Memantine hydrochloride
These highlights do not include all the information needed to use MEMANTINE HYDROCHLORIDE TABLETS USP safely and effectively. See full prescribing information for MEMANTINE HYDROCHLORIDE TABLETS USP. MEMANTINE hydrochloride tablets USP, for oral use Initial U.S. Approval: 2003
1b4a0162-9cb4-4ba6-8c02-95c2955734ae
HUMAN PRESCRIPTION DRUG LABEL
Sep 10, 2025
Lupin Pharmaceuticals, Inc.
DUNS: 089153071
Products 2
Detailed information about drug products covered under this FDA approval, including NDC codes, dosage forms, ingredients, and administration routes.
Memantine hydrochloride
Product Details
FDA regulatory identification and product classification information
FDA Identifiers
Product Classification
Product Specifications
INGREDIENTS (9)
Memantine hydrochloride
Product Details
FDA regulatory identification and product classification information
FDA Identifiers
Product Classification
Product Specifications
INGREDIENTS (12)
Drug Labeling Information
PACKAGE LABEL.PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL
PACKAGE LABEL.PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL
Memantine Hydrochloride Tablets, 5 mg
Bottle of 60 NDC #68180-229-07
Rx Only
Memantine Hydrochloride Tablets, 5 mg
10 X 10 Unit Dose NDC #68180-229-13
Rx Only
Memantine Hydrochloride Tablets, 10 mg
Bottle of 60 NDC #68180-230-07
Rx Only

Memantine Hydrochloride Tablets, 10 mg
10 X 10 Unit Dose NDC #68180-230-13
Rx Only

HOW SUPPLIED SECTION
16 HOW SUPPLIED/STORAGE AND HANDLING
5 mg Tablets:
Tan coloured, capsule shaped, biconvex, film-coated tablets, debossed with 'LU on one side and 'W01' on the other side.
Bottle of 60 NDC #68180-229-07
10 mg Tablets:
Grey coloured, capsule shaped, biconvex, film-coated tablets, debossed with 'LU' on one side and 'W02' on the other side.
Bottle of 60 NDC #68180-230-07
Store at 25°C (77°F); excursions permitted to 15° to 30°C (59° to 86°F) [see USP Controlled Room Temperature].
Preserve in tight containers.
SPL PATIENT PACKAGE INSERT SECTION
SPL PATIENT PACKAGE INSERT
Patient Information
Memantine Hydrochloride (me-MAN-teen HYE-droe-KLOR-ide)
Tablets USP
Read this Patient Information that comes with memantine hydrochloride tablets before you start taking it and each time you get a refill. There may be new information. This information does not take the place of talking to your doctor about your medical condition or your treatment.
What is Memantine Hydrochloride?
Memantine hydrochloride is a prescription medicine used for the treatment of moderate to severe dementia in people with Alzheimer's disease. Memantine hydrochloride belongs to a class of medicines called NMDA (N-methyl-D- aspartate) inhibitors.
It is not known if memantine hydrochloride is safe and effective in children.
Who should not take Memantine Hydrochloride Tablets?
Do not take memantine hydrochloride tablets if youare allergic to memantine or any of the ingredients in memantine hydrochloride tablets. See the end of this leaflet for a complete list of ingredients in memantine hydrochloride tablets.
**What should I tell my doctor before taking Memantine Hydrochloride Tablets? **
Before you take memantine hydrochloride tablets, tell your doctor if you:
- have or have had seizures
- have or have had problems passing urine
- have or have had bladder or kidney problems
- have liver problems
- have any other medical conditions
- are pregnant or plan to become pregnant. It is not known if memantine hydrochloride will harm your unborn baby.
- are breastfeeding or plan to breastfeed. It is not known if memantine passes into your breast milk. Talk to your doctor about the best way to feed your baby if you take memantine hydrochloride.
Tell your doctor about all the medicines you take, including prescription and nonprescription medicines, vitamins, and herbal supplements.
Taking memantine hydrochloride tablets with certain other medicines may affect each other. Taking memantine hydrochloride tablets with other medicines can cause serious side effects.
Especially tell your doctor if you take:
- other NMDA antagonists such as amantadine, ketamine, and dextromethorphan
- medicines that make your urine alkaline such as carbonic anhydrase inhibitors and sodium bicarbonate
Ask your doctor or pharmacist for a list of these medicines, if you are not sure.
Know the medicines you take. Keep a list of them to show your doctor and pharmacist when you get a new medicine.
