4)
pomalidomide
Product Details
FDA regulatory identification and product classification information
FDA Identifiers
Product Classification
Product Specifications
INGREDIENTS (4)
Drug Labeling Information
CONTRAINDICATIONS SECTION
4 CONTRAINDICATIONS
4.1 Pregnancy
POMALYST is contraindicated in females who are pregnant. POMALYST can cause fetal harm when administered to a pregnant female [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1) and Use in Specific Populations (8.1)]. Pomalidomide is a thalidomide analogue and is teratogenic in both rats and rabbits when administered during the period of organogenesis. If the patient becomes pregnant while taking this drug, the patient should be apprised of the potential risk to a fetus.
4.2 Hypersensitivity
POMALYST is contraindicated in patients who have demonstrated severe hypersensitivity (e.g., angioedema, anaphylaxis) to pomalidomide or any of the excipients [see Warnings and Precautions (5.7), Description (11)].
•
Pregnancy (4.1)
•
Hypersensitivity (4.2)
ADVERSE REACTIONS SECTION
6 ADVERSE REACTIONS
The following clinically significant adverse reactions are described in detail in other labeling sections:
•
Embryo-Fetal Toxicity [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1, 5.2)]
•
Venous and Arterial Thromboembolism [see Warnings and Precautions (5.3)]
•
Increased Mortality in Patients with Multiple Myeloma When Pembrolizumab Is Added to a Thalidomide Analogue and Dexamethasone [see Warnings and Precautions (5.4)]
•
Hematologic Toxicity [see Warnings and Precautions (5.5)]
•
Hepatotoxicity [see Warnings and Precautions (5.6)]
•
Severe Cutaneous Reactions [see Warnings and Precautions (5.7)]
•
Dizziness and Confusional State [see Warnings and Precautions (5.8)]
•
Neuropathy [see Warnings and Precautions (5.9)]
•
Risk of Second Primary Malignancies [see Warnings and Precautions (5.10)]
•
Tumor Lysis Syndrome [see Warnings and Precautions (5.11)]
•
Hypersensitivity [see Warnings and Precautions (5.12)]
6.1 Clinical Trials Experience
Because clinical trials are conducted under widely varying conditions, adverse reaction rates observed in the clinical trials of a drug cannot be directly compared to rates in the clinical trials of another drug and may not reflect the rates observed in practice.
Multiple Myeloma (MM)
In Trial 1, data were evaluated from 219 patients (safety population) who received treatment with POMALYST + Low-dose Dex (112 patients) or POMALYST alone (107 patients). Median number of treatment cycles was 5. Sixty-seven percent of patients in the study had a dose interruption of either drug due to adverse reactions. Forty-two percent of patients in the study had a dose reduction of either drug due to adverse reactions. The discontinuation rate due to adverse reactions was 11%.
In Trial 2, data were evaluated from 450 patients (safety population) who received treatment with POMALYST + Low-dose Dex (300 patients) or High-dose Dexamethasone (High-dose Dex) (150 patients). The median number of treatment cycles for the POMALYST + Low-dose Dex arm was 5. In the POMALYST + Low-dose Dex arm, 67% of patients had a dose interruption of POMALYST, the median time to the first dose interruption of POMALYST was 4.1 weeks. Twenty-seven percent of patients had a dose reduction of POMALYST, the median time to the first dose reduction of POMALYST was 4.5 weeks. Eight percent of patients discontinued POMALYST due to adverse reactions.
Tables 3 and 4 summarize the adverse reactions reported in Trials 1 and 2, respectively.
Table 3: Adverse Reactions in Any POMALYST Treatment Arm in Trial 1*
| ||||
|
All Adverse Reactions ≥10% in Either Arm |
Grade 3 or 4 ≥5% in Either Arm | |||
|
Body System |
POMALYSTa |
POMALYST + Low-dose Dex |
POMALYST |
POMALYST + Low-dose Dex |
|
