TALVEY
These highlights do not include all the information needed to use TALVEY safely and effectively. See full prescribing information for TALVEY. TALVEY™ (talquetamab-tgvs) injection, for subcutaneous use Initial U.S. Approval: 2023
9001355e-003d-4d4e-b4ce-337e0fd14952
HUMAN PRESCRIPTION DRUG LABEL
Aug 18, 2023
Janssen Biotech, Inc.
DUNS: 099091753
Products 2
Detailed information about drug products covered under this FDA approval, including NDC codes, dosage forms, ingredients, and administration routes.
talquetamab
Product Details
FDA regulatory identification and product classification information
FDA Identifiers
Product Classification
Product Specifications
INGREDIENTS (7)
talquetamab
Product Details
FDA regulatory identification and product classification information
FDA Identifiers
Product Classification
Product Specifications
INGREDIENTS (7)
Drug Labeling Information
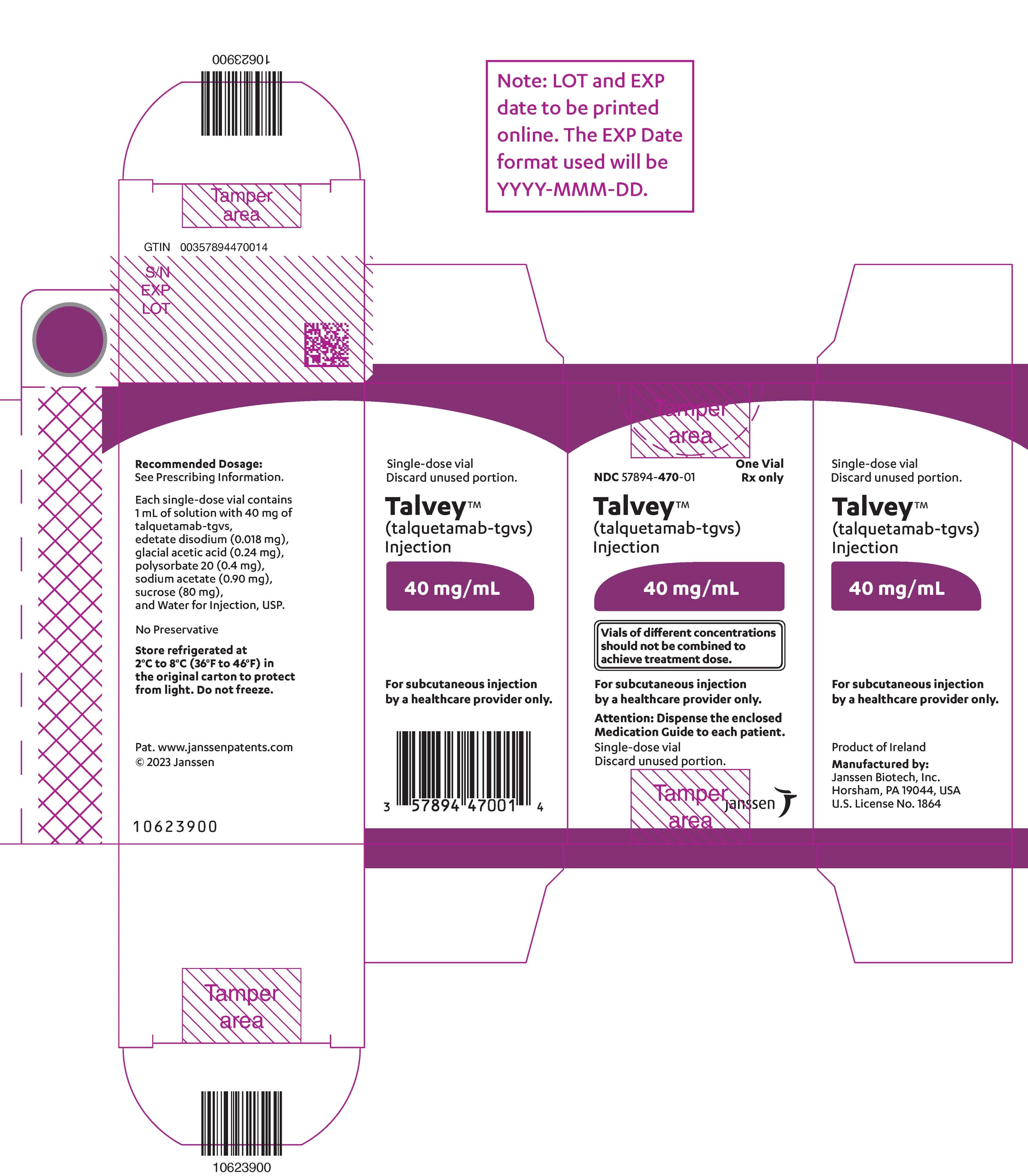
PACKAGE LABEL.PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL
PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL - 40 mg Vial Carton
NDC 57894-470-01
One Vial
Rx only
Talvey™
(talquetamab-tgvs)
Injection
40 mg/mL
Vials of different concentrations
should not be combined to
achieve treatment dose.
For subcutaneous injection
by a healthcare provider only.
Attention: Dispense the enclosed
Medication Guide to each patient.
Single-dose vial
Discard unused portion.
janssen
WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS SECTION
5 WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS
5.1 Cytokine Release Syndrome (CRS)
TALVEY can cause cytokine release syndrome, including life-threatening or fatal reactions [see Adverse Reactions (6.1)] .
In the clinical trial, CRS occurred in 76% of patients who received TALVEY at the recommended dosages, with Grade 1 CRS occurring in 57% of patients, Grade 2 in 17%, and Grade 3 in 1.5%. Recurrent CRS occurred in 30% of patients. Most events occurred following step-up dose 1 (29%) or step-up dose 2 (44%) at the recommended dosages. CRS occurred in 33% of patients with step-up dose 3 in the biweekly dosing schedule (N=153). CRS occurred in 30% of patients with the first 0.4 mg/kg treatment dose and in 12% of patients treated with the first 0.8 mg/kg treatment dose. The CRS rate for both dosing schedules combined was less than 3% for each of the remaining doses in Cycle 1 and less than 3% cumulatively from Cycle 2 onward. The median time to onset of CRS was 27 (range: 0.1 to 167) hours from the last dose, and the median duration was 17 (range: 0 to 622) hours. Clinical signs and symptoms of CRS include but are not limited to pyrexia, hypotension, chills, hypoxia, headache, and tachycardia. Potentially life-threatening complications of CRS may include cardiac dysfunction, acute respiratory distress syndrome, neurologic toxicity, renal and/or hepatic failure, and disseminated intravascular coagulation (DIC).
Initiate TALVEY therapy with step-up dosing and administer pre-treatment medications (corticosteroids, antihistamine, and antipyretics) prior to each dose of TALVEY in the step-up dosing schedule to reduce the risk of CRS. Monitor patients following administration accordingly. In patients who experience CRS, pre-treatment medications should be administered prior to the next TALVEY dose [see Dosage and Administration (2.2, 2.3)].
