gabapentin
These highlights do not include all the information needed to use gabapentin tablets safely and effectively. See full prescribing information for gabapentin tablets. GABAPENTIN Tablets, for oral useInitial U.S. Approval: 1993
3cfd04ab-e421-441f-a10e-e4dd1412974d
HUMAN PRESCRIPTION DRUG LABEL
Sep 5, 2025
Zydus Pharmaceuticals USA Inc.
DUNS: 156861945
Products 5
Detailed information about drug products covered under this FDA approval, including NDC codes, dosage forms, ingredients, and administration routes.
gabapentin
Product Details
FDA regulatory identification and product classification information
FDA Identifiers
Product Classification
Product Specifications
INGREDIENTS (9)
gabapentin
Product Details
FDA regulatory identification and product classification information
FDA Identifiers
Product Classification
Product Specifications
INGREDIENTS (9)
gabapentin
Product Details
FDA regulatory identification and product classification information
FDA Identifiers
Product Classification
Product Specifications
INGREDIENTS (9)
gabapentin
Product Details
FDA regulatory identification and product classification information
FDA Identifiers
Product Classification
Product Specifications
INGREDIENTS (14)
gabapentin
Product Details
FDA regulatory identification and product classification information
FDA Identifiers
Product Classification
Product Specifications
INGREDIENTS (14)
Drug Labeling Information
PACKAGE LABEL.PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL
PACKAGE LABEL.PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL
Gabapentin Tablets, 300 mg
90 Tablets
NDC 68382-608-16
Rx only
Zydus

Gabapentin Tablets, 450 mg
60 Tablets
NDC 68382-355-14
Rx only
Zydus

Gabapentin Tablets, 750 mg
60 Tablets
NDC 68382-356-14
Rx only
Zydus

Gabapentin Tablets, 600 mg
90 Tablets
NDC 68382-607-16
Rx only
Zydus

Gabapentin Tablets, 900 mg
60 Tablets
NDC 68382-357-14
Rx only
Zydus

INDICATIONS & USAGE SECTION
1 INDICATIONS AND USAGE
Gabapentin tablet is indicated for the management of postherpetic neuralgia.
Once-daily gabapentin tablets are not substitutable with other gabapentin products because of differing pharmacokinetic profiles that affect the frequency of administration.
Gabapentin tablet is indicated for the management of Postherpetic Neuralgia (PHN). (1)
Important Limitation (1)
Once-daily gabapentin tablets are not substitutable with other gabapentin products because of differing pharmacokinetic profiles that affect the frequency of administration (see Warnings and Precautions). (1)
(1)
WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS SECTION
5 WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS
Once-daily gabapentin tablets are not substitutable with other gabapentin products because of differing pharmacokinetic profiles that affect the frequency of administration.
The safety and effectiveness of gabapentin in patients with epilepsy has not been studied.
5.1 Suicidal Behavior and Ideation
Antiepileptic drugs (AEDs), including gabapentin, the active ingredient in gabapentin tablet, increase the risk of suicidal thoughts or behavior in patients taking these drugs for any indication. Suicidal behavior and ideation have also been reported in patients after discontinuation of gabapentin [see Warnings and Precautions (5.3)]. Patients treated with any AED for any indication should be monitored for the emergence or worsening of depression, suicidal thoughts or behavior, and/or any unusual changes in mood or behavior.
Pooled analyses of 199 placebo-controlled clinical trials (mono- and adjunctive therapy) of 11 different AEDs showed that patients randomized to one of the AEDs had approximately twice the risk (adjusted Relative Risk 1.8, 95% CI:1.2, 2.7) of suicidal thinking or behavior compared to patients randomized to placebo. In these trials, which had a median treatment duration of 12 weeks, the estimated incidence rate of suicidal behavior or ideation among 27,863 AED-treated patients was 0.43%, compared to 0.24% among 16,029 placebo-treated patients, representing an increase of approximately one case of suicidal thinking or behavior for every 530 patients treated. There were four suicides in drug-treated patients in the trials and none in placebo- treated patients, but the number is too small to allow any conclusion about drug effect on suicide.
The increased risk of suicidal thoughts or behavior with AEDs was observed as early as one week after starting drug treatment with AEDs and persisted for the duration of treatment assessed. Because most trials included in the analysis did not extend beyond 24 weeks, the risk of suicidal thoughts or behavior beyond 24 weeks could not be assessed.
The risk of suicidal thoughts or behavior was generally consistent among drugs in the data analyzed. The finding of increased risk with AEDs of varying mechanisms of action and across a range of indications suggests that the risk applies to all AEDs used for any indication. The risk did not vary substantially by age (5 to 100 years) in the clinical trials analyzed. Table 3 shows absolute and relative risk by indication for all evaluated AEDs.
Table 3 Risk by Indication for Antiepileptic Drugs (including gabapentin, the active ingredient in gabapentin tablet) in the Pooled Analysis|
** Indication** |
** Placebo Patients with Events Per 1,000 Patients** |
** Drug Patients with Events Per 1,000 Patients** |
** Relative Risk: Incidence of Events in Drug Patients/Incidence in Placebo Patients** |
** Risk Difference: Additional Drug Patients with Events Per 1,000 Patients** |
|
Epilepsy |
1 |
3.4 |
3.5 |
2.4 |
|
Psychiatric |
5.7 |
8.5 |
1.5 |
2.9 |
|
Other |
1 |
1.8 |
1.9 |
0.9 |
|
Total |
2.4 |
4.3 |
1.8 |
1.9 |
The relative risk for suicidal thoughts or behavior was higher in clinical trials for epilepsy than in clinical trials for psychiatric or other conditions, but the absolute risk differences were similar for the epilepsy and psychiatric indications.
Anyone considering prescribing gabapentin must balance the risk of suicidal thoughts or behavior with the risk of untreated illness. Epilepsy and many other illnesses for which products containing active components that are AEDs (such as gabapentin, the active component in gabapentin tablet) are prescribed are themselves associated with morbidity and mortality and an increased risk of suicidal thoughts and behavior. Should suicidal thoughts and behavior emerge during treatment, the prescriber needs to consider whether the emergence of these symptoms in any given patient may be related to the illness being treated.
