Levetiracetam
These highlights do not include all the information needed to use LEVETIRACETAM EXTENDED-RELEASE TABLETS safely and effectively. See full prescribing information for LEVETIRACETAM EXTENDED-RELEASE TABLETS. LEVETIRACETAM extended-release tablets, for oral use Initial U.S. Approval: 1999
c508a392-0603-477d-8a45-3ec550371111
HUMAN PRESCRIPTION DRUG LABEL
Jan 25, 2024
Westminster Pharmaceuticals, LLC
DUNS: 079516651
Products 2
Detailed information about drug products covered under this FDA approval, including NDC codes, dosage forms, ingredients, and administration routes.
Levetiracetam
Product Details
FDA regulatory identification and product classification information
FDA Identifiers
Product Classification
Product Specifications
INGREDIENTS (9)
Levetiracetam
Product Details
FDA regulatory identification and product classification information
FDA Identifiers
Product Classification
Product Specifications
INGREDIENTS (9)
Drug Labeling Information
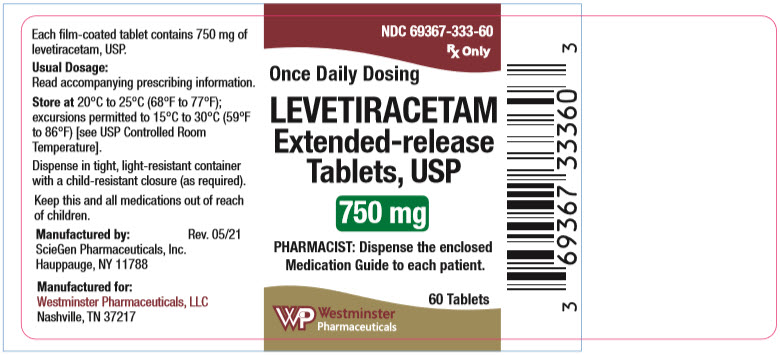
PACKAGE LABEL.PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL
PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL - 750 mg Tablet Bottle Label
NDC 69367-333-60
Rx Only
Once Daily Dosing
LEVETIRACETAM
Extended-release
Tablets, USP
750 mg
PHARMACIST: Dispense the enclosed
Medication Guide to each patient.
60 Tablets
Westminster
Pharmaceuticals
ADVERSE REACTIONS SECTION
6 ADVERSE REACTIONS
The following adverse reactions are discussed in more details in other sections of labeling:
- Behavioral abnormalities and Psychotic Symptoms [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)]
- Suicidal Behavior and Ideation [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2)]
- Somnolence and Fatigue [see Warnings and Precautions (5.3)]
- Anaphylaxis and Angioedema [see Warnings and Precautions (5.4)]
- Serious Dermatological Reactions [see Warnings and Precautions (5.5)]
- Coordination Difficulties [see Warnings and Precautions (5.6)]
- Hematologic Abnormalities [see Warnings and Precautions (5.8)]
6.1 Clinical Trials Experience
Because clinical trials are conducted under widely varying conditions, adverse reaction rates observed in the clinical trials of a drug cannot be directly compared to rates in the clinical trials of another drug and may not reflect the rates observed in practice.
Levetiracetam Extended-Release Tablets
In the controlled clinical study in patients with partial-onset seizures [see Clinical Studies (14.1)], the most common adverse reactions in patients receiving levetiracetam extended-release tablets in combination with other AEDs, for events with rates greater than placebo, were irritability and somnolence.
Table 3 lists adverse reactions that occurred in at least 5% of epilepsy patients receiving levetiracetam extended-release tablets in the placebo- controlled study and were numerically more common than in patients treated with placebo. In this study, either levetiracetam extended-release tablets or placebo was added to concurrent AED therapy.
Table 3: Adverse Reactions in the Placebo-Controlled, Adjunctive Study in Patients Experiencing Partial-Onset Seizures|
Levetiracetam extended-release tablets |
Placebo | |
|---|---|---|
|
Influenza |
8 |
4 |
|
Somnolence |
8 |
3 |
|
Irritability |
7 |
0 |
|
Nasopharyngitis |
7 |
5 |
|
Dizziness |
5 |
3 |
|
Nausea |
5 |
3 |
Discontinuation or Dose Reduction in the Levetiracetam Extended-Release Tablets Controlled Clinical Study
In the controlled clinical study, 5% of patients receiving levetiracetam extended-release tablets and 3% receiving placebo discontinued as a result of an adverse reaction. The adverse reactions that resulted in discontinuation and that occurred more frequently in levetiracetam extended-release tablets- treated patients than in placebo-treated patients were asthenia, epilepsy, mouth ulceration, rash, and respiratory failure. Each of these adverse reactions led to discontinuation in a levetiracetam extended-release tablets- treated patient and no placebo-treated patients.
