Ellence
These highlights do not include all the information needed to use ELLENCE safely and effectively. See full prescribing information for ELLENCE. ELLENCE (epirubicin hydrochloride injection) Initial U.S. Approval: 1999
0a03c798-a652-4895-b29c-3b521a89ba42
HUMAN PRESCRIPTION DRUG LABEL
Jul 13, 2023
Pharmacia & Upjohn Company LLC
DUNS: 618054084
Products 2
Detailed information about drug products covered under this FDA approval, including NDC codes, dosage forms, ingredients, and administration routes.
epirubicin hydrochloride
Product Details
FDA regulatory identification and product classification information
FDA Identifiers
Product Classification
Product Specifications
INGREDIENTS (5)
epirubicin hydrochloride
Product Details
FDA regulatory identification and product classification information
FDA Identifiers
Product Classification
Product Specifications
INGREDIENTS (5)
Drug Labeling Information
WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS SECTION
5 WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS
5.1 Cardiac Toxicity
ELLENCE and other anthracycline drugs can result in either early (or acute) or late (delayed) cardiac toxicity.
The principal manifestations of early cardiac toxicity are sinus tachycardia and/or electrocardiogram (ECG) abnormalities such as non-specific ST-T wave changes. However, tachycardia (including premature ventricular contractions and ventricular tachycardia), bradycardia, as well as atrioventricular and bundle-branch block have been reported. Early cardiac toxicity does not usually predict the subsequent occurrence of delayed cardiotoxicity and generally should not be considered a reason for suspending treatment with ELLENCE.
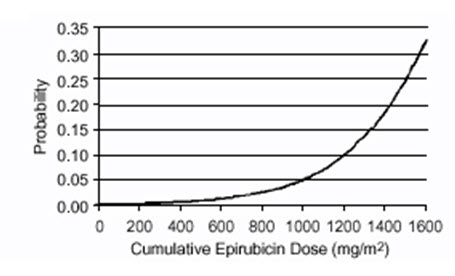
Delayed cardiac toxicity is manifested by reduced left ventricular ejection fraction (LVEF) and/or signs and symptoms of congestive heart failure (CHF). If it occurs, late cardiotoxicity usually develops late during therapy with ELLENCE or within 2 to 3 months after completion of treatment, but there are reports of it occurring several months to years after treatment termination. In a retrospective survey, including 9144 patients, mostly with solid tumors in advanced stages, the probability of developing CHF increased with increasing cumulative doses of ELLENCE (Figure 1). In another retrospective survey of 469 ELLENCE-treated patients with metastatic or early breast cancer, the reported risk of CHF was comparable to that observed in the larger study of over 9000 patients.
Given the risk of cardiac toxicity, cumulative doses of 900 mg/m2 ELLENCE should generally be avoided.
Figure 1. Risk of CHF in 9144 Patients Treated with ELLENCE
Prior history of cardiovascular disease, prior or concomitant radiotherapy to the mediastinal/pericardial area, previous therapy with other anthracyclines or anthracenediones, and concomitant use of other cardiotoxic drugs, increase the risk of developing late cardiac toxicity. Avoid administration of ELLENCE in combination with other cardiotoxic drugs. Although not formally tested, it is probable that the toxicity of ELLENCE and other anthracyclines or anthracenediones is additive. Cardiac toxicity with ELLENCE may occur at lower cumulative doses whether or not cardiac risk factors are present. Patients receiving ELLENCE after stopping treatment with other cardiotoxic drugs, especially those with long half-lives such as trastuzumab, may be at increased risk of developing cardiotoxicity [see Dosage and Administration (2) and Drug Interaction (7.1)].
Perform a baseline ECG and evaluation of LVEF prior to initiating treatment with ELLENCE. Monitor LVEF during the course of treatment and consider discontinuation of ELLENCE if LVEF decrease and/or signs or symptoms of CHF develop. Closely monitor patients with other risk factors for cardiac toxicity, particularly prior administration of anthracycline or anthracenedione.
5.2 Secondary Malignancies
The risk of developing secondary acute myelogenous leukemia and myelodysplastic syndrome (MDS), is increased following treatment with ELLENCE and other anthracyclines. Cumulative risk of secondary acute myelogenous leukemia or myelodysplastic syndrome (AML/MDS) of about 0.27% at 3 years, 0.46% at 5 years, and 0.55% at 8 years. These leukemias generally occur within 1 to 3 years of treatment [see Adverse Reactions (6.1)].
