Manufacturing Establishments4
FDA-registered manufacturing facilities and establishments involved in the production, packaging, or distribution of this drug product.
Janssen Pharmaceuticals, Inc.
985639841
Janssen Pharmaceuticals, Inc.
483237103
Vetter
Janssen Pharmaceuticals, Inc.
344217323
Janssen Pharmaceuticals, Inc.
858582083
Products4
Detailed information about drug products covered under this FDA approval, including NDC codes, dosage forms, ingredients, and administration routes.
RISPERDAL CONSTA
Product Details
RISPERDAL CONSTA
Product Details
RISPERDAL CONSTA
Product Details
RISPERDAL CONSTA
Product Details
Drug Labeling Information
Complete FDA-approved labeling information including indications, dosage, warnings, contraindications, and other essential prescribing details.
PACKAGE LABEL.PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL
PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL - 50 mg Kit Carton
50 mg
** Dose Pack**
Store Package
** in Refrigerator**
** (see bottom panel for**
** storage conditions)**
Rx only
** Single use only**
NDC50458-308-11
RisperdalCONSTA®
risperiDONE Long-Acting Injection
DOSE PACK CONTENTS:
- One 50 mg vial of risperidone extended-release microspheres for injection
- One pre-filled syringe containing 2 mL of diluent
- One Vial Adapter
- One 21-gauge UTW 1" Terumo SurGuard ®3 safety needle for deltoid injection
- One 20-gauge TW 2" Terumo SurGuard ®3 safety needle for gluteal injection
Do not substitute any components of the dose pack.
For deltoid or gluteal intramuscular injection only
** Each injection should be administered by a healthcare professional.**
PLEASE READ COMPLETE INSTRUCTIONS PRIOR TO USE.

RECENT MAJOR CHANGES SECTION
RECENT MAJOR CHANGES
|
Warnings and Precautions ( 5.3, 5.4) |
2/2021 |
|
Warnings and Precautions, Thrombotic Thrombocytopenic Purpura (5.14) |
Removed 2/2021 |
|
Warnings and Precautions, Antiemetic Effect (5.17) |
Removed 2/2021 |
|
Warnings and Precautions, Concomitant Illness (5.18) |
Removed 2/2021 |
DESCRIPTION SECTION
11 DESCRIPTION
RISPERDAL CONSTA ®contains risperidone, an atypical antipsychotic belonging to the chemical class of benzisoxazole derivatives. The chemical designation is 3-[2-[4-(6-fluoro-1,2-benzisoxazol-3-yl)-1-piperidinyl]ethyl]-6,7,8,9-tetrahydro-2-methyl-4H-pyrido[1,2-a]pyrimidin-4-one. Its molecular formula is C 23H 27FN 4O 2and its molecular weight is 410.49. The structural formula is:
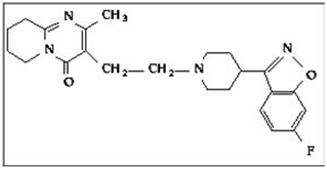
Risperidone is practically insoluble in water, freely soluble in methylene chloride, and soluble in methanol and 0.1 NHCl.
RISPERDAL CONSTA ®(risperidone) Long-Acting Injection is a combination of extended-release microspheres for injection and diluent for parenteral use.
The extended-release microspheres formulation is a white to off-white, free- flowing powder that is available in dosage strengths of 12.5 mg, 25 mg, 37.5 mg, or 50 mg risperidone per vial. Risperidone is micro-encapsulated in 7525 polylactide-co-glycolide (PLG) at a concentration of 381 mg risperidone per gram of microspheres.
The diluent for parenteral use is a clear, colorless solution. Composition of the diluent includes 1 mg/mL citric acid anhydrous, 1.27 mg/mL disodium hydrogen phosphate dihydrate, 1 mg/mL polysorbate 20, 22.5 mg/mL sodium carboxymethyl cellulose, 6 mg/mL sodium chloride, 0.54 mg/mL sodium hydroxide, and water for injection. The microspheres are suspended in the diluent prior to injection.
