Tobramycin
These highlights do not include all the information needed to use TOBRAMYCIN INHALATION SOLUTION safely and effectively. See full prescribing information for TOBRAMYCIN INHALATION SOLUTION. TOBRAMYCIN inhalation solution, for oral inhalation use Initial U.S. Approval: 1980
d03079d2-5617-4628-92b9-3caa757b22c0
HUMAN PRESCRIPTION DRUG LABEL
Aug 26, 2025
Teva Pharmaceuticals USA, Inc.
DUNS: 001627975
Products 1
Detailed information about drug products covered under this FDA approval, including NDC codes, dosage forms, ingredients, and administration routes.
Tobramycin
Product Details
FDA regulatory identification and product classification information
FDA Identifiers
Product Classification
Product Specifications
INGREDIENTS (6)
Drug Labeling Information
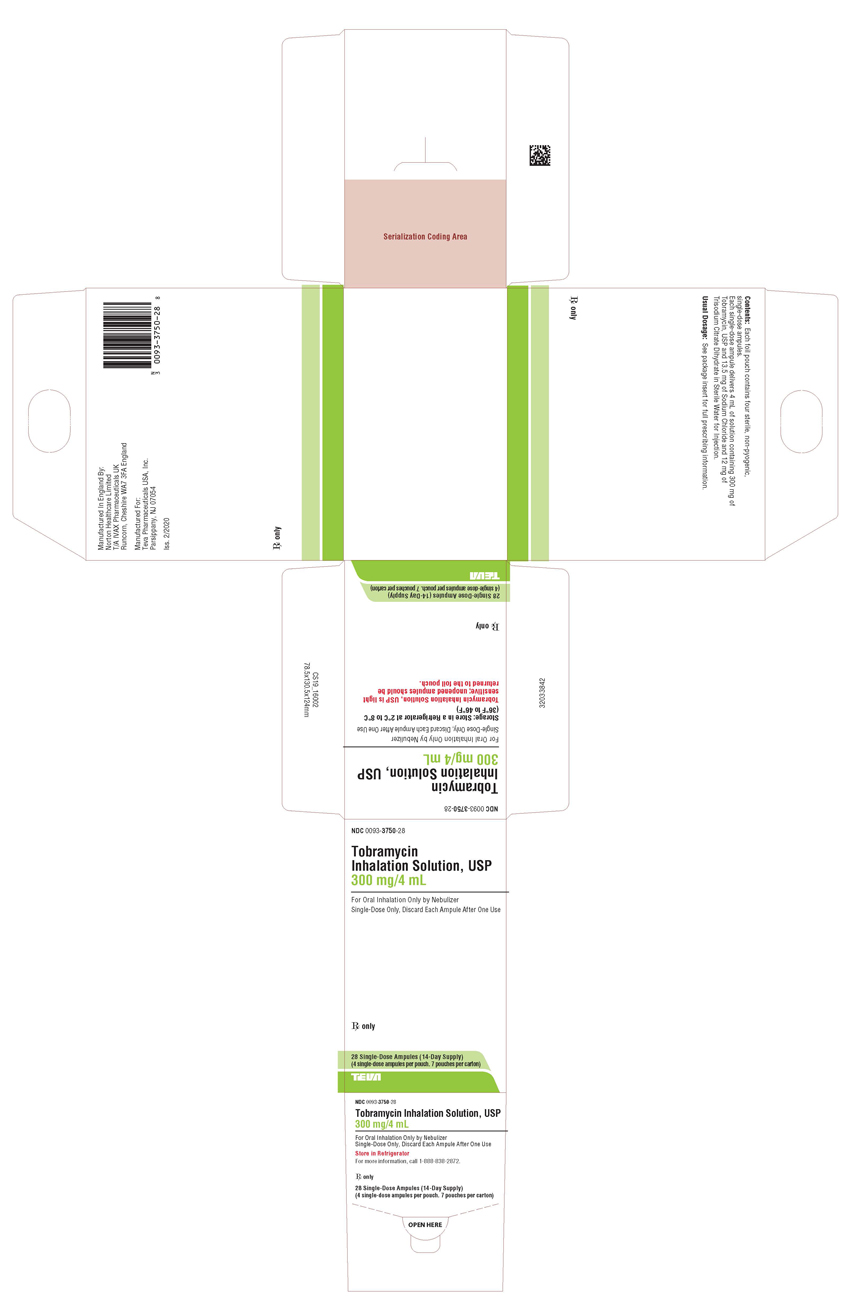
PACKAGE LABEL.PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL
PACKAGE LABEL.PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL
NDC 0093-3750-28
Tobramycin Inhalation Solution, USP
300 mg/4 mL
For Oral Inhalation Only by Nebulizer
Single-Dose Only, Discard Each Ampule After One Use
Storage: Store in a Refrigerator at 2°C to 8°C (36°F to 46°F)
Tobramycin Inhalation Solution, USP is light sensitive; unopened ampules
should be returned to the foil pouch.