Number (%) of patients with at least one adverse reaction |
107 (100) |
112 (100) |
98 (92) |
102 (91) |
|
** Blood and lymphatic system disorders** | ||||
|
Neutropenia b |
57 (53) |
55 (49) |
51 (48) |
46 (41) |
|
Anemia b |
41 (38) |
47 (42) |
25 (23) |
24 (21) |
|
Thrombocytopenia b |
28 (26) |
26 (23) |
24 (22) |
21 (19) |
|
Leukopenia |
14 (13) |
22 (20) |
7 (7) |
11 (10) |
|
Febrile neutropenia b |
<10% |
<10% |
6 (6) |
3 (3) |
|
Lymphopenia |
4 (4) |
17 (15) |
2 (2) |
8 (7) |
|
** General disorders and administration site conditions** | ||||
|
Fatigue and asthenia b |
62 (58) |
70 (63) |
13 (12) |
19 (17) |
|
Edema peripheral |
27 (25) |
19 (17) |
0 (0.0) |
0 (0.0) |
|
Pyrexia b |
25 (23) |
36 (32) |
<5% |
<5% |
|
Chills |
11 (10) |
14 (13) |
0 (0.0) |
0 (0.0) |
|
** Gastrointestinal disorders** | ||||
|
Nausea b |
39 (36) |
27 (24) |
<5% |
<5% |
|
Constipation b |
38 (36) |
41 (37) |
<5% |
<5% |
|
Diarrhea |
37 (35) |
40 (36) |
<5% |
<5% |
|
Vomiting b |
15 (14) |
16 (14) |
<5% |
0 (0.0) |
|
** Musculoskeletal and connective tissue disorders** | ||||
|
Back pain b |
37 (35) |
36 (32) |
15 (14) |
11 (10) |
|
Musculoskeletal chest pain |
25 (23) |
22 (20) |
<5% |
0 (0.0) |
|
Muscle spasms |
23 (21) |
22 (20) |
<5% |
<5% |
|
Arthralgia |
18 (17) |
17 (15) |
<5% |
<5% |
|
Muscular weakness |
15 (14) |
15 (13) |
6 (6) |
4 (4) |
|
Bone pain |
13 (12) |
8 (7) |
<5% |
<5% |
|
Musculoskeletal pain |
13 (12) |
19 (17) |
<5% |
<5% |
|
Pain in extremity |
8 (7) |
16 (14) |
0 (0.0) |
<5% |
|
** Infections and infestations** | ||||
|
Upper respiratory tract infection |
40 (37) |
32 (29) |
<5% |
<5% |
|
Pneumonia b |
30 (28) |
38 (34) |
21 (20) |
32 (29) |
|
Urinary tract infection b |
11 (10) |
19 (17) |
2 (2) |
10 (9) |
|
Sepsis b |
<10% |
<10% |
6 (6) |
5 (4) |
|
** Metabolism and nutrition disorders** | ||||
|
Decreased appetite |
25 (23) |
21 (19) |
<5% |
0 (0.0) |
|
Hypercalcemia b |
23 (21) |
13 (12) |
11 (10) |
1 (<1) |
|
Hypokalemia |
13 (12) |
13 (12) |
<5% |
<5% |
|
Hyperglycemia |
12 (11) |
17 (15) |
<5% |
<5% |
|
Hyponatremia |
12 (11) |
14 (13) |
<5% |
<5% |
|
Dehydration b |
<10% |
<10% |
5 (4.7) |
6 (5.4) |
|
Hypocalcemia |
6 (6) |
13 (12) |
0 (0.0) |
<5% |
|
** Respiratory, thoracic and mediastinal disorders** | ||||
|
Dyspnea b |
38 (36) |
50 (45) |
8 (7) |
14 (13) |
|
Cough |
18 (17) |
25 (22) |
0 (0.0) |
0 (0.0) |
|
Epistaxis |
18 (17) |
12 (11) |
<5% |
0 (0.0) |
|
Productive cough |
10 (9) |
14 (13) |
0 (0.0) |
0 (0.0) |
|
Oropharyngeal pain |
6 (6) |
12 (11) |
0 (0.0) |
0 (0.0) |
|
** Nervous system disorders** | ||||
|
Dizziness |
24 (22) |
20 (18) |
<5% |
<5% |
|
Peripheral neuropathy |
23 (21) |
20 (18) |
0 (0.0) |
0 (0.0) |
|
Headache |
16 (15) |
15 (13) |
0 (0.0) |
<5% |
|
Tremor |
11 (10) |
15 (13) |
0 (0.0) |
0 (0.0) |
|
** Skin and subcutaneous tissue disorders** | ||||
|
Rash |
22 (21) |
18 (16) |
0 (0.0) |
<5% |
|
Pruritus |
16 (15) |
10 (9) |
0 (0.0) |
0 (0.0) |
|
Dry skin |
10 (9) |
12 (11) |
0 (0.0) |
0 (0.0) |
|
Hyperhidrosis |
8 (7) |
18 (16) |
0 (0.0) |
0 (0.0) |
|
Night sweats |
5 (5) |
14 (13) |
0 (0.0) |
0 (0.0) |
|
** Investigations** | ||||
|
Blood creatinine increased b |
20 (19) |
11 (10) |
6 (6) |
3 (3) |
|
Weight decreased |
16 (15) |
10 (9) |
0 (0.0) |
0 (0.0) |
|
Weight increased |
1 (<1) |
12 (11) |
0 (0.0) |
0 (0.0) |
|
** Psychiatric disorders** | ||||
|
Anxiety |
14 (13) |
8 (7) |
0 (0.0) |
0 (0.0) |
|
Confusional state b |
13 (12) |
15 (13) |
6 (6) |
3 (3) |
|
Insomnia |
7 (7) |
18 (16) |
0 (0.0) |
0 (0.0) |
|
** Renal and urinary disorders** | ||||
|
Renal failure b |
16 (15) |
11 (10) |
9 (8) |
8 (7) |
|
a Percentage did not meet the criteria to be considered as an adverse reaction
for POMALYST for that category of event (i.e., all adverse events or Grade 3
or 4 adverse events). | ||||
|
All Adverse Reactions |