How should I take Memantine Hydrochloride Tablet?
- Your doctor will tell you how much memantine hydrochloride tablets to take and when to take it.
- Your doctor may change your dose if needed.
- Memantine hydrochloride tablets can be taken with food or without food.
- Do not use any tablets of memantine hydrochloride that are damaged or show signs of tampering.
- If you forget to take one dose of memantine hydrochloride tablet, do not double up on the next dose. You should take only the next dose as scheduled.
- If you have forgotten to take memantine hydrochloride tablets for several days, you should not take the next dose until you talk to your doctor.
- If you take too much memantine hydrochloride tablets, call your doctor or poison control center at 1-800-222-1222 right away, or go to the nearest hospital emergency room.
What are the possible side effects of Memantine Hydrochloride Tablets?
Memantine Hydrochloride Tablets may cause side effects, including:
The most common side effects of memantine hydrochloride tablets include:
- dizziness
- headache
- confusion
- constipation
These are not all the possible side effects of memantine hydrochloride tablets. For more information, ask your doctor or pharmacist.
Call your doctor for medical advice about side effects. You may report side effects to FDA at 1-800-FDA-1088.
How should I store Memantine Hydrochloride Tablets?
- Store memantine hydrochloride tablets at room temperature between 59°F to 77°F (15°C to 30°C).
What are the ingredients in Memantine Hydrochloride Tablets?
Active ingredient: memantine hydrochloride
Inactive ingredients: croscarmellose sodium, magnesium stearate, silicified microcrystalline cellulose and talc. In addition the following inactive ingredients are also present as components of the film coat: hypromellose, titanium dioxide, polyethylene glycol, FD&C Yellow No. 6/Sunset Yellow FCF Aluminium Lake and FD&C Blue No. 2/Indigo Carmine Aluminium Lake (5 mg tablets), and hypromellose, titanium dioxide, polyethylene glycol and iron oxide black (10 mg tablets).
Keep Memantine Hydrochloride Tablets and all medicines out of the reach of children.
General information about the safe and effective use of Memantine Hydrochloride Tablets.
Medicines are sometimes prescribed for purposes other than those listed in a Patient Information leaflet. Do not take memantine hydrochloride tablets for a condition for which it was not prescribed. Do not give memantine hydrochloride tablets to other people, even if they have the same condition. It may harm them.
This Patient Information leaflet summarizes the most important information about memantine hydrochloride tablets. If you would like more information, talk with your doctor. You can ask your doctor or pharmacist for information about memantine hydrochloride tablets that was written for healthcare professionals.
For more information, contact Lupin Pharmaceuticals, Inc. at 1-800-399-2561 or www.lupinpharmaceuticals.com or FDA at 1-800-FDA-1088 or www.fda.gov/medwatch.
This Patient Information has been approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration.
LUPIN and the
 are registered trademarks of Lupin Pharmaceuticals, Inc.
are registered trademarks of Lupin Pharmaceuticals, Inc.
Manufactured for:
Lupin Pharmaceuticals, Inc.
Naples, FL 34108
United States
Manufactured by:
Lupin Limited
Goa 403 722
INDIA
Revised: August 2025 ID#: 279612
DESCRIPTION SECTION
11 DESCRIPTION
Memantine hydrochloride is an orally active NMDA receptor antagonist. The chemical name for memantine hydrochloride is 1-amino-3,5-dimethyladamantane hydrochloride with the following structural formula:
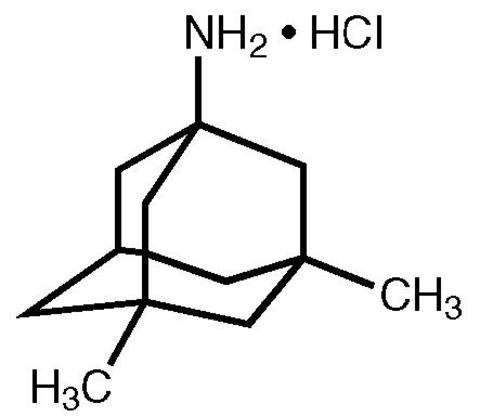
The molecular formula is C12H21N•HCl and the molecular weight is 215.76. Memantine hydrochloride occurs as a fine white to off-white powder and is soluble in water.
