KYPROLIS
These highlights do not include all the information needed to use KYPROLIS safely and effectively. See full prescribing information for KYPROLIS. KYPROLIS (carfilzomib) for injection, for intravenous use Initial U.S. Approval: 2012
ea66eb30-e665-4693-99a1-a9d3b4bbe2d6
HUMAN PRESCRIPTION DRUG LABEL
Jun 30, 2022
Onyx Pharmaceuticals, Inc.
DUNS: 789591724
Products 3
Detailed information about drug products covered under this FDA approval, including NDC codes, dosage forms, ingredients, and administration routes.
carfilzomib
Product Details
FDA regulatory identification and product classification information
FDA Identifiers
Product Classification
Product Specifications
INGREDIENTS (5)
carfilzomib
Product Details
FDA regulatory identification and product classification information
FDA Identifiers
Product Classification
Product Specifications
INGREDIENTS (5)
carfilzomib
Product Details
FDA regulatory identification and product classification information
FDA Identifiers
Product Classification
Product Specifications
INGREDIENTS (5)
Drug Labeling Information
PACKAGE LABEL.PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL
PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL
1 Single-Dose Vial
NDC 76075-101-01
AMGEN®
Kyprolis®
(carfilzomib) for Injection
60 mg/vial
60 mg/vial
Single-dose vial. Discard unused portion.
Reconstitution: Reconstitute with 29 mL Sterile Water for Injection, USP.
Dilution: May be further diluted with 5% Dextrose Injection, USP.
For Intravenous Administration Only
Rx Only

INDICATIONS & USAGE SECTION
1 INDICATIONS AND USAGE
1.1 Relapsed or Refractory Multiple Myeloma
- Kyprolis is indicated for the treatment of adult patients with relapsed or refractory multiple myeloma who have received one to three lines of therapy in combination with:
- Lenalidomide and dexamethasone; or
- Dexamethasone; or
- Daratumumab and dexamethasone; or
- Daratumumab and hyaluronidase-fihj and dexamethasone; or
- Isatuximab and dexamethasone.
- Kyprolis is indicated as a single agent for the treatment of adult patients with relapsed or refractory multiple myeloma who have received one or more lines of therapy.
Kyprolis is a proteasome inhibitor that is indicated:
- for the treatment of adult patients with relapsed or refractory multiple myeloma who have received one to three lines of therapy in combination with
- Lenalidomide and dexamethasone; or
- Dexamethasone; or
- Daratumumab and dexamethasone; or
- Daratumumab and hyaluronidase-fihj and dexamethasone; or
- Isatuximab and dexamethasone. (1, 14)
- as a single agent for the treatment of patients with relapsed or refractory multiple myeloma who have received one or more lines of therapy. (1, 14)
CONTRAINDICATIONS SECTION
4 CONTRAINDICATIONS
None.
None. (4)
RECENT MAJOR CHANGES SECTION
RECENT MAJOR CHANGES
|
Indications and Usage (1.1) |
11/2021 |
|
Indications and Usage (1.1) |
6/2022 |
|
Dosage and Administration (2.2) |
6/2022 |
|
Dosage and Administration (2.2) |
11/2021 |
DOSAGE & ADMINISTRATION SECTION
2 DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
2.1 Administration Precautions
Hydration
Adequate hydration is required prior to dosing in Cycle 1, especially in patients at high-risk of tumor lysis syndrome (TLS) or renal toxicity. Consider hydration with both oral fluids (30 mL per kg at least 48 hours before Cycle 1, Day 1) and intravenous fluids (250 mL to 500 mL of appropriate intravenous fluid prior to each dose in Cycle 1). If needed, give an additional 250 mL to 500 mL of intravenous fluids following Kyprolis administration. Continue oral and/or intravenous hydration, as needed, in subsequent cycles.
Monitor patients for evidence of volume overload and adjust hydration to individual patient needs, especially in patients with or at risk for cardiac failure [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1, 5.3)].
Electrolyte Monitoring
Monitor serum potassium levels regularly during treatment with Kyprolis [see Adverse Reactions (6.1)].
Premedications and Concomitant Medications
Premedicate with the recommended dose of dexamethasone for monotherapy or dexamethasone administered as part of the combination therapy [see Dosage and Administration (2.2)]. Administer dexamethasone orally or intravenously at least 30 minutes but no more than 4 hours prior to all doses of Kyprolis during Cycle 1 to reduce the incidence and severity of infusion-related reactions [see Warnings and Precautions (5.9)]. Reinstate dexamethasone premedication if these symptoms occur during subsequent cycles.
Provide thromboprophylaxis for patients being treated with Kyprolis in combination with other therapies [see Warnings and Precautions (5.8)].
