Telmisartan and Hydrochlorothiazide
These highlights do not include all the information needed to use TELMISARTAN AND HYDROCHLOROTHIAZIDE TABLETS safely and effectively. See full prescribing information for TELMISARTAN AND HYDROCHLOROTHIAZIDE TABLETS. TELMISARTAN and HYDROCHLOROTHIAZIDE tablets, for oral use Initial U.S. Approval: 2000
681dfb5c-fc5c-427e-81f6-4b4e934978a2
HUMAN PRESCRIPTION DRUG LABEL
Jan 13, 2023
Aurobindo Pharma Limited
DUNS: 650082092
Products 3
Detailed information about drug products covered under this FDA approval, including NDC codes, dosage forms, ingredients, and administration routes.
Telmisartan and Hydrochlorothiazide
Product Details
FDA regulatory identification and product classification information
FDA Identifiers
Product Classification
Product Specifications
INGREDIENTS (11)
Telmisartan and Hydrochlorothiazide
Product Details
FDA regulatory identification and product classification information
FDA Identifiers
Product Classification
Product Specifications
INGREDIENTS (11)
Telmisartan and Hydrochlorothiazide
Product Details
FDA regulatory identification and product classification information
FDA Identifiers
Product Classification
Product Specifications
INGREDIENTS (11)
Drug Labeling Information
DOSAGE & ADMINISTRATION SECTION
2 DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
2.1 Dosing Information
Initiate a patient whose blood pressure is not adequately controlled with telmisartan monotherapy 80 mg on telmisartan and hydrochlorothiazide tablets, 80 mg/12.5 mg orally once daily. Dose can be titrated up to 160 mg/25 mg after 2 to 4 weeks, if necessary.
Initiate a patient whose blood pressure is not adequately controlled by 25 mg once daily of hydrochlorothiazide, or is controlled but who experiences hypokalemia with this regimen on telmisartan and hydrochlorothiazide tablets 80 mg/12.5 mg once daily. Dose can be titrated up to 160 mg/25 mg after 2 to 4 weeks, if necessary.
Patients titrated to the individual components (telmisartan and hydrochlorothiazide) may instead receive the corresponding dose of telmisartan and hydrochlorothiazide tablets.
Telmisartan and hydrochlorothiazide tablets****may be administered with other antihypertensive drugs.
2.2 Dose Adjustment for Hepatic Impairment
Initiate patients with biliary obstructive disorders or hepatic insufficiency under close medical supervision using the 40 mg/12.5 mg combination. Telmisartan and hydrochlorothiazide tablets are not recommended for patients with severe hepatic impairment [see Use in Specific Populations (8.6) and Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)].
2.3 Important Administration Instructions
Telmisartan and hydrochlorothiazide tablets should not be removed from blisters until immediately before administration.
DESCRIPTION SECTION
11 DESCRIPTION
Telmisartan and hydrochlorothiazide tablets USP are a combination of telmisartan, an orally active angiotensin II antagonist acting on the AT1 receptor subtype, and hydrochlorothiazide, a thiazide diuretic.
Telmisartan, a non-peptide molecule, is chemically described as 4'-[(1,4'-dimethyl-2'-propyl[2,6'-bi-1H-benzimidazol]-1'-yl)methyl]-[1,1'-biphenyl]-2-carboxylic acid. Its molecular formula is C33H30N4O2, its molecular weight is 514.63, and its structural formula is:
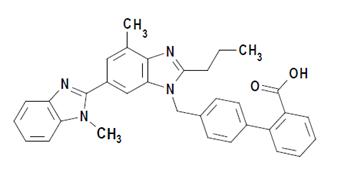
Telmisartan USP is a white or slightly yellowish, crystalline powder. It is
sparingly soluble in methylene chloride, slightly soluble in methanol,
practically insoluble in water. It dissolves in 1M sodium hydroxide.
