KOSELUGO
These highlights do not include all the information needed to use KOSELUGO safely and effectively. See full prescribing information for KOSELUGO.KOSELUGO (selumetinib) capsules, for oral useKOSELUGO (selumetinib) oral granulesInitial U.S. Approval: 2020
7d042c61-f28f-4ab5-ab10-d7558c0d49ff
HUMAN PRESCRIPTION DRUG LABEL
Sep 10, 2025
AstraZeneca Pharmaceuticals LP
DUNS: 054743190
Products 4
Detailed information about drug products covered under this FDA approval, including NDC codes, dosage forms, ingredients, and administration routes.
SELUMETINIB
Product Details
FDA regulatory identification and product classification information
FDA Identifiers
Product Classification
Product Specifications
INGREDIENTS (9)
SELUMETINIB
Product Details
FDA regulatory identification and product classification information
FDA Identifiers
Product Classification
Product Specifications
INGREDIENTS (9)
SELUMETINIB
Product Details
FDA regulatory identification and product classification information
FDA Identifiers
Product Classification
Product Specifications
INGREDIENTS (14)
SELUMETINIB
Product Details
FDA regulatory identification and product classification information
FDA Identifiers
Product Classification
Product Specifications
INGREDIENTS (17)
Drug Labeling Information
PACKAGE LABEL.PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL
Package/Label Display Panel 7.5 mg
NDC 0310-0640-60
Koselugo®
(selumetinib)
Oral granules
7.5 mg
Sprinkle oral granules on or mix
with smooth yogurt or fruit puree.
Dispense and store in original
bottlebelow 25° C (77°F) to
protect from light and moisture.
60 Capsules
Rx only Astrazeneca

INDICATIONS & USAGE SECTION
1 INDICATIONS AND USAGE
KOSELUGO is indicated for the treatment of pediatric patients 1 year of age and older with neurofibromatosis type 1 (NF1) who have symptomatic, inoperable plexiform neurofibromas (PN) [see Dosage and Administration (2)].
KOSELUGO is a kinase inhibitor indicated for the treatment of pediatric patients 1 year of age and older with neurofibromatosis type 1 (NF1) who have symptomatic, inoperable plexiform neurofibromas (PN). (1)
WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS SECTION
5 WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS
5.1 Cardiomyopathy
KOSELUGO can cause cardiomyopathy, defined as a decrease in left ventricular ejection fraction (LVEF) ≥10% below baseline. KOSELUGO has not been studied in patients with a history of clinically significant cardiac disease or LVEF less than 55% prior to treatment.
In the NF1 PN pediatric pool (N = 134), Grade 2 LVEF decrease [Grade 2 LVEF decrease (40%-50%; 10-19% drop from baseline)] occurred in 17% of evaluable patients. Decreased LVEF of ≥ 20% occurred in 0.7% of patients and resulted in dose interruption and dose reduction. Decreased LVEF resolved in 75% of these patients. The median time to first occurrence of LVEF decrease was approximately 12 months (median duration approximately 3 months) [see Adverse Reactions (6.1)].
Left ventricular dysfunction or decreased LVEF resulting in permanent discontinuation of KOSELUGO occurred in an unapproved population of adult patients with multiple tumor types who received KOSELUGO. Decreased LVEF resulting in permanent discontinuation of KOSELUGO occurred in a pediatric population with NF1 in an expanded access program.
Assess ejection fraction by echocardiogram prior to initiating treatment, every 3 months during the first year of treatment, every 6 months thereafter, and as clinically indicated. Withhold, reduce dose, or permanently discontinue KOSELUGO based on severity of adverse reaction [see Dosage and Administration (2.2)]. In patients who interrupt KOSELUGO for decreased LVEF, obtain an echocardiogram or a cardiac MRI every 3 to 6 weeks until resolution. Upon resolution of decreased LVEF to greater than or equal to the institutional LLN, obtain an echocardiogram or a cardiac MRI every 2 to 3 months or as directed by the cardiologist.
5.2 Ocular Toxicity
KOSELUGO can cause ocular toxicity, including blurred vision [see Adverse Reactions (6.1)Adverse Reactions (6.1)].
In the NF1 PN pediatric pool (N = 134), blurred vision, photophobia, cataracts, ocular hypertension, and retinal tear occurred in 13% of pediatric patients receiving KOSELUGO. Blurred vision resulted in dose interruption in 1.5% of patients. Ocular toxicity resolved in 76% of these patients.
Serious ocular toxicities including retinal vein occlusion (RVO) and retinal pigment epithelial detachment (RPED), occurred in an unapproved population of adult patients with multiple tumor types who received KOSELUGO as a single agent or in combination with other anti-cancer agents. RPED occurred in the pediatric population during treatment with single agent KOSELUGO and resulted in permanent discontinuation.
Conduct comprehensive ophthalmic assessments prior to initiating KOSELUGO, at regular intervals during treatment, and for new or worsening visual changes. Permanently discontinue KOSELUGO in patients with RVO. Withhold KOSELUGO in patients with RPED, follow up with optical coherence tomography assessments every 3 weeks until resolution, and resume KOSELUGO at a reduced dose. For other ocular toxicities, withhold, reduce dose, or permanently discontinue KOSELUGO based on severity of the adverse reaction [see Dosage and Administration (2.2)].
5.3 Gastrointestinal Toxicity
KOSELUGO can cause gastrointestinal toxicities, including diarrhea, vomiting, nausea and stomatitis [see Adverse Reactions (6.1)].
In the NF1 PN pediatric pool (N = 134), diarrhea occurred in 59% patients who received KOSELUGO, including Grade 3 in 10% of patients. Diarrhea resulting in permanent discontinuation occurred in 0.7% of patients. Diarrhea resulting in dose interruption occurred in 10% of patients. The median time to first onset of diarrhea was approximately 2 months and the median duration was 5 days.
Serious gastrointestinal toxicities, including perforation, colitis, ileus, and intestinal obstruction, occurred in an unapproved population of adult patients with multiple tumor types who received KOSELUGO as a single agent or in combination with other anti-cancer agents. Colitis occurred in an unapproved population of pediatric patients with multiple tumor types who received KOSELUGO as a single agent.
Advise patients to start an anti-diarrheal agent (e.g., loperamide) immediately after the first episode of unformed, loose stool and to increase fluid intake during diarrhea episodes. Withhold, reduce dose, or permanently discontinue KOSELUGO based on severity of adverse reaction [see Dosage and Administration (2.2)].
5.4 Skin Toxicity
KOSELUGO can cause rashes, including dermatitis acneiform [see Adverse Reactions (6.1)].
In the NF1 PN pediatric pool (N = 134), rash occurred in 68% of patients who received KOSELUGO. The most frequent rashes included dermatitis acneiform (47%) and maculopapular rash (31%). Pruritus (30%), alopecia (26%), and eczema (24%) occurred in patients who received KOSELUGO. Grade 3 rash occurred in 5% of patients. Rash resulted in dose interruption in 8% of patients and dose reduction in 3.7% of patients.
Other skin toxicities, including severe palmar-plantar erythrodysesthesia syndrome, occurred in an unapproved population of adult patients with multiple tumor types who received KOSELUGO as a single agent or in combination with other anti-cancer agents.
Monitor for severe skin rashes. Withhold, reduce dose, or permanently discontinue KOSELUGO based on severity of adverse reaction [see Dosage and Administration (2.2)].
5.5 Increased Creatine Phosphokinase
KOSELUGO can cause increased creatine phosphokinase [see Adverse Reactions (6.1)].
In the NF1 PN pediatric pool (N = 134), increased creatine phosphokinase (CPK) occurred in 55% of patients who received KOSELUGO, including Grade 3 or 4 in 6% of patients. Increased CPK resulted in dose interruption and dose reduction in 4% of patients. Increased CPK concurrent with myalgia occurred in 5% of patients, including one patient who permanently discontinued KOSELUGO for myalgia.
Rhabdomyolysis occurred in an unapproved adult population who received KOSELUGO as a single agent.
Obtain serum CPK prior to initiating KOSELUGO, periodically during treatment, and as clinically indicated. If increased CPK occurs, evaluate patients for rhabdomyolysis or other causes. Withhold, reduce dose, or permanently discontinue KOSELUGO based on severity of adverse reaction [see Dosage and Administration (2.2)].
5.6 Increased Levels of Vitamin E and Increased Risk of Bleeding (KOSELUGO
Capsules)
KOSELUGO capsules can cause increased levels of vitamin E and increased risk of bleeding.