Grade 3 or 4 | |||
|
Body System |
POMALYST + Low-dose Dex |
High-dose Dex |
POMALYST + Low-dose Dex |
High-dose Dex |
|
Number (%) of patients with at least one adverse reaction |
297 (99) |
149 (99) |
259 (86) |
127 (85) |
|
Blood and lymphatic system disorders | ||||
|
Neutropenia b |
154 (51) |
31 (21) |
145 (48) |
24 (16) |
|
Thrombocytopenia |
89 (30) a |
44 (29) a |
66 (22) a |
39 (26) a |
|
Leukopenia |
38 (13) |
8 (5) |
27 (9) |
5 (3) |
|
Febrile neutropenia b |
28 (9) |
0 (0.0) |
28 (9) |
0 (0.0) |
|
General disorders and administration site conditions | ||||
|
Fatigue and asthenia |
140 (47) |
64 (43) |
26 (9) a |
18 (12) a |
|
Pyrexia b |
80 (27) |
35 (23) |
9 (3) a |
7 (5) a |
|
Edema peripheral |
52 (17) |
17 (11) |
4 (1) a |
3 (2) a |
|
Pain |
11 (4) a |
3 (2) a |
5 (2) |
1 (<1) |
|
Infections and infestations | ||||
|
Upper respiratory tract infection b |
93 (31) |
19 (13) |
9 (3) |
1 (<1) |
|
Pneumonia b |
58 (19) |
20 (13) |
47 (16) |
15 (10) |
|
Neutropenic sepsis b |
3 (1) a |
0 (0.0) a |
3 (1) |
0 (0.0) |
|
Gastrointestinal disorders | ||||
|
Diarrhea |
66 (22) |
28 (19) |
3 (1) a |
2 (1) a |
|
Constipation |
65 (22) |
22 (15) |
7 (2) |
0 (0.0) |
|
Nausea |
45 (15) |
17 (11) |
3 (1) a |
2 (1) a |
|
Vomiting |
23 (8) |
6 (4) |
3 (1) |
0 (0.0) |
|
Musculoskeletal and connective tissue disorders | ||||
|
Back pain b |
59 (20) |
24 (16) |
15 (5) |
6 (4) |
|
Bone pain b |
54 (18) |
21 (14) |
22 (7) |
7 (5) |
|
Muscle spasms |
46 (15) |
11 (7) |
1 (<1) a |
1 (<1) a |
|
Arthralgia |
26 (9) |
7 (5) |
2 (<1) a |
1 (<1) a |
|
Pain in extremity |
20 (7) a |
9 (6) a |
6 (2) |
0 (0.0) |
|
Respiratory, thoracic and mediastinal disorders | ||||
|
Dyspnea b |
76 (25) |
25 (17) |
17 (6) |
7 (5) |
|
Cough |
60 (20) |
15 (10) |
2 (<1) a |
1 (<1) a |
|
Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease b |
5 (2) a |
0 (0.0) a |
4 (1) |
0 (0.0) |
|
Nervous system disorders | ||||
|
Peripheral neuropathy |
52 (17) |
18 (12) |
5 (2) a |
2 (1) a |
|
Dizziness |
37 (12) |
14 (9) |
4 (1) a |
2 (1) a |
|
Headache |
23 (8) |
8 (5) |
1 (<1) a |
0 (0.0) a |
|
Tremor |
17 (6) |
2 (1) |
2 (<1) a |
0 (0.0) a |
|
Depressed level of consciousness |
5 (2) a |
0 (0.0) a |
3 (1) |
0 (0.0) |
|
Metabolism and nutrition disorders | ||||
|
Decreased appetite |
38 (13) |
12 (8) |
3 (1) a |
2 (1) a |
|
Hypokalemia |
28 (9) a |
12 (8) a |
12 (4) |
4 (3) |
|
Hypocalcemia |
12 (4) a |
9 (6) a |
5 (2) |
1 (<1) |
|
Skin and subcutaneous tissue disorders | ||||
|
Rash |
23 (8) |
2 (1) |
3 (1) |
0 (0.0) |
|
Pruritus |
22 (7) |
5 (3) |
0 (0.0) a |
0 (0.0) a |
|
Hyperhidrosis |
15 (5) |
1 (<1) |
0 (0.0) a |
0 (0.0) a |
|
Investigations | ||||
|
Neutrophil count decreased |
15 (5) |
1 (<1) |
14 (5) |
1 (<1) |
|
Platelet count decreased |
10 (3) a |
3 (2) a |
8 (3) |
2 (1) |
|
White blood cell count decreased |
8 (3) a |
1 (<1) a |
8 (3) |
0 (0.0) |
|
Alanine aminotransferase increased |
7 (2) a |
2 (1) a |
5 (2) |
0 (0.0) |
|
Aspartate aminotransferase increased |
4 (1) a |
2 (1) a |
3 (1) |
0 (0.0) |
|
Lymphocyte count decreased |
3 (1) a |
1 (<1) a |
3 (1) |
0 (0.0) |
|
Renal and urinary disorders | ||||
|
Renal failure |
31 (10) a |
18 (12) a |
19 (6) |
8 (5) |
|
Injury, poisoning and procedural complications | ||||
|
Femur fracture b |
5 (2) a |
1 (<1) a |
5 (2) |
1 (<1) |
|
Reproductive system and breast disorders | ||||
|
Pelvic pain |
6 (2) a |
3 (2) a |
4 (1) |
0 (0.0) |
Other Adverse Reactions
Other adverse reactions of POMALYST in patients with MM, not described above, and considered important:
Cardiac Disorders: Myocardial infarction, Atrial fibrillation, Angina pectoris, Cardiac failure congestive
Ear and Labyrinth Disorders: Vertigo
Gastrointestinal disorders: Abdominal pain
General Disorders and Administration Site Conditions: General physical health deterioration, Non-cardiac chest pain, Multi-organ failure