Counsel patients to seek medical attention should signs or symptoms of CRS occur. At the first sign of CRS, immediately evaluate patient for hospitalization and institute treatment with supportive care based on severity and consider further management per current practice guidelines. Withhold TALVEY until CRS resolves or permanently discontinue based on severity [see Dosage and Administration (2.5)] .
TALVEY is available only through a restricted program under a REMS [see Warnings and Precautions (5.3)] .
5.2 Neurologic Toxicity including ICANS
TALVEY can cause serious, life-threatening, or fatal neurologic toxicity, including ICANS [see Adverse Reactions (6.1)] .
In the clinical trial, neurologic toxicity, including ICANS, occurred in 55% of patients who received TALVEY at the recommended dosages, with Grade 3 or 4 neurologic toxicity occurring in 6% of patients. The most frequent neurologic toxicities were headache (20%), encephalopathy (15%), sensory neuropathy (14%), and motor dysfunction (10%).
ICANS was reported in 9% of 265 patients where ICANS was collected and who received TALVEY at the recommended dosages [see Adverse Reactions (6.1)] . Recurrent ICANS occurred in 3% of patients. Most patients experienced ICANS following step-up dose 1 (3%), step-up dose 2 (3%), step-up dose 3 of the biweekly dosing schedule (1.8%), or the initial treatment dose of the weekly dosing schedule (2.6%) (N=156) or the biweekly dosing schedule (3.7%) (N=109). The median time to onset of ICANS was 2.5 (range: 1 to 16) days after the most recent dose with a median duration of 2 (range: 1 to 22) days. The onset of ICANS can be concurrent with CRS, following resolution of CRS, or in the absence of CRS. Clinical signs and symptoms of ICANS may include but are not limited to confusional state, depressed level of consciousness, disorientation, somnolence, lethargy, and bradyphrenia.
Monitor patients for signs and symptoms of neurologic toxicity during treatment. At the first sign of neurologic toxicity, including ICANS, immediately evaluate the patient and provide supportive care based on severity; withhold or permanently discontinue TALVEY based on severity and consider further management per current practice guidelines [see Dosage and Administration (2.5)].
Due to the potential for neurologic toxicity, patients receiving TALVEY are at risk of depressed level of consciousness. Advise patients to refrain from driving or operating heavy or potentially dangerous machinery during the step- up dosing schedule and for 48 hours after completion of the step-up dosing schedule [see Dosage and Administration (2.2)] and in the event of new onset of any neurological symptoms, until symptoms resolve.
TALVEY is available only through a restricted program under a REMS [see Warnings and Precautions (5.3)] .
5.3 TECVAYLI and TALVEY REMS
TALVEY is available only through a restricted program under a REMS called the TECVAYLI and TALVEY REMS because of the risks of CRS and neurologic toxicity, including ICANS [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1, 5.2)].
Notable requirements of the TECVAYLI and TALVEY REMS include the following:
- Prescribers must be certified with the program by enrolling and completing training.
- Prescribers must counsel patients receiving TALVEY about the risk of CRS and neurologic toxicity, including ICANS and provide patients with Patient Wallet Card.
- Pharmacies and healthcare settings that dispense TALVEY must be certified with the TECVAYLI and TALVEY REMS program and must verify prescribers are certified through the TECVAYLI and TALVEY REMS program.
- Wholesalers and distributers must only distribute TALVEY to certified pharmacies.
Further information about the TECVAYLI and TALVEY REMS program is available at www.TEC-TALREMS.com or by telephone at 1-855-810-8064.
5.4 Oral Toxicity and Weight Loss
TALVEY can cause oral toxicities, including dysgeusia, dry mouth, dysphagia, and stomatitis [see Adverse Reactions (6.1)] .
In the clinical trial, 80% of patients had oral toxicity, with Grade 3 occurring in 2.1% of patients who received TALVEY at the recommended dosages. The most frequent oral toxicities were dysgeusia (49%), dry mouth (34%), dysphagia (23%), and ageusia (18%). The median time to onset of oral toxicity was 15 (range: 1 to 634) days, and the median time to resolution to baseline was 43 (1 to 530) days. Oral toxicity did not resolve to baseline in 65% of patients.
TALVEY can cause weight loss [see Adverse Reactions (6.1)] . In the clinical trial, 62% of patients experienced weight loss, regardless of having an oral toxicity, including 29% of patients with Grade 2 (10% or greater) weight loss and 2.7% of patients with Grade 3 (20% or greater) weight loss. The median time to onset of Grade 2 or higher weight loss was 67 (range: 6 to 407) days, and the median time to resolution was 50 (range: 1 to 403) days. Weight loss did not resolve in 57% of patients who reported weight loss.
Monitor patients for signs and symptoms of oral toxicity. Counsel patients to seek medical attention should signs or symptoms of oral toxicity occur and provide supportive care as per current clinical practice including consultation with a nutritionist. Monitor weight regularly during therapy. Evaluate clinically significant weight loss further. Withhold TALVEY or permanently discontinue based on severity [see Dosage and Administration (2.5)] .
5.5 Infections
TALVEY can cause serious infections, including life-threatening or fatal infections [see Adverse Reactions (6.1)] .
In the clinical trial, serious infections occurred in 16% of patients, with fatal infections in 1.5% of patients. Grade 3 or 4 infections occurred in 17% of patients. The most common serious infections reported were bacterial infection (8%), which included sepsis, and COVID-19 (2.7%).
Monitor patients for signs and symptoms of infection prior to and during treatment with TALVEY and treat appropriately. Administer prophylactic antimicrobials according to local guidelines. Withhold or consider permanent discontinuation of TALVEY as recommended based on severity [see Dosage and Administration (2.5)] .
5.6 Cytopenias
TALVEY can cause cytopenias, including neutropenia and thrombocytopenia [see Adverse Reactions (6.1)] .
In the clinical trial, Grade 3 or 4 decreased neutrophils occurred in 35% of patients, and Grade 3 or 4 decreased platelets occurred in 22% of patients who received TALVEY. The median time to onset for Grade 3 or 4 neutropenia was 22 (range: 1 to 312) days, and the median time to resolution to Grade 2 or lower was 8 (range: 1 to 79) days. The median time to onset for Grade 3 or 4 thrombocytopenia was 12 (range: 2 to 183) days, and the median time to resolution to Grade 2 or lower was 10 (range: 1 to 64) days. Monitor complete blood counts during treatment and withhold TALVEY as recommended based on severity [see Dosage and Administration (2.5)] .
5.7 Skin Toxicity
TALVEY can cause serious skin reactions, including rash, maculo-papular rash, erythema, and erythematous rash [see Adverse Reactions (6.1)] .
In the clinical trial, skin reactions occurred in 62% of patients, with Grade 3 skin reactions in 0.3%. The median time to onset was 25 (range: 1 to 630) days. The median time to improvement to Grade 1 or less was 33 days.
Monitor for skin toxicity, including rash progression. Consider early intervention and treatment to manage skin toxicity. Withhold TALVEY as recommended based on severity [see Dosage and Administration (2.5)] .