Rx only
28 Single-Dose Ampules (14-Day Supply)
(4 single-dose ampules per pouch. 7 pouches per carton)
CLINICAL STUDIES SECTION
14 CLINICAL STUDIES
Two, double-blind, randomized, placebo-controlled, parallel group clinical studies (Study 1 and Study 2), which randomized and dosed 306 patients, were conducted in cystic fibrosis patients with P. aeruginosa. The osmolality of the drug formulation used in these studies differed from the to-be-marketed product. To rely upon the efficacy and safety established in the placebo- controlled studies, an additional study was conducted as a bridge to the to- be-marketed drug. The bridging study assessed the efficacy and tolerability of aerosolized Tobramycin Inhalation Solution with osmolality similar to tobramycin inhalation solution over a 4-week treatment in 324 patients with cystic fibrosis. Results of this study showed that the Tobramycin Inhalation Solution in this study had similar efficacy as that seen in the placebo- controlled studies.
The compressors in the placebo-controlled studies and the bridging study differed from the PARI VIOS compressor to be used with tobramycin inhalation solution. In vitro cascade impaction studies demonstrated that the various compressors used in the clinical trials delivered equivalent doses and respirable fractions of the to-be-marketed tobramycin inhalation solution and TOBI with the marketed compressor (PARI VIOS) when used with the same nebulizer (PARI LC Plus Reusable nebulizer).
All subjects enrolled in both efficacy studies had baseline FEV1 % predicted ≥40% and ≤80% (mean baseline FEV1 of 60% of predicted normal) and infected with P. aeruginosa. Subjects who were less than 6 years of age, or who had a baseline creatinine of ≥1.5 mg/dL, or who had Burkholderia cepacia isolated from sputum were excluded. A total of 190 patients, 29 in Study 1 and 161 in Study 2, received tobramycin inhalation solution therapy on an outpatient basis. Of these, 55% were males and 45% were females. Eighty-two (43.2%) patients were between 6 and 12 years of age, 54 (28.4%) patients were between 13 and 17 years of age, and the remaining 54 (28.4%) patients were greater than 17 years of age. Of the patients who received tobramycin inhalation solution, only 89.7% of patients in Study 1 had at least one concomitant medication, while all patients in Study 2 also received at least one concomitant medication. These concomitant medications include mucolytics, steroidal and nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, bronchodilators, rehabilitative physiotherapies and if necessary, antibiotics for bacterial infections other than P. aeruginosa.
Study 1
Study 1 was a double-blind, single cycle study that randomized 59 patients to receive tobramycin inhalation solution (n=29) or placebo (n=30) for one cycle of treatment (28 days on treatment followed by 28 days off treatment). All patients were ≤30 years of age (mean age 12.6 years) and 46% were females. All randomized patients were included in the primary analysis except for one patient who had missing baseline information.
Tobramycin inhalation solution significantly improved lung function compared with placebo as measured by the absolute change in FEV1 % predicted from baseline to the end of Cycle 1 dosing in the primary analysis population. Treatment with tobramycin inhalation solution and placebo resulted in absolute increases in FEV1 % predicted of 16% and 5%, respectively (LS mean difference = 11%; 95% CI: 3, 19; p=0.003). This analysis is adjusted for the covariate of baseline FEV1 % predicted, using multiple imputation for missing data. Figure 1 shows the average change in FEV1 % predicted over eight weeks.