Consider antiviral prophylaxis to decrease the risk of herpes zoster reactivation [see Adverse Reactions (6.1)].
Dose Calculation
For patients with body surface area (BSA) of 2.2 m2 or less, calculate the Kyprolis dose using actual BSA. Dose adjustments do not need to be made for weight changes of 20% or less.
For patients with a BSA greater than 2.2 m2, calculate the Kyprolis dose using a BSA of 2.2 m2.
2.2 Recommended Dosage
Once Weekly 20/70 mg/m2 (30-minute infusion)
Kyprolis once weekly 20/70 mg/m2 administered in combination with
- dexamethasone (Kd),
- daratumumab plus dexamethasone (DKd), or
- daratumumab and hyaluronidase-fihj plus dexamethasone (DKd).
The recommended starting dosage of Kyprolis is 20 mg/m2 on Cycle 1, Day 1. If tolerated, escalate the dose to 70 mg/m2 on Cycle 1, Day 8. Administer Kyprolis intravenously as a 30-minute infusion on Days 1, 8, and 15 of each 28-day cycle until disease progression or unacceptable toxicity as shown in Table 1 [see Clinical Studies (14.2)]. Administer dexamethasone 30 minutes to 4 hours before Kyprolis and 1 to 3 hours before daratumumab or daratumumab and hyaluronidase-fihj. For dosage instructions of combination agents with Kyprolis, see Clinical Studies sections 14.2 (Kd) and 14.3 (DKd). Refer to the Prescribing Information for dexamethasone, intravenous daratumumab, and subcutaneous daratumumab and hyaluronidase-fihj for additional dosage information.
Table 1: Kyprolis 20/70 mg/m2 Once Weekly (30-Minute Infusion)|
Cycle 1 | ||||||||||||
|
Week 1 |
Week 2 |
Week 3 |
Week 4 | |||||||||
|
Day 1 |
Day 2 |
Days 3-7 |
Day 8 |
Day 9 |
Days 10-14 |
Day 15 |
Day 16 |
Days 17-21 |
Day 22 |
Day 23 |
Days 24-28 | |
|
Kyprolis (mg/m2) |
20 |
|
|
70 |
|
|
70 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Cycles 2 and later | ||||||||||||
|
Week 1 |
Week 2 |
Week 3 |
Week 4 | |||||||||
|
Day 1 |
Day 2 |
Days 3-7 |
Day 8 |
Day 9 |
Days 10-14 |
Day 15 |
Day 16 |
Days 17-21 |
Day 22 |
Day 23 |
Days 24-28 | |
|
Kyprolis (mg/m2) |
70 |
|
|
70 |
|
|
70 |
|
|
|
|
|
Twice Weekly 20/56 mg/m2 (30-minute infusion)
Kyprolis twice weekly 20/56 mg/m2 administered as monotherapy or in combination with
- dexamethasone (Kd),
- daratumumab plus dexamethasone (DKd),
- daratumumab and hyaluronidase-fihj plus dexamethasone (DKd), or
- isatuximab plus dexamethasone (Isa-Kd).
The recommended starting dosage of Kyprolis is 20 mg/m2 on Cycle 1, Days 1 and 2. If tolerated, escalate the dose to 56 mg/m2 on Cycle 1, Day 8. Administer Kyprolis intravenously as a 30-minute infusion on Days 1, 2, 8, 9, 15, and 16 of each 28-day cycle as shown in Table 2 until disease progression or unacceptable toxicity [see Clinical Studies (Section 14)]. If given as monotherapy, administer 8 mg dexamethasone orally or intravenously 30 minutes to 4 hours before Kyprolis then as needed to minimize infusion-related reactions [see Dosage and Administration (2.1)]. Kyprolis given as monotherapy may be omitted on Days 8 and 9 of cycle 13 onward. For dosage instructions of combination agents administered with Kyprolis, see Clinical Studies sections 14.2 (Kd), 14.3 (DKd), 14.4 (Isa-Kd), and 14.5 (Monotherapy). Refer to the Prescribing Information for dexamethasone, intravenous daratumumab, subcutaneous daratumumab and hyaluronidase-fihj, and isatuximab for additional dosage information.