5.8 Hepatotoxicity
TALVEY can cause hepatotoxicity. In the clinical trial, elevated ALT occurred in 33% of patients, with Grade 3 or 4 ALT elevation occurring in 2.7%; elevated AST occurred in 31% of patients, with Grade 3 or 4 AST elevation occurring in 3.3%. Grade 3 or 4 elevations of total bilirubin occurred in 0.3% of patients [see Adverse Reactions (6.1)] . Liver enzyme elevation can occur with or without concurrent CRS.
Monitor liver enzymes and bilirubin at baseline and during treatment as clinically indicated. Withhold TALVEY or consider permanent discontinuation of TALVEY based on severity [see Dosage and Administration (2.5)] .
5.9 Embryo-Fetal Toxicity
Based on its mechanism of action, TALVEY may cause fetal harm when administered to a pregnant woman. Advise pregnant women of the potential risk to the fetus. Advise females of reproductive potential to use effective contraception during treatment with TALVEY and for 3 months after the last dose [see Use in Specific Populations (8.1, 8.3)] .
- Oral Toxicity and Weight Loss: Monitor for oral toxicity and weight loss. Withhold or permanently discontinue based on severity. ( 5.4)
- Infections: Can cause serious, life-threatening, or fatal infections. Monitor for signs and symptoms of infection; treat appropriately. Withhold or consider permanent discontinuation based on severity. ( 5.5)
- Cytopenias: Monitor complete blood counts. ( 5.6)
- Skin Toxicity: Monitor for skin toxicity, including rash progression, for early intervention and treat appropriately. Withhold as recommended based on severity. ( 5.7)
- Hepatotoxicity:Monitor liver enzymes and bilirubin at baseline and during treatment as clinically indicated. Withhold or consider permanent discontinuation based on severity. ( 5.8)
- Embryo-Fetal Toxicity: May cause fetal harm. Advise females of reproductive potential of the potential risk to the fetus and to use effective contraception. ( 5.9, 8.1, 8.3)
ADVERSE REACTIONS SECTION
6 ADVERSE REACTIONS
The following adverse reactions are also described elsewhere in the labeling:
- Cytokine Release Syndrome [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)]
- Neurologic Toxicity, including ICANS [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2)]
- Oral Toxicity and Weight Loss [see Warnings and Precautions (5.4)]
- Infections [see Warnings and Precautions (5.5)]
- Cytopenias [see Warnings and Precautions (5.6)]
- Skin Toxicity [see Warnings and Precautions (5.7)]
- Hepatotoxicity [see Warnings and Precautions (5.8)]
6.1 Clinical Trials Experience
Because clinical trials are conducted under widely varying conditions, adverse reaction rates observed in the clinical trials of a drug cannot be directly compared to rates in the clinical trials of another drug and may not reflect the rates observed in practice.
Relapsed/Refractory Multiple Myeloma
MonumenTAL-1
The safety of TALVEY was evaluated in 339 adult patients with relapsed or refractory multiple myeloma. Patients treated with the weekly dosing schedule received step-up doses of 0.01 mg/kg and 0.06 mg/kg of TALVEY followed by TALVEY 0.4 mg/kg subcutaneously weekly thereafter. Patients treated with the biweekly (every 2 weeks) dosing schedule received step-up doses of 0.01 mg/kg, 0.06 mg/kg, and 0.3 mg/kg (0.75 times the recommended step-up dose 3) followed by TALVEY 0.8 mg/kg subcutaneously every 2 weeks thereafter. The duration of exposure for the 0.4 mg/kg weekly regimen was 5.9 (range: 0.0 to 25.3) months (N=186) and for the 0.8 mg/kg biweekly (every 2 weeks) regimen, it was 3.7 (range: 0.0 to 17.9) months (N=153).
Serious adverse reactions occurred in 47% of patients who received TALVEY. Serious adverse reactions in ≥ 2% of patients included CRS (13%), bacterial infection (8%) including sepsis, pyrexia (4.7%), ICANS (3.8%), COVID-19 (2.7%), neutropenia (2.1%), and upper respiratory tract infection (2.1%).
Fatal adverse reactions occurred in 3.2% of patients who received TALVEY, including COVID**-**19 (0.6%), dyspnea (0.6%), general physical health deterioration (0.6%), bacterial infection (0.3%) including sepsis, basilar artery occlusion (0.3%), fungal infection (0.3%), infection (0.3%), and pulmonary embolism (0.3%).
Permanent discontinuation of TALVEY due to an adverse reaction occurred in 9% of patients. Adverse reactions which resulted in permanent discontinuation of TALVEY in > 1% of patients included ICANS.
Dosage interruptions of TALVEY due to an adverse reaction occurred in 56% of patients. Adverse reactions which required dosage interruption in > 5% of patients included pyrexia (15%), CRS (12%), upper respiratory tract infection (9%), COVID-19 (9%), bacterial infection (7%) including sepsis, neutropenia (6%), and rash (6%).
The most common adverse reactions (≥ 20%) were pyrexia, CRS, dysgeusia, nail disorder, musculoskeletal pain, skin disorder, rash, fatigue, weight decreased, dry mouth, xerosis, dysphagia, upper respiratory tract infection, diarrhea, hypotension, and headache. The most common Grade 3 or 4 laboratory abnormalities (≥ 30%) were lymphocyte count decreased, neutrophil count decreased, white blood cell decreased, and hemoglobin decreased.
Table 13 summarizes the adverse reactions in MonumenTAL-1.
Table 13: Adverse Reactions (≥10%) in Patients with Relapsed or Refractory Multiple Myeloma Who Received TALVEY in MonumenTAL-1|
TALVEY | ||
|---|---|---|
|
System Organ Class |
Any Grade |
Grade 3 or 4 |
|
Adverse reactions were graded based on CTCAE Version 4.03, with the exception of CRS, which was graded per ASTCT 2019 criteria. | ||
Þ ß à è ð ø ý £ ¥ Œ | ||
|
General disorders and administration site conditions | ||
|
Pyrexia * |
83 |
4.7 † |
|
Fatigue * |
37 |
3.5 † |
|
Chills |
19 |
0 |
|
Pain * |
18 |
1.8 † |
|
Edema * |
14 |
0 |
|
Injection site reaction * |
13 |
0 |
|
Immune system disorders | ||
|
Cytokine release syndrome |
76 |
1.5 † |
|
Gastrointestinal disorders | ||
|
Dysgeusia ठ|
70 |
0 |
|
Dry mouth § |
34 |
0 |
|
Dysphagia |
23 |
0.9 † |
|
Diarrhea † |
21 |
0.9 |
|
Stomatitis ¶ |
18 |
1.2 † |
|
Nausea |
18 |
0 |
|
Constipation |
16 |
0 |
|
Oral disorder # |
12 |
0 |
|
Skin and subcutaneous tissue disorders | ||
|
Nail disorder Þ |
50 |
0 |
|
Skin disorder ß |
41 |
0.3 † |
|
Rash à |
38 |
3.5 † |
|
Xerosis è |
30 |
0 |
|
Pruritus |
19 |
0.3 † |
|
Musculoskeletal and connective tissue disorders | ||
|
Musculoskeletal pain * |
43 |
3.2 † |
|
Investigations | ||
|
Weight decreased |
35 |
1.5 † |
|
Infections and infestations | ||
|
Upper respiratory tract infection * |
22 |
2.7 † |
|
Bacterial infection including sepsis ðø |
19 |
9 |
|
COVID-19 *ø |
11 |
2.7 |
|
Fungal infection ýø |
10 |
0.6 |
|
Vascular disorders | ||
|
Hypotension * |
21 |
2.9 |
|
Nervous system disorders | ||
|
Headache * |
21 |
0.6 † |
|
Encephalopathy £ |
15 |
1.8 † |
|
Sensory neuropathy ¥ |
14 |
0 |
|
Motor dysfunction Π|
10 |
0.6 † |
|
Metabolism and nutrition disorders | ||
|
Decreased appetite |
19 |
1.2 † |
|
Respiratory, thoracic and mediastinal disorders | ||
|
Cough * |
17 |
0 |
|
Dyspnea *ø |
11 |
1.8 |
|
Hypoxia * |
10 |
1.5 † |
|
Cardiac disorders | ||
|
Tachycardia * |
11 |
0.6 † |
Clinically relevant adverse reactions reported in <10% of patients who received TALVEY included ICANS and viral infection.