Immediate-Release Levetiracetam Tablets
Table 4 lists the adverse reactions in the controlled studies of immediate- release levetiracetam tablets in adult patients experiencing partial-onset seizures [see Clinical Studies (14.2)]. Although the pattern of adverse reactions in the levetiracetam extended-release tablets study seems somewhat different from that seen in partial-onset seizure controlled studies for immediate-release levetiracetam tablets, this is possibly due to the much smaller number of patients in this study compared to the immediate-release tablet studies. The adverse reactions for levetiracetam extended-release tablets are expected to be similar to those seen with immediate-release levetiracetam tablets.
Adults
In controlled clinical studies of immediate-release levetiracetam tablets as adjunctive therapy to other AEDs in adults with partial-onset seizures, the most common adverse reactions, for events with rates greater than placebo, were somnolence, asthenia, infection, and dizziness.
Table 4 lists adverse reactions that occurred in at least 1% of adult epilepsy patients receiving immediate-release levetiracetam tablets in placebo- controlled studies and were numerically more common than in patients treated with placebo. In these studies, either immediate-release levetiracetam tablets or placebo was added to concurrent AED therapy.
Table 4: Adverse Reactions in Pooled Placebo-Controlled, Adjunctive Studies in Adults Experiencing Partial-Onset Seizures|
Levetiracetam Tablets |
Placebo | |
|---|---|---|
|
Asthenia |
15 |
9 |
|
Somnolence |
15 |
8 |
|
Headache |
14 |
13 |
|
Infection |
13 |
8 |
|
Dizziness |
9 |
4 |
|
Pain |
7 |
6 |
|
Pharyngitis |
6 |
4 |
|
Depression |
4 |
2 |
|
Nervousness |
4 |
2 |
|
Rhinitis |
4 |
3 |
|
Anorexia |
3 |
2 |
|
Ataxia |
3 |
1 |
|
Vertigo |
3 |
1 |
|
Amnesia |
2 |
1 |
|
Anxiety |
2 |
1 |
|
Cough Increased |
2 |
1 |
|
Diplopia |
2 |
1 |
|
Emotional Lability |
2 |
0 |
|
Hostility |
2 |
1 |
|
Paresthesia |
2 |
1 |
|
Sinusitis |
2 |
1 |
Pediatric Patients 4 Years to <16 Years
In a pooled analysis of two controlled pediatric clinical studies in children 4 to 16 years of age with partial-onset seizures [see Clinical Studies (14.3)], the adverse reactions most frequently reported with the use of immediate-release levetiracetam in combination with other AEDs, and with greater frequency than in patients on placebo, were fatigue, aggression, nasal congestion, decreased appetite, and irritability.
Table 5 lists adverse reactions that occurred in at least 2% of pediatric patients treated with immediate-release levetiracetam and were more common than in pediatric patients on placebo. In these studies, either immediate- release levetiracetam or placebo was added to concurrent AED therapy. Adverse reactions were usually mild to moderate in intensity.
Table 5: Adverse Reactions in Pooled Placebo-Controlled, Adjunctive Studies in Pediatric Patients Ages 4 to 16 Years Experiencing Partial-Onset Seizures|
Levetiracetam Tablets |
Placebo | |
|---|---|---|
|
Headache |
19 |
15 |
|
Nasopharyngitis |
15 |
12 |
|
Vomiting |
15 |
12 |
|
Somnolence |
13 |
9 |
|
Fatigue |
11 |
5 |
|
Aggression |
10 |
5 |
|
Upper Abdominal Pain |
9 |
8 |
|
Cough |
9 |
5 |
|
Nasal Congestion |
9 |
2 |
|
Decreased Appetite |
8 |
2 |
|
Abnormal Behavior |
7 |
4 |
|
Dizziness |
7 |
5 |
|
Irritability |
7 |
1 |
|
Pharyngolaryngeal Pain |
7 |
4 |
|
Diarrhea |
6 |
2 |
|
Lethargy |
6 |
5 |
|
Insomnia |
5 |
3 |
|
Levetiracetam Tablets |
Placebo | |
|
Agitation |
4 |
1 |
|
Anorexia |
4 |
3 |
|
Head Injury |
4 |
0 |
|
Constipation |
3 |
1 |
|
Contusion |
3 |
1 |
|
Depression |
3 |
1 |
|
Fall |
3 |
2 |
|
Influenza |
3 |
1 |
|
Mood Altered |
3 |
1 |
|
Affect Lability |
2 |
1 |
|
Anxiety |
2 |
1 |
|
Arthralgia |
2 |
0 |
|
Confusional State |
2 |
0 |
|
Conjunctivitis |
2 |
0 |
|
Ear Pain |
2 |
1 |
|
Gastroenteritis |
2 |
0 |
|
Joint Sprain |
2 |
1 |
|
Mood Swings |
2 |
1 |
|
Neck Pain |
2 |
1 |
|
Rhinitis |
2 |
0 |
|
Sedation |
2 |
1 |
In controlled pediatric clinical studies in patients 4 to 16 years of age, 7% of patients treated with immediate-release levetiracetam tablets and 9% of patients on placebo discontinued as a result of an adverse event.