Study 2
Study 2 was a randomized, double-blind, 3-cycle, placebo-controlled trial. A total of 247 eligible patients were randomized 2:1 to receive three cycles of tobramycin inhalation solution (n=161) or placebo (n=86). As in Study 1, each cycle comprised 28 days on treatment followed by 28 days off treatment. All patients were ≤46 years of age (mean age 14.8 years) and 44.9% were females. In this study, two randomized patients in the placebo group were not included in the primary efficacy analysis; one withdrew consent without taking any trial medication and the other withdrew due to an adverse drug reaction.
Tobramycin inhalation solution significantly improved lung function compared with placebo as measured by the absolute change in FEV1 % predicted from baseline to the end of Cycle 3 “ON” period. Treatment with tobramycin inhalation solution and placebo resulted in absolute increases in FEV1 % predicted of 7% and 1%, respectively (LS mean difference = 6%; 95% CI: 3, 10; p<0.001). This analysis is adjusted for the covariate of baseline FEV1 % predicted, using multiple imputation for missing data. Figure 1 shows the average change in FEV1 % predicted over 24 weeks from Study 2.
Figure 1: FEV1 % of Predicted Normal – Absolute Change from Baseline (Adjusted mean) – ITT** Population**
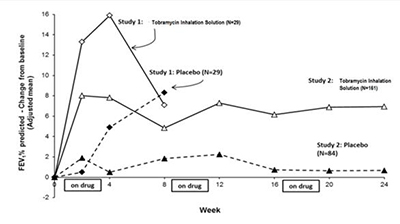
In Study 2, 9.9% of patients treated with tobramycin inhalation solution and 24.7% of patients who received placebo had unplanned hospitalizations due to the disease.
Also in Study 2, 6.2% of patients treated with tobramycin inhalation solution and 16.5% of placebo patients received parenteral tobramycin.
INSTRUCTIONS FOR USE SECTION
INSTRUCTIONS FOR USE
Tobramycin (toe" bra mye' sin) Inhalation Solution, USP
Follow the instructions below for taking tobramycin inhalation solution. If you have any questions, ask your healthcare provider or pharmacist.
Tobramycin inhalation solution is available as a 28-day supply containing 56 ampules including 14 foil pouches and as a 14-day supply containing 28 ampules including 7 foil pouches. Each foil pouch contains 4 tobramycin inhalation solution ampules.
Supplies you will need to take tobramycin inhalation solution (See Figure A):
- 1 ampule of tobramycin inhalation solution
- PARI LC PLUS reusable nebulizer
- PARI Vios compressor
- tubing to connect the nebulizer and compressor
- clean paper or cloth towels
- nose clips (optional)
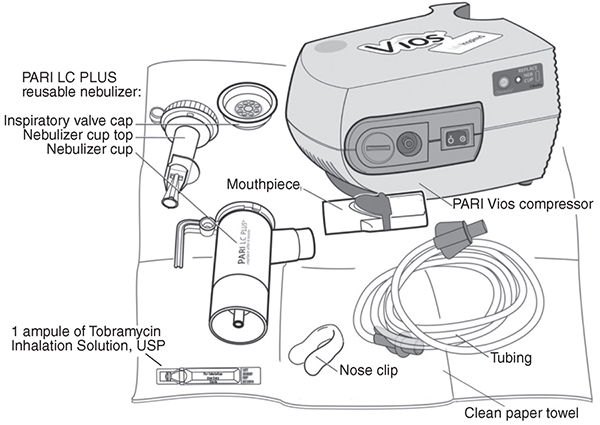
(Figure A)
Tobramycin inhalation solution is used only in a PARI LC PLUS re-usable Nebulizer connected to a PARI LC PLUS Vios air compressor. Make sure you know how to use your nebulizer machine before you use it to breathe in tobramycin inhalation solution.
Do not mix tobramycin inhalation solution with other medicines in your nebulizer.
Tobramycin inhalation solution comes in a sealed foil pouch. Do not open a sealed pouch until you are ready to use a dose of tobramycin inhalation solution. After opening the pouch, unused ready-to-use ampules should be returned to, and stored in, the pouch.
Getting ready:
- Put your PARI LC PLUS Reusable Nebulizer Top and Bottom (Nebulizer Cup) Assembly, Inspiratory Valve Cap, Mouthpiece with Valve, and Tubing on a clean and dry surface.