Table 14 summarizes select laboratory abnormalities in MonumenTAL-1.
Table 14: Select Laboratory Abnormalities (≥30%) That Worsened from Baseline in Patients with Relapsed or Refractory Multiple Myeloma Who Received TALVEY in MonumenTAL-1|
TALVEY * | ||
|---|---|---|
|
Laboratory Abnormality |
Any Grade |
Grade 3 or 4 |
|
Laboratory toxicity grades are derived based on the NCI CTCAE (National Cancer Institute Common Terminology Criteria for Adverse Events) Version 4.03. | ||
| ||
|
Hematology | ||
|
Lymphocyte count decreased |
90 |
80 |
|
White blood cell decreased |
73 |
35 |
|
Hemoglobin decreased |
67 |
30 |
|
Neutrophil count decreased |
64 |
35 |
|
Platelet count decreased |
62 |
22 |
|
Chemistry | ||
|
Albumin decreased |
66 |
2.1 |
|
Alkaline phosphatase increased |
49 |
1.5 |
|
Phosphate decreased |
44 |
13 |
|
Gamma-glutamyl transferase increased |
38 |
7 |
|
Alanine aminotransferase increased |
33 |
2.7 |
|
Potassium decreased |
31 |
4.4 |
|
Sodium decreased |
31 |
6 |
|
Aspartate aminotransferase increased |
31 |
3.3 |
The most common adverse reactions (≥20%) are pyrexia, CRS, dysgeusia, nail disorder, musculoskeletal pain, skin disorder, rash, fatigue, weight decreased, dry mouth, xerosis, dysphagia, upper respiratory tract infection, diarrhea, hypotension, and headache. ( 6.1)
The most common Grade 3 or 4 laboratory abnormalities (≥30%) are lymphocyte count decreased, neutrophil count decreased, white blood cell decreased, and hemoglobin decreased. ( 6.1)
To report SUSPECTED ADVERSE REACTIONS, contact Janssen Biotech, Inc. at 1-800-JANSSEN (1-800-526-7736) or FDA at 1-800-FDA-1088 or www.fda.gov/medwatch**.**
USE IN SPECIFIC POPULATIONS SECTION
8 USE IN SPECIFIC POPULATIONS
8.1 Pregnancy
Risk Summary
Based on the mechanism of action, TALVEY may cause fetal harm when administered to a pregnant woman [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.1)] . There are no available data on the use of TALVEY in pregnant women to evaluate for a drug associated risk. No animal reproductive or developmental toxicity studies have been conducted with talquetamab-tgvs.
Talquetamab-tgvs causes T-cell activation and cytokine release; immune activation may compromise pregnancy maintenance. Human immunoglobulin G (IgG) is known to cross the placenta; therefore, TALVEY has the potential to be transmitted from the mother to the developing fetus. Advise women of the potential risk to the fetus.
In the U.S. general population, the estimated background risk of major birth defects and miscarriage in clinically recognized pregnancies is 2% to 4% and 15% to 20%, respectively.
8.2 Lactation
Risk Summary
There is no information regarding the presence of talquetamab-tgvs in human milk, the effect on the breastfed child, or the effect on milk production. Maternal IgG is known to be present in human milk. The effects of local gastrointestinal exposure and limited systemic exposure in the breastfed child to TALVEY are unknown. Because of the potential for serious adverse reactions in a breastfed child, advise women not to breastfeed during treatment with TALVEY and for 3 months after the last dose.
8.3 Females and Males of Reproductive Potential
TALVEY may cause fetal harm when administered to a pregnant woman [see Use in Specific Populations (8.1)] .
Pregnancy Testing
Verify pregnancy status of females of reproductive potential prior to initiating TALVEY.
Contraception
Females
Advise females of reproductive potential to use effective contraception during treatment with TALVEY and for 3 months after the last dose.
8.4 Pediatric Use
The safety and efficacy of TALVEY have not been established in pediatric patients.
8.5 Geriatric Use
There were 339 patients in the clinical trial for relapsed or refractory multiple myeloma. Of the total number of TALVEY-treated patients in the study, 178 (53%) patients were 65 years of age and older, while 57 (17%) patients were 75 years of age and older. No overall differences in safety or effectiveness were observed in patients 65 to less than 74 years of age compared to younger patients. There was a higher rate of fatal adverse reactions in patients 75 years of age or older compared to younger patients [see Adverse Reactions (6.1)]. Clinical studies did not include sufficient numbers of patients 75 years of age or over to determine whether they respond differently from younger patients.
Lactation: Advise not to breastfeed. ( 8.2)
CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY SECTION
12 CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY
12.1 Mechanism of Action
Talquetamab-tgvs is a bispecific T-cell engaging antibody that binds to the CD3 receptor expressed on the surface of T-cells and G protein-coupled receptor class C group 5 member D (GPRC5D) expressed on the surface of multiple myeloma cells and non-malignant plasma cells, as well as healthy tissues such as epithelial cells in keratinized tissues of the skin and tongue.
In vitro, talquetamab-tgvs activated T-cells caused the release of proinflammatory cytokines and resulted in the lysis of multiple myeloma cells. Talquetamab-tgvs had anti-tumor activity in mouse models of multiple myeloma.
12.2 Pharmacodynamics
Serum concentrations of cytokines (IL-6, IL-10, TNF-α, and IFN-γ) and IL-2R were measured before and after administration of each step-up dose, the first three treatment doses at 0.4 mg/kg once weekly, and the first two treatment doses at 0.8 mg/kg every two weeks. Increased concentrations of IL-6, IL-10, and IL-2R were observed during this period.
