ORALTAG
These highlights do not include all the information needed to use ORALTAG safely and effectively. See full prescribing information for ORALTAG. ORALTAG™ (iohexol) for oral solution Initial U.S. Approval: 1985
fdeb1668-7126-48f7-aaf9-1dc3beb90bac
HUMAN PRESCRIPTION DRUG LABEL
Jan 5, 2023
Interpharma Praha, a.s.
DUNS: 644354706
Products 1
Detailed information about drug products covered under this FDA approval, including NDC codes, dosage forms, ingredients, and administration routes.
Iohexol
Product Details
FDA regulatory identification and product classification information
FDA Identifiers
Product Classification
Product Specifications
INGREDIENTS (1)
Drug Labeling Information
PACKAGE LABEL.PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL
PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL - Foil Pouch Label
NDC 54702-501-51
Oraltag™
(iohexol) for oral solution
Contains a single-use bottle with 9.7 g of iohexol powder
(equivalent to 4.5 g of carbon bound iodine)
For Oral Use Only
Nonsterile
Store at 20-25˚C (68-77˚F); excursions permitted to 15-30˚C (59-86˚F) [see USP]
Rx Only
Manufactured for Interpharma Praha, a.s.
Prague, Czech Republic
by Ultra Seal Corporation
New Paltz, New York
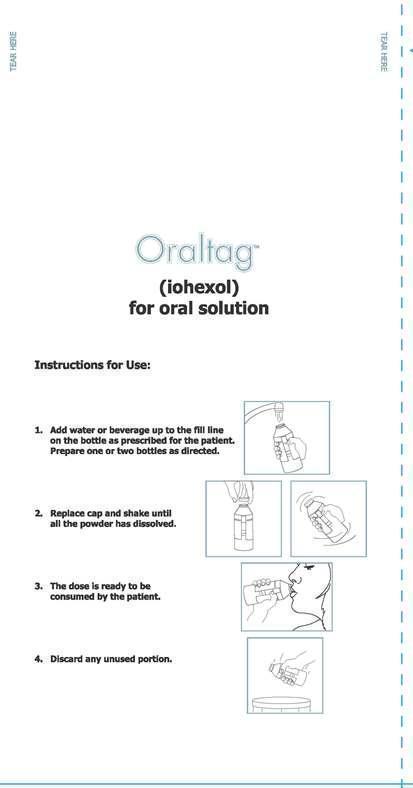
Instructions for Use:
1. Add water or beverage up to the fill line on the bottle as prescribed for the patient. Prepare one or two bottles as directed.
2. Replace cap and shake until all the powder has dissolved.
3. The dose is ready to be consumed by the patient.
4. Discard any unused portion.
CONTRAINDICATIONS SECTION
4 CONTRAINDICATIONS
Oraltag is contraindicated in patients with a known hypersensitivity to iodinated contrast agents, including iohexol [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2)] .
Hypersensitivity to iodinated contrast agents, including iohexol (4)
WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS SECTION
5 WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS
5.1 Risks Associated with Inadvertent Parenteral Administration
Oraltag is not a sterile product and is not suitable for a parenteral route of administration. Serious adverse reactions such as sepsis can occur if administered parenterally. Do not administer Oraltag parenterally.
5.2 Hypersensitivity Reactions
Administration of Oraltag can cause life-threatening hypersensitivity reactions including anaphylaxis [see Contraindications (4)] . Patients at increased risk include those with a previous reaction to an iodinated contrast agent and allergic disorders (i.e., bronchial asthma, allergic rhinitis, and food allergies). Emergency resuscitation equipment and trained personnel should be available.
5.3 Alteration of Thyroid Function Tests
Iodinated contrast agents may alter the results of thyroid function tests which depend on iodine estimation, e.g., radioactive iodine uptake test. Therefore, such testing, if indicated, should be performed prior to the administration of this preparation.
- Hypersensitivity reactions: life-threatening or fatal reactions can occur. Resuscitation equipment and personnel should be available ( 5.2)
- Thyroid function test alterations: Oraltag may alter tests which depend on iodine estimation. Perform such tests prior to Oraltag administration ( 5.3)
ADVERSE REACTIONS SECTION
6 ADVERSE REACTIONS
The following adverse reactions are described in greater detail in other sections:
- Hypersensitivity reactions [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2)]
6.1 Clinical Trials Experience
In studies involving 44 adult and 69 pediatric patients who received oral and intravenous iohexol for CT examinations of the abdomen, two reports of vomiting (2%) were noted.
6.2 Postmarketing Experience
Because these reactions are reported voluntarily from a population of uncertain size, it is not always possible to reliably estimate their frequency or establish a causal relationship to drug exposure.
The following adverse reactions have been reported following oral administration of the dilute, hypotonic solutions of iohexol (9 mgI/mL to 21 mgI/mL):
- Gastrointestinal: nausea, diarrhea
The most common adverse reactions (incidence < 2%) are nausea, vomiting, and diarrhea ( 6)
To report SUSPECTED ADVERSE REACTIONS, contact Interpharma Praha at 1-877-886-7040 or FDA at 1-800-FDA-1088 or www.fda.gov/medwatch.
NONCLINICAL TOXICOLOGY SECTION
13 NONCLINICAL TOXICOLOGY
13.1 Carcinogenesis, Mutagenesis, Impairment of Fertility
No long-term animal studies have been performed to evaluate carcinogenic potential or mutagenesis.
In animal reproduction studies, no evidence of impaired fertility was observed with intravenous administration of iohexol to rats and rabbits at doses up to 100 times the maximum recommended human intravenous dose.
