Products2
Detailed information about drug products covered under this FDA approval, including NDC codes, dosage forms, ingredients, and administration routes.
Lenalidomide
Product Details
Lenalidomide
Product Details
Drug Labeling Information
Complete FDA-approved labeling information including indications, dosage, warnings, contraindications, and other essential prescribing details.
PACKAGE LABEL.PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL
PACKAGE LABEL.PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL
NDC 0480-1245-21 Rx only
Lenalidomide Capsules
20 mg
WARNING: POTENTIAL FOR HUMAN BIRTH DEFECTS
PHARMACIST: Dispense the accompanying Medication Guide to each patient.
21 Capsules

RECENT MAJOR CHANGES SECTION
RECENT MAJOR CHANGES
|
Warnings and Precautions (5.1, 5.2) |
8/2021 |
|
Warnings and Precautions (5.1, 5.11) |
5/2022 |
DESCRIPTION SECTION
11 DESCRIPTION
Lenalidomide, a thalidomide analogue, is an immunomodulatory agent with antiangiogenic and antineoplastic properties. The chemical name is 3-(4-amino-1-oxo 1,3-dihydro-2H-isoindol-2-yl) piperidine-2,6-dione and it has the following chemical structure:
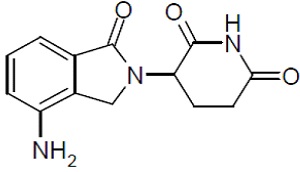
3-(4-amino-1-oxo 1,3-dihydro-2H-isoindol-2-yl) piperidine-2,6-dione
The empirical formula for lenalidomide is C13H13N3O3, and the gram molecular weight is 259.3.
Lenalidomide is a cream to light yellow color powder. It is soluble in organic solvent/water mixtures, and buffered aqueous solvents. Lenalidomide is more soluble in organic solvents and low pH solutions. Solubility was significantly lower in less acidic buffers, ranging from about 0.4 to 0.5 mg/ml. Lenalidomide has an asymmetric carbon atom and can exist as the optically active forms S(-) and R(+), and is produced as a racemic mixture with a net optical rotation of zero.
Lenalidomide is available in 2.5 mg and 20 mg capsules for oral administration. Each capsule contains lenalidomide as the active ingredient and the following inactive ingredients: anhydrous lactose. The capsule shell ingredients common for both strengths are gelatin and titanium dioxide. Additionally, the 20 mg capsule contains FD&C Blue #1, FD&C Yellow #6, and iron oxide yellow. Each capsule is printed with black ink, which includes black iron oxide, potassium hydroxide, propylene glycol, shellac, and strong ammonia solution.
CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY SECTION
12 CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY
12.1 Mechanism of Action
Lenalidomide is an analogue of thalidomide with immunomodulatory, antiangiogenic, and antineoplastic properties. Cellular activities of lenalidomide are mediated through its target cereblon, a component of a cullin ring E3 ubiquitin ligase enzyme complex. In vitro, in the presence of drug, substrate proteins (including Aiolos, Ikaros, and CK1α) are targeted for ubiquitination and subsequent degradation leading to direct cytotoxic and immunomodulatory effects. Lenalidomide inhibits proliferation and induces apoptosis of certain hematopoietic tumor cells including MM, mantle cell lymphoma, and del (5q) myelodysplastic syndromes in vitro. Lenalidomide causes a delay in tumor growth in some in vivo nonclinical hematopoietic tumor models including MM. Immunomodulatory properties of lenalidomide include increased number and activation of T cells and natural killer (NK) cells leading to direct and enhanced antibody-dependent cell-mediated cytotoxicity (ADCC) via increased secretion of interleukin-2 and interferon-gamma, increased numbers of NKT cells, and inhibition of pro-inflammatory cytokines (e.g., TNF-α and IL-6) by monocytes. In MM cells, the combination of lenalidomide and dexamethasone synergizes the inhibition of cell proliferation and the induction of apoptosis.
12.2 Pharmacodynamics
Cardiac Electrophysiology
The effect of lenalidomide on the QTc interval was evaluated in 60 healthy male subjects in a thorough QT study. At a dose two times the maximum recommended dose, lenalidomide did not prolong the QTc interval. The largest upper bound of the two-sided 90% CI for the mean differences between lenalidomide and placebo was below 10 ms.