Higher talquetamab-tgvs exposures (i.e., AUC and C max) are associated with higher incidence of some adverse reactions (including oral toxicity, nail toxicity, and skin reactions). The exposure-response relationships for effectiveness and the time course of pharmacodynamic response of talquetamab- tgvs have not been fully characterized.
12.3 Pharmacokinetics
The C maxand AUC tauof talquetamab-tgvs after subcutaneous administration increased proportionally over a dose range of 0.005 to 0.8 mg/kg weekly (0.01 to 2 times the recommended 0.4 mg/kg weekly treatment dose) and 0.8 to 1.2 mg/kg every two weeks (1 to 1.5 times the recommended 0.8 mg/kg every 2 weeks treatment dose). Ninety percent of steady state exposure was achieved 16 weeks after the first treatment dose for both regimens.
The C max, C trough, C avg, and accumulation ratios of talquetamab-tgvs are presented in Table 15.
Table 15: Pharmacokinetic Parameters of Talquetamab-tgvs Following the Dose at 16 Weeks After the First Treatment Dose for the Approved Recommended Subcutaneous Dosages in Patients with Relapsed or Refractory Multiple Myeloma|
Talquetamab-tgvs Dosage | ||
|---|---|---|
|
Parameter |
0.4 mg/kg every week |
0.8 mg/kg every 2 weeks |
|
C avg= Average concentration over the dosing interval; :C max= Maximum serum talquetamab-tgvs concentration; C trough= Serum talquetamab-tgvs concentration prior to next dose | ||
| ||
|
Exposure***** | ||
|
C max(ng/mL) |
2,940 (67%) |
3,410 (63%) |
|
C trough(ng/mL) |
2,410 (83%) |
1,930 (103%) |
|
C avg(ng/mL) |
2,730 (71%) |
2,770 (72%) |
|
Accumulation Ratio**†** | ||
|
C max |
4.4 |
1.8 |
|
C trough |
4.6 |
2.3 |
|
C avg |
5.1 |
2.0 |
Absorption
The geometric mean (coefficient of variation [CV] %) bioavailability of talquetamab-tgvs was 59% (22%) when administered subcutaneously.
The median (range) T maxof talquetamab-tgvs after the first and 17 thtreatment dose of 0.4 mg/kg weekly were 3.7 (0.9 to 7) days and 2.5 (0.9 to 5.9) days, respectively.
The median (range) T maxof talquetamab-tgvs after the first and 9 thtreatment dose of 0.8 mg/kg every 2 weeks were 3.4 (0.8 to 14) days and 3.6 (1 to 7.7) days, respectively.
Distribution
The geometric mean (CV%) volume of distribution of talquetamab-tgvs was 10.1 L (25%).
Elimination
Talquetamab-tgvs clearance decreases over time, with a mean (CV%) maximal reduction from the first treatment dose to 16 weeks after the first treatment dose of 40% (56%). The geometric mean (CV%) clearance is 0.90 L/day (63%) at 16 weeks after the first treatment dose. The mean (CV%) terminal half-life was 8.4 (41%) days after the first treatment dose and 12.2 (49%) days at 16 weeks after the first treatment dose.
Metabolism
Talquetamab-tgvs is expected to be metabolized into small peptides by catabolic pathways.
Specific Populations
The volume of distribution and clearance of talquetamab-tgvs increased with increasing bodyweight (40 kg to 143 kg).
There were no clinically significant differences in the pharmacokinetics of talquetamab-tgvs based on age (33 to 86 years), sex, race (White, Black or African American), ethnicity (Not Hispanic/Latino, Hispanic/Latino), mild or moderate renal impairment (creatinine clearance [CLcr] by Cockcroft-Gault equation: 30 to 89 mL/min) or mild (total bilirubin less than or equal to upper limit of normal [ULN] with AST greater than ULN or total bilirubin greater than 1 to 1.5 times ULN with any AST) or moderate (total bilirubin greater than 1.5 to less than 3 times ULN with any AST) hepatic impairment. The effects of severe renal impairment (CLcr less than 30 mL/min) or severe hepatic impairment (total bilirubin greater than 3 times ULN with any AST) on the pharmacokinetics of talquetamab-tgvs are unknown.
12.6 Immunogenicity
The observed incidence of anti-drug antibodies is highly dependent on the sensitivity and specificity of the assay. Differences in assay methods preclude meaningful comparisons of the incidence of anti-drug antibodies in the studies described below with the incidence of anti-drug antibodies in other studies, including those of talquetamab-tgvs or of other talquetamab products.
During treatment in MonumenTAL-1 (up to 25 months), 45/177 (25%) patients treated with subcutaneous TALVEY 0.4 mg/kg weekly (median follow-up 5.7 months) and 24/130 (18%) patients treated with subcutaneous TALVEY 0.8 mg/kg every 2 weeks (median follow-up 3.1 months) developed anti-talquetamab-tgvs antibodies. There was no identified clinically significant effect of anti- talquetamab-tgvs antibodies on the pharmacokinetics, pharmacodynamics, safety, or effectiveness of TALVEY.
HOW SUPPLIED SECTION
16 HOW SUPPLIED/STORAGE AND HANDLING
TALVEY™ (talquetamab-tgvs) injection is a sterile, preservative-free, colorless to light yellow solution supplied as follows:
- One 3 mg/1.5 mL (2 mg/mL) single-dose vial in a carton: NDC: 57894-469-01
- One 40 mg/mL single-dose vial in a carton: NDC: 57894-470-01
Store refrigerated at 2°C to 8°C (36°F to 46°F) in original carton to protect from light.
Do not freeze.
INFORMATION FOR PATIENTS SECTION
17 PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATION
Advise the patient to read the FDA-approved patient labeling (Medication Guide).
Cytokine Release Syndrome (CRS)
Discuss the signs and symptoms associated with CRS including, but not limited to, pyrexia, hypotension, chills, hypoxia, headache, and tachycardia. Counsel patients to seek medical attention should signs or symptoms of CRS occur. Advise patients that they should be hospitalized for 48 hours after administration of all doses within the TALVEY step-up dosing schedule [see Dosage and Administration (2.1, 2.5), Warnings and Precautions (5.1)] .
Neurologic Toxicity, including ICANS
Discuss the signs and symptoms associated with neurologic toxicity, including ICANS including headache, encephalopathy, sensory neuropathy, motor dysfunction, ICANS, confusional state, depressed level of consciousness, disorientation, somnolence, lethargy, and bradyphrenia. Counsel patients to seek medical attention should signs or symptoms of ICANS occur. Advise patients to refrain from driving or operating heavy or potentially dangerous machinery during the step-up dosing schedule and for 48 hours after completion of the step-up dosing schedule and in the event of new onset of any neurologic toxicity symptoms, until symptoms resolve [see Dosage and Administration (2.2, 2.5), Warnings and Precautions (5.2)].
TECVAYLI and TALVEY REMS
TALVEY is available only through a restricted program called the TECVAYLI and TALVEY REMS. Inform patients that they will be given a Patient Wallet Card that they should carry with them at all times and show to all of their healthcare providers. This card describes signs and symptoms of CRS and neurologic toxicity, including ICANS which, if experienced, should prompt the patient to immediately seek medical attention [see Warnings and Precautions (5.3)].