Hepatobiliary Disorders: Hyperbilirubinemia
Infections and Infestations: Pneumocystis jiroveci pneumonia, Respiratory syncytial virus infection, Neutropenic sepsis, Bacteremia, Pneumonia respiratory syncytial viral, Cellulitis, Urosepsis, Septic shock, Clostridium difficile colitis, Pneumonia streptococcal, Lobar pneumonia, Viral infection, Lung infection
Investigations: Alanine aminotransferase increased, Hemoglobin decreased
Injury, poisoning and procedural complications: Fall, Compression fracture, Spinal compression fracture
Metabolism and nutritional disorders: Hyperkalemia, Failure to thrive
Nervous system disorders: Depressed level of consciousness, Syncope
Psychiatric disorders: Mental status change
Renal and urinary disorders: Urinary retention, Hyponatremia
Reproductive system and breast disorders: Pelvic pain
Respiratory, thoracic, and mediastinal disorders: Interstitial lung disease, Pulmonary embolism, Respiratory failure, Bronchospasm
Vascular disorders: Hypotension
Kaposi Sarcoma (KS)
The safety of POMALYST in patients with KS was evaluated in Trial 12-C-0047 [see Clinical Studies (14.2)]. Twenty-eight patients received POMALYST 5 mg taken orally once daily on Days 1 through 21 of repeated 28-day cycles. The study excluded patients with procoagulant disorders or a history of venous or arterial thromboembolism. Patients received DVT prophylaxis with daily low dose aspirin. Across all patients treated on Trial 12-C-0047, 75% were exposed to pomalidomide for 6 months or longer and 25% were exposed for greater than one year.
Serious adverse reactions occurred in 18% (5/28) of patients who received POMALYST. The following serious adverse reactions each occurred in 1 patient: anemia, decreased neutrophil count, and hematuria.
Permanent discontinuation due to an adverse reaction occurred in 11% (3/28) of patients who received POMALYST.
Dosage interruptions due to an adverse reaction occurred in 14% (4/28) of patients who received POMALYST. The most frequent adverse reaction requiring dosage interruption was decreased neutrophil count, which occurred in 3 patients.
The POMALYST dose was reduced due to an adverse reaction in 1 patient due to gout.
Tables 5 and 6 summarize the adverse reactions and select laboratory abnormalities reported in Trial 12-C-0047.
Table 5: Adverse Reactions (≥ 20%) in Patients Who Received POMALYST in Trial 12-C-0047|
Adverse Reaction |
Grades 1-4 |
Grade 3 or 4 |
|
Rash, maculo-papular |
71 |
3.6 |
|
Constipation |
71 |
0 |
|
Fatigue |
68 |
0 |
|
Nausea |
36 |
0 |
|
Diarrhea |
32 |
3.6 |
|
Cough |
29 |
0 |
|
Dyspnea |
29 |
0 |
|
Peripheral Edema |
29 |
3.6 |
|
Upper respiratory tract infection |
29 |
0 |
|
Muscle spasms |
25 |
0 |
|
Hypothyroidism |
21 |
0 |
|
Dry skin |
21 |
0 |
|
Chills |
21 |
0 |
| ||
|
Laboratory Abnormality |
Grades 1-4* |
Grades 3-4* |
|
Hematology | ||
|
Decreased Absolute Neutrophil Count |
96 |
50 |
|
Decreased White Blood Cells |
79 |
3.6 |
|
Decreased Hemoglobin |
54 |
0 |
|
Decreased Platelets |
54 |
0 |
|
Chemistry | ||
|
Elevated Creatinine |
86 |
3.6 |
|
Elevated Glucose |
57 |
7 |
|
Decreased Albumin |
54 |
0 |
|
Decreased Phosphate |
54 |
25 |
|
Decreased Calcium |
50 |
0 |
|
Increased Alanine Aminotransferase (ALT) |
32 |
0 |
|
Increased Aspartate Aminotransferase (AST) |
25 |
0 |
|
Elevated Creatine Kinase |
25 |
7 |
|
Decreased Magnesium |
14 |
0 |
|
Elevated Alkaline Phosphate |
14 |
3.6 |
6.2 Postmarketing Experience
The following adverse reactions have been identified during postapproval use of POMALYST. Because these reactions are reported voluntarily from a population of uncertain size, it is not always possible to reliably estimate their frequency or establish a causal relationship to drug exposure.