- Wash your hands with soap and water.
Preparing your tobramycin inhalation solution dose:
Step 1: Open foil pouch. (See Figure B)
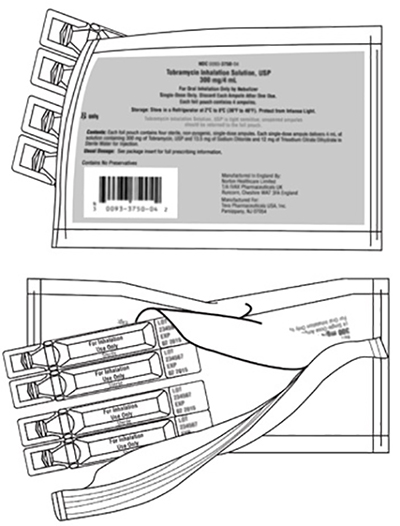
(Figure B)
Step 2: Separate 1 ampule by gently pulling apart at the bottom tabs (See Figure C) and use it right away.
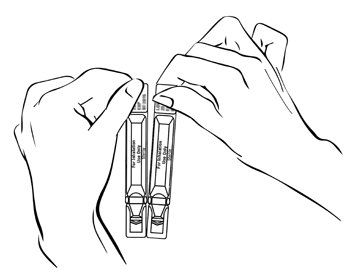
(Figure C)
**Step 3:**Hold the bottom tab on the tobramycin inhalation solution ampule with 1 hand (See Figure D). With your other hand, hold the top of the ampule and twist off the top of the ampule (See Figure D).
- Do not squeeze the ampule until you are ready to squeeze all the medicine into the Nebulizer Cup.
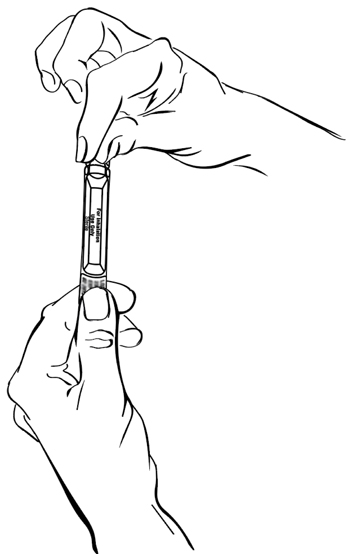
(Figure D)
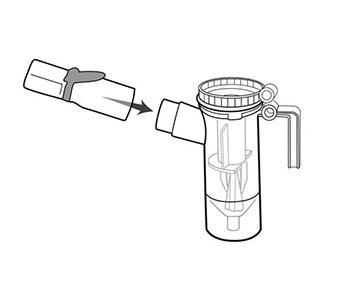
**Step 4:**Hold the Nebulizer Cup and twist off the Nebulizer Cup Top in a counter-clockwise direction
(See Figure E). Set the Top aside on a clean, dry surface.
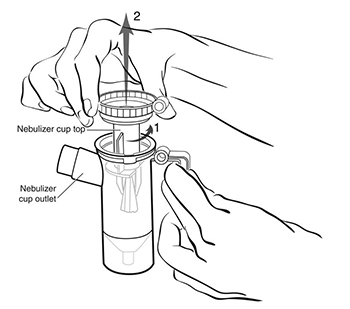
(Figure E)
Step 5: Squeeze all of the medicine from the ampule into the Nebulizer Cup (See Figure F).
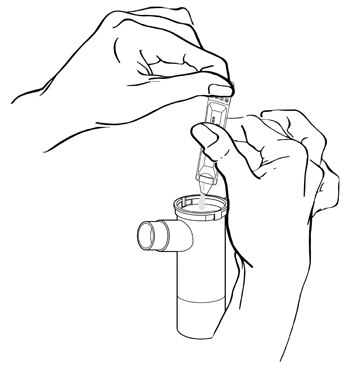
(Figure F)
Step 6: Line up the semi-circle on the Nebulizer Cup Top with the Nebulizer Cup Outlet and twist on the
Nebulizer Cup Top in a clock-wise direction until it is tight. (See Figure G).