Patients, their caregivers, and families should be informed that gabapentin tablet contains gabapentin which is also used to treat epilepsy and that AEDs increase the risk of suicidal thoughts and behavior and should be advised of the need to be alert for the emergence or worsening of the signs and symptoms of depression, any unusual changes in mood or behavior, or the emergence of suicidal thoughts, behavior, or thoughts about self-harm. Behaviors of concern should be reported immediately to healthcare providers.
5.2 Increased Risk of Adverse Reactions with Abrupt or Rapid
Discontinuation
After discontinuation of short-term and long-term treatment with gabapentin, withdrawal symptoms have been observed in some patients [see Adverse Reactions (6.2) and Drug Abuse and Dependence (9.3)]. Suicidal behavior and ideation have also been reported in patients after discontinuation of gabapentin [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)]. If gabapentin tablets is discontinued, this should be done gradually over a minimum of 1 week or longer (at the discretion of the prescriber).
5.3 Respiratory Depression
There is evidence from case reports, human studies, and animal studies associating gabapentin with serious, life-threatening, or fatal respiratory depression when co-administrated with central nervous system (CNS) depressants, including opioids, or in the setting of underlying respiratory impairment. When the decision is made to co-prescribe gabapentin with another CNS depressant, particularly an opioid, or to prescribe gabapentin to patients with underlying respiratory impairment, monitor patients for symptoms of respiratory depression and sedation, and consider initiating gabapentin at a low dose. The management of respiratory depression may include close observation, supportive measures, and reduction or withdrawal of CNS depressants (including gabapentin).
5.4 Tumorigenic Potential
In standard preclinical in vivo lifetime carcinogenicity studies, an unexpectedly high incidence of pancreatic acinar adenocarcinomas was identified in male, but not female, rats. The clinical significance of this finding is unknown.
In clinical trials of gabapentin therapy in epilepsy comprising 2,085 patient- years of exposure in patients over 12 years of age, new tumors were reported in 10 patients, and pre-existing tumors worsened in 11 patients, during or within 2 years after discontinuing the drug. However, no similar patient population untreated with gabapentin was available to provide background tumor incidence and recurrence information for comparison. Therefore, the effect of gabapentin therapy on the incidence of new tumors in humans or on the worsening or recurrence of previously diagnosed tumors is unknown.
5.5 Drug Reaction with Eosinophilia and Systemic Symptoms
(DRESS)/Multiorgan Hypersensitivity
Drug Reaction with Eosinophilia and Systemic Symptoms (DRESS), also known as Multiorgan Hypersensitivity, has been reported in patients taking antiepileptic drugs, including gabapentin. Some of these events have been fatal or life-threatening. DRESS typically, although not exclusively, presents with fever, rash, and/or lymphadenopathy in association with other organ system involvement, such as hepatitis, nephritis, hematological abnormalities, myocarditis, or myositis sometimes resembling an acute viral infection. Eosinophilia is often present. Because this disorder is variable in its expression, other organ systems not noted here may be involved.
It is important to note that early manifestations of hypersensitivity, such as fever or lymphadenopathy, may be present even though rash is not evident. If such signs or symptoms are present, the patient should be evaluated immediately. Gabapentin should be discontinued if an alternative etiology for the signs or symptoms cannot be established.
5.6 Laboratory Tests
Clinical trial data do not indicate that routine monitoring of clinical laboratory procedures is necessary for the safe use of gabapentin. The value of monitoring gabapentin blood concentrations has not been established.
- Once-daily gabapentin tablets are not substitutable with other gabapentin products
- Antiepileptic drugs, including gabapentin, the active ingredient in gabapentin tablet, increase the risk of suicidal thoughts or behavior (5.1)
- Abrupt or rapid discontinuation may increase the risk for seizures. Withdrawal symptoms or suicidal behavior and ideation have been observed after discontinuation. Taper gabapentin tablet gradually over a minimum of 1 week. (5.2)
- Respiratory depression may occur with gabapentin when used with concomitant CNS depressants or in the setting of underlying respiratory impairment. Monitor patients and adjust dosage as appropriate. (5.3)
ADVERSE REACTIONS SECTION
6 ADVERSE REACTIONS
The following adverse reactions are described elsewhere in the labeling:
- Suicidal Behavior and Ideation [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)]
- Increased Risk of Adverse Reactions with Abrupt or Rapid Discontinuation [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2)]
- Respiratory Depression [see Warnings and Precautions (5.3)]
- Tumorigenic Potential [see Warnings and Precautions (5.4)]
- Drug Reaction with Eosinophilia and Systemic Symptoms (DRESS)/Multiorgan Hypersensitivity [see Warnings and Precautions (5.5)]
- Laboratory Tests [see Warnings and Precautions (5.6)]
6.1 Clinical Trials Experience
Because clinical trials are conducted under widely varying conditions, adverse reaction rates observed in the clinical trials of a drug cannot be directly compared to rates in the clinical trials of another drug and may not reflect the rates observed in practice.
A total of 359 patients with neuropathic pain associated with postherpetic neuralgia have received gabapentin at doses up to 1,800 mg daily during placebo-controlled clinical studies. In clinical trials in patients with postherpetic neuralgia, 9.7% of the 359 patients treated with gabapentin and 6.9% of 364 patients treated with placebo discontinued prematurely due to adverse reactions. In the gabapentin treatment group, the most common reason for discontinuation due to adverse reactions was dizziness. Of gabapentin- treated patients who experienced adverse reactions in clinical studies, the majority of those adverse reactions were either "mild" or "moderate".
Table 4 lists all adverse reactions, regardless of causality, occurring in at least 1% of patients with neuropathic pain associated with postherpetic neuralgia in the gabapentin group for which the incidence was greater than in the placebo group.