Hydrochlorothiazide USP is white or practically white, practically odorless, crystalline powder with a molecular weight of 297.74. It is slightly soluble in water, freely soluble in sodium hydroxide solution, in n-butylamine and in dimethylformamide; sparingly soluble in methanol; insoluble in ether, in chloroform and in dilute mineral acids. Hydrochlorothiazide is chemically described as 6-chloro-3,4-dihydro-2H-1,2,4-benzothiadiazine-7-sulfonamide 1,1-dioxide. Its molecular formula is C7H8ClN3O4S2, and its structural formula is:
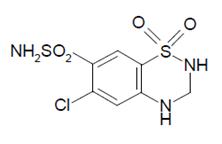
Telmisartan and hydrochlorothiazide tablets USP are formulated for oral administration in three combinations of 40 mg/12.5 mg, 80 mg/12.5 mg, and 80 mg/25 mg telmisartan and hydrochlorothiazide, respectively. The tablets contain the following inactive ingredients: colloidal silicon dioxide, hydroxypropyl cellulose, lactose monohydrate, mannitol, meglumine, povidone, sodium hydroxide pellets and sodium stearyl fumarate. In addition, the 40 mg/12.5 mg and 80 mg/12.5 mg tablets contain red ferric oxide and the 80 mg/25 mg tablets contain yellow ferric oxide. Telmisartan and hydrochlorothiazide tablets USP are hygroscopic and require protection from moisture.
Meets USP dissolution test 3.
NONCLINICAL TOXICOLOGY SECTION
13 NONCLINICAL TOXICOLOGY
13.1 Carcinogenesis, Mutagenesis, Impairment of Fertility
Telmisartan and Hydrochlorothiazide
No carcinogenicity, mutagenicity, or fertility studies have been conducted with the combination of telmisartan and hydrochlorothiazide.
Telmisartan
There was no evidence of carcinogenicity when telmisartan was administered in the diet to mice and rats for up to 2 years. The highest doses administered to mice (1000 mg/kg/day) and rats (100 mg/kg/day) are, on a mg/m2 basis, about 59 and 13 times, respectively, the maximum recommended human dose (MRHD) of telmisartan. These same doses have been shown to provide average systemic exposures to telmisartan >100 times and >25 times, respectively, the systemic exposure in humans receiving the MRHD of telmisartan (80 mg/day).
Genotoxicity assays did not reveal any telmisartan-related effects at either the gene or chromosome level. These assays included bacterial mutagenicity tests with Salmonella and E. coli (Ames), a gene mutation test with Chinese hamster V79 cells, a cytogenetic test with human lymphocytes, and a mouse micronucleus test.
No drug-related effects on the reproductive performance of male and female rats were noted at 100 mg/kg/day (the highest dose administered), about 13 times, on a mg/m2 basis, the MRHD of telmisartan. This dose in the rat resulted in an average systemic exposure (telmisartan AUC as determined on day 6 of pregnancy) at least 50 times the average systemic exposure in humans at the MRHD (80 mg/day).
Hydrochlorothiazide
Two-year feeding studies in mice and rats conducted under the auspices of the National Toxicology Program (NTP) uncovered no evidence of a carcinogenic potential of hydrochlorothiazide in female mice (at doses of up to approximately 600 mg/kg/day) or in male and female rats (at doses of up to approximately 100 mg/kg/day). The NTP, however, found equivocal evidence for hepatocarcinogenicity in male mice.
Hydrochlorothiazide was not genotoxic in vitro in the Ames mutagenicity assay of Salmonella typhimurium strains TA 98, TA 100, TA 1535, TA 1537, and TA 1538 and in the Chinese Hamster Ovary (CHO) test for chromosomal aberrations, or in vivo in assays using mouse germinal cell chromosomes, Chinese hamster bone marrow chromosomes, and the Drosophila sex-linked recessive lethal trait gene. Positive test results were obtained in the in vitro CHO Sister Chromatid Exchange (clastogenicity) assay, in the Mouse Lymphoma Cell (mutagenicity) assay, and in the Aspergillus nidulans non-disjunction assay.
Hydrochlorothiazide had no adverse effects on the fertility of mice and rats of either sex in studies wherein these species were exposed, via their diet, to doses of up to 100 and 4 mg/kg, respectively, prior to mating and throughout gestation.