RISPERDAL CONSTA ®is provided as a single-use dose pack, consisting of a vial containing the microspheres, a pre-filled syringe containing the diluent, a vial adapter, and two Terumo SurGuard ®3 Needles (a 21 G UTW 1-inch needle with needle protection device for deltoid administration and a 20 G TW 2-inch needle with needle protection device for gluteal administration).
DOSAGE FORMS & STRENGTHS SECTION
Highlight: Vial kits: 12.5 mg, 25 mg, 37.5 mg, and 50 mg ( 3)
3 DOSAGE FORMS AND STRENGTHS
RISPERDAL CONSTA ®is available in dosage strengths of 12.5 mg, 25 mg, 37.5 mg, and 50 mg risperidone. It is provided as a single-use dose pack, consisting of a vial containing the risperidone microspheres, a pre-filled syringe containing 2 mL of diluent for RISPERDAL CONSTA ®, a vial adapter, and two Terumo SurGuard ®3 Needles for intramuscular injection (a 21 G UTW 1-inch needle with needle protection device for deltoid administration and a 20 G TW 2-inch needle with needle protection device for gluteal administration).
CONTRAINDICATIONS SECTION
Highlight: * Known hypersensitivity to risperidone, paliperidone, or to any excipients in RISPERDAL CONSTA ®. ( 4)
4 CONTRAINDICATIONS
RISPERDAL CONSTA ®is contraindicated in patients with a known hypersensitivity to either risperidone or paliperidone, or to any of the excipients in the RISPERDAL CONSTA ®formulation. Hypersensitivity reactions, including anaphylactic reactions and angioedema, have been reported in patients treated with risperidone and in patients treated with paliperidone. Paliperidone is a metabolite of risperidone.
BOXED WARNING SECTION
WARNING: INCREASED MORTALITY IN ELDERLY PATIENTS WITH DEMENTIA-RELATED
PSYCHOSIS
See full prescribing information for complete boxed warning.
Elderly patients with dementia-related psychosis treated with antipsychotic drugs are at an increased risk of death. RISPERDAL CONSTA**®****is not approved for use in patients with dementia-related psychosis. (5.1) **
DRUG INTERACTIONS SECTION
Highlight: * Due to CNS effects, use caution when administering with other centrally-acting drugs. Avoid alcohol. ( 7.1)
- Due to hypotensive effects, hypotensive effects of other drugs with this potential may be enhanced. ( 7.2)
- Effects of levodopa and dopamine agonists may be antagonized. ( 7.3)
- Cimetidine and ranitidine increase the bioavailability of risperidone. ( 7.5)
- Clozapine may decrease clearance of risperidone. ( 7.6)
- Fluoxetine and paroxetine increase plasma concentrations of risperidone. ( 7.11)
- Carbamazepine and other enzyme inducers decrease plasma concentrations of risperidone. ( 7.12)
7 DRUG INTERACTIONS
The interactions of RISPERDAL CONSTA ®with coadministration of other drugs have not been systematically evaluated. The drug interaction data provided in this section is based on studies with oral RISPERDAL ®.
7.1 Centrally-Acting Drugs and Alcohol
Given the primary CNS effects of risperidone, caution should be used when RISPERDAL CONSTA ®is administered in combination with other centrally-acting drugs or alcohol.
7.2 Drugs with Hypotensive Effects
Because of its potential for inducing hypotension, RISPERDAL CONSTA ®may enhance the hypotensive effects of other therapeutic agents with this potential.
7.3 Levodopa and Dopamine Agonists
RISPERDAL CONSTA ®may antagonize the effects of levodopa and dopamine agonists.
7.4 Amitriptyline
Amitriptyline did not affect the pharmacokinetics of risperidone or of risperidone and 9-hydroxyrisperidone combined following concomitant administration with oral RISPERDAL ®.