12.3 Pharmacokinetics
Absorption
Following single and multiple doses of lenalidomide capsules in patients with MM or MDS, the maximum plasma concentrations occurred between 0.5 and 6 hours post-dose. The single and multiple dose pharmacokinetic disposition of lenalidomide is linear with AUC and Cmax values increasing proportionally with dose. Multiple doses of lenalidomide at the recommended dosage does not result in drug accumulation.
Administration of a single 25 mg dose of lenalidomide capsules with a high-fat meal in healthy subjects reduces the extent of absorption, with an approximate 20% decrease in AUC and 50% decrease in Cmax. In the trials where the efficacy and safety were established for lenalidomide capsules, the drug was administered without regard to food intake. Lenalidomide capsules can be administered with or without food.
The oral absorption rate of lenalidomide in patients with MCL is similar to that observed in patients with MM or MDS.
Distribution
In vitro [14C]-lenalidomide binding to plasma proteins is approximately 30%.
Lenalidomide is present in semen at 2 hours (1379 ng/ejaculate) and 24 hours (35 ng/ejaculate) after the administration of lenalidomide 25 mg daily.
Elimination
The mean half-life of lenalidomide is 3 hours in healthy subjects and 3 to 5 hours in patients with MM, MDS or MCL.
Metabolism
Lenalidomide undergoes limited metabolism. Unchanged lenalidomide is the predominant circulating component in humans. Two identified metabolites are 5-hydroxy-lenalidomide and N-acetyl-lenalidomide; each constitutes less than 5% of parent levels in circulation.
Excretion
Elimination is primarily renal. Following a single oral administration of [14C]-lenalidomide 25 mg to healthy subjects, approximately 90% and 4% of the radioactive dose was eliminated within ten days in urine and feces, respectively. Approximately 82% of the radioactive dose was excreted as lenalidomide in the urine within 24 hours. Hydroxy-lenalidomide and N-acetyl- lenalidomide represented 4.6% and 1.8% of the excreted dose, respectively. The renal clearance of lenalidomide exceeds the glomerular filtration rate.
Specific Populations
Renal Impairment: Eight subjects with mild renal impairment (creatinine clearance (CLcr) 50 to 79 mL/min calculated using Cockcroft-Gault), 9 subjects with moderate renal impairment (CLcr 30 to 49 mL/min), 4 subjects with severe renal impairment (CLcr < 30 mL/min), and 6 patients with end stage renal disease (ESRD) requiring dialysis were administered a single 25 mg dose of lenalidomide capsules. Three healthy subjects of similar age with normal renal function (CLcr > 80 mL/min) were also administered a single 25 mg dose of lenalidomide capsules. As CLcr decreased, half-life increased and drug clearance decreased linearly. Patients with moderate and severe impairment had a 3-fold increase in half-life and a 66% to 75% decrease in drug clearance compared to healthy subjects. Patients on hemodialysis (n=6) had an approximate 4.5-fold increase in half-life and an 80% decrease in drug clearance compared to healthy subjects. Approximately 30% of the drug in body was removed during a 4-hour hemodialysis session.
Adjust the starting dose of lenalidomide capsules in patients with renal impairment based on the CLcr value [see Dosage and Administration (2.6)].
Hepatic Impairment: Mild hepatic impairment (defined as total bilirubin > 1 to 1.5 times upper limit normal (ULN) or any aspartate transaminase greater than ULN) did not influence the disposition of lenalidomide. No pharmacokinetic data is available for patients with moderate to severe hepatic impairment.
Other Intrinsic Factors: Age (39 to 85 years), body weight (33 to 135 kg), sex, race, and type of hematological malignancies (MM, MDS or MCL) did not have a clinically relevant effect on lenalidomide clearance in adult patients.
Drug Interactions
Co-administration of a single dose or multiple doses of dexamethasone (40 mg) had no clinically relevant effect on the multiple dose pharmacokinetics of lenalidomide (25 mg).
Co-administration of lenalidomide capsules (25 mg) after multiple doses of a P-gp inhibitor such as quinidine (600 mg twice daily) did not significantly increase the Cmax or AUC of lenalidomide.
Co-administration of the P-gp inhibitor and substrate temsirolimus (25 mg), with lenalidomide capsules (25 mg) did not significantly alter the pharmacokinetics of lenalidomide, temsirolimus, or sirolimus (metabolite of temsirolimus).