Table 4 Treatment-Emergent Adverse Reaction Incidence in Controlled Trials in Neuropathic Pain Associated with Postherpetic Neuralgia (Events in at Least 1% of all Gabapentin-Treated Patients and More Frequent Than in the Placebo Group)|
** Body System – Preferred Term** |
** Gabapentin** |
** Placebo** |
|
** Ear and Labyrinth Disorders** |
1.4 |
0.5 |
|
** Gastrointestinal Disorders** |
3.3 |
2.7 |
|
** General Disorders** |
3.9 |
0.3 |
|
** Infections and Infestations** |
2.5 |
2.2 |
|
** Investigations** |
1.9 |
0.5 |
|
** Musculoskeletal and Connective Tissue Disorders** |
1.9 |
0.5 |
|
** Nervous System Disorders** |
10.9 |
2.2 |
In addition to the adverse reactions reported in Table 4 above, the following adverse reactions with an uncertain relationship to gabapentin were reported during the clinical development for the treatment of postherpetic neuralgia. Events in more than 1% of patients but equally or more frequently in the gabapentin-treated patients than in the placebo group included blood pressure increase, confusional state, gastroenteritis viral, herpes zoster, hypertension, joint swelling, memory impairment, nausea, pneumonia, pyrexia, rash, seasonal allergy, and upper respiratory infection.
6.2 Postmarketing and Other Experience with other Formulations of
Gabapentin
In addition to the adverse experiences reported during clinical testing of gabapentin, the following adverse experiences have been reported in patients receiving other formulations of marketed gabapentin. These adverse experiences have not been listed above and data are insufficient to support an estimate of their incidence or to establish causation. The listing is alphabetized: angioedema, blood glucose fluctuation, breast enlargement, bullous pemphigoid, elevated creatine kinase, elevated liver function tests, erythema multiforme, fever, hyponatremia, jaundice, movement disorder, Stevens-Johnson syndrome.
There are postmarketing reports of withdrawal symptoms after discontinuation of gabapentin. Reported adverse reactions include, but are not limited to, seizures, depression, suicidal ideation and behavior, agitation, confusion, disorientation, psychotic symptoms, anxiety, insomnia, nausea, pain, sweating, tremor, headache, dizziness, and malaise [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2)]. There are postmarketing reports of life-threatening or fatal respiratory depression in patients taking gabapentin with opioids or other central nervous system (CNS) depressants, or in the setting of underlying respiratory impairment.
The most common adverse reaction (greater than or equal to 5% and twice placebo) is dizziness. (6.1)
**To report SUSPECTED ADVERSE REACTIONS, contact Zydus Pharmaceuticals (USA) Inc. at 1-**877-993-8779 or FDA at 1-800-FDA-1088 or www.fda.gov/medwatch.
INFORMATION FOR PATIENTS SECTION
17 PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATION
Advise patients of the availability of a Medication Guide, and instruct them to read the Medication Guide prior to taking gabapentin tablets.
- Advise patients that once-daily gabapentin tablets are not substitutable with other formulations of gabapentin.
- Advise patients to take gabapentin only as prescribed. Gabapentin may cause dizziness, somnolence, and other signs and symptoms of CNS depression.
- Advise patients not to drive or operate other complex machinery until they have gained sufficient experience on gabapentin to gauge whether or not it adversely affects their mental and/or motor performance. Advise patients who require concomitant treatment with morphine to tell their prescriber if they develop signs of CNS depression such as somnolence. If this occurs the dose of gabapentin or morphine should be reduced accordingly.
- Advise patients that if they miss a dose of gabapentin to take it with food as soon as they remember. If it is almost time for the next dose, just skip the missed dose and take the next dose at the regular time. Do not take two doses at the same time.
- Advise patients that if they take too much gabapentin, to call their healthcare provider or poison control center, or go to the nearest emergency room right away.
Suicidal Thoughts and Behavior
Counsel patients, their caregivers, and families that AEDs, including gabapentin, the active ingredient in gabapentin tablet, may increase the risk of suicidal thoughts and behavior and of the need to be alert for the emergence or worsening of symptoms of depression, any unusual changes in mood or behavior, or the emergence of suicidal thoughts, behavior, or thoughts about self-harm. Instruct patients, caregivers, and families to report behaviors of concern immediately to healthcare providers. Also inform patients who plan to or have discontinued gabapentin tablets that suicidal thoughts and behavior can appear even after the drug is stopped [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)].
Respiratory Depression
Inform patients about the risk of respiratory depression. Include information that the risk is greatest for those using concomitant central nervous system (CNS) depressants (such as opioid analgesics) or in those with underlying respiratory impairment. Teach patients how to recognize respiratory depression and advise them to seek medical attention immediately if it occurs [see Warnings and Precautions (5.3)].
Dosing and Administration
Gabapentin is not substitutable with other gabapentin products because of differing
pharmacokinetic profiles that affect the frequency of administration.
The safety and effectiveness of gabapentin in patients with epilepsy has not been studied.
Advise patients that gabapentin should be taken orally once-daily with the evening meal. Gabapentin tablets should be swallowed whole. Do not split, crush, or chew the tablets [see Dosage and Administration (2.1)].
Use in Pregnancy
Advise patients to notify their healthcare provider if they become pregnant or intend to become pregnant during treatment with gabapentin tablets and to notify their physician if they are breast feeding or intend to breast feed during therapy [see Use in Specific Populations (8.1) and (8.2)].
Encourage patients to enroll in the North American Antiepileptic Drug (NAAED) Pregnancy Registry if they become pregnant. This registry is collecting information about the safety of antiepileptic drugs during pregnancy. To enroll, patients can call the toll-free number 1-888-233- 2334 [see Use in Specific Populations (8.1)].
®is the registered trademark of its owner.
Medication Guide available at www.zydususa.com/medguides or call 1-877-993-8779.
DOSAGE & ADMINISTRATION SECTION
2 DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
2.1 Postherpetic Neuralgia
Do not use Once-daily gabapentin tablets as a substitute for other gabapentin products.
Titrate gabapentin tablet to an 1,800 mg dose taken orally once daily with the evening meal. Gabapentin tablets should be swallowed whole. Do not split, crush, or chew the tablets.
If gabapentin dosing is reduced, discontinued, or substituted with an alternative medication, this should be done gradually over a minimum of one week or longer (at the discretion of the prescriber).
In adults with postherpetic neuralgia, gabapentin therapy should be initiated and titrated as follows:
Table 1 Gabapentin Recommended Titration Schedule|
** Day 1** |
** Day 2** |
** Days 3**** to**** 6** |
** Days 7**** to**** 10** |
** Days 11**** to**** 14** |
** Day 15** | |
|
Daily Dose |
300 mg |
600 mg |
900 mg |
1,200 mg |
1,500 mg |
1,800 mg |
2.2 Patients with Renal Impairment
In patients with stable renal function, creatinine clearance (CCr) can be reasonably well estimated using the equation of Cockcroft and Gault:
For females CCr=(0.85)(140-age)(weight)/[(72)(SCr)]
For males CCr=(140-age)(weight)/[(72)(SCr)]
where age is in years, weight is in kilograms and SCr is serum creatinine in mg/dL.
