Atenolol
Atenolol Tablets.
f4f06c00-9024-4e04-a882-0da2b24d8ff7
HUMAN PRESCRIPTION DRUG LABEL
Aug 7, 2023
Golden State Medical Supply, Inc.
DUNS: 603184490
Products 3
Detailed information about drug products covered under this FDA approval, including NDC codes, dosage forms, ingredients, and administration routes.
atenolol
Product Details
FDA regulatory identification and product classification information
FDA Identifiers
Product Classification
Product Specifications
INGREDIENTS (6)
atenolol
Product Details
FDA regulatory identification and product classification information
FDA Identifiers
Product Classification
Product Specifications
INGREDIENTS (6)
atenolol
Product Details
FDA regulatory identification and product classification information
FDA Identifiers
Product Classification
Product Specifications
INGREDIENTS (6)
Drug Labeling Information
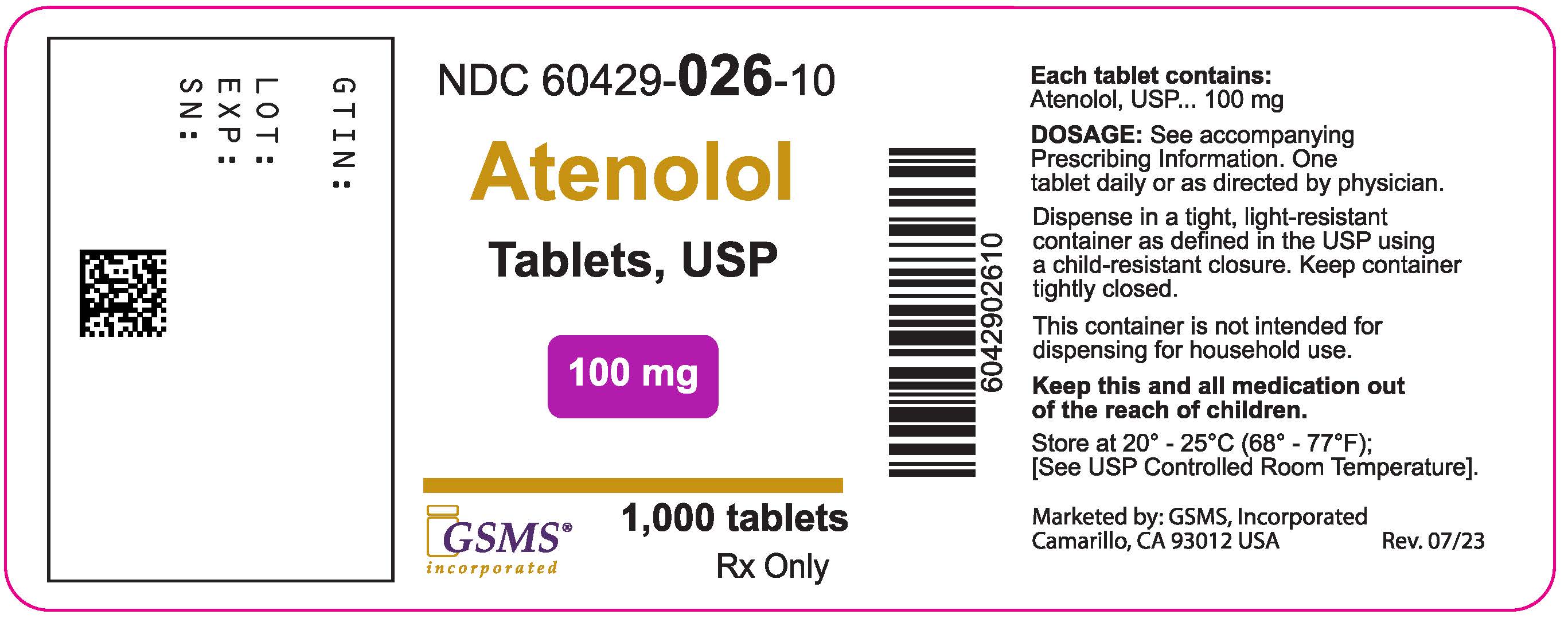
PACKAGE LABEL.PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL
PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL – 100 mg
NDC 60429-026-10
Atenolol
** Tablets, USP**
** 100 mg**
Rx only 1000 Tablets
Each tablet contains:
Atenolol, USP 100 mg
Dispense in a tight, light-resistant
container as defined in the USP
using a child-resistant closure.
Keep container tightly closed.
Keep this and all medication
** out of the reach of children.**
Store at 20° to 25°C (68° to 77°F).
** [See USP Controlled Room** **** ** Temperature.]**
Usual Dosage: One tablet daily or as
directed by physician. See accompanying
prescribing information.
Manufactured for:
Mylan Pharmaceuticals Inc.
Morgantown, WV 26505 U.S.A.
Made in Australia
Mylan.com
3389/0
RALP0757A
Marketed by:
GSMS, Inc.
Camarillo, CA USA 93012
OVERDOSAGE SECTION
OVERDOSAGE
Overdosage with atenolol tablets has been reported with patients surviving acute doses as high as 5 g. One death was reported in a man who may have taken as much as 10 g acutely.
The predominant symptoms reported following atenolol tablets overdose are lethargy, disorder of respiratory drive, wheezing, sinus pause and bradycardia. Additionally, common effects associated with overdosage of any beta-adrenergic blocking agent and which might also be expected in atenolol tablets overdose are congestive heart failure, hypotension, bronchospasm and/or hypoglycemia.
Treatment of overdose should be directed to the removal of any unabsorbed drug by induced emesis, gastric lavage, or administration of activated charcoal. Atenolol tablets can be removed from the general circulation by hemodialysis. Other treatment modalities should be employed at the physician’s discretion and may include:
Bradycardia
Atropine intravenously. If there is no response to vagal blockade, give isoproterenol cautiously. In refractory cases, a transvenous cardiac pacemaker may be indicated.
Heart Block (Second or Third Degree)
Isoproterenol or transvenous cardiac pacemaker.
Cardiac Failure
Digitalize the patient and administer a diuretic. Glucagon has been reported to be useful.
Hypotension
Vasopressors such as dopamine or norepinephrine (levarterenol). Monitor blood pressure continuously.
Bronchospasm
A beta 2 stimulant such as isoproterenol or terbutaline and/or aminophylline.
Hypoglycemia
Intravenous glucose.
Based on the severity of symptoms, management may require intensive support care and facilities for applying cardiac and respiratory support.