In addition, the following adverse reactions were seen in other controlled studies of immediate-release levetiracetam tablets: balance disorder, disturbance in attention, eczema, hyperkinesia, memory impairment, myalgia, personality disorders, pruritus, and blurred vision.
Comparison of Gender, Age and Race
There are insufficient data for levetiracetam extended-release tablets to support a statement regarding the distribution of adverse reactions by gender, age, and race.
6.2 Postmarketing Experience
The following adverse reactions have been identified during postapproval use of immediate-release levetiracetam tablets. Because these reactions are reported voluntarily from a population of uncertain size, it is not always possible to reliably estimate their frequency or establish a causal relationship to drug exposure.
The listing is alphabetized: abnormal liver function test, acute kidney injury, anaphylaxis, angioedema, agranulocytosis, choreoathetosis, drug reaction with eosinophilia and systemic symptoms (DRESS), dyskinesia, erythema multiforme, hepatic failure, hepatitis, hyponatremia, muscular weakness, obsessive-compulsive disorders (OCD), pancreatitis, pancytopenia (with bone marrow suppression identified in some of these cases), panic attack, thrombocytopenia, weight loss, and worsening of seizures including in patients with SCN8A mutations. Alopecia has been reported with immediate-release levetiracetam use; recovery was observed in majority of cases where immediate- release levetiracetam was discontinued.
Most common adverse reactions (incidence ≥5% more than placebo) include: somnolence and irritability (6.1)
To report SUSPECTED ADVERSE REACTIONS, contact Westminster Pharmaceuticals, LLC at 1-844-221-7294 or FDA at 1-800-FDA-1088 or www.fda.gov/medwatch.
USE IN SPECIFIC POPULATIONS SECTION
8 USE IN SPECIFIC POPULATIONS
8.1 Pregnancy
Pregnancy Exposure Registry
There is a pregnancy exposure registry that monitors pregnancy outcomes in women exposed to antiepileptic drugs (AEDs), including levetiracetam extended- release tablets during pregnancy. Encourage women who are taking levetiracetam extended-release tablets during pregnancy to enroll in the North American Antiepileptic Drug (NAAED) pregnancy registry by calling 1-888-233-2334 or visiting http://www.aedpregnancyregistry.org/.
Risk Summary
Prolonged experience with levetiracetam tablets in pregnant women has not identified a drug-associated risk of major birth defects or miscarriage, based on published literature, which includes data from pregnancy registries and reflects experience over two decades [see Human Data]. In animal studies, levetiracetam produced developmental toxicity (increased embryofetal and offspring mortality, increased incidences of fetal structural abnormalities, decreased embryofetal and offspring growth, neurobehavioral alterations in offspring) at doses similar to human therapeutic doses [see Animal Data].
In the U.S. general population, the estimated background risk of major birth defects and miscarriage in clinically recognized pregnancies is 2 to 4% and 15 to 20%, respectively. The background risk of major birth defects and miscarriage for the indicated population is unknown.
Clinical Considerations
Levetiracetam extended-release tablets levels may decrease during pregnancy [see Warnings and Precautions (5.9)].
Physiological changes during pregnancy may affect levetiracetam concentration. Decrease in levetiracetam plasma concentrations has been observed during pregnancy. This decrease is more pronounced during the third trimester. Dose adjustments may be necessary to maintain clinical response.