KOSELUGO capsules contain vitamin E (10 mg capsules contain 32 mg vitamin E as the excipient, D-alpha-tocopheryl polyethylene glycol 1000 succinate (TPGS); while KOSELUGO 25 mg capsules contain 36 mg vitamin E as TPGS). Vitamin E can inhibit platelet aggregation and antagonize vitamin K-dependent clotting factors. Daily vitamin E intake that exceeds the recommended or safe limits may increase the risk of bleeding. Supplemental vitamin E is not recommended if daily vitamin E intake (including the amount of vitamin E in KOSELUGO and supplement) will exceed the recommended or safe limits.
An increased risk of bleeding in patients may occur in patients who are co- administered vitamin-K antagonists or anti-platelet antagonists with KOSELUGO capsules. Monitor for bleeding in these patients. Increase international normalized ratio (INR) monitoring, as appropriate, in patients taking a vitamin-K antagonist. Perform anticoagulant assessments, including INR or prothrombin time, more frequently and adjust the dose of vitamin K antagonists or anti-platelet agents as appropriate.
KOSELUGO oral granules do not contain vitamin E [see Drug Interactions (7.1)].
5.7 Embryo-Fetal Toxicity
Based on findings from animal studies and its mechanism of action, KOSELUGO can cause fetal harm when administered to a pregnant woman. In animal reproduction studies, administration of selumetinib to mice during organogenesis caused reduced fetal weight, adverse structural defects, and effects on embryo fetal survival at approximate exposures > 5-times the human exposure at the clinical dose of 25 mg/m2 twice daily. Advise pregnant women of the potential risk to a fetus. Advise females of reproductive potential to use effective contraception during treatment with KOSELUGO and for 1 week after the last dose. Advise males with female partners of reproductive potential to use effective contraception during treatment with KOSELUGO and for 1 week after the last dose [see Use in Specific Populations (8.1, 8.3)].
•
Cardiomyopathy: Assess ejection fraction prior to initiating treatment, every 3 months during the first year, then every 6 months thereafter and as clinically indicated. Withhold, reduce the dose, or permanently discontinue KOSELUGO based on severity of adverse reaction. (2.3, 5.1)
•
Ocular Toxicity: Conduct ophthalmic assessments prior to initiating KOSELUGO, at regular intervals during treatment and for new or worsening visual changes. Permanently discontinue KOSELUGO for retinal vein occlusion (RVO). Withhold KOSELUGO for retinal pigment epithelial detachment (RPED), monitor with optical coherence tomography assessments until resolution, and resume at reduced dose. (2.3, 5.2)
•
Gastrointestinal Toxicity: Advise patients to start an anti-diarrheal agent immediately after the first episode of loose stool and to increase fluid intake. Withhold, reduce the dose, or permanently discontinue KOSELUGO based on severity of adverse reaction. (2.3, 5.3)
•
Skin Toxicity: Monitor for severe skin rashes. Withhold, reduce dose, or permanently discontinue KOSELUGO based on severity of adverse reaction. (2.3, 5.4)
•
Increased Creatine Phosphokinase (CPK): Increased CPK and rhabdomyolysis can occur. Obtain serum CPK prior to initiating KOSELUGO, periodically during treatment, and as clinically indicated. If increased CPK occurs, evaluate for rhabdomyolysis or other causes. Withhold, reduce the dose, or permanently discontinue KOSELUGO based on severity of adverse reaction. (2.3, 5.5)
•
Increased Vitamin E Levels and Increased Risk of Bleeding: (KOSELUGO Capsules): KOSELUGO capsules contain vitamin E and daily intake of vitamin E that exceeds the recommended or safe limits may increase the risk of bleeding. An increased risk of bleeding may occur in patients co-administered vitamin-K antagonists or anti-platelet agents. KOSELUGO oral granules do not contain vitamin E. (5.6)
ADVERSE REACTIONS SECTION
6 ADVERSE REACTIONS
The following clinically significant adverse reactions are described elsewhere in the labeling:
•
Cardiomyopathy [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)]
•
Ocular toxicity [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2)]
•
Gastrointestinal toxicity [see Warnings and Precautions (5.3)]
•
Skin toxicity [see Warnings and Precautions (5.4)]
•
Increased creatine phosphokinase [see Warnings and Precautions (5.5)]
6.1 Clinical Trials Experience
Because clinical trials are conducted under widely varying conditions, adverse reaction rates observed in the clinical trials of a drug cannot be directly compared to rates in the clinical trials of another drug and may not reflect the rates observed in practice.
The pooled safety population described in the WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS reflect exposure to KOSELUGO in 134 pediatric patients at the recommended dose in SPRINKLE (N = 36) (NCT05309668), in SPRINT Phase I (N = 24), SPRINT Phase II Stratum 1 (N = 50), and Phase I Food Effect Study (N = 24). Among the 134 pediatric patients, the duration of KOSELUGO exposure, including dose interruptions, was 12 months or longer (80%), more than 2 years (44%), or more than 3 years (37%). In this pooled safety population, the most common adverse reactions of any grade (incidence ≥ 40%) were vomiting (64%), diarrhea (59%), increased creatine phosphokinase (55%), dry skin (51%), paronychia (50%), nausea (49%), dermatitis acneiform (47%), and pyrexia (46%).
Neurofibromatosis Type 1 (NF1) with Inoperable Plexiform Neurofibromas (PN)
Pediatrics 2 18 years of Age (SPRINT Phase II Stratum 1)
The safety of KOSELUGO was evaluated in SPRINT Phase II Stratum 1 [see Clinical Studies (14)]. Eligible patients were 2-18 years of age with neurofibromatosis type 1 (NF1) who had inoperable plexiform neurofibromas (PN) that was causing significant morbidity. Patients were excluded for abnormal LVEF, uncontrolled hypertension (blood pressure > the 95th percentile for age, height, and sex), any current or past history of RVO or RPED, intraocular pressure > 21 mmHg (or upper limit of normal adjusted by age), uncontrolled glaucoma, and inability to swallow whole capsules. Patients received KOSELUGO 25 mg/m2 orally twice daily (n=50). Among these patients, 88% were exposed for 12 months or longer and 66% were exposed for greater than 2 years.
Serious adverse reactions occurred in 24% of patients who received KOSELUGO. Serious adverse reactions that occurred in 2 or more patients were anemia, hypoxia and diarrhea.
Permanent discontinuation due to an adverse reaction occurred in 12% of patients who received KOSELUGO. Adverse reactions resulting in permanent discontinuation of KOSELUGO included increased blood creatinine, increased weight, diarrhea, paronychia, malignant peripheral nerve sheath tumor, acute kidney injury, and skin ulcer.
Dosage interruptions and dose reductions due to adverse reactions occurred in 80% and 24% of patients who received KOSELUGO, respectively. Adverse reactions requiring a dosage interruption or reduction in ≥ 5% of patients were vomiting, paronychia, diarrhea, nausea, abdominal pain, rash, skin infection, influenza like illness, pyrexia and weight gain.
The most common adverse reactions (≥ 40%) were vomiting, rash (all), abdominal pain, diarrhea, nausea, dry skin, fatigue, musculoskeletal pain, pyrexia, acneiform rash, stomatitis, headache, paronychia, and pruritus.
Table 10 presents the adverse reactions in SPRINT Phase II Stratum 1.
Table 10 Adverse Reactions (≥ 20%) in Patients Who Received KOSELUGO in SPRINT Phase II Stratum 1
Þ ß à è ð | ||
|
Adverse Reaction |
KOSELUGO N=50 | |
|
All Grades (%) |
Grade ≥ 3 (%)* | |
|
Gastrointestinal | ||
|
Vomiting |
82 |
6 |
|
Abdominal pain* |
76 |
0 |
|
Diarrhea |
70 |
16 |
|
Nausea |
66 |
2 |
|
Stomatitis† |
50 |
0 |
|
Constipation |
34 |
0 |
|
Skin and Subcutaneous Tissue | ||
|
Rash (all)‡ |
80 |
6 |
|
Dry skin |
60 |
0 |
|
Rash acneiform§ |
50 |
4 |
|
Paronychia¶ |
48 |
6 |
|
Pruritus |
46 |
0 |
|
Dermatitis# |
36 |
4 |
|
Hair changesÞ |
32 |
0 |
|
Musculoskeletal and Connective Tissue | ||
|
Musculoskeletal painß |
58 |
0 |
|
General | ||
|
Fatigueà |
56 |
0 |
|
Pyrexia |
56 |
8 |
|
Edemaè |
20 |
0 |
|
Nervous System | ||
|
Headache |
48 |
2 |
|
Respiratory, Thoracic and Mediastinal | ||
|
Epistaxis |
28 |
0 |
|
Renal and Urinary System | ||
|
Hematuria |
22 |
2 |
|
Proteinuria |
22 |
0 |
|
Metabolism and Nutrition | ||
|
Decreased appetite |
22 |
0 |
|
Cardiac System | ||
|
Decreased ejection fraction |
22 |
0 |
|
Sinus tachycardia |
20 |
0 |
|
Infections | ||
|
Skin infectionð |
20 |
2 |
|
Clinically relevant adverse reactions that occurred < 20% of patients include:
•
Eye: visual impairment
•
Gastrointestinal Disorders: dry mouth
•
General Disorders: facial edema, including periorbital edema and face edema
•
Metabolism and Nutrition: increased weight
•
Renal and Urinary System: acute kidney injury
•
Respiratory, Thoracic & Mediastinal: dyspnea, including exertional dyspnea and dyspnea at rest
•
Vascular: hypertension
Table 11 presents the laboratory abnormalities in SPRINT Phase II Stratum 1.