Oral Toxicity and Weight Loss
Discuss the signs and symptoms of oral toxicities including dysgeusia, dry mouth, dysphagia, and stomatitis. Counsel patients to seek medical attention should signs or symptoms of oral toxicity occur. Advise patients that they may experience weight loss and to report weight loss. Advise patients that they may be referred to a nutritionist for consultation [see Dosage and Administration (2.5), Warnings and Precautions (5.4)] .
Infections
Discuss the signs and symptoms of serious infections [see Dosage and Administration (2.5), Warnings and Precautions (5.5)] .
Cytopenias
Discuss the signs and symptoms associated with neutropenia and thrombocytopenia [see Dosage and Administration (2.5), Warnings and Precautions (5.6)] .
Skin Toxicity
Discuss the signs and symptoms of skin reactions [see Dosage and Administration (2.5), Warnings and Precautions (5.7)] .
Hepatotoxicity
Advise patients that liver enzyme elevations may occur and that they should report symptoms that may indicate liver toxicity, including fatigue, anorexia, right upper abdominal discomfort, dark urine, or jaundice [see Warnings and Precautions (5.8)].
Embryo-Fetal Toxicity
Advise pregnant women and females of reproductive potential of the potential risk to a fetus. Advise females of reproductive potential to inform their healthcare provider if they are pregnant or become pregnant. Advise females of reproductive potential to use effective contraception during treatment with TALVEY and for 3 months after the last dose [see Warnings and Precautions (5.9), Use in Specific Populations (8.1, 8.3)] .
Lactation
Advise women not to breastfeed during treatment with TALVEY and for 3 months after the last dose [see Use in Specific Populations (8.2)] .
DOSAGE & ADMINISTRATION SECTION
2 DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
2.1 Important Dosing Information
Administer TALVEY subcutaneously according to the step-up dosing schedule in Tables 1 and 2 to reduce the incidence and severity of cytokine release syndrome (CRS) [see Dosage and Administration (2.2)] .
Administer pretreatment medications prior to each dose of TALVEY in the step- up dosing schedule as recommended [see Dosage and Administration (2.2, 2.3)].
TALVEY should only be administered by a qualified healthcare professional with appropriate medical support to manage severe reactions such as CRS and neurologic toxicity including immune effector cell-associated neurotoxicity syndrome (ICANS) [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1, 5.2)] .
Due to the risk of CRS and neurologic toxicity, including ICANS, patients should be hospitalized for 48 hours after administration of all doses within the TALVEY step-up dosing schedule [see Dosage and Administration (2.5)and Warnings and Precautions (5.1, 5.2)] .
2.2 Recommended Dosage
For subcutaneous injection.
Administer pretreatment medications prior to each dose of TALVEY in the step- up dosing schedule [see Dosage and Administration (2.3)] .
Administer TALVEY subcutaneously on a weekly or biweekly (every 2 weeks) dosing schedule according to Table 1 or Table 2. Continue treatment until disease progression or unacceptable toxicity.
Table 1: TALVEY Weekly Dosing Schedule|
Dosing schedule |
Day |
Dose * | |
|---|---|---|---|
| |||
|
Step-up dosing schedule |
Day 1 |
Step-up dose 1 |
0.01 mg/kg |
|
Day 4 † |
Step-up dose 2 |
0.06 mg/kg | |
|
Day 7 † |
First treatment dose |
0.4 mg/kg | |
|
Weekly dosing schedule |
One week after first treatment dose and weekly thereafter ‡ |
Subsequent treatment doses |
0.4 mg/kg once weekly |
|
Dosing schedule |
Day |
Dose * | |
|---|---|---|---|
| |||
|
Step-up dosing schedule |
Day 1 |
Step-up dose 1 |
0.01 mg/kg |
|
Day 4 † |
Step-up dose 2 |
0.06 mg/kg | |
|
Day 7 † |
Step-up dose 3 |
0.4 mg/kg | |
|
Day 10 ‡ |
First treatment dose |
0.8 mg/kg | |
|
Biweekly (every 2 weeks) dosing schedule |
Two weeks after first treatment dose and every 2 weeks thereafter § |
Subsequent treatment doses |
0.8 mg/kg every 2 weeks |
2.3 Recommended Pretreatment Medications
Administer the following pretreatment medications 1 to 3 hours before each dose of TALVEY in the step-up dosing schedule to reduce the risk of CRS [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)] .
- Corticosteroid (oral or intravenous dexamethasone, 16 mg or equivalent)
- Antihistamines (oral or intravenous diphenhydramine, 50 mg or equivalent)
- Antipyretics (oral or intravenous acetaminophen, 650 mg to 1,000 mg or equivalent)
Administration of pretreatment medications may be required for subsequent doses for patients who repeat doses within the TALVEY step-up dosing schedule due to dose delays (see Table 3or Table 4) or for patients who experienced CRS (see Table 5).
2.4 Dosage Delays
If a dose of TALVEY is delayed, restart therapy based on the recommendations in Table 3 and Table 4 and resume weekly or biweekly (every 2 weeks) dosing schedule accordingly [see Dosage and Administration (2.1)] ; if a dose is delayed by more than 28 days for an adverse reaction, evaluate the benefit- risk of restarting TALVEY. Administer pretreatment medications prior to restarting TALVEY and monitor patients following administration of TALVEY [see Dosage and Administration (2.2)].
Table 3: Recommendations for Restarting TALVEY after Dose Delay – Weekly Dosing Schedule|
Last Dose Administered |
Time from Last Dose Administered |
TALVEY Recommendation * |
|---|---|---|
| ||
|
0.01 mg/kg |
More than 7 days |
Restart TALVEY step-up dosing schedule at step-up dose 1 (0.01 mg/kg). |
|
0.06 mg/kg |
8 to 28 days |
Repeat step-up dose 2 (0.06 mg/kg) and continue TALVEY step-up dosing schedule. |
|
More than 28 days |
Restart TALVEY step-up dosing schedule at step-up dose 1 (0.01 mg/kg). | |
|
0.4 mg/kg |
8 to 28 days |
Continue TALVEY dosing schedule at treatment dose (0.4 mg/kg weekly). |
|
29 to 56 days |
Restart TALVEY step-up dosing schedule at step-up dose 2 (0.06 mg/kg). | |
|
More than 56 days |
Consider permanent discontinuation. If restarting TALVEY, begin with the step- up dosing schedule at step-up dose 1 (0.01 mg/kg). |
|
Last Dose Administered |
Time from Last Dose Administered |
TALVEY Recommendation * |
|---|---|---|
| ||
|
0.01 mg/kg |
More than 7 days |
Restart TALVEY step-up dosing schedule at step-up dose 1 (0.01 mg/kg). |
|
0.06 mg/kg |
8 to 28 days |
Repeat step-up dose 2 (0.06 mg/kg) and continue TALVEY step-up dosing schedule. |
|
More than 28 days |
Restart TALVEY step-up dosing schedule at step-up dose 1 (0.01 mg/kg). | |
|
0.4 mg/kg |
8 to 28 days |
Repeat step-up dose 3 (0.4 mg/kg) and continue TALVEY step-up dosing schedule. |
|
29 to 56 days |
Restart TALVEY step-up dosing schedule at step-up dose 2 (0.06 mg/kg). | |
|
More than 56 days |
Consider permanent discontinuation. If restarting TALVEY, begin with the step- up dosing schedule at step-up dose 1 (0.01 mg/kg). | |
|
0.8 mg/kg |
15 to 28 days |
Continue TALVEY dosing schedule at treatment dose (0.8 mg/kg every 2 weeks). |
|
29 to 56 days |
Restart TALVEY step-up dosing schedule at step-up dose 3 (0.4 mg/kg). | |
|
More than 56 days |
Consider permanent discontinuation. If restarting TALVEY, begin with the step- up dosing schedule at step-up dose 1 (0.01 mg/kg). |
2.5 Dosage Modifications for Adverse Reactions
Dose delays may be required to manage toxicities related to TALVEY [see Warnings and Precautions (5)] .