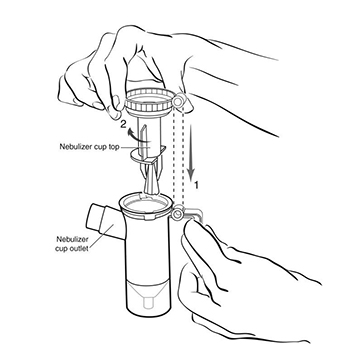
(Figure G)
Step 7: Push the mouthpiece straight onto the Nebulizer Cup Outlet (See Figure H).
(Figure H)
Step 8: Firmly push the Inspiratory Valve Cap straight down onto the Nebulizer Cup Top (See Figure I). The
Inspiratory Valve Cap should fit tightly.
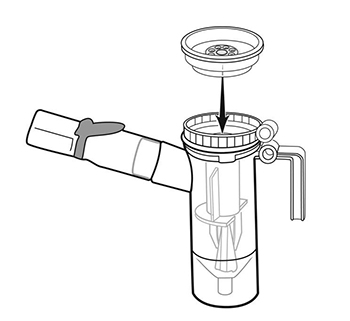
(Figure I)
Step 9: Connect 1 end of the tubing to the compressor air outlet. The tubing should fit tightly (See Figure J).
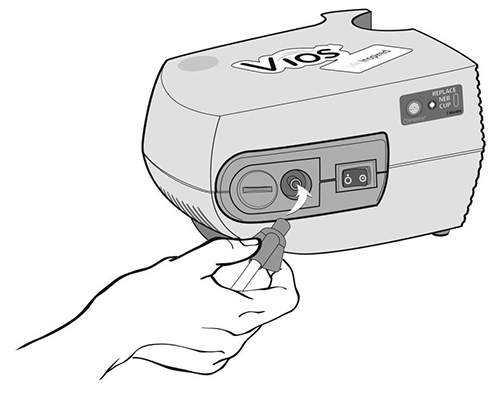
(Figure J)
Step 10: Plug your compressor plug into an electrical outlet (See Figure K).
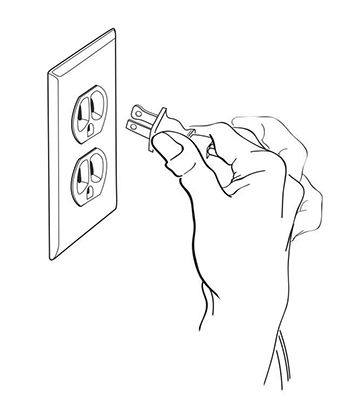
(Figure K)
Step 11: Hold the Nebulizer Cup upright and firmly push the free end of the tubing straight up onto the Air
Intake on the bottom of the Nebulizer Cup (See Figure L).Make sure to keep the Nebulizer Cup
** upright.**
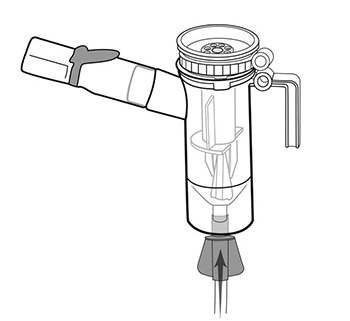
(Figure L)
Giving your tobramycin inhalation solution dose:
Step 12: Turn on the compressor (Figure M) and check the Mouthpiece. You should see a steady mist coming
from the Mouthpiece (Figure N).
- If you do not see a steady mist coming from the mouthpiece, check all tubing connections and make sure that the compressor is working the right way.
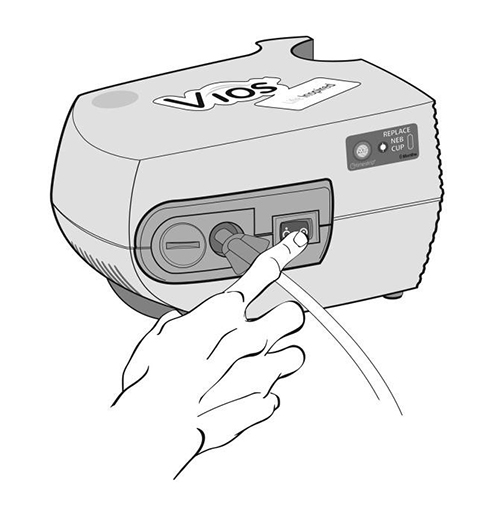
(Figure M)
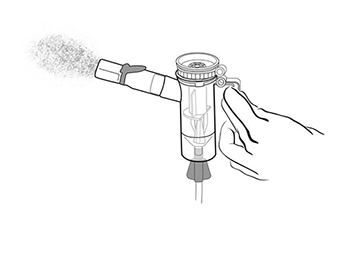
(Figure N)
Step 13: Sit or stand in a comfortable, upright position that will let you breathe normally. Place the
Mouthpiece between your teeth and on top of your tongue and breathe normally only through your
mouth (See Figure O).