Blood and Lymphatic System Disorders: Pancytopenia
Endocrine Disorders: Hypothyroidism, hyperthyroidism
Gastrointestinal Disorders: Gastrointestinal hemorrhage
Hepatobiliary Disorders: Hepatic failure (including fatal cases), elevated liver enzymes
Immune system Disorders: Allergic reactions (e.g., angioedema, anaphylaxis, urticaria), solid organ transplant rejection
Infections and Infestations: Hepatitis B virus reactivation, Herpes zoster, progressive multifocal leukoencephalopathy (PML)
Neoplasms benign, malignant and unspecified (incl cysts and polyps): Tumor lysis syndrome, basal cell carcinoma, and squamous cell carcinoma of the skin
Skin and Subcutaneous Tissue Disorders: Stevens-Johnson Syndrome, toxic epidermal necrolysis, drug reaction with eosinophilia and systemic symptoms (DRESS)
•
MM: Most common adverse reactions (≥30%) included fatigue and asthenia, neutropenia, anemia, constipation, nausea, diarrhea, dyspnea, upper-respiratory tract infections, back pain, and pyrexia (6.1).
•
KS: Most common adverse reactions including laboratory abnormalities (≥30%) are decreased absolute neutrophil count or white blood cells, elevated creatinine or glucose, rash, constipation, fatigue, decreased hemoglobin, platelets, phosphate, albumin, or calcium, increased ALT, nausea, and diarrhea (6.1).
**To report SUSPECTED ADVERSE REACTIONS, contactBristol Myers Squibb at 1-800-721-5072 or FDA at 1-800-FDA-1088 or **www.fda.gov/medwatch.
DRUG INTERACTIONS SECTION
7 DRUG INTERACTIONS
7.1 Drugs That Affect Pomalidomide Plasma Concentrations
CYP1A2 inhibitors:
In healthy subjects, co-administration of fluvoxamine, a strong CYP1A2 inhibitor, increased Cmax and AUC of pomalidomide by 24% and 125% respectively [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)]. Increased pomalidomide exposure may increase the risk of exposure related toxicities. Avoid co-administration of strong CYP1A2 inhibitors (e.g. ciprofloxacin and fluvoxamine). If co- administration is unavoidable, reduce the POMALYST dose [see Dosage and Administration (2.6)].
Strong CYP1A2 Inhibitors: Avoid concomitant use of strong CYP1A2 inhibitors. If concomitant use of a strong CYP1A2 inhibitor is unavoidable, reduce POMALYST dose to 2 mg (2.6, 7.1, 12.3).
CLINICAL STUDIES SECTION
14 CLINICAL STUDIES
14.1 Multiple Myeloma
Trial 1
Trial 1 was a phase 2, multicenter, randomized open-label study in patients with relapsed multiple myeloma (MM) who were refractory to their last myeloma therapy and had received lenalidomide and bortezomib. Patients were considered relapsed if they had achieved at least stable disease for at least 1 cycle of treatment to at least 1 prior regimen and then developed progressive disease. Patients were considered refractory if they experienced disease progression on or within 60 days of their last therapy. A total of 221 patients were randomized to receive POMALYST alone or POMALYST with Low-dose Dex. In Trial 1, the safety and efficacy of POMALYST 4 mg, once daily for 21 of 28 days, until disease progression, were evaluated alone and in combination with Low- dose Dex (40 mg/day given only on Days 1, 8, 15, and 22 of each 28-day cycle for patients aged 75 years or younger, or 20 mg/day given only on Days 1, 8, 15, and 22 of each 28-day cycle for patients aged greater than 75 years). Patients in the POMALYST alone arm were allowed to add Low-dose Dex upon disease progression.
Table 7 summarizes the baseline patient and disease characteristics in Trial
- The baseline demographics and disease characteristics were balanced and comparable between the study arms.
|
POMALYST |
POMALYST + Low-dose Dex | |
|---|---|---|
|
Data cutoff: 01 April 2011 | ||
|
Patient Characteristics | ||
|
Median age, years (range) |
61 (37-88) |
64 (34-88) |
|
Age distribution, n (%) | ||
|
<65 years |
65 (60.2) |
60 (53.1) |
|
≥65 years |
43 (39.8) |
53 (46.9) |
|
Sex, n (%) | ||
|
Male |
57 (52.8) |
62 (54.9) |
|
Female |
51 (47.2) |
51 (45.1) |
|
Race/ethnicity, n (%) | ||
|
White |
86 (79.6) |
92 (81.4) |
|
Black or African American |
16 (14.8) |
17 (15) |
|
All other race |
6 (5.6) |
4 (3.6) |
|
ECOG Performance, n (%) | ||
|
Status 0-1 |
95 (87.9) |
100 (88.5) |
|
Disease Characteristics | ||
|
Number of prior therapies | ||
|
Median (min, max) |
5 (2, 12) |
5 (2, 13) |
|
Prior transplant, n (%) |
82 (75.9) |
84 (74.3) |
|
Refractory to bortezomib and lenalidomide, n (%) |
64 (59.3) |
69 (61.1) |
Table 8 summarizes the analysis results of overall response rate (ORR) and duration of response (DOR), based on assessments by the Independent Review Adjudication Committee for the treatment arms in Trial 1. ORR did not differ based on type of prior antimyeloma therapy.