Table 11 Select Laboratory Abnormalities (≥ 15%) Worsening from Baseline in Patients Who Received KOSELUGO in SPRINT Phase II Stratum 1
| ||
|
Laboratory Abnormality |
KOSELUGO | |
|
All Grades (%)* |
Grade ≥ 3 (%) | |
|
Chemistry | ||
|
Increased creatine phosphokinase (CPK) |
79 |
7† |
|
Decreased albumin |
51 |
0 |
|
Increased aspartate aminotransferase (AST) |
41 |
2 |
|
Increased alanine aminotransferase (ALT) |
35 |
4 |
|
Increased lipase |
32 |
5 |
|
Increased potassium |
27 |
4 |
|
Decreased potassium |
18 |
2§ |
|
Increased alkaline phosphatase |
18 |
0 |
|
Increased amylase |
18 |
0 |
|
Increased sodium |
18 |
0 |
|
Decreased sodium |
16 |
0 |
|
Hematology | ||
|
Decreased hemoglobin |
41 |
4 |
|
Decreased neutrophils |
33 |
4 |
|
Decreased lymphocytes |
20 |
2 |
Pediatrics > 1 year of Age on KOSELUGO Granules (SPRINKLE)
The safety of KOSELUGO oral granules was evaluated in SPRINKLE (NCT05309668), a dose-finding and activity estimating, single-arm, multicenter study in 36 pediatric patients ages 1 year to less than 7 years with a clinical diagnosis of NF1-related symptomatic, inoperable PN. The study evaluated the pharmacokinetics (PK), safety, efficacy, and tolerability of KOSELUGO oral granules. Study patients were to receive KOSELUGO oral granules for 25 cycles at a dose equivalent to 25 mg/m2 BSA twice daily until disease progression or unacceptable toxicity. The median age was approximately 4 years (range: 1 to 7 years), 61% were male, 61% were White, 14% were Asian and 3% were Black or African American.
In the SPRINKLE study, the median duration of KOSELUGO oral granules treatment in pediatric patients with neurofibromatosis type 1 (NF1) plexiform neurofibromas (PN) was 11 months (range: 3 25 months). Serious adverse reactions occurred in 6% of patients who received KOSELUGO oral granules. Serious adverse reactions occurred in 1 patient each and included pyrexia, gastroenteritis and upper respiratory infection. A total of 31% of patients had an adverse reaction leading to a dosage interruption. Adverse reactions requiring a dosage interruption in ≥ 5% of patients were pyrexia, vomiting, diarrhea, upper respiratory infection, gastroenteritis and eczema. The most common adverse reactions (≥ 40%) were pyrexia, dry skin, and paronychia.
The observed safety profile of KOSELUGO oral granules in the SPRINKLE study was consistent with the known safety profile of KOSELUGO capsules.
Most common adverse reactions (≥ 40%) are: vomiting, diarrhea, increased creatine phosphokinase, dry skin, paronychia, nausea, dermatitis acneiform, and pyrexia. (6.1)
**To report SUSPECTED ADVERSE REACTIONS, contactAstraZeneca at 1-800-236-9933 or FDA at 1-800-FDA-1088 or **www.fda.gov/medwatch.
DRUG INTERACTIONS SECTION
7 DRUG INTERACTIONS
7.1 Effect of Other Drugs on KOSELUGO
|
Strong or Moderate CYP3A4 Inhibitors or Fluconazole | |
|
Clinical Impact |
• |
|
Management |
• |
|
Strong or Moderate CYP3A4 Inducers | |
|
Clinical Impact |
• |
|
Management |
• |
|
Vitamin E | |
|
Clinical Impact |
• |
|
Management |
• • |
•
Strong or Moderate CYP3A4 Inhibitors or Fluconazole: Avoid coadministration of strong or moderate CYP3A4 inhibitors or fluconazole with KOSELUGO. If coadministration cannot be avoided, reduce the dose of KOSELUGO. (2.5, 7.1)
•
Strong or Moderate CYP3A4 Inducers: Avoid concomitant use of strong and moderate CYP3A4 inducers. (7.1)
USE IN SPECIFIC POPULATIONS SECTION
8 USE IN SPECIFIC POPULATIONS
8.1 Pregnancy
Risk Summary
Based on findings from animal studies and its mechanism of action [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.1)], KOSELUGO can cause fetal harm when administered to a pregnant woman. There are no available data on the use of KOSELUGO in pregnant women to evaluate drug-associated risk. In animal reproduction studies, administration of selumetinib to mice during organogenesis caused reduced fetal weight, adverse structural defects, and effects on embryofetal survival at exposures approximately > 5 times the human exposure at the clinical dose of 25 mg/m2 twice daily (see Data). Advise pregnant women of the potential risk to the fetus.
In the U.S. general population, the estimated background risk of major birth defects and miscarriage in clinically recognized pregnancies is 2% to 4% and 15% to 20%, respectively.
Data
Animal Data
In embryo-fetal development studies in mice at doses > 2.5 mg/kg twice daily (~5-times the human exposure based on area under the curve [AUC] at the clinical dose of 25 mg/m2 twice daily), selumetinib caused increases in post- implantation loss, a reduction in mean fetal and litter weights, and an increased occurrence of open eye and cleft palate, but did not induce significant maternal toxicity.
Administration of selumetinib to pregnant mice from gestation Day 6 through lactation Day 20 resulted in reduced pup body weights and fewer pups met the pupil constriction criterion on day 21 post-partum. The incidence of malformations (e.g., prematurely open eye(s) and cleft palate) was increased even at the lowest dose of 0.5 mg/kg twice daily (maternal maximal concentration [Cmax] of ~0.6 times the human Cmax at the clinical dose of 25 mg/m2 twice daily).
8.2 Lactation
Risk Summary
There are no data on the presence of selumetinib or its active metabolite in human milk or their effects on the breastfed child or milk production. Selumetinib and its active metabolite were present in the milk of lactating mice (see Data). Due to the potential for adverse reactions in a breastfed child, advise women not to breastfeed during treatment with KOSELUGO and for 1 week after the last dose.
Data
Animal Data
Selumetinib and its active metabolite were present in milk from mice dosed with selumetinib throughout gestation and lactation, with a mean plasma/milk ratio of 1.5 in lactating dams dosed at 5 mg/kg twice daily. Administration of selumetinib to dams during gestation and early lactation was associated with adverse events in pups, including reduced growth rates and incidence of malformations [see Use in Specific Populations (8.1)].
8.3 Females and Males of Reproductive Potential
KOSELUGO can cause fetal harm when administered to a pregnant woman [see Use in Specific Populations (8.1)].
Pregnancy Testing
Verify the pregnancy status of females of reproductive potential prior to initiating KOSELUGO [see Use in Specific Populations (8.1)].
Contraception
Females
Advise females of reproductive potential to use effective contraception during treatment and for 1 week after the last dose.
Males
Advise male patients with female partners of reproductive potential to use effective contraception during treatment with KOSELUGO and for 1 week after the last dose.
8.4 Pediatric Use
The safety and effectiveness have been established in pediatric patients 1 year of age and older with NF1 who have inoperable PN and the information on this use is discussed throughout the labeling. The safety and effectiveness of KOSELUGO have not been established in pediatric patients younger than 1 years of age.
Animal Toxicity Data
In 3-month general toxicology studies, male rats receiving selumetinib at doses ≥ 10 mg/kg daily (~60-times the human exposure based on AUC at the clinical dose of 25 mg/m2 twice daily) showed growth plate dysplasia.
8.5 Geriatric Use
Clinical studies did not include patients 65 years of age and older.
8.6 Renal Impairment
No dose adjustment is recommended in patients with renal impairment or those with End Stage Renal Disease [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)].