5.3 Extravasation and Tissue Necrosis
Extravasation of ELLENCE can result in severe local tissue injury manifesting as blistering, ulceration, and necrosis requiring wide excision of the affected area and skin grafting. Extravasation should be considered if a patient experiences a burning or stinging sensation or shows other evidence indicating peri-venous infiltration or extravasation; however, extravasation may be present in patients who do not experience a stinging or burning sensation or when blood return is present on aspiration of the infusion needle.
Venous sclerosis may result from an injection into a small vessel or from repeated injections into the same vein. Administer ELLENCE slowly into the tubing of a freely running intravenous infusion. Patients receiving initial therapy at the recommended starting doses of 100–120 mg/m2 should have ELLENCE infused over 15–20 minutes. For patients who require lower ELLENCE starting doses due to organ dysfunction or who require modification of ELLENCE doses during therapy, the ELLENCE infusion time may be proportionally decreased, but should not be less than 3 minutes [see Dosage and Administration (2.3)]. If possible, avoid veins over joints or in extremities with compromised venous or lymphatic drainage. Facial flushing, as well as local erythematous streaking along the vein, may be indicative of excessively rapid administration. It may precede local phlebitis or thrombophlebitis.
Immediately terminate infusion and restart in another vein if a burning or stinging sensation indicates perivenous infiltration. Perivenous infiltration may occur without causing pain. If extravasation is suspected, immediately discontinue the intravenous injection or continuous intravenous infusion [see Dosage and Administration (2.3)]. Apply ice to the site intermittently for 15 minutes, 4 times a day for 3 days. If appropriate, administer dexrazoxane at the site of extravasation as soon as possible and within the first 6 hours after extravasation.
5.4 Severe Myelosuppression
ELLENCE can cause severe myelosuppression [see Adverse Reactions (6.1). Obtain complete blood counts prior to each treatment and carefully monitor patients during treatment for possible clinical complications due to myelosuppression. Delay the next dose of ELLENCE if severe myelosuppression has not improved. Consider dose reduction for patients with prolonged myelosuppression based on the severity of reaction [see Dosage and Administration (2.3)].
5.5 Use in Patients with Hepatic Impairment
The major route of elimination of epirubicin is the hepatobiliary system [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)]. Evaluate serum total bilirubin and AST levels before and during treatment with ELLENCE. Patients with elevated bilirubin or AST may experience slower clearance of drug with an increase in overall toxicity. Lower doses are recommended in these patients [see Dosage and Administration (2.2)]. Patients with severe hepatic impairment have not been evaluated; therefore, do not use ELLENCE in this patient population [see Contraindications (4)].
5.6 Use in Patients with Renal Impairment
Assess serum creatinine before and during therapy. Dosage adjustment is necessary in patients with serum creatinine >5 mg/dL [see Dosage and Administration (2.2) and Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)]. Patients undergoing dialysis have not been studied.
5.7 Tumor-Lysis Syndrome
ELLENCE can induce tumor lysis syndrome in patients with rapidly growing tumors. Evaluate blood uric acid levels, potassium, calcium, phosphate, and creatinine after initial treatment. Consider hydration, urine alkalinization, and prophylaxis with allopurinol to minimize hyperuricemia and potential complications of tumor lysis syndrome.
5.8 Immunosuppressant Effects/Increased Susceptibility to Infections
Administration of live or live-attenuated vaccines in patients immunocompromised by chemotherapeutic agents including epirubicin, may result in serious or fatal infections. Avoid vaccination with a live vaccine in patients receiving ELLENCE. Killed or inactivated vaccines may be administered; however, the response to such vaccines may be diminished.
5.9 Thrombophlebitis and Thromboembolic Events
Thrombophlebitis and thromboembolic events, including pulmonary embolism (in some cases fatal) have been reported with the use of ELLENCE.
5.10 Potentiation of Radiation Toxicity and Radiation Recall
ELLENCE can increase radiation-induced toxicity to the myocardium, mucosa, skin, and liver. Radiation recall, including but not limited to cutaneous and pulmonary toxicity, can occur in patients who receive ELLENCE after prior radiation therapy.