The dose of gabapentin should be adjusted in patients with reduced renal function, according to Table 2. Patients with reduced renal function must initiate gabapentin at a daily dose of 300 mg. Gabapentin should be titrated following the schedule outlined in Table 1. Daily dosing in patients with reduced renal function must be individualized based on tolerability and desired clinical benefit.
Table 2 Gabapentin Tablet Dosage Based on Renal Function|
** Once-daily dosing** | |
|
Creatinine Clearance (mL/min) |
Gabapentin Tablet Dose |
|
≥ 60 |
1,800 mg |
|
30 to 60 |
600 mg to 1,800 mg |
|
< 30 |
Gabapentin tablet should not be administered |
|
patients receiving hemodialysis |
Gabapentin tablet should not be administered |
- Gabapentin tablet should be titrated to an 1,800 mg dose taken orally, once-daily with the evening meal. Gabapentin tablets should be swallowed whole. Do not crush, split or chew the tablets. (2.1)
- If gabapentin dose is reduced, discontinued, or substituted with an alternative medication, this should be done gradually over a minimum of 1 week or longer (at the discretion of the prescriber). (2.1)
- Renal impairment: Dose should be adjusted in patients with reduced renal function. Gabapentin tablet should not be used in patients with CrCl less than 30 or in patients on hemodialysis. (2.2)
DOSAGE FORMS & STRENGTHS SECTION
3 DOSAGE FORMS AND STRENGTHS
- Gabapentin Tablets, 300 mg are white to off-white, oval, film-coated tablets debossed with "608" on one side and plain on theother side.
- Gabapentin Tablets, 450 mg are white to off-white, oval shaped, beveled edge, film coated tablets debossed with "355" on oneside and plain on the other side.
- Gabapentin Tablets, 600 mg are white to off-white, oval, beveled edge film coated tablets debossed with "607" on one side andplain on the other side.
- Gabapentin Tablets, 750 mg are white to off-white, oval shaped, beveled edge, film coated tablets debossed with "356" on oneside and plain on the other side.
- Gabapentin Tablets, 900 mg are white to off-white, oval shaped, beveled edge, film coated tablets debossed with "357" on oneside and plain on the other side.
- Tablets: 300 mg, 450 mg, 600 mg,750 mg and 900 mg (3)
USE IN SPECIFIC POPULATIONS SECTION
8 USE IN SPECIFIC POPULATIONS
8.1 Pregnancy
Pregnancy Exposure Registry
There is a pregnancy exposure registry that monitors pregnancy outcomes in women exposed to gabapentin, including gabapentin, during pregnancy. Encourage women who are taking gabapentin during pregnancy to enroll in the North American Antiepileptic Drug (NAAED) Pregnancy Registry by calling the toll free number 1-888-233-2334 or visiting https://www.aedpregnancyregistry.org/.
Risk Summary
Available data from published prospective and retrospective cohort studies, and case reports over decades of use with gabapentin during pregnancy have not identified a drug-associated risk of major birth defects. The available data are insufficient to evaluate a drug-associated risk of miscarriage and other maternal or fetal outcomes. In nonclinical studies in mice, rats, and rabbits, gabapentin was developmentally toxic (increased fetal skeletal and visceral abnormalities, and increased embryofetal mortality) when administered to pregnant animals at doses similar to those used clinically (see Data).
Postmarketing data suggest that extended gabapentin use with opioids close to delivery may increase the risk of neonatal withdrawal versus opioids alone [see Clinical Considerations]. Although there is at least one report of neonatal withdrawal syndrome in an infant exposed to gabapentin alone during pregnancy, there are no comparative epidemiologic studies evaluating this association. Therefore, it is not known whether exposure to gabapentin alone late in pregnancy may cause withdrawal signs and symptoms.
The estimated background risk of major birth defects and miscarriage for the indicated populations is unknown. All pregnancies have a background risk of birth defect, loss, or other adverse outcomes. In the U.S. general population, the estimated background risk of major birth defects and miscarriage in clinically recognized pregnancies is 2% to 4% and 15% to 20%, respectively.
Clinical Considerations
Fetal/Neonatal Adverse Reactions
Neonatal withdrawal syndrome has been reported in newborns exposed to gabapentin in utero for an extended period of time when also exposed to opioids close to delivery. Neonatal withdrawal signs and symptoms reported have included tachypnea, vomiting, diarrhea, hypertonia, irritability, sneezing, poor feeding, hyperactivity, abnormal sleep pattern and tremor. Reported signs and symptoms that may also be related to withdrawal include tongue thrusting, wandering eye movements while awake, back arching, and continuous extremity movements. Observe neonates exposed to gabapentin tablets and opioids for signs and symptoms of neonatal withdrawal and manage accordingly.
Data
Animal Data
When pregnant mice received oral doses of gabapentin (1,000 or 3,000 mg/kg/day, approximately 3 to 8 times the maximum recommended dose of 1,800 mg on a mg/m2 basis) during the period of organogenesis, embryofetal toxicity (increased incidences of skeletal variations) was observed. The no effect level was 500 mg/kg/day, representing approximately the maximum recommended human dose [MRHD] on a mg/m2 basis.
When rats were dosed prior to and during mating, and throughout gestation, pups from all dose groups (500, 1,000 and 2,000 mg/kg/day) were affected. These doses are equivalent to approximately 3 to 11 times the MRHD on a mg/m2 basis. There was an increased incidence of hydroureter and/or hydronephrosis in rats in a study of fertility and general reproductive performance at 2,000 mg/kg/day with no effect at 1,000 mg/kg/day, in a teratology study at 1,500 mg/kg/day with no effect at 300 mg/kg/day, and in a perinatal and postnatal study at all doses studied (500, 1,000 and 2,000 mg/kg/day). The doses at which the effects occurred are approximately 3 to 11 times the maximum recommended dose of 1,800 mg on a mg/m2 basis; the no-effect doses were approximately 5 times (Fertility and General Reproductive Performance study) and approximately equal to (Teratogenicity study) the MRHD on a mg/m2 basis. Other than hydroureter and hydronephrosis, the etiologies of which are unclear, the incidence of malformations was not increased compared to controls in offspring of mice, rats, or rabbits given doses up to 8 times (mice), 10 times (rats), or 16 times (rabbits) the human daily dose on a mg/m2 basis.