8.7 Hepatic Impairment
Selumetinib exposures increased in patients with moderate or severe hepatic impairment [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)]. Reduce the dose of KOSELUGO for patients with moderate hepatic impairment (Child-Pugh B). A recommended dosage of KOSELUGO for use in patients with severe hepatic impairment (Child-Pugh C) has not been established [see Dosage and Administration (2.3)].
•
Lactation: Advise not to breastfeed. (8.2)
CLINICAL STUDIES SECTION
14 CLINICAL STUDIES
14.1 Neurofibromatosis Type 1 (NF1) with Inoperable Plexiform Neurofibromas
(PN)
SPRINT Phase II Stratum 1 NF1 PN Patients (2 to < 18 years of age)
The efficacy of KOSELUGO was evaluated in SPRINT Phase II Stratum 1, an open- label, multicenter, single arm trial (NCT01362803). Eligible patients were required to have NF1 with inoperable PN, defined as a PN that could not be completely removed without risk for substantial morbidity due to encasement of, or close proximity to, vital structures, invasiveness, or high vascularity of the PN. Patients were also required to have significant morbidity related to the target PN. Morbidities that were present in > 20% of patients included disfigurement, motor dysfunction, pain, airway dysfunction, visual impairment, and bladder/bowel dysfunction. Patients received KOSELUGO 25 mg/m2 orally twice daily until disease progression or unacceptable toxicity.
The major efficacy outcome measure was overall response rate (ORR), defined as the percentage of patients with complete response (defined as disappearance of the target PN) or confirmed partial response (defined as ≥ 20% reduction in PN volume confirmed at a subsequent tumor assessment within 3-6 months). The target PN, defined as the PN that caused relevant clinical symptoms or complications (PN related morbidities), was evaluated for response rate using centrally read volumetric magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) analysis per Response Evaluation in Neurofibromatosis and Schwannomatosis (REiNS) criteria. Tumor response was evaluated at baseline and while on treatment after every 4 cycles for 2 years, and then every 6 cycles. An additional efficacy outcome measure was duration of response (DoR).
A total of 50 pediatric patients received KOSELUGO. The median age was 10.2 years (range 3.5 to 17.4 years); 60% were male; and 84% were White, 8% were Black and 2% were Asian.
Efficacy results are provided in Table 12. The median time to onset of response was 7.2 months (range: 3.3 months to 1.6 years).
Table 12 Efficacy Results from SPRINT Phase II Stratum 1|
Efficacy Parameter |
SPRINT |
|---|---|
| |
|
Overall Response Rate*† | |
|
Overall Response Rate, n (%) |
33 (66%) |
|
95% CI |
(51, 79) |
|
Complete Response‡ |
0 |
|
Confirmed Partial Response, n (%)‡ |
33 (66%) |
|
Duration of Response§ | |
|
Median (95% CI) months |
NR (41.2 – NE) |
|
DoR ≥ 24 months, n (%) |
26 (79%) |
|
DoR ≥ 36 months, n (%) |
21 (64%) |
|
CI – confidence interval, DoR – duration of response, NE – not evaluable, NR – not reached. |
An independent centralized review of tumor response per REiNS criteria (data cut-off June 2018) resulted in an ORR of 44% (95% CI: 30, 59).
DOSAGE FORMS & STRENGTHS SECTION
3 DOSAGE FORMS AND STRENGTHS
Capsules:
•
10 mg selumetinib: white to off-white, opaque, hard capsule sealed with a clear band and marked with “SEL 10” in black ink.
•
25 mg selumetinib: blue, opaque, hard capsule sealed with a clear band and marked with “SEL 25” in black ink.
Oral Granules:
•
5 mg selumetinib: Off-white to light-yellow free-flowing oral granules contained within capsules. The capsules have a yellow cap and white body. The cap is printed with “sel 5” in black ink, and body is printed with a sprinkle capsule image indicating opening.
•
7.5 mg selumetinib: Off-white to light-yellow free-flowing oral granules contained within capsules. The capsules have a pink cap and white body. The cap is printed with “sel 7.5” in black ink, and body is printed with a sprinkle capsule image indicating opening.
Capsules: 10 mg and 25 mg of selumetinib. (3)
Oral Granules: 5 mg and 7.5 mg of selumetinib. (3)
RECENT MAJOR CHANGES SECTION
RECENT MAJOR CHANGES
Indications and Usage (1) 09/2025
Dosage and Administration (2.1, 2.2, 2.3, 2.4, 2.5) 09/2025
Warnings and Precautions (5.1, 5.2, 5.3, 5.4, 5.5, 5.6) 09/2025
DOSAGE & ADMINISTRATION SECTION
2 DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
2.1 Recommended Dosage
The recommended dosage of KOSELUGO capsules (see Table 1) and KOSELUGO oral granules (see Table 2) for pediatric patients 1 year of age and older, based on body surface area, is 25 mg/m2 orally twice daily, until disease progression or unacceptable toxicity [see Dosage and Administration (2.2)].
Table 1 Recommended Dosage: KOSELUGO Capsules
| |
|
Body Surface Area* |
KOSELUGO Capsules |
|
0.55 – 0.69 m2 |
20 mg in the morning and 10 mg in the evening |
|
0.70 – 0.89 m2 |
20 mg twice daily |
|
0.90 – 1.09 m2 |
25 mg twice daily |
|
1.10 – 1.29 m2 |
30 mg twice daily |
|
1.30 – 1.49 m2 |
35 mg twice daily |
|
1.50 – 1.69 m2 |
40 mg twice daily |
|
1.70 – 1.89 m2 |
45 mg twice daily |
|
≥ 1.90 m2 |
50 mg twice daily |
| |
|
Body Surface Area* |
KOSELUGO Oral Granules |
|
0.40 – 0.59 m2 |
12.5 mg twice daily |
|
0.60 – 0.69 m2 |
15 mg twice daily |
|
0.70 – 0.89 m2 |
20 mg twice daily |
|
0.90 – 1.09 m2 |
25 mg twice daily |
|
1.10 – 1.29 m2 |
30 mg twice daily |
|
1.30 – 1.49 m2 |
35 mg twice daily |
|
1.50 – 1.69 m2 |
40 mg twice daily |
|
1.70 – 1.89 m2 |
45 mg twice daily |
|
≥ 1.90 m2 |
50 mg twice daily |
2.2 Administration
KOSELUGO is available in two dosage forms: KOSELUGO capsules and KOSELUGO oral granules. Prescribe KOSELUGO oral granules for patients who have difficulty swallowing whole capsules.
KOSELUGO Capsules
•
Administer KOSELUGO capsules to patients who can swallow a whole capsule.
•
Swallow KOSELUGO capsules whole. Do not open, chew or crush KOSELUGO capsules.
•
KOSELUGO capsules may be administered with or without food.
KOSELUGO Oral Granules
•
Administer KOSELUGO oral granules to patients who have difficulty swallowing a whole capsule.
•
Sprinkle KOSELUGO oral granules on or mix with a small amount (about 1 to 3 teaspoons) of smooth yogurt, or fruit puree containing the following fruits: apple, banana, pear, or strawberry and consume within 30 minutes of preparation. If not consumed within 30 minutes of preparation, discard and prepare a new dose. If a dose has been partially consumed within 30 minutes of preparation, discard remainder of the dose and do not prepare a new dose, aim to complete dosing within 30 minutes next time.
•
The KOSELUGO oral granules should be free-flowing. Do NOT use if the oral granules are clumped or stuck inside the capsule shell. Instruct the patient or caregiver to contact their pharmacy if this happens.
•
Discard the empty capsule shells after use.
•
Do NOT swallow, chew, or dissolve the capsule shells of KOSELUGO oral granules.
•
Do NOT chew or crush the KOSELUGO oral granules. Do NOT add oral granules to liquids.
•
Do NOT mix KOSELUGO oral granules in grapefruit or any juice, fruit puree or jam containing Seville orange.
Missed Dose
If a dose of KOSELUGO capsules or KOSELUGO oral granules is missed, make up that dose unless the next dose is due within 6 hours.
Vomiting
If vomiting occurs after taking a dose of KOSELUGO capsules or KOSELUGO oral granules, do not take an additional dose. Take the next dose at the regular scheduled time.
2.3 Dosage Modifications for Adverse Reactions
The recommended dose reductions for adverse reactions for KOSELUGO capsules and KOSELUGO oral granules are provided in Tables 3 and 4, respectively.
