Nebivolol
NEBIVOLOL TABLETS. These highlights do not include all the information needed to use safely and effectively. See full prescribing information for . Initial U.S. Approval: 2007
c9d8edb5-5312-ad38-e053-2995a90a7154
HUMAN PRESCRIPTION DRUG LABEL
Aug 24, 2023
Golden State Medical Supply, Inc.
DUNS: 603184490
Products 4
Detailed information about drug products covered under this FDA approval, including NDC codes, dosage forms, ingredients, and administration routes.
Nebivolol
Product Details
FDA regulatory identification and product classification information
FDA Identifiers
Product Classification
Product Specifications
INGREDIENTS (11)
Nebivolol
Product Details
FDA regulatory identification and product classification information
FDA Identifiers
Product Classification
Product Specifications
INGREDIENTS (11)
Nebivolol
Product Details
FDA regulatory identification and product classification information
FDA Identifiers
Product Classification
Product Specifications
INGREDIENTS (11)
Nebivolol
Product Details
FDA regulatory identification and product classification information
FDA Identifiers
Product Classification
Product Specifications
INGREDIENTS (11)
Drug Labeling Information
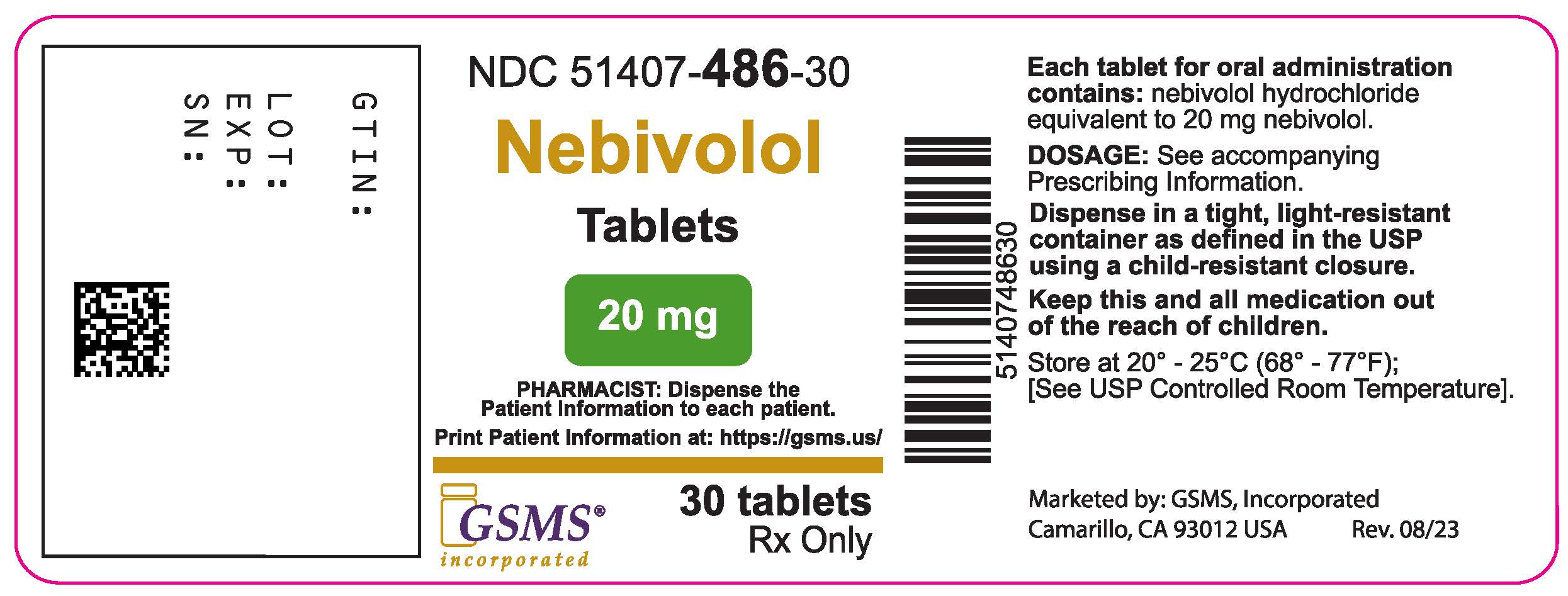
PACKAGE LABEL.PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL
PACKAGE/LABEL PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL
NDC 51407-486-30
Nebivolol Tablets, 20 mg
** Rx only**
** 30 Tablets**
DRUG INTERACTIONS SECTION
7 DRUG INTERACTIONS
7.1 CYP2D6 Inhibitors
Use caution when nebivolol is co-administered with CYP2D6 inhibitors (quinidine, propafenone, fluoxetine, paroxetine, etc.) [see Clinical Pharmacology ( 12.5)].