When pregnant rabbits were treated with gabapentin during the period of organogenesis, an increase in embryofetal mortality was observed at 60, 300, and 1,500 mg/kg/day (0.6 to 16 times the MRHD on a mg/m2basis).
In a published study, gabapentin (400 mg/kg/day) was administered by intraperitoneal injection to neonatal mice during the first postnatal week, a period of synaptogenesis in rodents (corresponding to the last trimester of pregnancy in humans). Gabapentin caused a marked decrease in neuronal synapse formation in brains of intact mice and abnormal neuronal synapse formation in a mouse model of synaptic repair. Gabapentin has been shown in vitro to interfere with activity of the α2δ subunit of voltage-activated calcium channels, a receptor involved in neuronal synaptogenesis. The clinical significance of these findings is unknown.
8.2 Lactation
Risk Summary
Gabapentin is present in human milk following oral administration. Adverse effects on the breastfed infant have not been reported. There are no data on the effects of the drug on milk production. The developmental and health benefits of breastfeeding should be considered along with the mother's clinical need for gabapentin and any potential adverse effects on the breastfed infant from gabapentin or from the underlying maternal condition.
8.4 Pediatric Use
The safety and effectiveness of gabapentin in the management of postherpetic neuralgia in patients less than 18 years of age has not been studied.
8.5 Geriatric Use
The total number of patients treated with gabapentin in controlled clinical trials in patients with postherpetic neuralgia was 359, of which 63% were 65 years of age or older. The types and incidence of adverse events were similar across age groups except for peripheral edema, which tended to increase in incidence with age.
Gabapentin is known to be substantially excreted by the kidney. Reductions in gabapentin dose should be made in patients with age-related compromised renal function [see Dosage and Administration (2.2)].
8.6 Hepatic Impairment
Because gabapentin is not metabolized, studies have not been conducted in patients with hepatic impairment.
8.7 Renal Impairment
Gabapentin is known to be substantially excreted by the kidney. Dosage adjustment is necessary in patients with impaired renal function. Gabapentin should not be administered in patients with CrCL between 15 and 30 or in patients undergoing hemodialysis [see Dosage and Administration (2.2)].
- Elderly: Reductions in gabapentin dose should be made in patients with age-related compromised renal function. (8.5)
- Renal impairment: Dosage adjustment is necessary for patients with impaired renal function. (8.7)
DRUG ABUSE AND DEPENDENCE SECTION
9 DRUG ABUSE AND DEPENDENCE
9.1 Controlled Substance
Gabapentin tablets contains gabapentin, which is not a controlled substance.
9.3 Dependence
Physical dependence is a state that develops as a result of physiological adaptation in response to repeated drug use, manifested by withdrawal signs and symptoms after abrupt
discontinuation or a significant dose reduction of a drug.
After discontinuation of short-term and long-term treatment with gabapentin, withdrawal symptoms have been observed in some patients. Withdrawal symptoms may occur shortly after discontinuation, usually within 48 hours. In the postmarketing setting, reported adverse reactions have included, but not been limited to, seizures, depression, suicidal ideation and behavior, agitation, confusion, disorientation, psychotic symptoms, anxiety, insomnia, nausea, pain, sweating, tremor, headache, dizziness, and malaise. The abuse and dependence potential of gabapentin tablets has not been evaluated in human studies.
DESCRIPTION SECTION
11 DESCRIPTION
Gabapentin tablet contains gabapentin, a gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA) analogue, as the active pharmaceutical ingredient.
Gabapentin's chemical name is 1-(aminomethyl)cyclohexaneacetic acid; with a molecular formula of C9H17NO2 and a molecular weight of 171.24 g/mol.
Gabapentin chemical structural formula is:
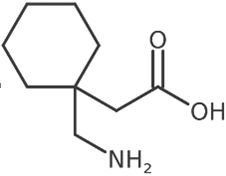
Gabapentin, USP is a white to off-white, crystalline powder with a pKa1 of 3.7 and a pKa2 of 10.7. It is freely soluble in water and in alkaline and acidic solutions. The log of the partition coefficient (n-octanol/ 0.05M phosphate buffer) at pH 7.4 is -1.25.
Each gabapentin tablet intended for oral administration contains 300 mg, 450 mg, 600 mg, 750 mg or 900 mg of gabapentin. In addition, each tablet contains the following inactive ingredients: copovidone, hypromellose, magnesium stearate, microcrystalline cellulose, polyethylene glycol, polyethylene oxide, povidone, talc and titanium dioxide.
CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY SECTION
12 CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY
12.1 Mechanism of Action
The mechanism of action by which gabapentin exerts its analgesic action is unknown but in animal models of analgesia, gabapentin prevents allodynia (pain-related behavior in response to a normally innocuous stimulus) and hyperalgesia (exaggerated response to painful stimuli). Gabapentin prevents pain-related responses in several models of neuropathic pain in rats and mice (e.g., spinal nerve ligation models, spinal cord injury model, acute herpes zoster infection model). Gabapentin also decreases pain-related responses after peripheral inflammation (carrageenan footpad test, late phase of formulin test), but does not alter immediate pain-related behaviors (rat tail flick test, formalin footpad acute phase). The relevance of these models to human pain is not known.
Gabapentin is structurally related to the neurotransmitter GABA (gamma- aminobutyric acid), but it does not modify GABAA or GABAB radioligand binding, it is not converted metabolically into GABA or a GABA agonist, and it is not an inhibitor of GABA uptake or degradation. In radioligand binding assays at concentrations up to 100 μM, gabapentin did not exhibit affinity for a number of other receptor sites, including benzodiazepine, glutamate, N-methyl-D- aspartate (NMDA), quisqualate, kainate, strychnine-insensitive or strychnine- sensitive glycine; alpha 1, alpha 2, or beta adrenergic; adenosine A1 or A2; cholinergic, muscarinic, or nicotinic; dopamine D1 or D2; histamine H1; serotonin S1 or S2; opiate mu, delta, or kappa; cannabinoid 1; voltage- sensitive calcium channel sites labeled with nitrendipine or diltiazem; or at voltage-sensitive sodium channel sites labeled with batrachotoxinin A20-alpha- benzoate. Gabapentin did not alter the cellular uptake of dopamine, noradrenaline, or serotonin.