Table 2: Kyprolis 20/56 mg/m2 Twice Weekly (30-Minute Infusion)
| ||||||||||||
|
Cycle 1 | ||||||||||||
|
Week 1 |
Week 2 |
Week 3 |
Week 4 | |||||||||
|
Day 1 |
Day 2 |
Days 3-7 |
Day 8 |
Day 9 |
Days 10-14 |
Day 15 |
Day 16 |
Days 17-21 |
Day 22 |
Day 23 |
Days 24-28 | |
|
Kyprolis******* (mg/m2)** |
20 |
20 |
|
56 |
56 |
|
56 |
56 |
|
|
|
|
|
Cycles 2 and later | ||||||||||||
|
Week 1 |
Week 2 |
Week 3 |
Week 4 | |||||||||
|
Day 1 |
Day 2 |
Days 3-7 |
Day 8 |
Day 9 |
Days 10-14 |
Day 15 |
Day 16 |
Days 17-21 |
Day 22 |
Day 23 |
Days 24-28 | |
|
Kyprolis (mg/m2) |
56 |
56 |
|
56 |
56 |
|
56 |
56 |
|
|
|
|
Twice Weekly 20/27 mg/m2 (10-minute infusion)
Kyprolis twice weekly 20/27mg/m2 is administered as monotherapy or in combination with lenalidomide and dexamethasone (KRd).
The recommended starting dosage of Kyprolis is 20 mg/m2 in Cycle 1 on Days 1 and 2. If tolerated, escalate the dose to 27 mg/m2 on Day 8 of Cycle 1 and thereafter. Administer Kyprolis intravenously as a 10-minute infusion [see Clinical Studies (14.4)]. In Cycles 1 through 12, administer Kyprolis on Days 1, 2, 8, 9, 15 and 16 of each 28-day cycle as shown in Table 3. From Cycle 13, administer Kyprolis on Days 1, 2, 15 and 16 of each 28-day cycle. If given as monotherapy, premedicate with dexamethasone 4 mg orally or intravenously 30 minutes to 4 hours before each Kyprolis dose in Cycle 1, then as needed to minimize infusion-related reactions [see Dosage and Administration (2.1)]. Continue Kyprolis with the regimens shown in Table 3 until disease progression or unacceptable toxicity occurs. When combined with lenalidomide and dexamethasone, discontinue Kyprolis after Cycle 18 and continue lenalidomide and dexamethasone until disease progression or unacceptable toxicity occurs. For dosage instructions of combination agents with Kyprolis, see Clinical Studies sections 14.1 (KRd) and 14.5 (Monotherapy). Refer to the Prescribing Information for dexamethasone and lenalidomide for additional dosage information.
Table 3: Kyprolis 20/27 mg/m2 Twice Weekly (10-Minute Infusion)
| ||||||||||
|
Cycle 1 | ||||||||||
|
Week 1 |
Week 2 |
Week 3 |
Week 4 | |||||||
|
Day 1 |
Day 2 |
Days 3-7 |
Day 8 |
Day 9 |
Days 10-14 |
Day 15 |
Day 16 |
Days 17-21 |
Days 22-28 | |
|
Kyprolis (mg/m2)***** |
20 |
20 |
|
27 |
27 |
|
27 |
27 |
|
|
|
Cycles 2 to 12 | ||||||||||
|
Week 1 |
Week 2 |
Week 3 |
Week 4 | |||||||
|
Day 1 |
Day 2 |
Days 3-7 |
Day 8 |
Day 9 |
Days 10-14 |
Day 15 |
Day 16 |
Days 17-21 |
Days 22-28 | |
|
Kyprolis (mg/m2) |
27 |
27 |
|
27 |
27 |
|
27 |
27 |
|
|
|
Cycles 13 and later**†** | ||||||||||
|
Week 1 |
Week 2 |
Week 3 |
Week 4 | |||||||
|
Day 1 |
Day 2 |
Days 3-7 |
Day 8 |
Day 9 |
Days 10-14 |
Day 15 |
Day 16 |
Days 17-21 |
Days 22-28 | |
|
Kyprolis (mg/m2) |
27 |
27 |
|
|
|
|
27 |
27 |
|
|
2.3 Dosage Modifications for Adverse Reactions
Recommended actions and dosage modifications for Kyprolis are presented in Table 4. Dose level reductions are presented in Table 5. See the lenalidomide, intravenous daratumumab, subcutaneous daratumumab and hyaluronidase-fihj, isatuximab, and dexamethasone Prescribing Information respectively for recommended dosage modifications associated with each product.
Table 4: Dosage Modifications for Adverse Reactions*|
ANC = absolute neutrophil count | |
| |
|
Hematologic Toxicity |
Recommended Action |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Renal Toxicity |
Recommended Action |
|
|
|
Other Non-hematologic Toxicity |
Recommended Action |
|
|
|
Regimen |
Kyprolis Frequency |
Dose |
First Dose Reduction |
Second Dose Reduction |
Third Dose Reduction |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Note: Infusion times remain unchanged during dose reduction(s). | |||||
| |||||
|
Kyprolis and Dexamethasone |
Once weekly |
70 mg/m2 |
56 mg/m2 |
45 mg/m2 |
36 mg/m2* |
|
Kyprolis and Dexamethasone |
Twice weekly |
56 mg/m2 |
45 mg/m2 |
36 mg/m2 |
27 mg/m2* |
|
Kyprolis, Lenalidomide, and Dexamethasone |
Twice weekly |
27 mg/m2 |
20 mg/m2 |
15 mg/m2* |
— |
2.4 Dosage Modifications for Hepatic Impairment
For patients with mild (total bilirubin 1 to 1.5 × ULN and any AST or total bilirubin ≤ ULN and AST > ULN) or moderate (total bilirubin > 1.5 to 3 × ULN and any AST) hepatic impairment, reduce the dose of Kyprolis by 25% [see Use in Specific Populations (8.6), Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)].