Table 3 Recommended Dose Reductions for KOSELUGO Capsules for Adverse Reactions|
Body Surface Area |
First Dose Reduction |
Second Dose Reduction | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Morning |
Evening |
Morning |
Evening | |
|
0.55 – 0.69 m2 |
10 |
10 |
10 mg once daily | |
|
0.70 – 0.89 m2 |
20 |
10 |
10 |
10 |
|
0.90 – 1.09 m2 |
25 |
10 |
10 |
10 |
|
1.10 – 1.29 m2 |
25 |
20 |
20 |
10 |
|
1.30 – 1.49 m2 |
25 |
25 |
25 |
10 |
|
1.50 – 1.69 m2 |
30 |
30 |
25 |
20 |
|
1.70 – 1.89 m2 |
35 |
30 |
25 |
20 |
|
≥ 1.90 m2 |
35 |
35 |
25 |
25 |
|
Permanently discontinue KOSELUGO capsules in patients unable to tolerate two dose reductions. |
|
Body Surface Area |
First Dose Reduction |
Second Dose Reduction | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Morning |
Evening |
Morning |
Evening | |
|
0.40 – 0.59 m2 |
10 |
10 |
7.5 |
7.5 |
|
0.60 – 0.69 m2 |
12.5 |
12.5 |
10 |
10 |
|
0.70 – 0.89 m2 |
15 |
15 |
12.5 |
12.5 |
|
0.90 – 1.09 m2 |
20 |
20 |
15 |
15 |
|
1.10 – 1.29 m2 |
22.5 |
22.5 |
15 |
15 |
|
1.30 – 1.49 m2 |
25 |
25 |
25 |
10 |
|
1.50 – 1.69 m2 |
30 |
30 |
25 |
20 |
|
1.70 – 1.89 m2 |
35 |
30 |
25 |
20 |
|
≥ 1.90 m2 |
35 |
35 |
25 |
25 |
|
Permanently discontinue KOSELUGO oral granules in patients unable to tolerate two dose reductions. |
The recommended dosage modifications of KOSELUGO capsules and KOSELUGO oral granules for adverse reactions are provided in Table 5.
Table 5 Recommended Dosage Modifications for Adverse Reactions|
Severity of Adverse Reaction |
Recommended Dosage Modifications for KOSELUGO capsules and KOSELUGO oral granules |
|---|---|
|
Cardiomyopathy [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)] | |
|
• |
Withhold until resolution. Resume at reduced dose. |
|
• • |
Permanently discontinue. |
|
Ocular Toxicity [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2)] | |
|
• |
Withhold until resolution. Resume at reduced dose. |
|
• |
Permanently discontinue. |
|
Gastrointestinal Toxicity [see Warnings and Precautions (5.3)] | |
|
• |
Withhold until improved to Grade 0 or 1. Resume at same dose. Permanently discontinue if no improvement within 3 days. |
|
• |
Permanently discontinue. |
|
• |
Permanently discontinue. |
|
Skin Toxicity [see Warnings and Precautions (5.4)] | |
|
• |
Withhold until improvement. Resume at reduced dose. |
|
Increased Creatine Phosphokinase (CPK) [see Warnings and Precautions (5.5)] | |
|
• • |
Withhold until improved to Grade 0 or 1. Resume at reduced dose. Permanently discontinue if no improvement within 3 weeks. |
|
• |
Permanently discontinue. |
|
Other Adverse Reactions [see Adverse Reactions (6.1)] | |
|
• • |
Withhold KOSELUGO until improved to Grade 0 or 1. Resume at reduced dose. |
|
• |
Withhold KOSELUGO until improved to Grade 0 or 1. Resume at reduced dose. Consider discontinuation. |
- Per National Cancer Institute Common Terminology Criteria for Adverse Events version 4.03
2.4 Dosage Modifications for Hepatic Impairment
Severe Hepatic Impairment
The recommended dosage of KOSELUGO for use in patients with severe hepatic impairment (Child Pugh C) has not been established [see Use in Specific Populations (8.7)].
Moderate Hepatic Impairment
The recommended dosage of KOSELUGO capsules (see Table 6) and KOSELUGO oral granules (see Table 7) for pediatric patients 1 year of age or older with moderate hepatic impairment (Child Pugh B) is based on body surface area; 20 mg/m2 orally twice daily, until disease progression or unacceptable toxicity [see Dosage and Administration (2.2)].
Table 6 Recommended Dosage of KOSELUGO Capsules for Moderate Hepatic Impairment|
Body Surface Area |
Moderate Hepatic Impairment | |
|---|---|---|
|
Morning |
Evening | |
|
0.55 – 0.69 m2 |
10 |
10 |
|
0.70 – 0.89 m2 |
20 |
10 |
|
0.90 – 1.09 m2 |
20 |
20 |
|
1.10 – 1.29 m2 |
25 |
25 |
|
1.30 – 1.49 m2 |
30 |
25 |
|
1.50 – 1.69 m2 |
35 |
30 |
|
1.70 – 1.89 m2 |
35 |
35 |
|
≥ 1.90 m2 |
40 |
40 |
|
Body Surface Area |
Moderate Hepatic Impairment | |
|---|---|---|
|
Morning |
Evening | |
|
0.40 – 0.59 m2 |
10 |
10 |
|
0.60 – 0.69 m2 |
12.5 |
12.5 |
|
0.70 – 0.89 m2 |
15 |
15 |
|
0.90 – 1.09 m2 |
20 |
20 |
|
1.10 – 1.29 m2 |
25 |
25 |
|
1.30 – 1.49 m2 |
30 |
25 |
|
1.50 – 1.69 m2 |
35 |
30 |
|
1.70 – 1.89 m2 |
35 |
35 |
|
≥ 1.90 m2 |
40 |
40 |
2.5 Dosage Modifications for Drug Interactions
Strong or Moderate CYP3A4 Inhibitors or Fluconazole
Avoid coadministration of strong or moderate CYP3A4 inhibitors or fluconazole with KOSELUGO. If coadministration with strong or moderate CYP3A4 inhibitors or fluconazole cannot be avoided, reduce the KOSELUGO dosage as recommended in Table 8 (KOSELUGO capsules) and Table 9 (KOSELUGO oral granules). After discontinuation of the strong or moderate CYP3A4 inhibitor or fluconazole for 3 elimination half-lives, resume the KOSELUGO dose that was taken prior to initiating the inhibitor or fluconazole [see Drug Interactions (7.1)].
Table 8 Recommended Dosage of KOSELUGO Capsules for Coadministration with Strong or Moderate CYP3A4 Inhibitors or Fluconazole|
Body Surface Area |
If the current dosage is 25 mg/m2 twice daily, reduce to 20
mg/m2 twice daily |
If the current dosage is 20 mg/m2 twice daily, reduce to 15
mg/m2 twice daily | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Morning |
Evening |
Morning |
Evening | |
|
0.55 – 0.69 m2 |
10 |
10 |
10 mg once daily | |
|
0.70 – 0.89 m2 |
20 |
10 |
10 |
10 |
|
0.90 – 1.09 m2 |
20 |
20 |
20 |
10 |
|
1.10 – 1.29 m2 |
25 |
25 |
25 |
10 |
|
1.30 – 1.49 m2 |
30 |
25 |
25 |
20 |
|
1.50 – 1.69 m2 |
35 |
30 |
25 |
25 |
|
1.70 – 1.89 m2 |
35 |
35 |
30 |
25 |
|
≥ 1.90 m2 |
40 |
40 |
30 |
30 |
|
Body Surface Area |
If the current dosage is 25 mg/m2 twice daily, reduce to 20
mg/m2 twice daily |
If the current dosage is 20 mg/m2 twice daily, reduce to 15
mg/m2 twice daily | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Morning |
Evening |
Morning |
Evening | |
|
0.40 – 0.59 m2 |
10 |
10 |
7.5 |
7.5 |
|
0.60 – 0.69 m2 |
12.5 |
12.5 |
10 |
7.5 |
|
0.70 – 0.89 m2 |
15 |
15 |
10 |
10 |
|
0.90 – 1.09 m2 |
20 |
20 |
15 |
15 |
|
1.10 – 1.29 m2 |
25 |
25 |
25 |
10 |
|
1.30 – 1.49 m2 |
30 |
25 |
25 |
20 |
|
1.50 – 1.69 m2 |
35 |
30 |
25 |
25 |
|
1.70 – 1.89 m2 |
35 |
35 |
30 |
25 |
|
≥ 1.90 m2 |
40 |
40 |
30 |
30 |
•
KOSELUGO capsules: The recommended dosage is 25 mg/m2, swallowed whole, taken orally twice daily with or without food (see Table 1). (2.1, 2.2)
•
KOSELUGO oral granules: The recommended dosage is equivalent to 25 mg/m2, sprinkled onto or mixed with soft food and taken orally twice daily (see Table 2). (2.1, 2.2)
•
Moderate hepatic impairment (Child Pugh B): The recommended dosage is 20 mg/m2 orally twice daily (see Tables 6 and 7). (2.2, 2.4)
•
Severe hepatic impairment (Child Pugh C): The recommended dosage has not been established. (2.4, 8.7)
•
Strong or Moderate CYP3A4 Inhibitors or Fluconazole: If coadministration with strong or moderate CYP3A4 inhibitors or fluconazole cannot be avoided, reduce the dose of KOSELUGO (see Tables 8 and 9). (2.5)
DESCRIPTION SECTION
11 DESCRIPTION
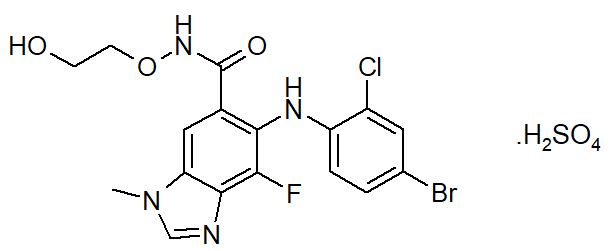
KOSELUGO contains selumetinib sulfate, a kinase inhibitor. The chemical name is 5-[(4-bromo-2-chlorophenyl)amino]-4-fluoro-6-[(2-hydroxyethoxy)carbamoyl]-1-methyl-1H-benzimidazol-3-ium hydrogen sulfate. The molecular formula for selumetinib sulfate is C17H17BrClFN4O7S and the relative molecular mass is 555.76 g/mol. Selumetinib sulfate has the following structural formula:
Selumetinib sulfate is a white to yellow monomorphic crystalline powder that exhibits a pH dependent solubility. Selumetinib sulfate is freely soluble at pH < 1.5, sparingly soluble in the pH range at 1.5 to 3 and slightly soluble at pH > 3. Selumetinib sulfate has two ionizable functions with pKa values of 2.8 and 8.4.