Memantine hydrochloride Tablets are available for oral administration as capsule-shaped, biconvex, film-coated tablets, containing memantine hydrochloride 5 mg and 10 mg. The tablets also contain the following inactive ingredients: croscarmellose sodium, magnesium stearate, silicified microcrystalline cellulose and talc. In addition the following inactive ingredients are also present as components of the film coat: hypromellose, titanium dioxide, polyethylene glycol, FD&C Yellow No. 6/Sunset Yellow FCF Aluminium Lake and FD&C Blue No. 2/Indigo Carmine Aluminium Lake (5 mg tablets), and hypromellose, titanium dioxide, polyethylene glycol and iron oxide black (10 mg tablets).
CLINICAL STUDIES SECTION
14 CLINICAL STUDIES
The effectiveness of memantine hydrochloride as a treatment for patients with moderate to severe Alzheimer's disease was demonstrated in 2 randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled clinical studies (Studies 1 and 2) conducted in the United States that assessed both cognitive function and day to day function. The mean age of patients participating in these two trials was 76 with a range of 50 to 93 years. Approximately 66% of patients were female and 91% of patients were Caucasian. A third study (Study 3), carried out in Latvia, enrolled patients with severe dementia, but did not assess cognitive function as a planned endpoint. Study Outcome Measures: In each U.S. study, the effectiveness of memantine hydrochloride was determined using both an instrument designed to evaluate overall function through caregiver-related assessment, and an instrument that measures cognition. Both studies showed that patients on memantine hydrochloride experienced significant improvement on both measures compared to placebo.
Day-to-day function was assessed in both studies using the modified Alzheimer's disease Cooperative Study-Activities of Daily Living inventory (ADCS-ADL). The ADCS-ADL consists of a comprehensive battery of ADL questions used to measure the functional capabilities of patients. Each ADL item is rated from the highest level of independent performance to complete loss. The investigator performs the inventory by interviewing a caregiver familiar with the behavior of the patient. A subset of 19 items, including ratings of the patient's ability to eat, dress, bathe, telephone, travel, shop, and perform other household chores has been validated for the assessment of patients with moderate to severe dementia. This is the modified ADCS-ADL, which has a scoring range of 0 to 54, with the lower scores indicating greater functional impairment.
The ability of memantine hydrochloride to improve cognitive performance was assessed in both studies with the Severe Impairment Battery (SIB), a multi- item instrument that has been validated for the evaluation of cognitive function in patients with moderate to severe dementia. The SIB examines selected aspects of cognitive performance, including elements of attention, orientation, language, memory, visuospatial ability, construction, praxis, and social interaction. The SIB scoring range is from 0 to 100, with lower scores indicating greater cognitive impairment.
Study 1 (Twenty-Eight-Week Study)
In a study of 28 weeks duration, 252 patients with moderate to severe probable Alzheimer's disease (diagnosed by DSM-IV and NINCDS-ADRDA criteria, with Mini- Mental State Examination scores ≥ 3 and ≤ 14 and Global Deterioration Scale Stages 5 to 6) were randomized to memantine hydrochloride or placebo. For patients randomized to memantine hydrochloride, treatment was initiated at 5 mg once daily and increased weekly by 5 mg/day in divided doses to a dose of 20 mg/day (10 mg twice a day).
Effects on the ADCS-ADL
Figure 1 shows the time course for the change from baseline in the ADCS-ADL score for patients in the two treatment groups completing the 28 weeks of the study. At 28 weeks of treatment, the mean difference in the ADCS-ADL change scores for the memantine-treated patients compared to the patients on placebo was 3.4 units. Using an analysis based on all patients and carrying their last study observation forward (LOCF analysis), memantine hydrochloride treatment was statistically significantly superior to placebo.
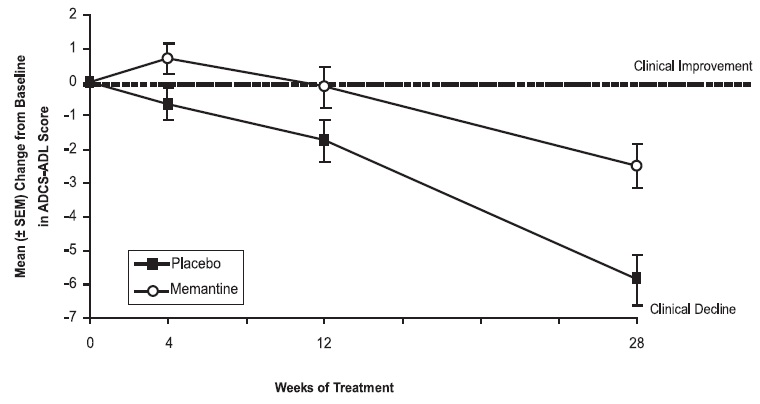
Figure 1: Time course of the change from baseline in ADCS-ADL score for patients completing 28 weeks of treatment.