7.5 Cimetidine and Ranitidine
Cimetidine and ranitidine increased the bioavailability of oral risperidone by 64% and 26%, respectively. However, cimetidine did not affect the AUC of risperidone and 9-hydroxyrisperidone combined, whereas ranitidine increased the AUC of risperidone and 9-hydroxyrisperidone combined by 20%.
7.6 Methylphenidate
Concomitant use with methylphenidate, when there is change in dosage of either medication, may increase the risk of extrapyramidal symptoms (EPS). Monitor for symptoms of EPS with concomitant use of RISPERDAL CONSTA ®and methylphenidate [see Adverse Reactions (6.2)] .
7.7 Clozapine
Chronic administration of clozapine with risperidone may decrease the clearance of risperidone.
7.8 Lithium
Repeated doses of oral RISPERDAL ®(3 mg twice daily) did not affect the exposure (AUC) or peak plasma concentrations (C max) of lithium (N=13).
7.9 Valproate
Repeated doses of oral RISPERDAL ®(4 mg once daily) did not affect the pre- dose or average plasma concentrations and exposure (AUC) of valproate (1000 mg/day in three divided doses) compared to placebo (N=21). However, there was a 20% increase in valproate peak plasma concentration (C max) after concomitant administration of oral RISPERDAL ®.
7.10 Digoxin
Oral RISPERDAL ®(0.25 mg twice daily) did not show a clinically relevant effect on the pharmacokinetics of digoxin.
7.11 Topiramate
Oral RISPERDAL ®administered at doses from 1–6 mg/day concomitantly with topiramate 400 mg/day resulted in a 23% decrease in risperidone C maxand a 33% decrease in risperidone AUC 0–12 hourat steady state. Minimal reductions in the exposure to risperidone and 9-hydroxyrisperidone combined, and no change for 9-hydroxyrisperidone were observed. This interaction is unlikely to be of clinical significance. There was no clinically relevant effect of oral RISPERDAL ®on the pharmacokinetics of topiramate.
7.12 Drugs That Inhibit CYP 2D6 and Other CYP Isozymes
Risperidone is metabolized to 9-hydroxyrisperidone by CYP 2D6, an enzyme that is polymorphic in the population and that can be inhibited by a variety of psychotropic and other drugs [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)] . Drug interactions that reduce the metabolism of risperidone to 9-hydroxyrisperidone would increase the plasma concentrations of risperidone and lower the concentrations of 9-hydroxyrisperidone. Analysis of clinical studies involving a modest number of poor metabolizers (n≅70 patients) does not suggest that poor and extensive metabolizers have different rates of adverse effects. No comparison of effectiveness in the two groups has been made.
In vitrostudies showed that drugs metabolized by other CYP isozymes, including 1A1, 1A2, 2C9, 2C19, and 3A4, are only weak inhibitors of risperidone metabolism.
Fluoxetine and Paroxetine
Fluoxetine (20 mg once daily) and paroxetine (20 mg once daily), CYP 2D6 inhibitors, have been shown to increase the plasma concentration of risperidone 2.5–2.8 fold and 3–9 fold respectively. Fluoxetine did not affect the plasma concentration of 9-hydroxyrisperidone. Paroxetine lowered the concentration of 9-hydroxyrisperidone by about 10%. When either concomitant fluoxetine or paroxetine is initiated or discontinued, the physician should re-evaluate the dose of RISPERDAL CONSTA ®. When initiation of fluoxetine or paroxetine is considered, patients may be placed on a lower dose of RISPERDAL CONSTA ®between 2 to 4 weeks before the planned start of fluoxetine or paroxetine therapy to adjust for the expected increase in plasma concentrations of risperidone. When fluoxetine or paroxetine is initiated in patients receiving the recommended dose of 25 mg RISPERDAL CONSTA ®, it is recommended to continue treatment with the 25-mg dose unless clinical judgment necessitates lowering the RISPERDAL CONSTA ®dose to 12.5 mg or necessitates interruption of RISPERDAL CONSTA ®treatment. When RISPERDAL CONSTA ®is initiated in patients already receiving fluoxetine or paroxetine, a starting dose of 12.5 mg can be considered. The efficacy of the 12.5 mg dose has not been investigated in clinical trials. [see also Dosage and Administration (2.5)] . The effects of discontinuation of concomitant fluoxetine or paroxetine therapy on the pharmacokinetics of risperidone and 9-hydroxyrisperidone have not been studied.