7.2 Hypotensive Agents
Do not use nebivolol tablets with other β-blockers. Closely monitor patients receiving catecholamine-depleting drugs, such as reserpine or guanethidine, because the added β-blocking action of nebivolol may produce excessive reduction of sympathetic activity. In patients who are receiving nebivolol tablets and clonidine, discontinue nebivolol tablets for several days before the gradual tapering of clonidine.
7.3 Digitalis Glycosides
Both digitalis glycosides and β-blockers slow atrioventricular conduction and decrease heart rate. Concomitant use can increase the risk of bradycardia.
7.4 Calcium Channel Blockers
Nebivolol can exacerbate the effects of myocardial depressants or inhibitors of AV conduction, such as certain calcium antagonists (particularly of the phenylalkylamine [verapamil] and benzothiazepine [diltiazem] classes), or antiarrhythmic agents, such as disopyramide.
- CYP2D6 enzyme inhibitors may increase nebivolol levels. ( 7.1)
- Reserpine or clonidine may produce excessive reduction of sympathetic activity. ( 7.2)
- Both digitalis glycosides and β-blockers slow atrioventricular conduction and decrease heart rate. Concomitant use can increase the risk of bradycardia. ( 7.3)
- Verapamil- or diltiazem-type calcium channel blockers may cause excessive reductions in heart rate, blood pressure, and cardiac contractility. ( 7.4)
DOSAGE & ADMINISTRATION SECTION
2 DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
2.1 Hypertension
The dose of nebivolol must be individualized to the needs of the patient. For most patients, the recommended starting dose is 5 mg once daily, with or without food, as monotherapy or in combination with other agents. For patients requiring further reduction in blood pressure, the dose can be increased at 2-week intervals up to 40 mg. A more frequent dosing regimen is unlikely to be beneficial.
Renal Impairment
****In patients with severe renal impairment (ClCr less than 30 mL/min) the
recommended initial dose is 2.5 mg once daily; titrate up slowly if needed.
Nebivolol has not been studied in patients receiving dialysis [see Clinical Pharmacology ( 12.4)] .
Hepatic Impairment
****In patients with moderate hepatic impairment, the recommended initial
dose is 2.5 mg once daily; titrate up slowly if needed. Nebivolol has not been
studied in patients with severe hepatic impairment and therefore it is not
recommended in that population [see Clinical Pharmacology ( 12.4)] .
2.2 Subpopulations
Geriatric Patients
****It is not necessary to adjust the dose in the elderly [see Use in Specific Populations ( 8.5)].
CYP2D6 Polymorphism
****No dose adjustments are necessary for patients who are CYP2D6 poor
metabolizers. The clinical effect and safety profile observed in poor
metabolizers were similar to those of extensive metabolizers [see Clinical Pharmacology ( 12.3)].
Can be taken with and without food. Individualize to the needs of the patient and monitor during up-titration. ( 2)
- Hypertension: Most patients start at 5 mg once daily. Dose can be increased at 2-week intervals up to 40 mg. ( 2.1)
CLINICAL STUDIES SECTION
14 CLINICAL STUDIES
14.1 Hypertension
The antihypertensive effectiveness of nebivolol as monotherapy has been demonstrated in three randomized, double-blind, multi-center, placebo- controlled trials at doses ranging from 1.25 to 40 mg for 12 weeks (Studies 1, 2, and 3). A fourth placebo-controlled trial demonstrated additional antihypertensive effects of nebivolol at doses ranging from 5 to 20 mg when administered concomitantly with up to two other antihypertensive agents (ACE inhibitors, angiotensin II receptor antagonists, and thiazide diuretics) in patients with inadequate blood pressure control.