2.5 Recommended Dosage for End Stage Renal Disease
For patients with end stage renal disease who are on hemodialysis, administer Kyprolis after the hemodialysis procedure.
2.6 Preparation and Administration
Kyprolis vials contain no antimicrobial preservatives and are intended for single-dose only. The reconstituted solution contains carfilzomib at a concentration of 2 mg/mL.
Read the complete preparation instructions prior to reconstitution. Parenteral drug products should be inspected visually for particulate matter and discoloration prior to administration, whenever solution and container permit.
Reconstitution/Preparation Steps:
- Remove vial from refrigerator just prior to use.
- Calculate the dose (mg/m2) and number of vials of Kyprolis required using the patient's BSA at baseline.
- Aseptically reconstitute each Kyprolis vial only with Sterile Water for Injection, USP using the volumes described in Table 6. Use a 21-gauge or larger needle (0.8 mm or smaller external diameter needle) to reconstitute each vial by slowly injecting Sterile Water for Injection, USP through the stopper and directing the Sterile Water for Injection, USP onto the INSIDE WALL OF THE VIAL to minimize foaming.There is no data to support the use of closed system transfer devices with Kyprolis.
|
Strength |
Amount of Sterile Water for Injection, USP required for reconstitution |
|---|---|
|
10 mg vial |
5 mL |
|
30 mg vial |
15 mL |
|
60 mg vial |
29 mL |
- Gently swirl and/or invert the vial slowly for about 1 minute, or until complete dissolution. DO NOT SHAKE to avoid foam generation. If foaming occurs, allow the solution to settle in the vial until foaming subsides (approximately 5 minutes) and the solution is clear.
- Visually inspect for particulate matter and discoloration prior to administration. The reconstituted product should be a clear, colorless solution and should not be administered if any discoloration or particulate matter is observed.
- Discard any unused portion left in the vial. DO NOT pool unused portions from the vials. DO NOT administer more than one dose from a vial.
- Administer Kyprolis directly by intravenous infusion or in a 50 mL to 100 mL intravenous bag containing5% Dextrose Injection, USP. Do not administer as an intravenous push or bolus.
- When administering in an intravenous bag, use a 21-gauge or larger gauge needle (0.8 mm or smaller external diameter needle) to withdraw the calculated dose from the vial anddilute into 50 mL or 100 mL intravenous bag containing only 5% Dextrose Injection, USP (based on the calculated total dose and infusion time).
- Flush the intravenous administration line with normal saline or 5% Dextrose Injection, USP immediately before and after Kyprolis administration.
- Do not mix Kyprolis with or administer as an infusion with other medicinal products.
The stabilities of reconstituted Kyprolis under various temperature and container conditions are shown in Table 7.
Table 7: Stability of Reconstituted Kyprolis|
Storage Conditions of Reconstituted Kyprolis |
Stability* per Container | ||
|---|---|---|---|
|
Vial |
Syringe |
Intravenous Bag | |
| |||
|
Refrigerated 2°C to 8°C (36°F to 46°F) |
24 hours |
24 hours |
24 hours |
|
Room Temperature 15°C to 30°C (59°F to 86°F) |
4 hours |
4 hours |
4 hours |
- Hydrate prior to and following Kyprolis as needed. (2.1)
- Premedicate prior to all Cycle 1 doses and if infusion-related reactions develop or reappear. (2.1)
- The recommended dosing regimens are as follows. See Full Prescribing Information for additional dosage information. (2.2)
|
Regimen |
Dosage |
Infusion Time |
|---|---|---|
|
Kyprolis and Dexamethasone (Kd) or |
20/70 mg/m2 once weekly |
30 minutes |
|
Kyprolis and Dexamethasone (Kd) or |
20/56 mg/m2 twice weekly |
30 minutes |
|
Kyprolis, Lenalidomide and Dexamethasone (KRd) or |
20/27 mg/m2 twice weekly |
10 minutes |
DOSAGE FORMS & STRENGTHS SECTION
3 DOSAGE FORMS AND STRENGTHS
For injection: 10 mg, 30 mg and 60 mg as a lyophilized cake or powder in single-dose vial for reconstitution.