Erythromycin
There were no significant interactions between oral RISPERDAL ®and erythromycin.
7.13 Carbamazepine and Other CYP 3A4 Enzyme Inducers
Carbamazepine co-administration with oral RISPERDAL ®decreased the steady- state plasma concentrations of risperidone and 9-hydroxyrisperidone by about 50%. Plasma concentrations of carbamazepine did not appear to be affected. Co- administration of other known CYP 3A4 enzyme inducers (e.g., phenytoin, rifampin, and phenobarbital) with risperidone may cause similar decreases in the combined plasma concentrations of risperidone and 9-hydroxyrisperidone, which could lead to decreased efficacy of RISPERDAL CONSTA ®treatment. At the initiation of therapy with carbamazepine or other known hepatic enzyme inducers, patients should be closely monitored during the first 4–8 weeks, since the dose of RISPERDAL CONSTA ®may need to be adjusted. A dose increase, or additional oral RISPERDAL ®, may need to be considered. On discontinuation of carbamazepine or other CYP 3A4 hepatic enzyme inducers, the dosage of RISPERDAL CONSTA ®should be re-evaluated and, if necessary, decreased. Patients may be placed on a lower dose of RISPERDAL CONSTA ®between 2 to 4 weeks before the planned discontinuation of carbamazepine or other CYP 3A4 enzyme inducers to adjust for the expected increase in plasma concentrations of risperidone plus 9-hydroxyrisperidone. For patients treated with the recommended dose of 25 mg RISPERDAL CONSTA ®and discontinuing from carbamazepine or other CYP 3A4 enzyme inducers, it is recommended to continue treatment with the 25-mg dose unless clinical judgment necessitates lowering the RISPERDAL CONSTA ®dose to 12.5 mg or necessitates interruption of RISPERDAL CONSTA ®treatment. The efficacy of the 12.5 mg dose has not been investigated in clinical trials. [see also Dosage and Administration (2.5)]
7.14 Drugs Metabolized by CYP 2D6
In vitrostudies indicate that risperidone is a relatively weak inhibitor of CYP 2D6. Therefore, RISPERDAL CONSTA ®is not expected to substantially inhibit the clearance of drugs that are metabolized by this enzymatic pathway. In drug interaction studies, oral RISPERDAL ®did not significantly affect the pharmacokinetics of donepezil and galantamine, which are metabolized by CYP 2D6.
USE IN SPECIFIC POPULATIONS SECTION
Highlight: * Pregnancy: May cause extrapyramidal and/or withdrawal symptoms in neonates with third trimester exposure. ( 8.1)
- Renal or Hepatic Impairment: dose appropriately with oral RISPERDAL ®prior to initiating treatment with RISPERDAL CONSTA ®. A lower starting dose of RISPERDAL CONSTA ®of 12.5 mg may be appropriate in some patients. ( 2.4)
- Pediatric Use: safety and effectiveness not established in patients less than 18 years of age. ( 8.4)
- Elderly: dosing for otherwise healthy elderly patients is the same as for healthy nonelderly. Elderly may be more predisposed to orthostatic effects than nonelderly. ( 8.5)
8 USE IN SPECIFIC POPULATIONS
8.1 Pregnancy
Pregnancy Exposure Registry
There is a pregnancy exposure registry that monitors pregnancy outcomes in women exposed to atypical antipsychotics, including RISPERDAL CONSTA ®, during pregnancy. Healthcare providers are encouraged to register patients by contacting the National Pregnancy Registry for Atypical Antipsychotics at 1-866-961-2388 or online at http://womensmentalhealth.org/clinical-and- research-programs/pregnancyregistry/.