- Nose clips may help you breathe only through your mouth and not through your nose.
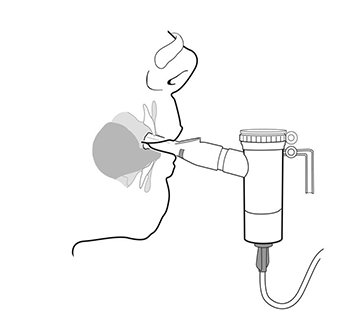
(Figure O)
Step 14: Keep breathing in your tobramycin inhalation solution dose for at least 15 minutes. You will know that you have received
****your full dose of medicine when you hear a “spitting noise” coming from the Mouthpiece for at least
1 minute and the Nebulizer Cup is empty.
After your tobramycin inhalation solution dose:
Step 15: Clean and disinfect your nebulizer (see manufacturer’s instructions).
Care and Use of Your PARI Vios**®**** Compressor**
Follow the manufacturer’s instructions for care and use of your compressor.
How should I store tobramycin inhalation solution?
- Store tobramycin inhalation solution in the refrigerator at 36°F to 46°F (2°C to 8°C) until needed.
- After removing from the refrigerator, or if refrigeration is not available, tobramycin inhalation solution foil pouches (opened or unopened) may be stored at room temperatureup to 77 °F (25 °C) for up to 28 days.
- If tobramycin inhalation solution is not stored in the refrigerator but at room temperature up to 77 °F (25 °C) it may turn dark. If tobramycin inhalation solution turns dark, it does not change how well tobramycin inhalation solution works. Tobramycin inhalation solution can still be used as long as it is stored at room temperatureup to 77 °F (25 °C).
- Do not use tobramycin inhalation solution after the expiration date printed on the ampule.
- Keep tobramycin inhalation solution ampules in the foil pouch and away from light.
- Return unopened ampules to the foil pouch *Keep tobramycin inhalation solution and all medicines out of the reach of children.
This Patient Information and Instructions for Use have been approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration.
Brands listed are the trademark of their respective owners.
Manufactured In England By:
Norton Healthcare Limited
****T/A IVAX Pharmaceuticals UK
****Runcorn, Cheshire WA7 3FA England
Manufactured For:
Teva Pharmaceuticals USA, Inc.
****Parsippany, NJ 07054
Iss. 2/2020
DESCRIPTION SECTION
11 DESCRIPTION
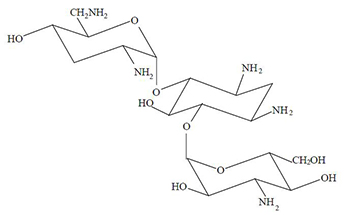
Tobramycin inhalation solution, USP is a sterile, clear, colorless to yellow, non-pyrogenic, aqueous solution with pH and salinity adjusted. Tobramycin inhalation solution, USP is administered by a compressed air driven reusable nebulizer. The chemical formula for tobramycin is C18H37N5O9 and the molecular weight is 467.51. Tobramycin, USP is O-3-amino-3-deoxy-α-D- glucopyranosyl-(1→4)-O-[2,6-diamino-2,3,6-trideoxy-α-D-ribo- hexopyranosyl-(1→6)]-2-deoxy-L-streptamine.
The structural formula for tobramycin, USP is:
Each single-dose 4 mL ampule of tobramycin inhalation solution, USP contains one 300 mg dose of tobramycin, USP with sodium chloride and trisodium citrate dihydrate in sterile water for injection. Sulfuric acid and sodium hydroxide are used, as needed, to adjust the pH to 5.0. Nitrogen is used for sparging and filling. The formulation contains no preservatives.