Table 8: Trial 1 Results|
a Results are prior to the addition of dexamethasone. | ||
|
POMALYST****a |
POMALYST + Low-dose Dex | |
|
Response | ||
|
Overall Response Rate (ORR),b n (%) |
8 (7.4) |
33 (29.2) |
|
95% CI for ORR (%) |
(3.3, 14.1) |
(21.0, 38.5) |
|
Complete Response (CR), n (%) |
0 (0.0) |
1 (0.9) |
|
Partial Response (PR), n (%) |
8 (7.4) |
32 (28.3) |
|
Duration of Response (DOR) | ||
|
Median, months |
NE |
7.4 |
|
95% CI for DOR (months) |
NE |
(5.1, 9.2) |
Trial 2
Trial 2 was a Phase 3 multi-center, randomized, open-label study, where POMALYST + Low-dose Dex therapy was compared to High-dose Dex in adult patients with relapsed and refractory MM, who had received at least two prior treatment regimens, including lenalidomide and bortezomib, and demonstrated disease progression on or within 60 days of the last therapy. Patients with creatinine clearance ≥ 45mL/min qualified for the trial. A total of 455 patients were enrolled in the trial: 302 in the POMALYST + Low-dose Dex arm and 153 in the High-dose Dex arm. Patients in the POMALYST + Low-dose Dex arm were administered 4 mg POMALYST orally on Days 1 to 21 of each 28-day cycle. Dexamethasone (40 mg) was administered once per day on Days 1, 8, 15 and 22 of a 28-day cycle. Patients > 75 years of age started treatment with 20 mg dexamethasone using the same schedule. For the High-dose Dex arm, dexamethasone (40 mg) was administered once per day on Days 1 through 4, 9 through 12, and 17 through 20 of a 28-day cycle. Patients > 75 years of age started treatment with 20 mg dexamethasone using the same schedule. Treatment continued until patients had disease progression.
Baseline patient and disease characteristics were balanced and comparable between the study arms, as summarized in Table 9. Overall, 94% of patients had disease refractory to lenalidomide, 79% had disease refractory to bortezomib and 74% had disease refractory to both lenalidomide and bortezomib.
Table 9: Baseline Demographic and Disease-Related Characteristics – Trial 2|
Data cutoff: 01March 2013 | ||
|
POMALYST + Low-dose Dex |
High-dose Dex | |
|
(N=302) |
(N=153) | |
|
Patient Characteristics | ||
|
Median Age, years (range) |
64 (35, 84) |
65 (35, 87) |
|
Age Distribution n (%) | ||
|
< 65 years |
158 (52) |
74 (48) |
|
≥ 65 years |
144 (48) |
79 (52) |
|
Sex n (%) | ||
|
Male |
181 (60) |
87 (57) |
|
Female |
121 (40) |
66 (43) |
|
Race/Ethnicity n (%) | ||
|
White |
244 (81) |
113 (74) |
|
Black or African American |
4 (1) |
3 (2) |
|
Asian |
4 (1) |
0 (0) |
|
Other Race |
2 (1) |
2 (1) |
|
Not Collected |
48 (16) |
35 (23) |
|
ECOG Performance n (%) | ||
|
Status 0 |
110 (36) |
36 (24) |
|
Status 1 |
138 (46) |
86 (56) |
|
Status 2 |
52 (17) |
25 (16) |
|
Status 3 |
0 (0) |
3 (2) |
|
Missing |
2 (1) |
3 (2) |
|
Disease Characteristics | ||
|
Number of Prior Therapies | ||
|
Median, (Min, Max) |
5 (2, 14) |
5 (2, 17) |
|
Prior stem cell transplant n (%) |
214 (71) |
105 (69) |
|
Refractory to bortezomib and lenalidomide n (%) |
225 (75) |
113 (74) |
Table 10 summarizes the progression free survival (PFS) and overall response rate (ORR) based on the assessment by the Independent Review Adjudication Committee (IRAC) review at the final PFS analysis and overall survival (OS) at the OS analysis. PFS was significantly longer with POMALYST + Low-dose Dex than High-dose Dex: HR 0.45 (95% CI: 0.35-0.59 p < 0.001). OS was also significantly longer with POMALYST + Low-dose Dex than High-dose Dex: HR 0.70 (95% CI: 0.54-0.92 p = 0.009). The Kaplan-Meier curves for PFS and OS for the ITT population are provided in Figures 1 and 2, respectively.