5.11 Embryo-Fetal Toxicity
Based on findings from animals and its mechanism of action, ELLENCE can cause fetal harm when administered to a pregnant woman; avoid the use of ELLENCE during the 1st trimester. Available human data do not establish the presence or absence of major birth defects and miscarriage related to the use of epirubicin during the 2nd and 3rd trimesters. In animal reproduction studies, epirubicin was embryo-fetal lethal and caused structural abnormalities in rats and rabbits at doses less than the maximum recommended human dose on a body surface area basis. Advise pregnant women and females of reproductive potential of the potential risk to a fetus. Advise female patients of reproductive potential to use effective contraception during treatment and for 6 months after the last dose of ELLENCE. Advise male patients with female partners of reproductive potential to use effective contraception during treatment and for 3 months after the last dose of ELLENCE. Advise male patients with pregnant partners to use condoms during treatment and for at least 7 days after the last dose of ELLENCE [see Use in Specific Populations (8.1, 8.3), Clinical Pharmacology (12.1), and Nonclinical Toxicology (13.1)].
•
Use in Patients with Hepatic Impairment: Monitor serum total bilirubin and AST levels before and during treatment with ELLENCE. In patients with elevated serum AST or serum total bilirubin, dosage reductions or discontinuation may be required (2.3, 5.5).
•
Tumor Lysis Syndrome: Evaluate blood uric acid levels, potassium, calcium, phosphate, and creatinine after initial treatment. Consider hydration, urine alkalinization, and prophylaxis with allopurinol to minimize potential complications of hyperuricemia and tumor lysis syndrome (5.7).
•
Thrombophlebitis and Thromboembolic Events: Thrombophlebitis and thromboembolic events, including pulmonary embolism (in some cases fatal) have been reported with the use of ELLENCE. Venous sclerosis may result from an injection into a small vessel or from repeated injections into the same vein (5.9).
•
Administration of live or live-attenuated vaccines in patients immunocompromised by chemotherapeutic agents including ELLENCE, may result in serious or fatal infections (5.7).
•
Potentiation of Radiation Toxicity and Radiation Recall: Administration of ELLENCE after previous radiation therapy may induce an inflammatory recall reaction at the site of the irradiation (5.10).
•
Embryo-Fetal Toxicity: ELLENCE can cause fetal harm. Advise patients of the potential risk to a fetus and to use effective contraception (5.11, 8.1, 8.3).
DOSAGE & ADMINISTRATION SECTION
2 DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
2.1 Important Administration Instructions
When possible, to reduce the risk of developing cardiotoxicity in patients receiving ELLENCE after stopping treatment with other cardiotoxic agents, especially those with long half-lives such as trastuzumab, delay ELLENCE-based therapy until the other agents have cleared from the circulation [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)].
Antiemetics may reduce nausea and vomiting; consider use of antiemetics before administration of ELLENCE or when clinically indicated, particularly when given in conjunction with other emetigenic drugs [see Adverse Reactions (6.1)].
Patients administered the 120 mg/m2 regimen of ELLENCE should receive prophylactic antibiotic therapy.
2.2 Recommended Dose
The recommended dose of ELLENCE is 100 to 120 mg/m2 administered as an intravenous bolus [see Dosage and Administration (2.4)].
The following regimens are recommended:
|
CEF-120: |
Cyclophosphamide |
75 mg/m2 oral on Days 1 to 14 |
|
ELLENCE |
60 mg/m2 intravenously on Days 1 and 8 | |
|
5-Fluorouracil |
500 mg/m2 intravenously on Days 1 and 8 | |
|
Repeat every 28 days for 6 cycles | ||
|
FEC-100: |
5-Fluorouracil |
500 mg/m2 intravenously on Day 1 |
|
ELLENCE |
100 mg/m2 intravenously on Day 1 | |
|
Cyclophosphamide |
500 mg/m2 intravenously on Day 1 | |
|
Repeat every 21 days for 6 cycles |
Administer ELLENCE in repeated 3- to 4-week cycles. The total dose of ELLENCE may be given on Day 1 of each cycle or divided equally and given on Days 1 and 8 of each cycle.