See Table 5, Table 6, and Table 7for recommended actions for the management of CRS, ICANS, and neurologic toxicity. See Table 8for recommended dose modifications for other adverse reactions.
Cytokine Release Syndrome (CRS)
Identify CRS based on clinical presentation [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)] . Evaluate and treat other causes of fever, hypoxia, and hypotension. If CRS is suspected, withhold TALVEY until CRS resolves or permanently discontinue based on severity, manage according to the recommendations in Table 5, consider further management per current practice guidelines. Administer supportive therapy for CRS, which may include intensive care for severe or life-threatening CRS. Consider laboratory testing to monitor for disseminated intravascular coagulation (DIC), hematology parameters, as well as pulmonary, cardiac, renal, and hepatic function.
Table 5: Recommendations for Management of CRS|
CRS Grade * |
Presenting Symptoms |
Actions |
|---|---|---|
| ||
|
Grade 1 |
Temperature ≥100.4°F (38°C) † |
|
|
Grade 2 |
Temperature ≥100.4°F (38°C) †with either:
|
|
|
Grade 3 |
Temperature ≥100.4°F (38°C) †with either:
|
Duration less than 48 hours
|
|
Recurrent or duration greater than or equal to 48 hours
| ||
|
Grade 4 |
Temperature ≥100.4°F (38°C) †with either:
|
|
Neurologic Toxicity, including ICANS
At the first sign of neurologic toxicity, including ICANS, withhold TALVEY and consider neurology evaluation. Rule out other causes of neurologic symptoms. Provide supportive therapy, which may include intensive care, for severe or life-threatening neurologic toxicities, including ICANS [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2)] . Manage ICANS and neurologic toxicity according to the recommendations in Table 6 and Table 7 and consider further management per current practice guidelines.
Table 6: Recommendations for Management of ICANS|
Grade * |
Presenting Symptoms † |
Actions |
|---|---|---|
| ||
|
Grade 1 |
ICE score 7–9 ‡, |
|
|
Grade 2 |
ICE score 3–6 ‡, |
|
|
Grade 3 |
ICE score 0–2 ‡,
or raised intracranial pressure: focal/local edema on neuroimaging §. |
First Occurrence of Grade 3 ICANS:
Recurrent Grade 3 ICANS:
|
|
Grade 4 |
ICE score 0 ‡
or seizures §, either:
or motor findings §:
or raised intracranial pressure/cerebral edema §, with signs/symptoms such as:
|
|
|
Adverse Reaction |
Severity * |
Actions |
|---|---|---|
| ||
|
Neurologic Toxicity *(excluding ICANS) |
Grade 1 |
|
|
Grade 2 |
| |
|
Grade 3 (Recurrent) |
|
Other Adverse Reactions
The recommended dose modifications for other adverse reactions are provided in Table 8.
Table 8: Recommended Dose Modifications for Other Adverse Reactions|
Adverse Reaction |
Severity |
Dose Modification |
|---|---|---|
| ||
|
Oral Toxicity and Weight Loss [see Warnings and Precautions (5.4)] |
Grade 1–2 |
|
|
Grade 3 |
| |
|
Grade 4 |
| |
|
Infections [see Warnings and Precautions (5.5)] |
All Grades |
|
|
Grade 3 |
| |
|
Grade 4 |
Consider permanent discontinuation of TALVEY.
| |
|
Cytopenias [see Warnings and Precautions (5.6)] |
Absolute neutrophil count less than 0.5 × 10 9/L |
|
|
Febrile neutropenia |
| |
|
Hemoglobin less than 8 g/dL |
| |
|
Platelet count less than 25,000/mcL |
| |
|
Skin Reactions [see Warnings and Precautions (5.7)] |
Grade 3–4 |
|
|
Other Non-hematologic Adverse Reactions ‡[see Warnings and Precautions (5.8)and Adverse Reactions (6.1)] |
Grade 3 |
|
|
Grade 4 |
Consider permanent discontinuation of TALVEY.
|
2.6 Preparation and Administration
Administer TALVEY via subcutaneous injection by a healthcare provider.
TALVEY should be administered by a healthcare provider with adequate medical personnel and appropriate medical equipment to manage severe reactions, including CRS and neurologic toxicity, including ICANS [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1, 5.2)] .
TALVEY 3 mg/1.5 mL (2 mg/mL) vial and TALVEY 40 mg/mL vial are supplied as ready-to-use solution for injection that do not need dilution prior to administration.
Do not combine TALVEY vials of different concentrations to achieve treatment dose.
Use aseptic technique to prepare and administer TALVEY.
Preparation
Refer to the following reference tables for the preparation of TALVEY.
- Use Table 9 to determine total dose, injection volume, and number of vials required based on patient's actual body weight for the 0.01 mg/kg dose using TALVEY 3 mg/1.5 mL (2 mg/mL) vial.
|
Body Weight |
Total Dose |
Volume of Injection (mL) |
Number of Vials | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
0.01 mg/kg |
35 to 39 |
0.38 |
0.19 |
1 |
|
40 to 45 |
0.42 |
0.21 |
1 | |
|
46 to 55 |
0.5 |
0.25 |
1 | |
|
56 to 65 |
0.6 |
0.3 |
1 | |
|
66 to 75 |
0.7 |
0.35 |
1 | |
|
76 to 85 |
0.8 |
0.4 |
1 | |
|
86 to 95 |
0.9 |
0.45 |
1 | |
|
96 to 105 |
1 |
0.5 |
1 | |
|
106 to 115 |
1.1 |
0.55 |
1 | |
|
116 to 125 |
1.2 |
0.6 |
1 | |
|
126 to 135 |
1.3 |
0.65 |
1 | |
|
136 to 145 |
1.4 |
0.7 |
1 | |
|
146 to 155 |
1.5 |
0.75 |
1 | |
|
156 to 160 |
1.6 |
0.8 |
1 |
- Use Table 10 to determine total dose, injection volume, and number of vials required based on patient's actual body weight for the 0.06 mg/kg dose using TALVEY 3 mg/1.5 mL (2 mg/mL) vial.