For injection: 10 mg, 30 mg or 60 mg lyophilized powder in single-dose vial for reconstitution. (3)
USE IN SPECIFIC POPULATIONS SECTION
8 USE IN SPECIFIC POPULATIONS
8.1 Pregnancy
Risk Summary
Kyprolis can cause fetal harm based on findings from animal studies and its mechanism of action [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.1)]. There are no available data on Kyprolis use in pregnant women to evaluate for drug-associated risks. Kyprolis caused embryo-fetal lethality in rabbits at doses lower than the clinical dose (see Data). Advise pregnant women of the potential risk to the fetus.
The estimated background risk of major birth defects and miscarriage for the indicated population is unknown. All pregnancies have a background risk of birth defect, loss, or other adverse outcomes. In the U.S. general population, the estimated background risk of major birth defects and miscarriage in clinically recognized pregnancies is 2%–4% and 15%–20%, respectively.
Data
Animal Data
Carfilzomib administered intravenously to pregnant rats and rabbits during the period of organogenesis was not teratogenic at doses up to 2 mg/kg/day in rats and 0.8 mg/kg/day in rabbits. In rabbits, there was an increase in pre- implantation loss at ≥ 0.4 mg/kg/day and an increase in early resorptions and post-implantation loss and a decrease in fetal weight at the maternally toxic dose of 0.8 mg/kg/day. The doses of 0.4 and 0.8 mg/kg/day in rabbits are approximately 20% and 40%, respectively, of the recommended dose in humans of 27 mg/m2 based on BSA.
8.2 Lactation
Risk Summary
There are no data on the presence of Kyprolis in human milk, the effects on the breastfed child, or the effects of the drug on milk production. Because of the potential for serious adverse reactions in the breastfed child, advise women not to breastfeed during treatment with Kyprolis and for 2 weeks after treatment.
8.3 Females and Males of Reproductive Potential
Based on its mechanism of action and findings in animals, Kyprolis can cause fetal harm when administered to a pregnant woman [see Use in Specific Populations (8.1)].
Pregnancy Testing
Conduct pregnancy testing on females of reproductive potential prior to initiating Kyprolis treatment.
Contraception
Females
Advise females of reproductive potential to use effective contraception during treatment with Kyprolis and for 6 months following the last dose.
Males
Advise males with female sexual partners of reproductive potential to use effective contraception during treatment with Kyprolis and for 3 months following the last dose.
Infertility
Based on the mechanism of action, Kyprolis may have an effect on either male or female fertility [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.1), Nonclinical Toxicology (13.1)]. There are no data on the effect of Kyprolis on human fertility.
8.4 Pediatric Use
The safety and effectiveness of Kyprolis in pediatric patients have not been established.
8.5 Geriatric Use
Of the 2,837 patients with relapsed or refractory multiple myeloma exposed to Kyprolis in monotherapy and combination therapy studies [see Clinical Studies (14.1, 14.2, 14.3, 14.4, 14.5)], 50% were 65 years and older, while 13% were 75 years and older. The incidence of serious adverse reactions was 50% in patients < 65 years of age, 60% in patients 65 to 74 years of age, and 63% in patients ≥ 75 years of age. Of the 308 patients in CANDOR who received DKd, 47% of patients were 65 years and older, while 9% were 75 years and older. Fatal adverse reactions in the DKd arm of CANDOR occurred in 6% of patients <65 years of age, 14% of patients between 65 to 74 years of age, and 14% of patients ≥ 75 years of age [see Adverse Reactions (6.1)]. No overall differences in effectiveness were observed between older and younger patients.
8.6 Hepatic Impairment
Reduce the dose of Kyprolis by 25% in patients with mild (total bilirubin 1 to 1.5 × ULN and any AST or total bilirubin ≤ ULN and AST > ULN) or moderate (total bilirubin > 1.5 to 3 × ULN and any AST) hepatic impairment. A recommended dosage of Kyprolis has not been established for patients with severe hepatic impairment (total bilirubin > 3 × ULN and any AST) [see Dosage and Administration (2.4), Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)].
The incidence of serious adverse reactions was higher in patients with mild, moderate, and severe hepatic impairment combined (22/35 or 63%) than in patients with normal hepatic function (3/11 or 27%) [see Warnings and Precautions (5.12), Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)].
- Geriatric Use: In the Kyprolis clinical trials, the incidence of adverse reactions was greater in patients ≥ 75 years of age. (8.5)
- Hepatic Impairment: Reduce the dose of Kyprolis by 25% in patients with mild or moderate hepatic impairment. (2.4)
- Patients on Hemodialysis: Administer Kyprolis after the hemodialysis procedure. (2.1)
- Lactation: Advise women not to breastfeed. (8.2)
OVERDOSAGE SECTION
10 OVERDOSAGE
Acute onset of chills, hypotension, renal insufficiency, thrombocytopenia, and lymphopenia has been reported following a dose of 200 mg of Kyprolis administered in error.