KOSELUGO (selumetinib) 10 mg capsules for oral use, contain 10 mg selumetinib (equivalent to 12.1 mg selumetinib sulfate) and the excipient, vitamin E polyethylene glycol succinate. The capsule shell contains carnauba wax, carrageenan, hypromellose, potassium chloride, purified water, and titanium dioxide. The capsule is imprinted with black ink that contains ammonium hydroxide, iron oxide black, propylene glycol, and shellac.
KOSELUGO (selumetinib) 25 mg capsules for oral use, contain 25 mg selumetinib (equivalent to 30.25 mg selumetinib sulfate) and the excipient, vitamin E polyethylene glycol succinate. The capsule shell contains carnauba wax and/or cornstarch, carrageenan, FD&C blue 2, ferric oxide yellow, hypromellose, potassium chloride, purified water, and titanium dioxide. The capsule is imprinted with black ink that contains carnauba wax, FD&C Blue 2 aluminum lake, ferric oxide red, ferric oxide yellow, glyceryl monooleate, and shellac.
KOSELUGO (selumetinib) 5 mg oral granules contain 5 mg selumetinib (equivalent to 6.05 mg selumetinib sulfate). The uncoated cores contain selumetinib sulfate, glyceryl dibehenate, and stearoyl polyoxylglycerides. The granule coating contains acetone, hypromellose acetate succinate, and stearic acid. The capsule shell contains ferric oxide yellow, hypromellose, and titanium dioxide. The capsule shell is imprinted with black ink that contains butyl alcohol, dehydrated alcohol, ferric oxide black, isopropyl alcohol, potassium hydroxide, propylene glycol, purified water, shellac, and strong ammonia solution.
KOSELUGO (selumetinib) 7.5 mg oral granules contain 7.5 mg selumetinib (equivalent to 9.08 mg selumetinib sulfate). The uncoated cores contain selumetinib sulfate, glyceryl dibehenate, and stearoyl polyoxylglycerides. The granule coating contains acetone, hypromellose acetate succinate, and stearic acid. The capsule shell contains ferric oxide red, hypromellose, and titanium dioxide. The capsule shell is imprinted with black ink that contains butyl alcohol, dehydrated alcohol, ferric oxide black, isopropyl alcohol, potassium hydroxide, propylene glycol, purified water, shellac, and strong ammonia solution.
CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY SECTION
12 CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY
12.1 Mechanism of Action
Selumetinib is an inhibitor of mitogen-activated protein kinase kinases 1 and 2 (MEK1/2). MEK1/2 proteins are upstream regulators of the extracellular signal-related kinase (ERK) pathway. Both MEK and ERK are critical components of the RAS-regulated RAF-MEK-ERK pathway, which is often activated in different types of cancers.
In genetically modified mouse models of NF1 that generate neurofibromas that recapitulate the genotype and phenotype of human NF1, oral dosing of selumetinib inhibited ERK phosphorylation, and reduced neurofibroma numbers, volume, and proliferation.
12.2 Pharmacodynamics
The exposure-response relationship and time course of pharmacodynamic response for the safety and effectiveness of KOSELUGO have not been fully characterized.
Cardiac Electrophysiology
At a dose 1.5-times the maximum recommended dose, KOSELUGO does not prolong the QT/QTc interval to any clinically relevant extent.
12.3 Pharmacokinetics
At the recommended dosage of 25 mg/m2 of KOSELUGO capsules twice daily in pediatric patients (2 to ≤ 18 years old), the mean maximum plasma concentration (Cmax) (coefficient of variation [CV%]) following the first dose and at steady state was 731 (62%) ng/mL and 798 (52%) ng/mL, respectively. The mean area under the plasma drug concentration curve (AUC0-12h) following the first dose was 2009 (35%) ng•h/mL and the AUC0 6h at steady state was 1958 (41%) ng•h/mL. Selumetinib AUC and Cmax increases proportionally over a dose range from 20 mg/m2 to 30 mg/m2 (0.8- to 1.2-times the recommended dose). The accumulation was 1.1-fold following administration of KOSELUGO 25 mg/m2 twice daily.
At the recommended dosage of 25 mg/m2 of KOSELUGO oral granules (sprinkled on smooth yogurt, smooth fruit sauce, smooth fruit puree, or smooth fruit jam) twice daily in pediatric patients (> 1 year old to < 7 years old), the AUC0-24h following the first dose of KOSELUGO oral granules was within the range of that in patients administered KOSELUGO capsules.
No clinically relevant differences in the pharmacokinetics of selumetinib were observed following administration of a single-dose of either the granule or capsule dosage forms of KOSELUGO at equivalent dosages, under fasted and fed conditions, in healthy adults.
Absorption
The mean absolute oral bioavailability of KOSELUGO capsules was 62% in healthy adults. The median time to peak plasma concentrations (Tmax) at steady state in pediatric patients was 1 to 1.5 hours.
Effect of Food
KOSELUGO capsules Cmax and AUC decreased by 24% and 8%, respectively, following a low-fat meal (400 calories, 25% fat) in adolescent patients with NF1 and inoperable PN administered multiple doses of 25 mg/m2 twice daily and Tmax was delayed by approximately 0.6 hours.
KOSELUGO oral granules Cmax and AUC decreased by 39% and 4%, respectively, following a low-fat meal (400 to 500 calories, 25% fat) in healthy adults and Tmax was delayed by approximately 1.3 hours.
A population PK analysis including children and adolescent patients with NF1 and inoperable PN, adult patients with cancers, and healthy adults showed that a low- or high-fat meal had no clinically relevant effect on the AUC of selumetinib.
Distribution
The mean apparent volume of distribution at steady state (Vss) of selumetinib across a dose range of 20 mg/m2 to 30 mg/m2 (0.8- to 1.2-times the recommended dosage) ranged from 78 L to 171 L in pediatric patients.
The plasma protein binding was 98.4% in humans in vitro. Selumetinib binds to serum albumin (96%) and α-1 acid glycoprotein (< 35%).
Elimination
In pediatric patients, selumetinib had an apparent oral clearance (CL/F) of 8.8 L/hr and a mean elimination half-life of approximately 6.2 hours following a dose of 25 mg/m2.
Metabolism
Selumetinib is primarily metabolized by CYP3A4 and to a lesser extent by CYP2C19, CYP1A2, CYP2C9, CYP2E1, and CYP3A5. Selumetinib also undergoes glucuronidation by UGT1A1 and UGT1A3. It is estimated that 56% of the observed intrinsic clearance of selumetinib could be attributed to CYP metabolism and about 29% attributed to direct glucuronidation by UGT enzymes in vitro. The active metabolite, N desmethyl selumetinib, is generated by CYP2C19 and CYP1A2 with additional contribution by CYP2C9 and CYP2A6, and metabolized through the same routes as selumetinib.
