Methocarbamol
Methocarbamol Tablets USP Rx Only
f8bfb5cb-b7d0-4e09-b6bd-97a51d82c991
HUMAN PRESCRIPTION DRUG LABEL
Feb 5, 2024
XLCare Pharmaceuticals Inc.
DUNS: 080991142
Products 2
Detailed information about drug products covered under this FDA approval, including NDC codes, dosage forms, ingredients, and administration routes.
Methocarbamol
Product Details
FDA regulatory identification and product classification information
FDA Identifiers
Product Classification
Product Specifications
INGREDIENTS (9)
Methocarbamol
Product Details
FDA regulatory identification and product classification information
FDA Identifiers
Product Classification
Product Specifications
INGREDIENTS (9)
Drug Labeling Information
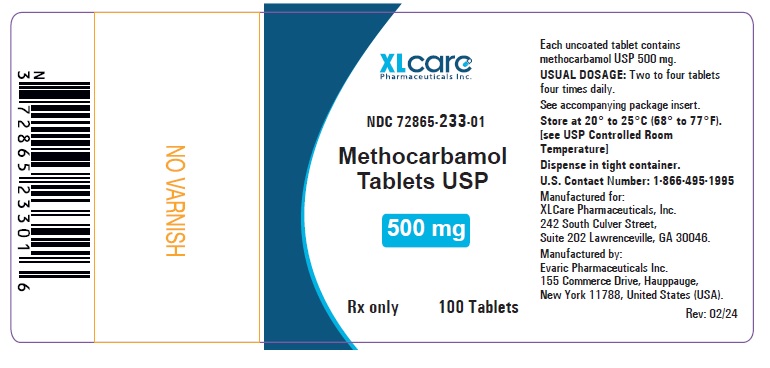
PACKAGE LABEL.PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL
PACKAGE LABEL.PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL
Container Label for Methocarbamol Tablets 500 mg, 100s Count.
Container Label for Methocarbamol Tablets 750 mg, 100s Count.

INDICATIONS & USAGE SECTION
INDICATIONS AND USAGE
Methocarbamol tablets are indicated as an adjunct to rest, physical therapy, and other measures for the relief of discomfort associated with acute, painful musculoskeletal conditions. The mode of action of methocarbamol has not been clearly identified, but may be related to its sedative properties. Methocarbamol does not directly relax tense skeletal muscles in man.
CONTRAINDICATIONS SECTION
CONTRAINDICATIONS
Methocarbamol tablets are contraindicated in patients hypersensitive to methocarbamol or to any of the tablet components.
ADVERSE REACTIONS SECTION
ADVERSE REACTIONS
Adverse reactions reported coincident with the administration of methocarbamol
include:
Body as a whole: Anaphylactic reaction, angioneurotic edema, fever, headache
Cardiovascular system: Bradycardia, flushing, hypotension, syncope,
thrombophlebitis
Digestive system:Dyspepsia, jaundice (including cholestatic jaundice), nausea
and vomiting
Hemic and lymphatic system:Leukopenia
Immune system: Hypersensitivity reactions
Nervous system:Amnesia, confusion, diplopia, dizziness or lightheadedness,
drowsiness, insomnia, mild muscular incoordination, nystagmus, sedation,
seizures (including grand mal), vertigo
Skin and special senses: Blurred vision, conjunctivitis, nasal congestion,
metallic taste, pruritus, rash, urticaria
DESCRIPTION SECTION
DESCRIPTION
Methocarbamol tablets USP a carbamate derivative of guaifenesin, is a central
nervous system (CNS) depressant with sedative and musculoskeletal relaxant
properties.
The chemical name of methocarbamol is 3-(2-methoxyphenoxy)-1, 2-propanediol
1-carbamate and has the empirical formula C 11H 15NO 5. Its molecular weight
is 241.24. The structural formula is shown below.
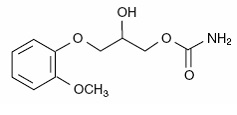
Methocarbamol is a white powder, sparingly soluble in water and chloroform,
soluble in alcohol (only with heating) and propylene glycol, and insoluble in
benzene and n-hexane.