In vitro studies with radiolabeled gabapentin have revealed a gabapentin binding site in areas of rat brain including neocortex and hippocampus. A high-affinity binding protein in animal brain tissue has been identified as an auxiliary subunit of voltage-activated calcium channels. However, functional correlates of gabapentin binding, if any, remain to be elucidated. It is hypothesized that gabapentin antagonizes thrombospondin binding to α2δ-1 as a receptor involved in excitatory synapse formation and suggested that gabapentin may function therapeutically by blocking new synapse formation.
12.2 Pharmacodynamics
No pharmacodynamic studies have been conducted with gabapentin.
12.3 Pharmacokinetics
Absorption
Gabapentin is absorbed from the proximal small bowel by a saturable L-amino transport system. Gabapentin bioavailability is not dose proportional; as the dose is increased, bioavailability decreases.
When gabapentin (1,800 mg once daily) and gabapentin immediate release (600 mg three times a day) were administered with high fat meals (50% of calories from fat), gabapentin has a higher Cmax and lower AUC at steady state compared to gabapentin immediate release (Table 5). Time to reach maximum plasma concentration (Tmax) for gabapentin is 8 hours, which is about 4 hours to 6 hours longer compared to gabapentin immediate release.
Table 5 Mean ± SD Steady-State Pharmacokinetics for Gabapentin and Gabapentin Immediate Release in Healthy Subjects under high-fat high calorie fed state (Day 5, n = 21)|
$Tmax is presented as median (range); | ||
| ||
|
** Pharmacokinetic Parameter** |
** Gabapentin** |
** Gabapentin Immediate Release** |
|
** AUC0-24** |
132.8 ± 34.7 |
141.3 ± 29.8 |
|
** C****max** (mcg/mL) |
9.59 ± 2.33 |
8.54 ± 1.72 |
|
** C****min** (mcg/mL) |
1.84 ± 0.65 |
2.6 ± 0.78 |
|
** Tmax (hr)**$ |
8 (3 to 12) |
2 (1 to 5)* |
The single dose pharmacokinetic parameters of 900 mg strength under high fat- high calorie fed state and low fat-low calorie fed state are presented shown in Table 6.
Mean ± SD Single-Dose Pharmacokinetic parameters for Gabapentin 900 mg strength in Healthy Subjects (n = 27)|
$Tmax is presented as median (range) | ||
|
** Pharmacokinetic** |
** Gabapentin**** 1,800 mg (2 x 900 mg tablets)** | |
|
** High fat- high calorie fed state** |
** Low fat- low calorie fed state** | |
|
Cmax (mcg/mL) |
9.49 ± 1.93 |
6.50 ± 2.16 |
|
AUCt (mcg hr/mL) |
127.2 ± 42.8 |
79.1 ± 39.4 |
|
AUCinf (mcg.hr/mL) |
133.2 ± 43.2 |
84.8 ± 39.4 |
|
Tmax (hr)$ |
7 (4-12) |
4 (3-12) |
Do not use once-daily gabapentin tablets as a substitute for other gabapentin products because of differing pharmacokinetic profiles that affect frequency of administration.
Gabapentin should be taken with evening meals. If it is taken on an empty stomach, the bioavailability will be substantially lower.
Administration of gabapentin with food increases the rate and extent of absorption of gabapentin compared to the fasted state. Cmax of gabapentin increases 33% to 84% and AUC of gabapentin increases 33% to 118% with food depending on the fat content of the meal. Gabapentin should be taken with food.
Distribution
Gabapentin is less than 3% bound to plasma proteins. After 150 mg intravenous administration, the mean**±SD volume of distribution is 58±**6 L.
Elimination
Gabapentin is eliminated by renal excretion as unchanged drug.
In patients with normal renal function given gabapentin immediate release 1,200 to 3,000 mg/day, the drug elimination half-life (t1/2) was 5 hours to 7 hours. Elimination kinetics do not change with dose level or multiple doses.
Metabolism
Gabapentin is not appreciably metabolized in humans.
Excretion
Gabapentin elimination rate constant, plasma clearance, and renal clearance are directly proportional to creatinine clearance. In elderly patients and patients with impaired renal function, plasma clearance is reduced. Gabapentin can be removed from plasma by hemodialysis.
Dosage adjustment in patients with compromised renal function is necessary. In patients undergoing hemodialysis, gabapentin should not be administered [see Dosage and Administration (2.2)].
12.4 Special Populations
Renal Insufficiency
As renal function decreases, renal and plasma clearances and the apparent elimination rate constant decrease, while Cmax and t1/2 increase.
In patients (N=60) with creatinine clearance of at least 60, 30 to 59 or less than 30 mL/min, the median renal clearance rates for a 400 mg single dose of gabapentin immediate release were 79, 36 and 11 mL/min, respectively, and the median t1/2 values were 9.2, 14, and 40 hours, respectively.
Dosage adjustment is necessary in patients with impaired renal function [see Dosage and Administration (2.2)].
Hemodialysis
In a study in anuric adult subjects (N=11), the apparent elimination half-life of gabapentin on nondialysis days was about 132 hours; during dialysis the apparent half-life of gabapentin was reduced to 3.8 hours. Hemodialysis thus has a significant effect on gabapentin elimination in anuric subjects. Gabapentin should not be administered in patients undergoing hemodialysis. Alternative formulations of gabapentin products should be considered in patients undergoing hemodialysis.
Elderly
Apparent oral and renal clearances of gabapentin decrease with increasing age, although this may be related to the decline in renal function with age. Reductions in gabapentin dose should be made in patients with age-related compromised renal function [see Dosage and Administration (2.2)].
Hepatic Impairment
Because gabapentin is not metabolized, studies have not been conducted in patients with hepatic impairment.
Pediatrics
The pharmacokinetics of gabapentin have not been studied in patients less than 18 years of age.