N desmethyl selumetinib represents less than 10% of selumetinib levels in human plasma, but is approximately 3- to 5-times more potent than the parent compound, contributing to about 21% to 35% of the overall pharmacologic activity.
Excretion
After a single oral dose of radiolabeled selumetinib 75 mg (1.5 times the recommended dose) to healthy adults, 59% of the dose was recovered in feces (19% as unchanged) and 33% in urine (< 1% as parent).
Specific Populations
Racial or Ethnic Groups
No clinically meaningful effect on the pharmacokinetics of selumetinib or N desmethyl selumetinib were observed based on race (White, Asian, Black).
Patients with Renal Impairment
Following administration of a single dose of 50 mg, selumetinib exposures were similar in subjects with End Stage Renal Disease (CLcr < 15 mL/min) who required dialysis compared to subjects with normal renal function (CLcr ≥ 90 mL/min).
Patients with Hepatic Impairment
Following administration of a single-dose of selumetinib, dose normalized total AUC0-INF decreased by 14% in subjects with mild hepatic impairment (Child Pugh A), and increased by 59% in subjects with moderate hepatic impairment (Child Pugh B) and by 57% in subjects with severe hepatic impairment (Child Pugh class C) compared to subjects with normal hepatic function. Selumetinib unbound AUC0-INF decreased by 31% in subjects with mild hepatic impairment (Child Pugh A), and increased by 41% in subjects with moderate hepatic impairment (Child Pugh B), and 3.2-fold in subjects with severe hepatic impairment (Child Pugh C) compared to subjects with normal hepatic function.
Drug Interaction Studies
Clinical Studies and Model Informed Approaches
Effect of Strong or Moderate CYP3A4 Inhibitors: Concomitant use of itraconazole (strong CYP3A4 inhibitor) increased selumetinib AUC by 49% and Cmax by 19%. Concomitant use of erythromycin (moderate CYP3A4 inhibitor) is predicted to increase selumetinib AUC by 41% and Cmax by 23%.
Effect of Fluconazole: Concomitant use of fluconazole (strong CYP2C19 inhibitor and moderate CYP3A4 inhibitor) increased selumetinib AUC by 53% and Cmax by 26%.
Effect of Strong or Moderate CYP3A4 Inducers: Concomitant use of rifampicin (strong CYP3A4 inducer) decreased selumetinib AUC by 51% and Cmax by 26%. Concomitant use of efavirenz (moderate CYP3A4 inducer) is predicted to decrease selumetinib AUC by 38% and Cmax by 22%.
In Vitro Studies
CYP Enzymes: Selumetinib does not inhibit CYP1A2, CYP2A6, CYP2B6, CYP2C8, CYP2C9, CYP2C19, CYP2D6, CYP3A4, or CYP2E1. Selumetinib does not induce CYP3A4, CYP1A2, or CYP2B6.
Transporter Systems: Selumetinib does not inhibit breast cancer resistance protein (BCRP), P-glycoprotein (P gp), OATP1B1, OATP1B3, OCT2, OAT1, OAT3, MATE1, or MATE2K transporters.
Selumetinib is a substrate of BCRP and P gp transporters.
NONCLINICAL TOXICOLOGY SECTION
13 NONCLINICAL TOXICOLOGY
13.1 Carcinogenesis, Mutagenesis, Impairment of Fertility
Carcinogenicity
Selumetinib was not carcinogenic in a 6-month study in rasH2 transgenic mice at exposures 24-times (males) and 36-times (females) and in 2-year carcinogenicity study in rats at exposures 20-times (male) and 15-times the human exposure (AUC) at the clinical dose of 25 mg/m2.
Mutagenicity
Selumetinib was not mutagenic or clastogenic in vitro. Selumetinib did result in an increase in micronucleated immature erythrocytes (chromosome aberrations) in mouse micronucleus studies, predominantly via an aneugenic mode of action, but at doses > 160 mg/kg (~38-times the human Cmax at the clinical dose of 25 mg/m2).
Impairment of Fertility
In a 6-month mouse study, selumetinib did not affect male mating performance at any dose up to 20 mg/kg twice daily (approximately 33-times the human exposure based on AUC at the clinical dose of 25 mg/m2 twice daily). In female mice exposed to selumetinib at 12.5 mg/kg twice daily, mating performance and fertility were not affected. The NOAEL for both maternal toxicity and effects on reproductive performance was 2.5 mg/kg twice daily (approximately 5-times the human exposure based on AUC at the clinical dose of 25 mg/m2 twice daily).
13.2 Animal Toxicology and/or Pharmacology
In a 26-week repeat-dose toxicology study, selumetinib at a dose of 20 mg/kg (approximately 33-times the human exposure based on AUC at the clinical dose of 25 mg/m2 twice daily) led to significant urinary tract obstruction as well as inflammation and luminal hemorrhage of the urethra leading to early death in male mice.
HOW SUPPLIED SECTION
16 HOW SUPPLIED/STORAGE AND HANDLING
How Supplied
Selumetinib Capsules
|
Strength |
Description |
Capsules per Bottle |
NDC Number |
|
10 mg |
White to off-white, opaque, hard capsule sealed with a clear band and marked with “SEL 10” in black ink. |
60 |
0310-0610-60 |
|
28 |
0310-0610-28 | ||
|
25 mg |
Blue, opaque, hard capsule sealed with a clear band and marked with “SEL 25” in black ink. |
60 |
0310-0625-60 |
|
28 |
0310-0625-28 |
Selumetinib Oral Granules
|
Strength |
Description |
Capsules per Bottle |
NDC Number |
|---|---|---|---|
|
5 mg |
Off‑white to light‑yellow free‑flowing oral granules contained within capsules. The capsules have a yellow cap and white body. The cap is printed with “sel 5” in black ink, and body is printed with a sprinkle capsule image indicating opening. |
60 |
0310‑0635‑60 |
|
7.5 mg |
Off‑white to light‑yellow free‑flowing oral granules contained within capsules. The capsules have a pink cap and white body where the cap is printed with “sel 7.5” in black ink, and body is printed with a sprinkle capsule image indicating opening. |
60 |
0310‑0640‑60 |
Storage
KOSELUGO Capsules
Store KOSELUGO capsules at 20°C to 25°C (68°F to 77°F) with excursions permitted to 15°C to 30°C (59°F to 86°F) [see USP Controlled Room Temperature]. Dispense and store in the original bottle to protect from light and moisture. Do not remove desiccant. Keep the bottle tightly closed after first opening.
KOSELUGO Oral Granules
Store and transport KOSELUGO oral granules refrigerated at 2°C to 8°C (36°F to 46°F). After receipt, patients may store at room temperature 20°C to 25°C (68°F to 77°F). Do NOT exceed 30°C (86°F). KOSELUGO oral granules may clump together or stick to the capsule shell if exposed to high temperatures, which may lead to underdose. Dispense and store in the original bottle to protect from light and moisture. Do not remove desiccant. Keep the bottle tightly closed after first opening.
INFORMATION FOR PATIENTS SECTION
17 PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATION
Advise the patient to read the FDA-approved patient labeling (Patient Information and Instructions for Use).
Cardiomyopathy
Advise patients and caregivers that KOSELUGO can cause a reduction in LVEF and to immediately report any signs or symptoms of cardiomyopathy to their healthcare provider [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)].
Ocular Toxicity
Advise patients and caregivers that KOSELUGO can cause ocular toxicity that can lead to blindness and to contact their healthcare provider if the patient experiences any changes in their vision [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2)].
Gastrointestinal Toxicity
Advise patients and caregivers that KOSELUGO can cause diarrhea and to contact their healthcare provider at the onset of diarrhea [see Warnings and Precautions (5.3)].
Skin Toxicity
Advise patients and caregivers that KOSELUGO can cause serious skin toxicities and to contact their healthcare provider for severe skin changes [see Warnings and Precautions (5.4)].
Increased Creatine Phosphokinase
Advise patients and caregivers that KOSELUGO can cause increased CPK and to report any signs and symptoms of muscle pain or weakness to their healthcare provider [see Warnings and Precautions (5.5)].
Increased Vitamin E Levels and Risk of Bleeding
Advise patients and caregivers to notify their healthcare provider if they are taking a supplement containing vitamin E, a vitamin-K antagonist or an anti- platelet agent [see Warnings and Precautions (5.6)].