Methocarbamol tablets USP are available as 500 mg and 750 mg tablets for oral
administration. Methocarbamol tablets USP 500 mg and 750 mg contain the
following inactive ingredients: sodium lauryl sulfate, sodium starch
glycolate, povidone K 90, polyethylene glycol, magnesium stearate, colloidal
silicon dioxide, low substituted hydroxypropyl cellulose and stearic acid.
CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY SECTION
CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY
The mechanism of action of methocarbamol in humans has not been established, but may be due to general central nervous system (CNS) depression. It has no direct action on the contractile mechanism of striated muscle, the motor end plate or the nerve fiber.
Pharmacokinetics
In healthy volunteers, the plasma clearance of methocarbamol ranges between
0.20 and 0.80 L/h/kg, the mean plasma elimination half-life ranges between 1
and 2 hours, and the plasma protein binding ranges between 46% and 50%.
Methocarbamol is metabolized via dealkylation and hydroxylation. Conjugation
of methocarbamol also is likely. Essentially all methocarbamol metabolites are
eliminated in the urine. Small amounts of unchanged methocarbamol also are
excreted in the urine.
Special populations
Elderly
The mean (± SD) elimination half-life of methocarbamol in elderly healthy
volunteers (mean (± SD) age, 69 (± 4) years) was slightly prolonged compared
to a younger (mean (± SD) age, 53.3 (± 8.8) years), healthy population (1.5 (±
0.4) hours versus 1.1 (± 0.27) hours, respectively). The fraction of bound
methocarbamol was slightly decreased in the elderly versus younger volunteers
(41 to 43% versus 46 to 50%, respectively).
Renally impaired
The clearance of methocarbamol in 8 renally-impaired patients on maintenance
hemodialysis was reduced about 40% compared to 17 normal subjects, although
the mean (± SD) elimination half-life in these two groups was similar: 1.2 (±
0.6) versus 1.1 (± 0.3) hours, respectively.
Hepatically impaired
In 8 patients with cirrhosis secondary to alcohol abuse, the mean total
clearance of methocarbamol was reduced approximately 70% compared to that
obtained in 8 age- and weight-matched normal subjects. The mean (± SD)
elimination half-life in the cirrhotic patients and the normal subjects was
3.38 (± 1.62) hours and 1.11 (± 0.27) hours, respectively. The percent of
methocarbamol bound to plasma proteins was decreased to approximately 40 to
45% compared to 46 to 50% in the normal subjects.
WARNINGS SECTION
WARNINGS
Since methocarbamol may possess a general CNS depressant effect, patients
receiving methocarbamol tablets should be cautioned about combined effects
with alcohol and other CNS depressants.
Safe use of methocarbamol tablets has not been established with regard to
possible adverse effects upon fetal development. There have been reports of
fetal and congenital abnormalities following in utero exposure to
methocarbamol. Therefore, methocarbamol tablets should not be used in women
who are or may become pregnant and particularly during early pregnancy unless
in the judgment of the physician the potential benefits outweigh the possible
hazards**(seePRECAUTIONS,Pregnancy).**
Use In Activities Requiring Mental Alertness
Methocarbamol may impair mental and/or physical abilities required for performance of hazardous tasks, such as operating machinery or driving a motor vehicle. Patients should be cautioned about operating machinery, including automobiles, until they are reasonably certain that methocarbamol therapy does not adversely affect their ability to engage in such activities.
DOSAGE & ADMINISTRATION SECTION
DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
Methocarbamol Tablets USP, 500 mg – Adults:
Initial dosage: 3 tablets q.i.d.
Maintenance dosage: 2 tablets q.i.d.
Methocarbamol Tablets USP, 750 mg – Adults:
Initial dosage: 2 tablets q.i.d.
Maintenance dosage: 1 tablet q.4h. or 2 tablets t.i.d.
Six grams a day are recommended for the first 48 to 72 hours of treatment.
(For severe conditions 8 grams a day may be administered). Thereafter, the
dosage can usually be reduced to approximately 4 grams a day.