2.3 Dose Modifications
ELLENCE dosage adjustments for hematologic and non-hematologic toxicities within a cycle of treatment, is based on nadir platelet counts <50,000/mm3, absolute neutrophil counts (ANC) <250/mm3, neutropenic fever, or Grades 3/4 nonhematologic toxicity. Reduce ELLENCE Day 1 dose in subsequent cycles to 75% of the Day 1 dose given in the current cycle. Delay Day 1 chemotherapy in subsequent courses of treatment until platelet counts are ≥100,000/mm3, ANC ≥1500/mm3, and nonhematologic toxicities have recovered to ≤ Grade 1.
Cardiac Toxicity
Discontinue ELLENCE in patients who develop signs or symptoms of cardiomyopathy [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)].
Bone Marrow Dysfunction
Consider administering a lower starting dose (75–90 mg/m2) for heavily pretreated patients, patients with pre-existing bone marrow depression, or in the presence of neoplastic bone marrow infiltration [see Warnings and Precautions (5.4)]. For patients receiving a divided dose of ELLENCE (Day 1 and Day 8), the Day 8 dose should be 75% of Day 1 if platelet counts are 75,000–100,000/mm3 and ANC is 1000 to 1499/mm3. If Day 8 platelet counts are <75,000/mm3, ANC <1000/mm3, or Grades 3/4 nonhematologic toxicity has occurred, omit the Day 8 dose.
Hepatic Impairment
In patients with elevated serum AST or serum total bilirubin concentrations [see Warnings and Precautions (5.5) and Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)], reduce dosage as follows:
•
Bilirubin 1.2 to 3 mg/dL or AST 2 to 4 times upper limit of normal 1/2 of recommended starting dose
•
Bilirubin > 3 mg/dL or AST > 4 times upper limit of normal 1/4 of recommended starting dose
Renal Impairment
Consider lower doses in patients with severe renal impairment (serum creatinine > 5 mg/dL) [see Warnings and Precautions (5.6) and Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)].
2.4 Preparation and Administration Precautions
Preparation
Storage of the solution for injection at refrigerated conditions can result in the formation of a gelled product. This gelled product will return to a slightly viscous to mobile solution after 2 to a maximum of 4 hours equilibration at controlled room temperature (15–25°C).
Inspect parenteral drug products visually for particulate matter and discoloration prior to administration, whenever solution and container permit.
ELLENCE is a cytotoxic drug. Follow applicable special handling and disposable procedures1 [see References (15)].
Incompatibilities
Avoid prolonged contact with any solution of an alkaline pH as it will result in hydrolysis of the drug. Do not mix ELLENCE with heparin or fluorouracil due to chemical incompatibility that may lead to precipitation.
ELLENCE can be used in combination with other antitumor agents, but do not mix with other drugs in the same syringe.
Administration
Administer ELLENCE into the tubing of a freely flowing intravenous infusion (0.9% sodium chloride or 5% glucose solution). Patients receiving initial therapy at the recommended starting doses of 100–120 mg/m2 should generally have ELLENCE infused over 15–20 minutes.
For patients who require lower ELLENCE starting doses due to organ dysfunction or who require modification of ELLENCE doses during therapy, the ELLENCE infusion time may be proportionally decreased, but should not be less than 3 minutes. This technique is intended to minimize the risk of thrombosis or perivenous extravasation, which could lead to severe cellulitis, vesication, or tissue necrosis.
A direct push injection isnot recommended due to the risk of extravasation, which may occur even in the presence of adequate blood return upon needle aspiration. Venous sclerosis may result from injection into small vessels or repeated injections into the same vein [see Warnings and Precautions (5.3)].
Storage
Use ELLENCE within 24 hours of first penetration of the rubber stopper. Discard any unused solution.
•
The recommended starting dose of ELLENCE is 100 to 120 mg/m2. Dosage reductions are possible when given in certain combinations (2.2).
•
Administer intravenously in repeated 3- to 4-week cycles, either total dose on Day 1 of each cycle or divided equally and given on Days 1 and 8 of each cycle (2.2).
•
Consider use of antiemetics when given in conjunction with other emetigenic drugs (2.1).
•
Patients administered the 120 mg/m2 regimen of ELLENCE should receive prophylactic antibiotic therapy (2.1).
•
Adjust dosage after the first treatment cycle based on hematologic and nonhematologic toxicities (2.3).
•
Reduce dose in patients with hepatic impairment (2.3, 8.6).
•
Consider lower doses in patients with severe renal impairment (2.3, 8.7).