Risk Summary
Neonates exposed to antipsychotic drugs during the third trimester of pregnancy are at risk for extrapyramidal and/or withdrawal symptoms following delivery (see Clinical Considerations) . Overall, available data from published epidemiologic studies of pregnant women exposed to risperidone have not established a drug-associated risk of major birth defects, miscarriage, or adverse maternal or fetal outcomes (see Data). There are risks to the mother associated with untreated schizophrenia or bipolar I disorder and with exposure to antipsychotics, including RISPERDAL CONSTA ®, during pregnancy (see Clinical Considerations) . Risperidone has been detected in plasma in adult subjects up to 8 weeks after a single-dose administration of RISPERDAL CONSTA ®[see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)] . The clinical significance of RISPERDAL CONSTA ®administered before pregnancy or anytime during pregnancy is not known.
Oral administration of risperidone to pregnant mice caused cleft palate at doses 3 to 4 times the maximum recommended human dose (MRHD) with maternal toxicity observed at 4-times the MRHD based on mg/m 2body surface area. Risperidone was not teratogenic in rats or rabbits at doses up to 6-times the MRHD based on mg/m 2body surface area. Increased stillbirths and decreased birth weight occurred after oral risperidone administration to pregnant rats at 1.5-times the MRHD based on mg/m 2body surface area. Learning was impaired in offspring of rats when the dams were dosed at 0.6-times the MRHD and offspring mortality increased at doses 0.1 to 3 times the MRHD based on mg/m 2body surface area.
The estimated background risk of major birth defects and miscarriage for the indicated population is unknown. All pregnancies have a background risk of birth defect, loss, or other adverse outcomes. In the U.S. general population, the estimated background risk of major birth defects and miscarriage in clinically recognized pregnancies is 2–4% and 15–20%, respectively.
Clinical Considerations
Disease-associated maternal and/or embryo/fetal risk
There is a risk to the mother from untreated schizophrenia or bipolar I disorder, including increased risk of relapse, hospitalization, and suicide. Schizophrenia and bipolar I disorder are associated with increased adverse perinatal outcomes, including preterm birth. It is not known if this is a direct result of the illness or other comorbid factors.
Fetal/Neonatal Adverse Reactions
Extrapyramidal and/or withdrawal symptoms, including agitation, hypertonia, hypotonia, tremor, somnolence, respiratory distress, and feeding disorder have been reported in neonates who were exposed to antipsychotic drugs, including RISPERDAL CONSTA ®, during the third trimester of pregnancy. These symptoms have varied in severity. Monitor neonates for extrapyramidal and/or withdrawal symptoms and manage symptoms appropriately. Some neonates recovered within hours or days without specific treatment; others required prolonged hospitalization.
Data
Human Data
Published data from observational studies, birth registries, and case reports on the use of atypical antipsychotics during pregnancy do not report a clear association with antipsychotics and major birth defects. A prospective observational study including 6 women treated with risperidone demonstrated placental passage of risperidone. A retrospective cohort study from a Medicaid database of 9258 women exposed to antipsychotics during pregnancy did not indicate an overall increased risk for major birth defects. There was a small increase in the risk major of birth defects (RR=1.26, 95% CI 1.02–1.56) and of cardiac malformations (RR=1.26, 95% CI 0.88–1.81) in a subgroup of 1566 women exposed to risperidone during the first trimester of pregnancy; however, there is no mechanism of action to explain the difference in malformation rates.