Figure 2 shows the cumulative percentages of patients from each of the treatment groups who had attained at least the change in the ADCS-ADL shown on the X axis. The curves show that both patients assigned to memantine hydrochloride and placebo have a wide range of responses and generally show deterioration (a negative change in ADCS-ADL compared to baseline), but that the memantine group is more likely to show a smaller decline or an improvement. (In a cumulative distribution display, a curve for an effective treatment would be shifted to the left of the curve for placebo, while an ineffective or deleterious treatment would be superimposed upon or shifted to the right of the curve for placebo).
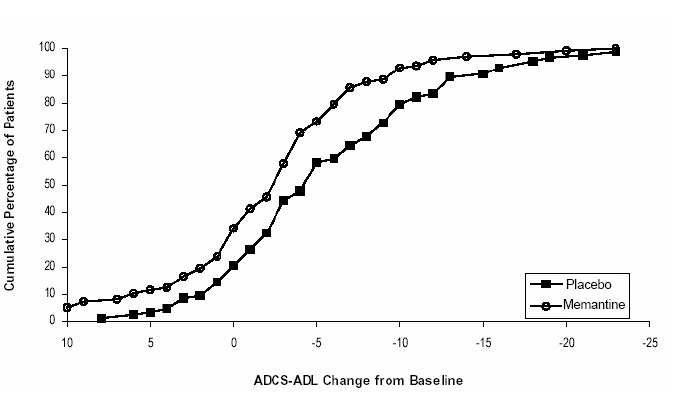
Figure 2: Cumulative percentage of patients completing 28 weeks of double- blind treatment with specified changes from baseline in ADCS-ADL scores.
Effects on the SIB
Figure 3 shows the time course for the change from baseline in SIB score for the two treatment groups over the 28 weeks of the study. At 28 weeks of treatment, the mean difference in the SIB change scores for the memantine- treated patients compared to the patients on placebo was 5.7 units. Using an LOCF analysis, memantine treatment was statistically significantly superior to placebo.
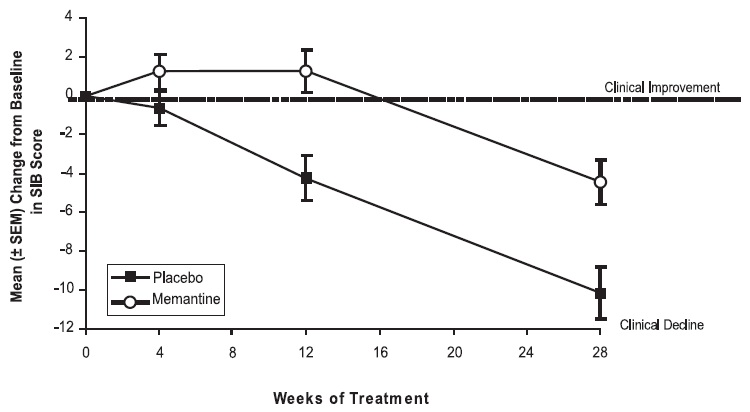
Figure 3: Time course of the change from baseline in SIB score for patients completing 28 weeks of treatment.
Figure 4 shows the cumulative percentages of patients from each treatment group who had attained at least the measure of change in SIB score shown on the X axis. The curves show that both patients assigned to memantine hydrochloride and placebo have a wide range of responses and generally show deterioration, but that the memantine hydrochloride group is more likely to show a smaller decline or an improvement.
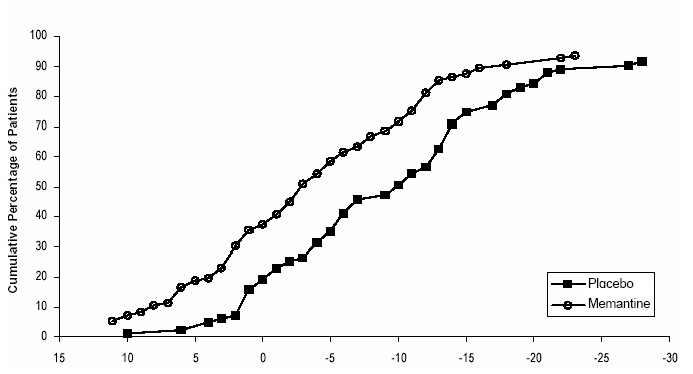
Figure 4: Cumulative percentage of patients completing 28 weeks of double- blind treatment with specified changes from baseline in SIB scores.