Table 10: Trial 2 Results|
Note: CI=Confidence interval; HD-Dex=High dose dexamethasone; IRAC=Independent
Review Adjudication Committee; LD-Dex=Low dose dexamethasone. | ||
|
POMALYST + Low-dose Dex |
High-dose Dex | |
|
(N=302) |
(N=153) | |
|
Progression Free Survival Time | ||
|
Number (%) of events |
164 (54.3) |
103 (67.3) |
|
Mediana (2-sided 95% CI) (months) |
3.6 [3.0, 4.6] |
1.8 [1.6, 2.1] |
|
Hazard Ratio (Pom+LD-Dex:HD-Dex) 2-Sided 95% CIb |
0.45 [0.35, 0.59] | |
|
Log-Rank Test 2-sided P-Valuec |
<0.001 | |
|
Overall Survival Timed | ||
|
Number (%) of deaths |
147 (48.7) |
86 (56.2) |
|
Mediana (2-sided 95% CI) (months) |
12.4 [10.4, 15.3] |
8.0 [6.9, 9.0] |
|
Hazard Ratio (Pom+LD-Dex:HD-Dex) 2-Sided 95% CIe |
0.70 [0.54, 0.92] | |
|
Log-Rank Test 2-sided P-Value f, g |
0.009 | |
|
Overall Response Rate, n (%) |
71 (23.5) |
6 (3.9) |
|
Complete Response |
1 (0.3) |
0 |
|
Very Good Partial Response |
8 (2.6) |
1 (0.7) |
|
Partial Response |
62 (20.5) |
5 (3.3) |
Figure 1: Progression Free Survival Based on IRAC Review of Response by IMWG Criteria (Stratified Log Rank Test) (ITT Population)
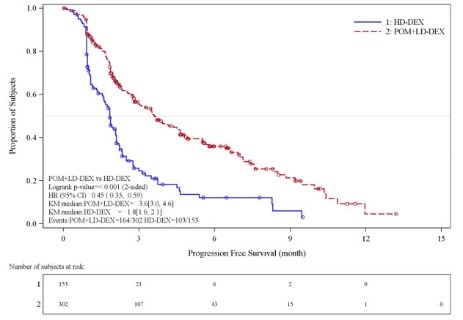
Data cut-off: 07 Sep 2012
Figure 2: Kaplan-Meier Curve of Overall Survival (ITT Population)
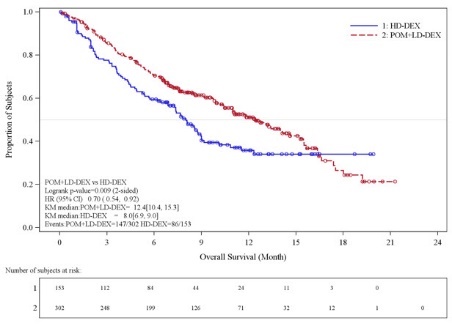
Data cutoff: 01 Mar 2013
14.2 Kaposi Sarcoma
The clinical trial 12-C-0047 (NCT01495598), was an open label, single center, single arm clinical study that evaluated the safety and efficacy of POMALYST in patients with Kaposi sarcoma (KS). A total of 28 patients (18 HIV-positive, 10 HIV-negative) received POMALYST 5 mg orally once daily on Days 1 through 21 of each 28-day cycle until disease progression or unacceptable toxicity. All HIV-positive patients continued highly active antiretroviral therapy (HAART). The trial excluded patients with symptomatic pulmonary or visceral KS, history of venous or arterial thromboembolism, or procoagulant disorders. Patients received thromboprophylaxis with aspirin 81 mg once daily throughout therapy.
The median age was 52.5 years, all were male, 75% were White, and 14% Black or African American. Seventy-five percent of patients had advanced disease (T1) at the time of enrollment, 11% had ≥ 50 lesions, and 75% had received prior chemotherapy.
The major efficacy outcome measure was overall response rate (ORR), which included complete response (CR), clinical complete response (cCR), and partial response (PR). Response was assessed by the investigator according to the AIDS Clinical Trial Group (ACTG) Oncology Committee response criteria for KS. The median time to first response was 1.8 months (0.9 to 7.6). Efficacy results are presented in Table 11.
Table 11: Trial 12-C-0047 Results|
CI: confidence interval, ORR: overall response rate, CR: complete response,
PR: partial response | |||
|
All Patients |
HIV-Positive |
HIV-Negative | |
|
ORR 1, n (%) |
20 (71) |
12 (67) |
8 (80) |
|
[95% CI] |
[51, 87] |
(41, 87) |
(44, 98) |
|
CR 1, n (%) |
4 (14) |
3 (17) |
1 (10) |
|
PR, n (%) |
16 (57) |
9 (50) |
7 (70) |
|
Duration of Response, KS 2, |
12.1 |
12.5 |
10.5 |
|
Median in months [95% CI]3 |
[7.6, 16.8] |
[6.5, 24.9] |
[3.9, 24.2] |
|
Duration of Response, KS (%) | |||
|
Percent greater than 12 months |
50 |
58 |
38 |
|
Percent greater than 24 months |
20 |
17 |
25 |
HOW SUPPLIED SECTION
16 HOW SUPPLIED/STORAGE AND HANDLING
Dark blue opaque cap and yellow opaque body, imprinted "POML" on the cap in white ink and "1 mg" on the body in black ink
|
1 mg bottles of 21 |
(NDC 59572-501-21) | |
|
1 mg bottles of 100 |
(NDC 59572-501-00) |
Dark blue opaque cap and orange opaque body, imprinted "POML" on the cap and "2 mg" on the body in white ink
|
2 mg bottles of 21 |
(NDC 59572-502-21) | |
|
2 mg bottles of 100 |
(NDC 59572-502-00) |
Dark blue opaque cap and green opaque body, imprinted "POML" on the cap and "3 mg" on the body in white ink
|
3 mg bottles of 21 |
(NDC 59572-503-21) | |
|
3 mg bottles of 100 |
(NDC 59572-503-00) |
Dark blue opaque cap and blue opaque body, imprinted "POML" on the cap and "4 mg" on the body in white ink
|
4 mg bottles of 21 |
(NDC 59572-504-21) | |
|
4 mg bottles of 100 |
(NDC 59572-504-00) |
Store at 20°C-25°C (68°F-77°F); excursions permitted to 15°C-30°C (59°F-86°F) [see USP Controlled Room Temperature].