HOW SUPPLIED SECTION
HOW SUPPLIED
Methocarbamol tablets USP, 500 mg are white to off white, capsule shaped,
tablets debossed with ‘H’ on scored side and ‘114’ on unscored side. They are
supplied as follows:
Bottles of 100 NDC 72865-233-01
Bottles of 500 NDC 72865-233-05
Methocarbamol tablets USP, 750 mg are white to off white, capsule shaped,
tablets debossed with ‘H’ on one side and ‘115’ on other side. They are
supplied as follows:
Bottles of 100 NDC 72865-234-01
Bottles of 500 NDC 72865-234-05
Store at 20° to 25°C (68° to 77°F). [see USP Controlled Room Temperature].
Dispense in tight container.
Manufactured for:
XLCare Pharmaceuticals, Inc.
242 South Culver Street, Suite 202,
Lawrenceville, GA 30046.
Manufactured by:
Evaric Pharmaceuticals Inc.
155 Commerce Drive, Hauppauge,
New York 11788, United States (USA).
Revised: 02/2024
PRECAUTIONS SECTION
PRECAUTIONS
Information for Patients
Patients should be cautioned that methocarbamol may cause drowsiness or dizziness, which may impair their ability to operate motor vehicles or machinery.
Because methocarbamol may possess a general CNS-depressant effect, patients should be cautioned about combined effects with alcohol and other CNS depressants.
Drug Interactions
SeeWARNINGSand****PRECAUTIONS for interaction with CNS
drugs and alcohol.
Methocarbamol may inhibit the effect of pyridostigmine bromide. Therefore,
methocarbamol should be used with caution in patients with myasthenia gravis
receiving anticholinesterase agents.
Drug/Laboratory Test Interactions
Methocarbamol may cause a color interference in certain screening tests for 5-hydroxyindoleacetic acid (5-HIAA) using nitrosonaphthol reagent and in screening tests for urinary vanillylmandelic acid (VMA) using the Gitlow method.
Carcinogenesis, Mutagenesis, Impairment of Fertility
Long-term studies to evaluate the carcinogenic potential of methocarbamol have not been performed. No studies have been conducted to assess the effect of methocarbamol on mutagenesis or its potential to impair fertility.
Pregnancy
Teratogenic effects -Pregnancy Category C
Animal reproduction studies have not been conducted with methocarbamol. It is
also not known whether methocarbamol can cause fetal harm when administered to
a pregnant woman or can affect reproduction capacity. Methocarbamol tablets
should be given to a pregnant woman only if clearly needed.
Safe use of methocarbamol tablets has not been established with regard to
possible adverse effects upon fetal development. There have been reports of
fetal and congenital abnormalities following in utero exposure to
methocarbamol. Therefore, methocarbamol tablets should not be used in women
who are or may become pregnant and particularly during early pregnancy unless
in the judgment of the physician the potential benefits outweigh the possible
hazards (seeWARNINGS).
Nursing Mothers
Methocarbamol and/or its metabolites are excreted in the milk of dogs; however, it is not known whether methocarbamol or its metabolites are excreted in human milk. Because many drugs are excreted in human milk, caution should be exercised when methocarbamol tablets are administered to a nursing woman.
Pediatric Use
Safety and effectiveness of methocarbamol tablets in pediatric patients below the age of 16 have not been established.
OVERDOSAGE SECTION
OVERDOSAGE
Limited information is available on the acute toxicity of methocarbamol.
Overdose of methocarbamol is frequently in conjunction with alcohol or other
CNS depressants and includes the following symptoms: nausea, drowsiness,
blurred vision, hypotension, seizures, and coma.
In post-marketing experience, deaths have been reported with an overdose of
methocarbamol alone or in the presence of other CNS depressants, alcohol or
psychotropic drugs.
Treatment
Management of overdose includes symptomatic and supportive treatment. Supportive measures include maintenance of an adequate airway, monitoring urinary output and vital signs, and administration of intravenous fluids if necessary. The usefulness of hemodialysis in managing overdose is unknown.