Study 2 (Twenty-Four-Week Study)
In a study of 24 weeks duration, 404 patients with moderate to severe probable Alzheimer's disease (diagnosed by NINCDS-ADRDA criteria, with Mini-Mental State Examination scores ≥ 5 and ≤ 14) who had been treated with donepezil for at least 6 months and who had been on a stable dose of donepezil for the last 3 months were randomized to memantine or placebo while still receiving donepezil. For patients randomized to memantine, treatment was initiated at 5 mg once daily and increased weekly by 5 mg/day in divided doses to a dose of 20 mg/day (10 mg twice a day).
Effects on the ADCS-ADL
Figure 5 shows the time course for the change from baseline in the ADCS-ADL score for the two treatment groups over the 24 weeks of the study. At 24 weeks of treatment, the mean difference in the ADCS-ADL change scores for the memantine/donepezil treated patients (combination therapy) compared to the patients on placebo/donepezil (monotherapy) was 1.6 units. Using an LOCF analysis, memantine /donepezil treatment was statistically significantly superior to placebo/donepezil.
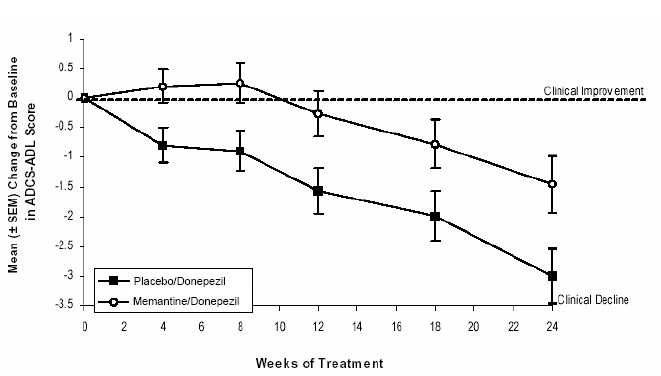
Figure 5: Time course of the change from baseline in ADCS-ADL score for patients completing 24 weeks of treatment.
Figure 6 shows the cumulative percentages of patients from each of the treatment groups who had attained at least the measure of improvement in the ADCS-ADL shown on the X axis. The curves show that both patients assigned to memantine/donepezil and placebo/donepezil have a wide range of responses and generally show deterioration, but that the memantine/donepezil group is more likely to show a smaller decline or an improvement.
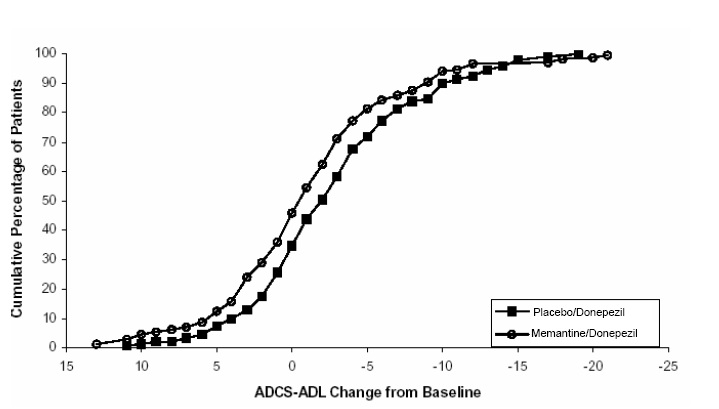
Figure 6: Cumulative percentage of patients completing 24 weeks of double- blind treatment with specified changes from baseline in ADCS-ADL scores.
Effects on the SIB:
Figure 7 shows the time course for the change from baseline in SIB score for the two treatment groups over the 24 weeks of the study. At 24 weeks of treatment, the mean difference in the SIB change scores for the memantine/donepezil-treated patients compared to the patients on placebo/donepezil was 3.3 units. Using an LOCF analysis, memantine/donepezil treatment was statistically significantly superior to placebo/donepezil.