There is no known specific antidote for Kyprolis overdosage. In the event of overdose, monitor patients for adverse reactions and provide supportive care as appropriate.
DESCRIPTION SECTION
11 DESCRIPTION
Carfilzomib is a proteasome inhibitor. The chemical name for carfilzomib is (2S)-N-((S)-1-((S)-4-methyl-1-((R)-2-methyloxiran-2-yl)-1-oxopentan-2-ylcarbamoyl)-2-phenylethyl)-2-((S)-2-(2-morpholinoacetamido)-4-phenylbutanamido)-4-methylpentanamide. Carfilzomib has the following structure:
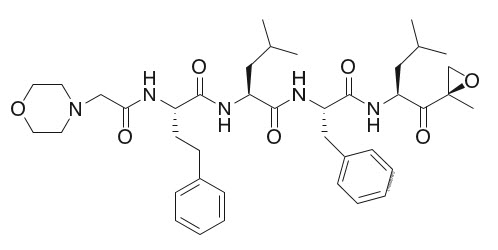
Carfilzomib is a crystalline substance with a molecular weight of 719.9. The molecular formula is C40H57N5O7. Carfilzomib is practically insoluble in water and very slightly soluble in acidic conditions.
Kyprolis for injection, for intravenous use is a sterile, white to off-white lyophilized powder in a single-dose vial. Each 10 mg vial contains 10 mg of carfilzomib, 500 mg sulfobutylether beta-cyclodextrin, and 9.6 mg anhydrous citric acid and sodium hydroxide for pH adjustment (target pH 3.5). Each 30 mg vial contains 30 mg of carfilzomib, 1500 mg sulfobutylether beta-cyclodextrin, and 28.8 mg anhydrous citric acid and sodium hydroxide for pH adjustment (target pH 3.5). Each 60 mg vial contains 60 mg of carfilzomib, 3000 mg sulfobutylether beta-cyclodextrin, 57.7 mg citric acid, and sodium hydroxide for pH adjustment (target pH 3.5).
CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY SECTION
12 CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY
12.1 Mechanism of Action
Carfilzomib is a tetrapeptide epoxyketone proteasome inhibitor that irreversibly binds to the N-terminal threonine-containing active sites of the 20S proteasome, the proteolytic core particle within the 26S proteasome. Carfilzomib had antiproliferative and proapoptotic activities in vitro in solid and hematologic tumor cells. In animals, carfilzomib inhibited proteasome activity in blood and tissue and delayed tumor growth in models of multiple myeloma, hematologic, and solid tumors.
12.2 Pharmacodynamics
Intravenous carfilzomib administration resulted in suppression of proteasome chymotrypsin-like (CT-L) activity when measured in blood 1 hour after the first dose. Doses of carfilzomib ≥ 15 mg/m2 with or without lenalidomide and dexamethasone induced a ≥ 80% inhibition of the CT-L activity of the proteasome. In addition, carfilzomib, 20 mg/m2 intravenously as a single agent, resulted in a mean inhibition of the low molecular mass polypeptide 2 (LMP2) and multicatalytic endopeptidase complex-like 1 (MECL1) subunits of the proteasome ranging from 26% to 32% and 41% to 49%, respectively. Proteasome inhibition was maintained for ≥ 48 hours following the first dose of carfilzomib for each week of dosing.
12.3 Pharmacokinetics
Carfilzomib at doses between 20 mg/m2 and 70 mg/m2 administered as a 30-minute infusion resulted in dose-dependent increases in maximum plasma concentrations (Cmax) and area under the curve over time to infinity (AUC0-INF) in patients with multiple myeloma. A dose-dependent increase in Cmax and AUC0-INF was also observed between carfilzomib 20 mg/m2 and 56 mg/m2 as a 2- to 10-minute infusion in patients with relapsed or refractory multiple myeloma. A 30-minute infusion resulted in a similar AUC0-INF, but 2- to 3-fold lower Cmax than that observed with a 2- to 10-minute infusion at the same dose. There was no evidence of carfilzomib accumulation following repeated administration of carfilzomib 70 mg/m2 as a 30-minute once weekly infusion or 15 and 20 mg/m2 as a 2- to 10-minute twice weekly infusion.
Table 21 lists the estimated mean average daily area under the curve in the first cycle (AUCC1,avg), average daily area under the curve at steady-state (AUCss) and Cmax at the highest dose in the first cycle (Cmax,C1) for the different dosing regimens.