Embryo-Fetal Toxicity
•
Advise pregnant women and females of reproductive potential of the potential risk to a fetus. Advise females of reproductive potential to inform their healthcare provider of a known or suspected pregnancy [see Warnings and Precautions (5.7), Use in Specific Populations (8.1)].
•
Advise females of reproductive potential to use effective contraception during treatment with KOSELUGO and for 1 week after the last dose [see Use in Specific Populations (8.3)].
•
Advise males with female partners of reproductive potential to use effective contraception during treatment with KOSELUGO and for 1 week after the last dose [see Use in Specific Populations (8.3), Nonclinical Toxicology (13.1)].
Lactation
Advise women not to breastfeed during treatment with KOSELUGO and for 1 week after the last dose [see Use in Specific Populations (8.2)].
Drug Interactions
Advise patients and caregivers to inform their healthcare provider of all concomitant medications, including prescription medicines, over-the-counter drugs, vitamins, and herbal products. Inform patients to avoid St. John’s wort, grapefruit or grapefruit juice while taking KOSELUGO [see Drug Interactions (7)].
Dosing and Administration
Inform patients and caregivers on how to take KOSELUGO and what to do for missed or vomited doses [see Dosage and Administration (2.1)].
Distributed by:
AstraZeneca Pharmaceuticals LP
Wilmington, DE 19850
© AstraZeneca 2025
INSTRUCTIONS FOR USE SECTION
Instructions for Use
|
INSTRUCTIONS FOR USE KOSELUGO**®**** (ko SEL u go)** (selumetinib) oral granules | |
|
This Instructions for Use contains information on how to take or give KOSELUGO oral granules. Read this Instructions for Use before taking or giving KOSELUGO oral granules and each time you get a refill. There may be new information. This information does not take the place of talking to your healthcare provider about your or your child’s medical condition or treatment. Talk to your healthcare provider or pharmacist if you have any questions about how to take or give KOSELUGO oral granules. | |
|
Important Information You Need to Know Before Taking or Giving KOSELUGO oral granules • • • • • • • • • • Supplies needed to prepare a dose of KOSELUGO oral granules: • • • • | |
|
Preparing KOSELUGO oral granules | |
|
Step 1: Wash and dry your hands thoroughly. |
|
|
Step 2: Open the bottle(s) and take out the number of capsule(s) needed for your prescribed dose of KOSELUGO oral granules. |
|
|
Step 3: Add a small amount (about 1 to 3 teaspoons) of smooth yogurt, or fruit puree containing apple, banana, pear, or strawberry onto the spoon or into a small cup. • |
|
|
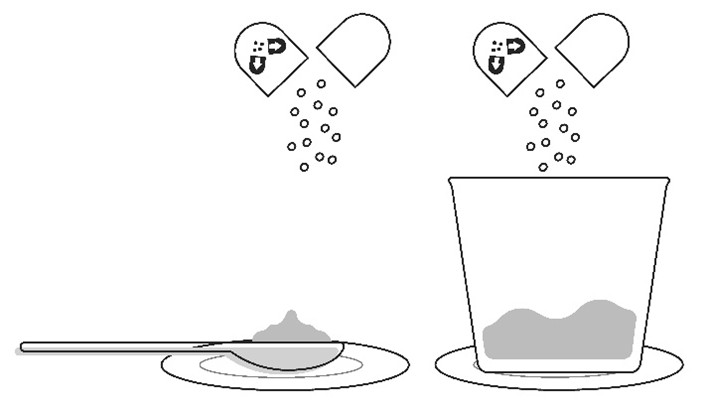
Step 4: Place the spoon or cup on the paper towel or plate. Carefully open the capsule(s) one at a time and sprinkle the entire contents of the capsule (oral granules) onto the food that is on the spoon or in the small cup. • • |
Important: The oral granules should flow freely inside the capsule.Do not use the capsule if the oral granules are clumped or stuck inside the capsule shell. Contact your pharmacy if this happens. |
|
Taking or giving KOSELUGO oral granules | |
|
**Step 5:**Take or give the KOSELUGO oral granules and food mixture within 30 minutes of preparing the dose. Swallow the mixture without chewing while seated upright.Do not save for future use. Note: • • |
|
|
Step 6: If you used a cup to prepare KOSELUGO oral granules, add more of the same food into the cup and take or give all of the mixture to make sure you get the full dose. |
|
|
Clean up • • | |
|
Storing KOSELUGO oral granules • • • • • Keep KOSELUGO and all medicines out of the reach of children. | |
|
Disposing of KOSELUGO oral granules • | |
|
Distributed by: AstraZeneca Pharmaceuticals LP, Wilmington, DE 19850 ©AstraZeneca 2025 For more information, go to website www.KOSELUGO.com or call 1 800 236 9933. |
This Instructions for Use has been approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration. approved: Sep/2025
SPL PATIENT PACKAGE INSERT SECTION
|
Patient Information | |
|
KOSELUGO**®**** (ko SEL u go)** (selumetinib) capsules, for oral use |
KOSELUGO® (ko SEL u go) (selumetinib) oral granules |
|
What is KOSELUGO? KOSELUGO is a prescription medicine that is used to treat children 1 year of age and older with neurofibromatosis type 1 (NF1) who have plexiform neurofibromas that cannot be completely removed by surgery. It is not known if KOSELUGO is safe and effective in children under 1 years of age. | |
|
Before taking KOSELUGO, tell your healthcare provider about all of your medical conditions, including if you: • • • • Females who are able to become pregnant: ∘ ∘ ∘ Males with female partners who are able to become pregnant: ∘ • ∘ ∘ Tell your healthcare provider about all the medicines you take, including prescription and over-the-counter medicines, vitamins, or herbal supplements. Certain medicines may affect the way KOSELUGO works. Especially tell your healthcare provider if you are taking a supplement containing vitamin E, aspirin, blood thinners, or other medicines to treat blood clots. KOSELUGO capsules contain vitamin E, which may increase your risk of bleeding. | |
|
How should I take KOSELUGO? • • • • • • KOSELUGO comes in capsules and oral granules. • ∘ ∘ ∘ • ∘ ∘ ∘ ∘ ∘ ∘ ∘ ∘ ∘ ∘ | |
|
What should I avoid while taking KOSELUGO? Avoid St John’s wort, grapefruit or grapefruit juice, and Seville orange during treatment with KOSELUGO. | |
|
What are the possible side effects of KOSELUGO? KOSELUGO may cause serious side effects, including: • | |
|
∘ ∘ ∘ |
∘ ∘ |
|
• | |
|
∘ ∘ |
∘ ∘ |
|
• • | |
|
∘ ∘ ∘ ∘ |
∘ ∘ ∘ ∘ |
|
Increased level of an enzyme called creatine phosphokinase (CPK) in your blood and muscle problems. Muscle problems are common with KOSELUGO and can also be severe. Treatment with KOSELUGO may increase the level of enzyme in your blood called creatine phosphokinase (CPK), which may be a sign of muscle damage. Increased level of CPK in the blood is common during treatment with KOSELUGO and can also be severe. Your healthcare provider should do a blood test to check your blood levels of CPK before and during treatment with KOSELUGO. Tell your healthcare provider right away if you get any of the following signs or symptoms: | |
|
∘ ∘ |
∘ |
|
Your healthcare provider may change your dose, temporarily stop, or permanently stop treatment with KOSELUGO if you have any of these side effects. The most common side effects of KOSELUGO include: | |
|
∘ ∘ ∘ ∘ |
∘ ∘ ∘ ∘ |
|
These are not all of the possible side effects of KOSELUGO. Call your doctor for medical advice about side effects. You may report side effects to FDA at 1 800 FDA 1088. | |
|
How should I store KOSELUGO? • • • • • Keep KOSELUGO and all medicines out of the reach of children. | |
|
General information about the safe and effective use of KOSELUGO. Medicines are sometimes prescribed for purposes other than those listed in a Patient Information leaflet.Do not use KOSELUGO for a condition for which it was not prescribed.Do not give KOSELUGO to other people, even if they have the same symptoms you have. It may harm them. You can ask your pharmacist or healthcare provider for information about KOSELUGO that is written for a healthcare professional. | |
|
What are the ingredients in KOSELUGO? Active ingredient: selumetinib. KOSELUGO capsule inactive ingredients: • • • • • KOSELUGO oral granule inactive ingredients: • • • • • • Distributed by: AstraZeneca Pharmaceuticals LP, Wilmington, DE 19850 ©AstraZeneca 2025 For more information, go to website www.KOSELUGO.com or call 1-800-236-9933 |
This Patient Information has been approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration. Revised: 09/2025