Data
Human Data
While available studies cannot definitively establish the absence of risk, data from the published literature and pregnancy registries have not established an association with levetiracetam use during pregnancy and major birth defects or miscarriage.
Animal Data
When levetiracetam (0 mg/kg/day, 400 mg/kg/day, 1,200 mg/kg/day, or 3,600 mg/kg/day) was administered orally to pregnant rats during the period of organogenesis, reduced fetal weights and increased incidence of fetal skeletal variations were observed at the highest dose tested. There was no evidence of maternal toxicity. The no-effect dose for adverse effects on embryofetal developmental in rats (1,200 mg/kg/day) is approximately 4 times the maximum recommended human dose (MRHD) of 3,000 mg on a body surface area (mg/m2) basis.
Oral administration of levetiracetam (0 mg/kg/day, 200 mg/kg/day, 600 mg/kg/day, or 1,800 mg/kg/day) to pregnant rabbits during the period of organogenesis resulted in increased embryofetal mortality and incidence of fetal skeletal variations at the mid and high dose and decreased fetal weights and increased incidence of fetal malformations at the high dose, which was associated with maternal toxicity. The no-effect dose for adverse effects on embryofetal development in rabbits (200 mg/kg/day) is approximately equivalent to the MRHD on a mg/m2 basis.
Oral administration of levetiracetam (0 mg/kg/day, 70 mg/kg/day, 350 mg/kg/day, or 1,800 mg/kg/day) to female rats throughout pregnancy and lactation led to an increased incidence of fetal skeletal variations, reduced fetal body weight, and decreased growth in offspring at the mid and high doses and increased pup mortality and neurobehavioral alterations in offspring at the highest dose tested. There was no evidence of maternal toxicity. The no- effect dose for adverse effects on pre- and postnatal development in rats (70 mg/kg/day) is less than the MRHD on a mg/m2 basis.
Oral administration of levetiracetam to rats during the latter part of gestation and throughout lactation produced no adverse developmental or maternal effects at doses of up to 1,800 mg/kg/day (6 times the MRHD on a mg/m2 basis).
8.2 Lactation
Risk Summary
Levetiracetam is excreted in human milk. There are no data on the effects of levetiracetam extended-release tablets on the breastfed infant, or the effects on milk production.
The developmental and health benefits of breastfeeding should be considered along with the mother's clinical need for levetiracetam extended-release tablets and any potential adverse effects on the breastfed infant from levetiracetam extended-release tablets or from the underlying maternal condition.
8.4 Pediatric Use
Safety and effectiveness in patients 12 years of age and older have been established based on pharmacokinetic data in adults and adolescents using levetiracetam extended-release tablets and efficacy and safety data in controlled pediatric studies using immediate-release levetiracetam [see Adverse Reactions (6.1), Clinical Pharmacology (12.3), and Clinical Studies (14.1)].
Safety and effectiveness in pediatric patients below the age of 12 have not been established.
A 3-month, randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled study was performed to assess the neurocognitive and behavioral effects of immediate-release levetiracetam as adjunctive therapy in 98 pediatric patients with inadequately controlled partial seizures, ages 4 to 16 years (levetiracetam N=64; placebo N=34). The target dose of immediate-release levetiracetam was 60 mg/kg/day. Neurocognitive effects were measured by the Leiter-R Attention and Memory (AM) Battery, which assesses various aspects of a child's memory and attention. Although no substantive differences were observed between the placebo- and levetiracetam-treated groups in the median change from baseline in this battery, the study was not adequate to assess formal statistical non- inferiority between the drug and placebo. The Achenbach Child Behavior Checklist (CBCL/6 to 18), a standardized validated tool used to assess a child's competencies and behavioral/emotional problems, was also assessed in this study. An analysis of the CBCL/6 to 18 indicated a worsening in aggressive behavior, one of the eight syndrome scores, in patients treated with levetiracetam [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)].
Juvenile Animal Toxicity Data
Studies of levetiracetam in juvenile rats (dosed on postnatal days 4 through 52) and dogs (dosed from postnatal weeks 3 through 7) at doses of up to 1,800 mg/kg/day (approximately 7 and 24 times, respectively, the maximum recommended pediatric dose of 60 mg/kg/day on a mg/m2 basis) did not demonstrate adverse effects on postnatal development.
8.5 Geriatric Use
There were insufficient numbers of elderly subjects in controlled trials of epilepsy to adequately assess the effectiveness of levetiracetam extended- release tablets in these patients. It is expected that the safety of levetiracetam extended-release tablets in elderly patients 65 and over would be comparable to the safety observed in clinical studies of immediate-release levetiracetam tablets.
