SUPPRELIN
These highlights do not include all the information needed to use SUPPRELIN LA safely and effectively. See full prescribing information for LA. LA (histrelin acetate) subcutaneous implant Initial U.S. Approval: 1991
d8fb000e-3cc9-4803-b71d-2cc597661977
HUMAN PRESCRIPTION DRUG LABEL
Apr 27, 2022
Endo Pharmaceuticals Inc.
DUNS: 178074951
Products 1
Detailed information about drug products covered under this FDA approval, including NDC codes, dosage forms, ingredients, and administration routes.
histrelin acetate
Product Details
FDA regulatory identification and product classification information
FDA Identifiers
Product Classification
Product Specifications
INGREDIENTS (6)
Drug Labeling Information
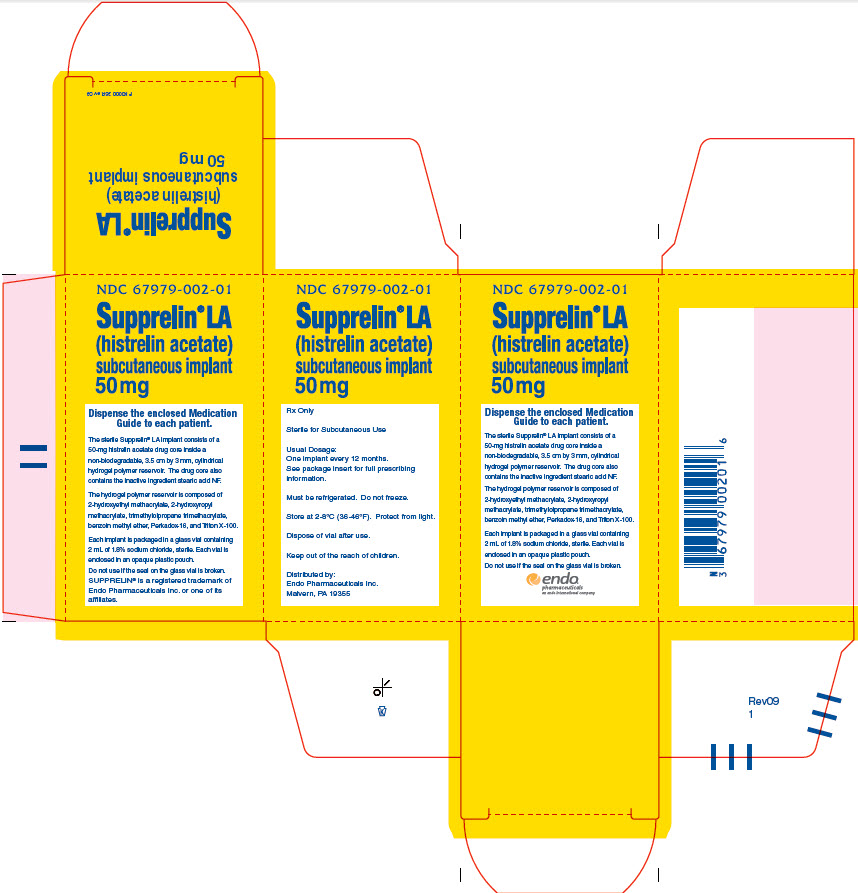
PACKAGE LABEL.PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL
Package Label – Principle Display Panel – Carton Label
WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS SECTION
5 WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS
5.1 Initial Agonistic Action
SUPPRELIN LA, like other GnRH agonists, initially causes a transient increase in serum concentrations of estradiol in females and testosterone in both sexes during the first week of treatment. Patients may experience worsening of symptoms or onset of new symptoms during this period. However, within 4 weeks of histrelin therapy, suppression of gonadal steroids occurs and manifestations of puberty decrease.
5.2 Implant Breakage
Implant insertion is a surgical procedure and it is important that the insertion instructions are followed to avoid potential complications. The insertion and removal of the implant should be done aseptically. Proper surgical technique is critical in minimizing adverse events related to the insertion and the removal of the histrelin implant. On occasion, localizing and/or removal of implant products have been difficult and imaging techniques were used, including ultrasound, CT, or MRI (note: the histrelin implant is not radiopaque). In some cases the implant broke during removal and multiple pieces were recovered. Confirm that the entire implant has been removed. If the implant was not retrieved completely, the remaining pieces should be removed following the instructions in the Suggested Removal Procedure section [see Dosage and Administration (2.2 )]. Rare events of spontaneous extrusion of the implant have been observed in clinical trials. During SUPPRELIN LA treatment, patients should be evaluated for evidence of clinical and biochemical suppression of CPP manifestations (see Section 5.6, Monitoring and Laboratory tests). Detailed instructions on the insertion and removal procedures of the implant are provided above [see Dosage and Administration (2.2)].
5.3 Psychiatric Events
Psychiatric events have been reported in patients taking GnRH agonists, including SUPPRELIN LA. Postmarketing reports with this class of drugs include symptoms of emotional lability, such as crying, irritability, impatience, anger, and aggression. Monitor for development or worsening of psychiatric symptoms during treatment with SUPPRELIN LA [see Adverse Reactions (6)].
5.4 Convulsions
Postmarketing reports of convulsions have been observed in patients receiving GnRH agonists, including SUPPRELIN LA. Reports with GnRH agonists have included patients with a history of seizures, epilepsy, cerebrovascular disorders, central nervous system anomalies or tumors, and patients on concomitant medications that have been associated with convulsions such as bupropion and SSRIs. Convulsions have also been reported in patients in the absence of any of the conditions mentioned above.
5.5 Pseudotumor Cerebri (Idiopathic Intracranial Hypertension)
Pseudotumor cerebri (idiopathic intracranial hypertension) have been reported in pediatric patients receiving GnRH agonists. Monitor patients for signs and symptoms of pseudotumor cerebri, including headache, papilledema, blurred vision, diplopia, loss of vision, pain behind the eye or pain with eye movement, tinnitus, dizziness, and nausea.
5.6 Monitoring and Laboratory Tests
LH, FSH and estradiol or testosterone should be monitored at 1 month post implantation then every 6 months thereafter. Additionally, height (for calculation of height velocity) and bone age should be assessed every 6-12 months.
- Initial Agnostic Action: Initial transient increases of estradiol and/or testosterone may cause a temporary worsening of symptoms (5.1).
- Implant Breakage: Have been observed during implant removal. Monitor luteinizing hormone, follicle stimulating hormone or testosterone for suppression of CPP (5.2, 5.6)
- Psychiatric Events: Have been reported in patients taking GnRH agonists. Events include emotional lability, such as crying, irritability, impatience, anger, and aggression. Monitor for development or worsening of psychiatric symptoms (5.3).
- Convulsions: Have been observed in patients receiving GnRH agonists with or without a history of seizures, epilepsy, cerebrovascular disorders, central nervous system anomalies or tumors, and in patients on concomitant medications that have been associated with convulsions (5.4).
- Pseudotumor Cerebri (Idiopathic Intracranial Hypertension): Have been reported in pediatric patients receiving GnRH agonists. Monitor patients for headache, papilledema, and blurred vision. (5.5)