Animal Data
Oral administration of risperidone to pregnant mice during organogenesis caused cleft palate at 10 mg/kg/day which is 3 times the MRHD of 16 mg/day based on mg/m 2body surface area; maternal toxicity occurred at 4 times the MRHD. Risperidone was not teratogenic when administered orally to rats at 0.6 to 10 mg/kg/day and rabbits at 0.3 to 5 mg/kg/day, which are up to 6 times the MRHD of 16 mg/day risperidone based on mg/m 2body surface area. Learning was impaired in offspring of rats dosed orally throughout pregnancy at 1 mg/kg/day which is 0.6 times the MRHD and neuronal cell death increased in fetal brains of offspring of rats dosed during pregnancy at 1 and 2 mg/kg/day which are 0.6 and 1.2 times the MRHD based on mg/m 2body surface area; postnatal development and growth of the offspring were also delayed.
Rat offspring mortality increased during the first 4 days of lactation when pregnant rats were dosed throughout gestation at 0.16 to 5 mg/kg/day which are 0.1 to 3 times the MRHD of 16 mg/day based on mg/m 2body surface area. It is not known whether these deaths were due to a direct effect on the fetuses or pups or to effects on the dams; a no-effect dose could not be determined. The rate of stillbirths was increased at 2.5 mg/kg or 1.5 times the MRHD based on mg/m 2body surface area.
In a rat cross-fostering study the number of live offspring was decreased, the number of stillbirths increased, and the birth weight was decreased in offspring of drug-treated pregnant rats. In addition, the number of deaths increased by Day 1 among offspring of drug-treated pregnant rats, regardless of whether or not the offspring were cross-fostered. Risperidone also appeared to impair maternal behavior in that offspring body weight gain and survival (from Day 1 to 4 of lactation) were reduced in offspring born to control but reared by drug-treated dams. All of these effects occurred at 5 mg/kg which is 3 times the MRHD based on mg/m 2and the only dose tested in the study.
8.2 Lactation
Risk Summary
Limited data from published literature reports the presence of risperidone and its metabolite, 9-hydroxyrisperidone, in human breast milk at relative infant dose ranging between 2.3% and 4.7% of the maternal weight-adjusted dosage. There are reports of sedation, failure to thrive, jitteriness, and extrapyramidal symptoms (tremors and abnormal muscle movements) in breastfed infants exposed to risperidone (see Clinical Considerations). Risperidone has been detected in plasma in adult subjects up to 8 weeks after a single-dose administration of RISPERDAL CONSTA ®[see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)] , and the clinical significance on the breastfed infant is not known. There is no information on the effects of risperidone on milk production. The developmental and health benefits of breastfeeding should be considered along with the mother's clinical need for RISPERDAL CONSTA ®and any potential adverse effects on the breastfed child from RISPERDAL CONSTA ®or from the mother's underlying condition.
Clinical Considerations
Infants exposed to RISPERDAL CONSTA ®through breastmilk should be monitored for excess sedation, failure to thrive, jitteriness, and extrapyramidal symptoms (tremors and abnormal muscle movements).
8.3 Females and Males of Reproductive Potential
Infertility
Females
Based on the pharmacologic action of risperidone (D 2receptor antagonism), treatment with RISPERDAL CONSTA ®may result in an increase in serum prolactin levels, which may lead to a reversible reduction in fertility in females of reproductive potential [see Warnings and Precautions (5.6)].
8.4 Pediatric Use
Safety and effectiveness of RISPERDAL CONSTA ®in pediatric patients have not been established. However, juvenile animal toxicology studies have been conducted with oral risperidone.