There were 347 subjects in clinical studies of immediate-release levetiracetam that were 65 and over. No overall differences in safety were observed between these subjects and younger subjects. There were insufficient numbers of elderly subjects in controlled trials of epilepsy to adequately assess the effectiveness of immediate-release levetiracetam in these patients.
Levetiracetam is known to be substantially excreted by the kidney, and the risk of adverse reactions to this drug may be greater in patients with impaired renal function. Because elderly patients are more likely to have decreased renal function, care should be taken in dose selection, and it may be useful to monitor renal function [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)].
8.6 Renal Impairment
The effect of levetiracetam extended-release tablets on renally impaired patients was not assessed in the controlled study. However, it is expected that the effect on levetiracetam extended-release tablets-treated patients would be similar to the effect seen in controlled studies of immediate-release levetiracetam tablets. Clearance of levetiracetam is decreased in patients with renal impairment and is correlated with creatinine clearance [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)]. Dose adjustment is recommended for patients with impaired renal function [see Dosage and Administration (2.2)].
Pregnancy: Plasma levels of levetiracetam may be decreased and therefore need to be monitored closely during pregnancy. Based on animal data, may cause fetal harm (5.9, 8.1)
DOSAGE & ADMINISTRATION SECTION
2 DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
2.1 Recommended Dosing
For adults and adolescent patients, the recommended dosing for monotherapy and adjunctive therapy is the same; as outlined below.
Adults and Adolescents 12 Years of Age and Older Weighing 50 kg or More
Initiate treatment with a dose of 1,000 mg once daily. The once daily dosage may be adjusted in increments of 1,000 mg every 2 weeks to a maximum recommended daily dose of 3,000 mg/day once daily.
Administration
Levetiracetam extended-release tablets are administered once daily. Levetiracetam extended-release tablets should be swallowed whole. The tablets should not be chewed, broken, or crushed.
2.2 Dosage Adjustments in Adult Patients with Renal Impairment
Levetiracetam extended-release tablets dosing must be individualized according to the patient's renal function status. Recommended dosage adjustments for adults are shown in Table 1. In order to calculate the dose recommended for patients with renal impairment, creatinine clearance adjusted for body surface area must be calculated. To do this, an estimate of the patient's creatinine clearance (CLcr) in mL/min must first be calculated using the following formula:
|
CLcr= |
[140-age (years)] × weight (kg) |
(× 0.85 for female patients) | |
|
72 × serum creatinine (mg/dL) |
Then CLcr is adjusted for body surface area (BSA) as follows:
|
CLcr (mL/min/1.73m2)= |
CLcr (mL/min) |
× 1.73 | |
|
BSA subject (m2) |
|
Group |
Creatinine Clearance |
Dosage (mg) |
Frequency |
|---|---|---|---|
|
Normal |
|
1,000 to 3,000 |
Every 24 hours |
|
Mild |
50 to 80 |
1,000 to 2,000 |
Every 24 hours |
|
Moderate |
30 to 50 |
500 to 1,500 |
Every 24 hours |
|
Severe |
< 30 |
500 to 1,000 |
Every 24 hours |
2.3 Discontinuation of Levetiracetam Extended-Release Tablets
Avoid abrupt withdrawal from levetiracetam extended-release tablets in order to reduce the risk of increased seizure frequency and status epilepticus [see Warnings and Precautions (5.7)].
Initiate treatment with a dose of 1,000 mg once daily; increase by 1,000 mg every 2 weeks to a maximum recommended dose of 3,000 mg once daily (2)
See full prescribing information for use in patients with impaired renal function (2.1)
HOW SUPPLIED SECTION
16 HOW SUPPLIED/STORAGE AND HANDLING
16.1 How Supplied
Levetiracetam extended-release tablets, USP 500 mg are white, oval-shaped, film-coated tablets, debossed with "SG" on one side and "189" on other side. They are supplied in white HDPE bottles containing 60 tablets (NDC 69367-332-60).
Levetiracetam extended-release tablets, USP 750 mg are white, oval-shaped, film-coated tablets, debossed with "SG" on one side and "190" on other side. They are supplied in white HDPE bottles containing 60 tablets (NDC 69367-333-60).
16.2 Storage
Store at 20° to 25°C (68° to 77°F); excursions permitted to 15° to 30°C (59° to 86°F) [see USP Controlled Room Temperature].