Table 21: Carfilzomib Exposure Parameters for Different Dosing Regimens|
Estimated Parameters (%CV) |
20/27 mg/m2 twice weekly with 2- to 10-minute infusion |
20/56 mg/m2 twice weekly with 30-minute infusion |
20/70 mg/m2 once weekly with 30-minute infusion |
|---|---|---|---|
|
CV = Coefficient of variation | |||
|
AUCC1,avg (ng∙hr/mL) |
95 (40) |
170 (35) |
114 (36) |
|
AUCss (ng∙hr/mL) |
111 (34) |
228 (28) |
150 (35) |
|
Cmax,C1 (ng/mL) |
1282 (17) |
1166 (29) |
1595 (36) |
Distribution
The mean steady-state volume of distribution of a 20 mg/m2 dose of carfilzomib was 28 L. Carfilzomib is 97% bound to human plasma proteins over the concentration range of 0.4 to 4 micromolar in vitro.
Elimination
Carfilzomib has a half-life of ≤ 1 hour on Day 1 of Cycle 1 following intravenous doses ≥ 15 mg/m2. The half-life was similar when administered either as a 30-minute infusion or a 2- to 10-minute infusion. The systemic clearance ranged from 151 to 263 L/hour.
Metabolism
Carfilzomib is rapidly metabolized. Peptidase cleavage and epoxide hydrolysis were the principal pathways of metabolism. Cytochrome P450 (CYP)-mediated mechanisms contribute a minor role in overall carfilzomib metabolism.
Excretion
Approximately 25% of the administered dose of carfilzomib was excreted in urine as metabolites in 24 hours. Urinary and fecal excretion of the parent compound was negligible (0.3% of total dose).
Specific Populations
Age (35-89 years), sex, race or ethnicity (80% White, 11% Black, 6% Asians, 3% Hispanics), and mild to severe renal impairment (creatinine clearance 15-89 mL/min) did not have clinically meaningful effects on the pharmacokinetics of carfilzomib.
Patients with Hepatic Impairment
Compared to patients with normal hepatic function, patients with mild (total bilirubin 1 to 1.5 × ULN and any AST or total bilirubin ≤ ULN and AST > ULN) and moderate (total bilirubin > 1.5 to 3 × ULN and any AST) hepatic impairment had approximately 50% higher carfilzomib AUC. The pharmacokinetics of carfilzomib has not been evaluated in patients with severe hepatic impairment (total bilirubin > 3 × ULN and any AST).
Patients with Renal Impairment
Relative to patients with normal renal function, ESRD patients on hemodialysis showed 33% higher carfilzomib AUC. Since hemodialysis clearance of Kyprolis concentrations has not been studied, the drug should be administered after the hemodialysis procedure.
Drug Interaction Studies
Clinical Studies
Effect of Carfilzomib on Sensitive CYP3A Substrate: Midazolam (a sensitive CYP3A substrate) pharmacokinetics was not affected by concomitant administration of carfilzomib.
In Vitro Studies
Effect of Carfilzomib on Cytochrome P450 (CYP) Enzymes: Carfilzomib showed direct and time-dependent inhibition of CYP3A but did not induce CYP1A2 and CYP3A4 in vitro.
Effect of Transporters on Carfilzomib: Carfilzomib is a P-glycoprotein (P-gp) substrate in vitro.
Effect of Carfilzomib on Transporters: Carfilzomib inhibits P-gp in vitro. However, given that Kyprolis is administered intravenously and is extensively metabolized, the pharmacokinetics of Kyprolis is unlikely to be affected by P-gp inhibitors or inducers.
NONCLINICAL TOXICOLOGY SECTION
13 NONCLINICAL TOXICOLOGY
13.1 Carcinogenesis, Mutagenesis, Impairment of Fertility
Carcinogenicity studies have not been conducted with carfilzomib.
Carfilzomib was clastogenic in the in vitro chromosomal aberration test in peripheral blood lymphocytes. Carfilzomib was not mutagenic in the in vitro bacterial reverse mutation (Ames) test and was not clastogenic in the in vivo mouse bone marrow micronucleus assay.
Fertility studies with carfilzomib have not been conducted. No effects on reproductive tissues were noted during 28-day repeat-dose rat and monkey toxicity studies or in 6-month rat and 9-month monkey chronic toxicity studies.
13.2 Animal Toxicology and/or Pharmacology
Cardiovascular Toxicity
Monkeys administered a single bolus intravenous dose of carfilzomib at 3 mg/kg (approximately 1.3 times recommended dose in humans of 27 mg/m2 based on BSA) experienced hypotension, increased heart rate, and increased serum levels of troponin-T.