Care should be exercised in handling of POMALYST. Do not open or crush POMALYST capsules. If powder from POMALYST contacts the skin, wash the skin immediately and thoroughly with soap and water. If POMALYST contacts the mucous membranes, flush thoroughly with water.
Follow procedures for proper handling and disposal of hazardous drugs. 1
SPL MEDGUIDE SECTION
|
This Medication Guide has been approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration. |
Revised: March 2023 | ||
|
MEDICATION GUIDE | |||
|
What is the most important information I should know about POMALYST? | |||
|
Before you begin taking POMALYST, you must read and agree to all of the instructions in the POMALYST REMS® program. For more information, call 1-888-423-5436 or go to www.pomalystrems.com. Before prescribing POMALYST, your healthcare provider will explain the POMALYST REMS program to you and have you sign the Patient-Physician Agreement Form. | |||
|
POMALYST can cause serious side effects including: | |||
|
• POMALYST is similar to the medicine thalidomide (THALOMID). We know thalidomide can cause severe life-threatening birth defects. POMALYST has not been tested in pregnant females. POMALYST has harmed unborn animals in animal testing. o o o o o If you miss your period or have unusual bleeding, you will need to have a pregnancy test and receive counseling. o o Healthcare providers and patients should report all cases of pregnancy to: o o o o o • Before taking POMALYST, tell your healthcare provider: o o o Call your healthcare provider or get medical help right away if you get any of the following during treatment with POMALYST: • • • | |||
|
What is POMALYST? | |||
|
POMALYST is a prescription medicine used to treat adults with: | |||
|
• o o • • | |||
|
It is not known if POMALYST is safe and effective in children. | |||
|
Who should not take POMALYST? | |||
|
Do not take POMALYST if you: | |||
|
• • | |||
|
What should I tell my healthcare provider before taking POMALYST? | |||
|
Before you take POMALYST, tell your healthcare provider if you: | |||
|
• • • • • | |||
|
Tell your healthcare provider about all the medicines you take, including prescription and over-the-counter medicines, vitamins, and herbal supplements. POMALYST and other medicines may affect each other, causing serious side effects. Talk with your healthcare provider before taking any new medicines. | |||
|
Know the medicines you take. Keep a list of them to show your healthcare provider and pharmacist. | |||
|
How should I take POMALYST? • • • • • • • • | |||
|
What should I avoid while taking POMALYST? | |||
|
• • • • • • | |||
|
What are the possible side effects of POMALYST? | |||
|
POMALYST can cause serious side effects, including: | |||
|
• • • | |||
|
o o |
o o o | ||
|
• Call your healthcare provider if you develop any of the following signs or symptoms during treatment with POMALYST: | |||
|
o |
o |
o o | |
|
Get emergency medical help right away if you develop any of the following signs or symptoms during treatment with POMALYST: | |||
|
o o o |
o o | ||
|
• • • • | |||
|
Your healthcare provider may tell you to stop taking POMALYST if you develop certain serious side effects during treatment. | |||
|
The most common side effects of POMALYST in people with Multiple Myeloma include: | |||
|
o o o |
o o o |
o o | |
|
The most common side effects of POMALYST in people with KS include: | |||
|
o o o o o |
o o o o | ||
|
These are not all the possible side effects of POMALYST. | |||
|
Call your doctor for medical advice about side effects. You may report side effects to FDA at 1-800-FDA-1088. | |||
|
How should I store POMALYST? | |||
|
• • | |||
|
Keep POMALYST and all medicines out of the reach of children. | |||
|
General information about the safe and effective use of POMALYST. | |||
|
Medicines are sometimes prescribed for purposes other than those listed in a Medication Guide. Do not take POMALYST for conditions for which it was not prescribed. Do not give POMALYST to other people, even if they have the same symptoms you have. It may harm them and may cause birth defects. | |||
|
If you would like more information, talk with your healthcare provider. You can ask your healthcare provider or pharmacist for information about POMALYST that is written for health professionals. | |||
|
For more information, call 1-888-423-5436 or go to www.pomalystrems.com. | |||
|
What are the ingredients in POMALYST? | |||
|
Active ingredient: pomalidomide | |||
|
Inactive ingredients: mannitol, pregelatinized starch, and sodium stearyl fumarate. | |||
|
The 1-mg capsule shell contains gelatin, titanium dioxide, FD&C blue 2, yellow
iron oxide, white ink, and black ink. | |||
|
Marketed by: Bristol-Myers Squibb Company, Princeton, NJ 08543 USA |