|
Body Weight |
Total Dose |
Volume of Injection (mL) |
Number of Vials | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
0.06 mg/kg |
35 to 39 |
2.2 |
1.1 |
1 |
|
40 to 45 |
2.6 |
1.3 |
1 | |
|
46 to 55 |
3 |
1.5 |
1 | |
|
56 to 65 |
3.6 |
1.8 |
2 | |
|
66 to 75 |
4.2 |
2.1 |
2 | |
|
76 to 85 |
4.8 |
2.4 |
2 | |
|
86 to 95 |
5.4 |
2.7 |
2 | |
|
96 to 105 |
6 |
3 |
2 | |
|
106 to 115 |
6.6 |
3.3 |
3 | |
|
116 to 125 |
7.2 |
3.6 |
3 | |
|
126 to 135 |
7.8 |
3.9 |
3 | |
|
136 to 145 |
8.4 |
4.2 |
3 | |
|
146 to 155 |
9 |
4.5 |
3 | |
|
156 to 160 |
9.6 |
4.8 |
4 |
- Use Table 11 to determine total dose, injection volume, and number of vials required based on patient's actual body weight for the 0.4 mg/kg dose using TALVEY 40 mg/mL vial.
|
Body Weight |
Total Dose |
Volume of Injection (mL) |
Number of Vials | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
0.4 mg/kg |
35 to 39 |
14.8 |
0.37 |
1 |
|
40 to 45 |
16 |
0.4 |
1 | |
|
46 to 55 |
20 |
0.5 |
1 | |
|
56 to 65 |
24 |
0.6 |
1 | |
|
66 to 75 |
28 |
0.7 |
1 | |
|
76 to 85 |
32 |
0.8 |
1 | |
|
86 to 95 |
36 |
0.9 |
1 | |
|
96 to 105 |
40 |
1 |
1 | |
|
106 to 115 |
44 |
1.1 |
2 | |
|
116 to 125 |
48 |
1.2 |
2 | |
|
126 to 135 |
52 |
1.3 |
2 | |
|
136 to 145 |
56 |
1.4 |
2 | |
|
146 to 155 |
60 |
1.5 |
2 | |
|
156 to 160 |
64 |
1.6 |
2 |
- Use Table 12 to determine total dose, injection volume, and number of vials required based on patient's actual body weight for the 0.8 mg/kg dose using TALVEY 40 mg/mL vial.
|
Body Weight |
Total Dose |
Volume of Injection (mL) |
Number of Vials | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
0.8 mg/kg |
35 to 39 |
29.6 |
0.74 |
1 |
|
40 to 45 |
34 |
0.85 |
1 | |
|
46 to 55 |
40 |
1 |
1 | |
|
56 to 65 |
48 |
1.2 |
2 | |
|
66 to 75 |
56 |
1.4 |
2 | |
|
76 to 85 |
64 |
1.6 |
2 | |
|
86 to 95 |
72 |
1.8 |
2 | |
|
96 to 105 |
80 |
2 |
2 | |
|
106 to 115 |
88 |
2.2 |
3 | |
|
116 to 125 |
96 |
2.4 |
3 | |
|
126 to 135 |
104 |
2.6 |
3 | |
|
136 to 145 |
112 |
2.8 |
3 | |
|
146 to 155 |
120 |
3 |
3 | |
|
156 to 160 |
128 |
3.2 |
4 |
- Parenteral drug products should be inspected visually for particulate matter and discoloration prior to administration, whenever solution and container permit. Check that the TALVEY solution for injection is colorless to light yellow. Do not use if the solution is discolored, cloudy, or if foreign particles are present.
- Remove the appropriate strength TALVEY vial(s) from refrigerated storage [2°C to 8°C (36°F to 46°F)] and equilibrate to ambient temperature [15°C to 30°C (59°F to 86°F)] for at least 15 minutes. Do not warm TALVEY in any other way.
- Once equilibrated, gently swirl the vial for approximately 10 seconds to mix. Do not shake.
- Withdraw the required injection volume of TALVEY from the vial(s) into an appropriately sized syringe using a transfer needle.
- Each injection volume should not exceed 2 mL. Divide doses requiring greater than 2 mL equally into multiple syringes.
- TALVEY is compatible with stainless steel injection needles and polypropylene or polycarbonate syringe material.
- Replace the transfer needle with an appropriately sized needle for injection.
Administration
- Inject the required volume of TALVEY into the subcutaneous tissue of the abdomen (preferred injection site). Alternatively, TALVEY may be injected into the subcutaneous tissue at other sites (e.g., thigh). If multiple injections are required, TALVEY injections should be at least 2 cm apart.
- Do not inject into tattoos or scars or areas where the skin is red, bruised, tender, hard or not intact.
- Any unused medicinal product or waste material should be disposed in accordance with local requirements.
Storage
The prepared syringes should be administered immediately. If immediate administration is not possible, store the TALVEY solution refrigerated at 2°C to 8°C (36°F to 46°F) for up to 24 hours followed by at room temperature of 15°C to 30°C (59°F to 86°F) for up to 24 hours. Discard if stored for more than 24 hours refrigerated or more than 24 hours at room temperature. If stored in the refrigerator, allow the solution to come to room temperature before administration.
- For subcutaneous injection. ( 2.2)
- Patients should be hospitalized for 48 hours after all doses within the step-up dosing schedule. ( 2.1)
- Administer pretreatment medications as recommended. ( 2.3)
- See Full Prescribing Information for instructions on preparation and administration. ( 2.6)
|
TALVEY Weekly Dosing Schedule ( 2.2) | |||
|---|---|---|---|
|
Dosing schedule |
Day |
Dose * | |
| |||
|
Step-up dosing schedule |
Day 1 |
Step-up dose 1 |
0.01 mg/kg |
|
Day 4 † |
Step-up dose 2 |
0.06 mg/kg | |
|
Day 7 † |
First treatment dose |
0.4 mg/kg | |
|
Weekly dosing schedule |
One week after first treatment dose and weekly thereafter ‡ |
Subsequent treatment doses |
0.4 mg/kg once weekly |
|
TALVEY Biweekly (Every 2 Weeks) Dosing Schedule ( 2.2) | |||
|---|---|---|---|
|
Dosing schedule |
Day |
Dose * | |
| |||
|
Step-up dosing schedule |
Day 1 |
Step-up dose 1 |
0.01 mg/kg |
|
Day 4 † |
Step-up dose 2 |
0.06 mg/kg | |
|
Day 7 † |
Step-up dose 3 |
0.4 mg/kg | |
|
Day 10 ‡ |
First treatment dose |
0.8 mg/kg | |
|
Biweekly (every 2 weeks) dosing schedule |
Two weeks after first treatment dose and every 2 weeks thereafter § |
Subsequent treatment doses |
0.8 mg/kg every 2 weeks |