Gender
Although no formal study has been conducted to compare the pharmacokinetics of gabapentin in men and women, it appears that the pharmacokinetic parameters for males and females are similar and there are no significant gender differences.
Race
Pharmacokinetic differences due to race have not been studied. Because gabapentin is primarily renally excreted and there are no important racial differences in creatinine clearance, pharmacokinetic differences due to race are not expected.
CLINICAL STUDIES SECTION
14 CLINICAL STUDIES
The efficacy of gabapentin for the management of postherpetic neuralgia was established in a double-blind, placebo-controlled, multicenter study. This study enrolled patients between the age of 21 to 89 with postherpetic neuralgia persisting for at least 6 months following healing of herpes zoster rash and a minimum baseline pain intensity score of at least 4 on an 11-point numerical pain rating scale ranging from 0 (no pain) to 10 (worst possible pain).
This 11-week study compared gabapentin 1,800 mg once daily with placebo. A total of 221 and 231 patients were treated with gabapentin or placebo, respectively. The study treatment including titration for all patients comprised a 10-week treatment period followed by 1-week of dose tapering. Double-blind treatment began with titration starting at 300 mg/day and titrated up to a total daily dose of 1,800 mg over 2 weeks, followed by 8 weeks fixed dosing at 1,800 mg once daily, and then 1 week of dose tapering. During the 8-week stable dosing period, patients took 3 active or placebo tablets each night with the evening meal. During baseline and treatment, patients recorded their pain in a daily diary using an 11-point numeric pain rating scale. The mean baseline pain score was 6.6 and 6.5 for gabapentin and placebo-treated patients, respectively.
Treatment with gabapentin statistically significantly improved the endpoint mean pain score from baseline. For various degrees of improvement in pain from baseline to study endpoint, Figure 1 shows the fraction of patients achieving that degree of improvement. The figure is cumulative, so that patients whose change from baseline is, for example, 50%, are also included at every level of improvement below 50%. Patients who did not complete the study were assigned 0% improvement.
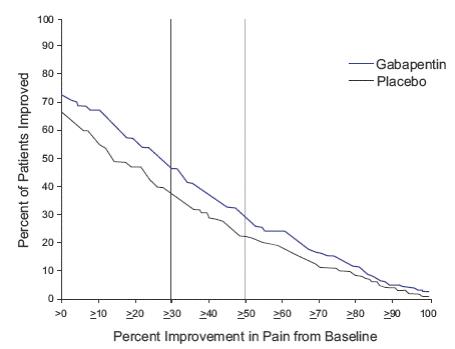
Figure 1: Percent of Patients Achieving Various Levels of Pain Relief
HOW SUPPLIED SECTION
16 HOW SUPPLIED/STORAGE AND HANDLING
Gabapentin Tablets, 300 mg are white to off-white, oval, film-coated tablets debossed with "608" on one side and plain on the other side and are supplied as follows:
NDC 68382-608-16 in bottle of 90 tablets with child-resistant closure
NDC 68382-608-05 in bottle of 500 tablets
NDC 68382-608-77 in unit-dose blister cartons of 100 (10 x 10) unit dose tablets
Gabapentin Tablets, 450 mg are white to off-white, oval shaped, beveled edge, film coated tablets debossed with "355" on one side and plain on the other side and are supplied as follows:
NDC 68382-355-14 in bottle of 60 tablets with child-resistant closure
NDC 68382-355-01 in bottle of 100 tablets with child-resistant closure
Gabapentin Tablets, 600 mg are white to off-white, oval, beveled edge film coated tablets debossed with "607" on one side and plain on the other side and are supplied as follows:
NDC 68382-607-16 in bottle of 90 tablets with child-resistant closure
NDC 68382-607-05 in bottle of 500 tablets
NDC 68382-607-77 in unit-dose blister cartons of 100 (10 x 10) unit dose tablets
Gabapentin Tablets, 750 mg are white to off-white, oval shaped, beveled edge, film coated tablets debossed with "356" on one side and plain on the other side and are supplied as follows:
NDC 68382-356-14 in bottle of 60 tablets with child-resistant closure
NDC 68382-356-01 in bottle of 100 tablets with child-resistant closure
Gabapentin Tablets, 900 mg are white to off-white, oval shaped, beveled edge, film coated tablets debossed with "357" on one side and plain on the other side. and are supplied as follows:
NDC 68382-357-14in bottle of 60 tablets with child-resistant closure
NDC 68382-357-01in bottle of 100 tablets with child-resistant closure
Storage
Store at 20°C to 25°C (68°F to 77°F); excursions permitted to 15ºC to 30ºC (59ºF to 86ºF) [See USP Controlled Room Temperature].
Keep out of reach of children.
SPL UNCLASSIFIED SECTION
Made in India.
Distributed by:
Zydus Pharmaceuticals (USA) Inc.
Pennington, NJ 08534
Rev.: 06/25
This Medication Guide has been approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration.
SPL MEDGUIDE SECTION
MEDICATION GUIDE
Gabapentin (gab" a pen' tin) Tablets
Read this Medication Guide before you start taking gabapentin and each time you get a refill. There may be new information. This information does not take the place of talking to your healthcare provider about your medical condition or treatment. If you have any questions about gabapentin, ask your healthcare provider or pharmacist.
What is the most important information I should know about gabapentin?
**Do not stop taking gabapentin without first talking with your healthcare provider.**Stopping gabapentin suddenly can cause serious problems.
**Like other antiepileptic drugs, gabapentin, the active ingredient in gabapentin tablet, may cause suicidal thoughts or actions in a very small number of people, about 1 in 500. This can happen while you take gabapentin tablet or after stopping.**However, it is not known if gabapentin is safe and effective in people with seizure problems (epilepsy). Therefore, gabapentin tablet should not be used in place of other gabapentin products.
Call a healthcare provider right away if you have any of these symptoms, especially if they are new, worse, or worry you:
- thoughts about suicide or dying
- attempts to commit suicide
- serious breathing problems
- new or worse depression
- new or worse anxiety
- feeling agitated or restless
- panic attacks
- trouble sleeping (insomnia)
- new or worse irritability
- acting aggressive, being angry, or violent
- acting on dangerous impulses
- an extreme increase in activity and talking (mania)
- other unusual changes in behavior or mood
How can I watch for early symptoms of suicidal thoughts and actions?