The three monotherapy trials included a total of 2016 patients (1811 nebivolol tablets, 205 placebo) with mild to moderate hypertension who had baseline diastolic blood pressures (DBP) of 95 to 109 mmHg. Patients received either nebivolol tablets or placebo once daily for twelve weeks. Two of these monotherapy trials (Studies 1 and 2) studied 1716 patients in the general hypertensive population with a mean age of 54 years, 55% males, 26% non- Caucasians, 7% diabetics and 6% genotyped as PMs. The third monotherapy trial (Study 3) studied 300 Black patients with a mean age of 51 years, 45% males, 14% diabetics, and 3% as PMs.
Placebo-subtracted blood pressure reductions by dose for each study are presented inTable 2. Most studies showed increasing response to doses above 5 mg.
Table 2. Placebo-Subtracted Least-Square Mean Reductions in Trough Sitting Systolic/Diastolic Blood Pressure (SiSBP/SiDBP mmHg) by Dose in Studies with Once Daily Nebivolol Tablets
|
Nebivolol dose (mg) | ||||||
|
1.25 |
2.5 |
5.0 |
10 |
20 |
30-40 | |
|
Study 1 |
-6.6*/-5.1* |
-8.5*/-5.6* |
-8.1*/-5.5* |
-9.2*/-6.3* |
-8.7*/-6.9* |
-11.7*/-8.3* |
|
Study 2 |
-3.8/-3.2* |
-3.1/-3.9* |
-6.3*/-4.5* | |||
|
Study 3 ¶ |
-1.5/-2.9 |
-2.6/-4.9* |
-6.0*/-6.1* |
-7.2*/-6.1* |
-6.8*/-5.5* | |
|
Study 4 ^ |
-5.7*/-3.3* |
-3.7*/-3.5* |
-6.2*/-4.6* |
- p<0.05 based on pair-wise comparison vs. placebo
¶Study enrolled only African Americans.
^Study on top of one or two other antihypertensive medications.
Study 4 enrolled 669 patients with a mean age of 54 years, 55% males, 54% Caucasians, 29% Blacks, 15% Hispanics, 1% Asians, 14% diabetics, and 5% PMs. Nebivolol tablets, 5 mg to 20 mg, administered once daily concomitantly with stable doses of up to two other antihypertensive agents (ACE inhibitors, angiotensin II receptor antagonists, and thiazide diuretics) resulted in significant additional antihypertensive effects over placebo compared to baseline blood pressure.
Effectiveness was similar in subgroups analyzed by age and sex. Effectiveness was established in Blacks, but as monotherapy the magnitude of effect was somewhat less than in Caucasians.
The blood pressure lowering effect of nebivolol was seen within two weeks of treatment and was maintained over the 24-hour dosing interval.
There are no trials of nebivolol tablets demonstrating reductions in cardiovascular risk in patients with hypertension, but at least one pharmacologically similar drug has demonstrated such benefits.
INFORMATION FOR PATIENTS SECTION
17 PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATION
See FDA-approved patient labeling (Patient Information).
Patient Advice
Advise patients to take nebivolol tablets regularly and continuously, as
directed. Nebivolol tablets can be taken with or without food. If a dose is
missed, take the next scheduled dose only (without doubling it). Do not
interrupt or discontinue nebivolol tablets without consulting the physician.
Patients should know how they react to this medicine before they operate automobiles, use machinery, or engage in other tasks requiring alertness.
Advise patients to consult a physician if any difficulty in breathing occurs, or if they develop signs or symptoms of worsening congestive heart failure such as weight gain or increasing shortness of breath, or excessive bradycardia.
Caution patients subject to spontaneous hypoglycemia, or diabetic patients receiving insulin or oral hypoglycemic agents, that β-blockers may mask some of the manifestations of hypoglycemia, particularly tachycardia.
Inform patients or caregivers that there is a risk of hypoglycemia when nebivolol tablets are given to patients who are fasting or who are vomiting. Instruct patients or caregivers how to monitor for signs of hypoglycemia [see Warnings and Precautions ( 5.5)] .
All brand names listed are the registered trademarks of their respective owners and are not trademarks of ANI Pharmaceuticals, Inc.
Manufactured by:
ANI Pharmaceuticals, Inc.
Baudette, MN 56623

10465 Rev 07/23
Marketed by:
GSMS, Inc.
Camarillo, CA USA 93012