Chronic Administration
Repeated bolus intravenous administration of carfilzomib at ≥ 2 mg/kg/dose in rats and 2 mg/kg/dose in monkeys using dosing schedules similar to those used clinically resulted in mortalities that were due to toxicities occurring in the cardiovascular (cardiac failure, cardiac fibrosis, pericardial fluid accumulation, cardiac hemorrhage/degeneration), gastrointestinal (necrosis/hemorrhage), renal (glomerulonephropathy, tubular necrosis, dysfunction), and pulmonary (hemorrhage/inflammation) systems. The dose of 2 mg/kg/dose in rats is approximately half the recommended dose in humans of 27 mg/m2 based on BSA. The dose of 2 mg/kg/dose in monkeys is approximately equivalent to the recommended dose in humans based on BSA.
HOW SUPPLIED SECTION
16 HOW SUPPLIED/STORAGE AND HANDLING
How Supplied
Kyprolis (carfilzomib) is supplied as:
- An individually packaged single-dose vial containing 10 mg of carfilzomib as a white to off-white lyophilized cake or powder: NDC 76075-103-01.
- An individually packaged single-dose vial containing 30 mg of carfilzomib as a white to off-white lyophilized cake or powder: NDC 76075-102-01.
- An individually packaged single-dose vial containing 60 mg of carfilzomib as a white to off-white lyophilized cake or powder: NDC 76075-101-01.
Storage and Handling
Unopened vials should be stored refrigerated 2°C to 8°C (36°F to 46°F). Retain in original package to protect from light.
INFORMATION FOR PATIENTS SECTION
17 PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATION
Discuss the following with patients prior to treatment with Kyprolis:
Cardiac Toxicities: Advise patients of the risks and symptoms of cardiac failure and ischemia [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)].
Dehydration: Counsel patients to avoid dehydration, since patients receiving Kyprolis therapy may experience vomiting and/or diarrhea. Instruct patients to seek medical advice if they experience symptoms of dehydration [see Warnings and Precautions (5.3)].
Respiratory: Advise patients that they may experience cough or shortness of breath (dyspnea) during treatment with Kyprolis. This most commonly occurs within a day of dosing. Advise patients to contact their healthcare provider if they experience shortness of breath [see Warnings and Precautions (5.6)].
Venous Thrombosis: Inform patients of the risk of venous thromboembolism and discuss the options for prophylaxis. Advise patients to seek immediate medical attention for symptoms of venous thrombosis or embolism [see Warnings and Precautions (5.8)].
Infusion-Related Reactions: Advise patients of the risk of infusion-related reactions and discuss the common signs and symptoms of infusion-related reactions with the patients [see Warnings and Precautions (5.9)].
Bleeding: Inform patients that they may bruise or bleed more easily or that it may take longer to stop bleeding and to report to their healthcare provider any prolonged, unusual or excessive bleeding. Instruct patients on the signs of occult bleeding [see Warnings and Precautions (5.10)].
Hepatic: Inform patients of the risk of developing hepatic failure. Advise patients to contact their healthcare provider for symptoms of hepatitis including worsening fatigue or yellow discoloration of skin or eyes [see Warnings and Precautions (5.12)].
Other: Inform patients to contact their healthcare provider if they experience neurologic symptoms such as headaches, confusion, dizziness or loss of balance, difficulty talking or walking, decreased strength or weakness on one side of the body, seizures, or visual loss [see Warnings and Precautions (5) and Adverse Reactions (6)].
Driving/Operating Machines: Advise patients that Kyprolis may cause fatigue, dizziness, fainting, and/or drop in blood pressure. Advise patients not to drive or operate machinery if they experience any of these symptoms [see Adverse Reactions (6.1)].
Embryo-Fetal Toxicity: Advise females of the potential risk to the fetus. Advise females of reproductive potential to inform their healthcare provider immediately of a known or suspected pregnancy. Advise female patients to use effective contraceptive during treatment with Kyprolis and for 6 months following the last dose. Advise male patients with female sexual partners of reproductive potential to use effective contraception during treatment with Kyprolis and for 3 months following the last dose [see Warnings and Precautions (5.17), Use in Specific Populations (8.1, 8.3)].
Lactation: Advise patients to avoid breastfeeding while receiving Kyprolis and for 2 weeks after the last dose [see Use in Specific Populations (8.2)].
Concomitant Medications: Advise patients to discuss with their healthcare provider any medication they are currently taking prior to starting treatment with Kyprolis, or prior to starting any new medication(s) during treatment with Kyprolis.
SPL UNCLASSIFIED SECTION
AMGEN®
Kyprolis® (carfilzomib)
Manufactured for:
Onyx Pharmaceuticals, Inc.
One Amgen Center Drive
Thousand Oaks, CA 91320-1799 U.S.A.
Patent: http://pat.amgen.com/kyprolis
©2012-2022 Amgen Inc. All rights reserved.
1XXXXXX
V26