- Pay attention to any changes, especially sudden changes, in mood, behaviors, thoughts, or feelings.
- Keep all follow-up visits with your healthcare provider as scheduled.
- Call your healthcare provider between visits as needed, especially if you are worried about symptoms.
Serious breathing problems
- Serious breathing problems can occur when gabapentin is taken with other medicines that can cause severe sleepiness or decreased awareness, or when it is taken by someone who already has breathing problems. Watch for increased sleepiness or decreased breathing when starting gabapentin or when the dose is increased. Get help right away if breathing problems occur.
Do not stop taking gabapentin without first talking with your healthcare provider.
- Stopping gabapentin suddenly can cause serious problems.
What is gabapentin?
Gabapentin is a prescription medicine used in adults, 18 years and older, to treat:
- pain from damaged nerves (neuropathic pain) that follows healing of shingles (a painful rash that comes after a herpes zoster infection).
It is not known if gabapentin is safe and effective in people with seizure problems (epilepsy).
It is not known if gabapentin is safe and effective in children under 18 years of age with postherpetic pain.
Gabapentin tablet is not substitutable with other gabapentin products.
Who should not take gabapentin?
Do not take gabapentin tablet if you are allergic to gabapentin or any of the ingredients in gabapentin tablet. See the end of this Medication Guide for a complete list of ingredients in gabapentin tablet.
What should I tell my healthcare provider before taking gabapentin?
Before taking gabapentin, tell your healthcare provider if you:
- have or have had depression, mood problems or suicidal thoughts or behavior
- have breathing problems
- have seizures
- have kidney problems or get kidney dialysis
- are pregnant or plan to become pregnant. It is not known if gabapentin can harm your unborn baby. Tell your healthcare provider right away if you become pregnant while taking gabapentin. You and your healthcare provider will decide if you should take gabapentin while you are pregnant.
If you become pregnant while taking gabapentin, talk to your healthcare provider about registering with the North American Antiepileptic Drug (NAAED) Pregnancy Registry. The purpose of this registry is to collect information about the safety of antiepileptic drugs, including gabapentin, the active ingredient in gabapentin tablet, during pregnancy. You can enroll in this registry by calling 1-888-233-2334.
- are breastfeeding or plan to breastfeed. Gabapentin passes into your breast milk. Talk to your healthcare provider about the best way to feed your baby during treatment with gabapentin.
Tell your healthcare provider about all the medicines you take including prescription and non-prescription medicines, vitamins or herbal supplements. Especially tell your healthcare provider if you take any opioid pain medicine (such as oxycodone), or medicines for anxiety (such as lorazepam) or insomnia (such as zolpidem). You may have a higher chance for dizziness, sleepiness or serious breathing problems if these medicines are taken with gabapentin.
Taking gabapentin with certain other medicines can cause side effects or affect how well they work. Do not start or stop other medicines without talking to your healthcare provider.
Know the medicines you take. Keep a list of them and show it to your healthcare provider and pharmacist when you get a new medicine.
How should I take gabapentin?
- Take gabapentin exactly as prescribed. Your healthcare provider will tell you how much gabapentin to take and when to take it. Take gabapentin at the same time each day. *Do not change your dose or stop taking gabapentin without talking with your healthcare provider. If you stop taking gabapentin suddenly, you may experience side effects. Talk with your healthcare provider about how to stop gabapentin slowly.
- Take gabapentin with food one time each day with your evening meal.
- Take gabapentin tablets whole. Do not split, crush, or chew gabapentin tablets before swallowing.
- Your healthcare provider may change your dose of gabapentin. Do not change your dose of gabapentin without talking to your healthcare provider.
- If you miss a dose, take it as soon as you remember with food. If it is almost time for your next dose, just skip the missed dose. Take the next dose at your regular time.Do not take two doses at the same time.
- If you take too much gabapentin, call your healthcare provider or poison control center, or go to the nearest emergency room right away.
- If you are taking an antacid containing aluminum hydroxide and magnesium hydroxide, it is recommended that gabapentin be taken at least 2 hours following administration of the antacid.
What should I avoid while taking gabapentin?
- Do not drink alcohol or take other medicines that make you sleepy or dizzy while taking gabapentin without first talking to your healthcare provider. Taking gabapentin with alcohol or medicines that cause sleepiness or dizziness may make your sleepiness or dizziness worse.
- Do not operate heavy machines or do other dangerous activities until you know how gabapentin affects you. Gabapentin can slow your thinking and motor skills.
What are the possible side effects of gabapentin?
The most common side effect of gabapentin is:
- dizziness
Tell your healthcare provider about any side effect that bothers you or that does not go away.
These are not all the possible side effects of gabapentin. For more information, ask your healthcare provider or pharmacist.
Call your doctor for medical advice about side effects. You may report side effects to FDA at 1-800-FDA-1088.
How should I store gabapentin tablets?
- Store gabapentin tablets at 20°C to 25°C (68°F to 77°F).
- Gabapentin tablets come in child-resistant bottles of 60's, 90's and 100's. *Keep gabapentin and all medicines out of the reach of children.
General information about the safe and effective use of gabapentin
Medicines are sometimes prescribed for purposes other than those listed in a Medication Guide. Do not use gabapentin for a condition for which it was not prescribed. Do not give gabapentin to other people, even if they have the same symptoms you have. It may harm them.
This Medication Guide summarizes the most important information about gabapentin. If you would like more information, talk with your healthcare provider. You can ask your healthcare provider or pharmacist for information about gabapentin that is written for health professionals.
Please address all medical inquiries to, MedicalAffairs@zydususa.com or Tel.: 1-877-993-8779.
What are the ingredients in gabapentin tablet?
Active ingredient: gabapentin, USP
Inactive ingredients: copovidone, hypromellose, magnesium stearate, microcrystalline cellulose, polyethylene glycol, polyethylene oxide, povidone, talc and titanium dioxide.
Medication Guide available at www.zydususa.com/medguides or call 1-877-993-8779.
RECENT MAJOR CHANGES SECTION
RECENT MAJOR CHANGES
|
Warnings and Precautions (5.1, 5.2) |
04/2025 |
|
Warnings and Precautions (5.1, 5.2) |
04/2025 |