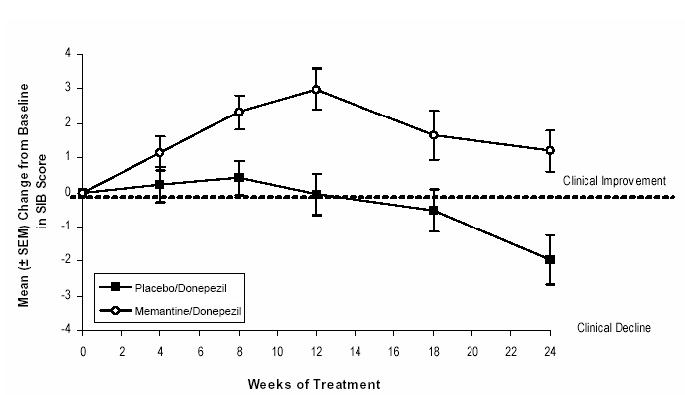
Figure 7: Time course of the change from baseline in SIB score for patients completing 24 weeks of treatment.
Figure 8 shows the cumulative percentages of patients from each treatment group who had attained at least the measure of improvement in SIB score shown on the X axis. The curves show that both patients assigned to memantine/donepezil and placebo/donepezil have a wide range of responses, but that the memantine /donepezil group is more likely to show an improvement or a smaller decline.
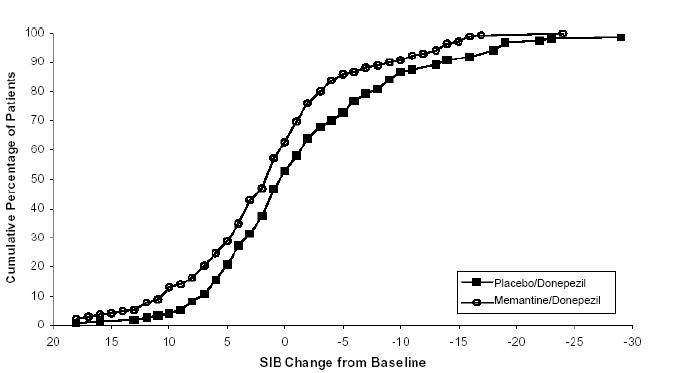
Figure 8: Cumulative percentage of patients completing 24 weeks of double- blind treatment with specified changes from baseline in SIB scores.
Study 3 (Twelve-Week Study)
In a double-blind study of 12 weeks duration, conducted in nursing homes in Latvia, 166 patients with dementia according to DSM-III-R, a Mini-Mental State Examination score of <10, and Global Deterioration Scale staging of 5 to 7 were randomized to either memantine or placebo. For patients randomized to memantine, treatment was initiated at 5 mg once daily and increased to 10 mg once daily after 1 week. The primary efficacy measures were the care dependency subscale of the Behavioral Rating Scale for Geriatric Patients (BGP), a measure of day-to-day function, and a Clinical Global Impression of Change (CGI-C), a measure of overall clinical effect. No valid measure of cognitive function was used in this study. A statistically significant treatment difference at 12 weeks that favored memantine over placebo was seen on both primary efficacy measures. Because the patients entered were a mixture of Alzheimer's disease and vascular dementia, an attempt was made to distinguish the two groups and all patients were later designated as having either vascular dementia or Alzheimer's disease, based on their scores on the Hachinski Ischemic Scale at study entry. Only about 50% of the patients had computerized tomography of the brain. For the subset designated as having Alzheimer's disease, a statistically significant treatment effect favoring memantine over placebo at 12 weeks was seen on both the BGP and CGI-C.
INFORMATION FOR PATIENTS SECTION
17 PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATION
See FDA-approved patient labeling (Patient Information).
To assure safe and effective use of memantine hydrochloride, the following information and instructions provided in the patient information section should be discussed with patients and caregivers.
Patients/caregivers should be instructed to follow the dose titration schedule provided by their physician or healthcare professional for memantine hydrochloride. They should be warned not to use any tablets of memantine hydrochloride that are damaged or show signs of tampering.
If a patient misses a single dose of memantine hydrochloride, that patient should not double up on the next dose. The next dose should be taken as scheduled. If a patient fails to take memantine hydrochloride tablets for several days, dosing should not be resumed without consulting that patient's healthcare professional.
LUPIN and the
 are registered trademarks of Lupin Pharmaceuticals, Inc.
are registered trademarks of Lupin Pharmaceuticals, Inc.
Manufactured for:
Lupin Pharmaceuticals, Inc.
Naples, FL 34108
United States
Manufactured by:
Lupin Limited
Goa 403 722
INDIA
Revised: August 2025