Juvenile Animal Studies
Juvenile dogs were treated with oral risperidone from weeks 10 to 50 of age (equivalent to the period of childhood through adolescence in humans), at doses of 0.31, 1.25, or 5 mg/kg/day, which are 1.2, 3.4 and 13.5 times the MRHD of 6 mg/day for children, based on mg/m 2body surface area. Bone length and density were decreased with a no-effect dose of 0.31 mg/kg/day; this dose produced plasma AUC of risperidone plus its active metabolite paliperidone (9-hydroxy-risperidone) that were similar to those in children and adolescents receiving the MRHD of 6 mg/day. In addition, sexual maturation was delayed at all doses in both males and females. The above effects showed little or no reversibility in females after a 12 week drug-free recovery period. Juvenile rats, treated with oral risperidone from days 12 to 50 of age (equivalent to the period of infancy through adolescence in humans) showed impaired learning and memory performance (reversible only in females), with a no-effect dose of 0.63 mg/kg/day which is 0.5 times the MRHD of 6 mg/day for children, based on mg/m 2body surface area. This dose produced plasma AUC of risperidone plus paliperidone about half the exposure observed in humans at the MRHD. No other consistent effects on neurobehavioral or reproductive development were seen up to the highest tested dose of 1.25 mg/kg/day which is 1 time the MRHD and produced plasma AUC of risperidone plus paliperidone that were about two thirds of those observed in humans at the MRHD of 6 mg/day for children.
8.5 Geriatric Use
In an open-label study, 57 clinically stable, elderly patients (≥ 65 years old) with schizophrenia or schizoaffective disorder received RISPERDAL CONSTA ®every 2 weeks for up to 12 months. In general, no differences in the tolerability of RISPERDAL CONSTA ®were observed between otherwise healthy elderly and nonelderly patients. Therefore, dosing recommendations for otherwise healthy elderly patients are the same as for nonelderly patients. Because elderly patients exhibit a greater tendency to orthostatic hypotension than nonelderly patients, elderly patients should be instructed in nonpharmacologic interventions that help to reduce the occurrence of orthostatic hypotension (e.g., sitting on the edge of the bed for several minutes before attempting to stand in the morning and slowly rising from a seated position). In addition, monitoring of orthostatic vital signs should be considered in elderly patients for whom orthostatic hypotension is of concern [see Warnings and Precautions (5.7)] .
Concomitant use with Furosemide in Elderly Patients with Dementia-Related Psychosis
In two of four placebo-controlled trials in elderly patients with dementia- related psychosis, a higher incidence of mortality was observed in patients treated with furosemide plus oral risperidone when compared to patients treated with oral risperidone alone or with oral placebo plus furosemide. No pathological mechanism has been identified to explain this finding, and no consistent pattern for cause of death was observed. An increase of mortality in elderly patients with dementia-related psychosis was seen with the use of oral risperidone regardless of concomitant use with furosemide. RISPERDAL CONSTA ®is not approved for the treatment of patients with dementia-related psychosis. [see Boxed Warningand Warnings and Precautions (5.1)] .
8.6 Renal or Hepatic Impairment
In patients with renal or hepatic impairment, carefully titrate with oral risperidone prior to initiating treatment with RISPERDAL CONSTA ®[see Dosage and Administration (2.4)].
Patients with renal impairment may have less ability to eliminate risperidone than patients with normal renal function. Patients with impaired hepatic function may have an increase in the free fraction of risperidone, possibly resulting in an enhanced effect [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)] .
8.7 Patients with Parkinson's Disease or Lewy Body Dementia
Patients with Parkinson's Disease or Dementia with Lewy Bodies can experience increased sensitivity to RISPERDAL CONSTA ®. Manifestations can include confusion, obtundation, postural instability with frequent falls, extrapyramidal symptoms, and clinical features consistent with neuroleptic malignant syndrome.
SPL UNCLASSIFIED SECTION
Product of Ireland
Risperidone active ingredient is manufactured by:
Janssen Pharmaceutical
Wallingstown, Little Island, County Cork, Ireland
Microspheres are manufactured by:
Alkermes, Inc.
Wilmington, Ohio
Diluent is manufactured by:
Vetter Pharma Fertigung GmbH & Co. KG
Langenargen, Germany
or
Cilag AG
Schaffhausen, Switzerland
RISPERDAL CONSTA ®is manufactured for:
Janssen Pharmaceuticals, Inc.
Titusville, NJ 08560
©2007 Janssen Pharmaceutical Companies