In vitro studies demonstrated that lenalidomide is a substrate of P-glycoprotein (P-gp). Lenalidomide is not a substrate of human breast cancer resistance protein (BCRP), multidrug resistance protein (MRP) transporters MRP1, MRP2, or MRP3, organic anion transporters (OAT) OAT1 and OAT3, organic anion transporting polypeptide 1B1 (OATP1B1), organic cation transporters (OCT) OCT1 and OCT2, multidrug and toxin extrusion protein (MATE) MATE1, and organic cation transporters novel (OCTN) OCTN1 and OCTN2. Lenalidomide is not an inhibitor of P-gp, bile salt export pump (BSEP), BCRP, MRP2, OAT1, OAT3, OATP1B1, OATP1B3, or OCT2. Lenalidomide does not inhibit or induce CYP450 isoenzymes. Also, lenalidomide does not inhibit bilirubin glucuronidation formation in human liver microsomes with UGT1A1 genotyped as UGT1A1*1/1, UGT1A11/28, and UGT1A128/*28.
DOSAGE & ADMINISTRATION SECTION
Highlight: * MM combination therapy: 25 mg once daily orally on Days 1 to 21 of repeated 28-day cycles. (2.1).
- MDS: 10 mg once daily (2.2).
- MCL: 25 mg once daily orally on Days 1 to 21 of repeated 28-day cycles (2.3).
- Renal impairment: Adjust starting dose based on the creatinine clearance value (2.6).
- For concomitant therapy doses, see Full Prescribing Information (2.1, 14.1).
2 DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
2.1 Recommended Dosage for Multiple Myeloma
Lenalidomide Capsules Combination Therapy
The recommended starting dose of lenalidomide capsules is 25 mg orally once daily on Days 1 to 21 of repeated 28-day cycles in combination with dexamethasone. Refer to Section 14.1 for specific dexamethasone dosing. For patients greater than 75 years old, the starting dose of dexamethasone may be reduced [see Clinical Studies (14.1)]. Treatment should be continued until disease progression or unacceptable toxicity.
In patients who are not eligible for auto-HSCT, treatment should continue until disease progression or unacceptable toxicity. For patients who are auto- HSCT-eligible, hematopoietic stem cell mobilization should occur within 4 cycles of a lenalidomide-containing therapy [see Warnings and Precautions (5.12)].
Dose Adjustments for Hematologic Toxicities During MM Treatment
Dose modification guidelines, as summarized in Table 1 below, are recommended to manage Grade 3 or 4 neutropenia or thrombocytopenia or other Grade 3 or 4 toxicity judged to be related to lenalidomide capsules.
Table 1: Dose Adjustments for Hematologic Toxicities for MM|
Platelet counts | |
|
** Thrombocytopenia in MM** | |
|
********When Platelets |
Recommended Course Days 1 to 21 of repeated 28-day cycle |
|
Fall below 30,000/mcL |
Interrupt lenalidomide capsules treatment, follow CBC weekly |
|
Return to at least 30,000/mcL |
Resume lenalidomide capsules at next lower dose. Do not dose below 2.5 mg daily |
|
For each subsequent drop below 30,000/mcL |
Interrupt lenalidomide capsules treatment |
|
Return to at least 30,000/mcL |
Resume lenalidomide capsules at next lower dose. Do not dose below 2.5 mg daily |
|
Absolute Neutrophil counts (ANC) | |
|
** Neutropenia in MM** | |
|
** When Neutrophils** |
Recommended Course Days 1 to 21 of repeated 28-day cycle |
|
Fall below 1,000/mcL |
Interrupt lenalidomide capsules treatment, follow CBC weekly |
|
Return to at least 1,000/mcL and neutropenia is |
Resume lenalidomide capsules at 25 mg daily or initial starting dose |
|
Return to at least 1,000/mcL and if other toxicity |
Resume lenalidomide capsules at next lower dose. Do not dose below 2.5 mg daily |
|
For each subsequent drop below 1,000/mcL |
Interrupt lenalidomide capsules treatment |
|
Return to at least 1,000/mcL |
Resume lenalidomide capsules at next lower dose. Do not dose below 2.5 mg daily |
2.2 Recommended Dosage for Myelodysplastic Syndromes
The recommended starting dose of lenalidomide capsules is 10 mg daily. Treatment is continued or modified based upon clinical and laboratory findings. Continue treatment until disease progression or unacceptable toxicity.
Dose Adjustments for Hematologic Toxicities During MDS Treatment
Patients who are dosed initially at 10 mg and who experience thrombocytopenia should have their dosage adjusted as follows:
Platelet counts
If thrombocytopenia develops WITHIN 4 weeks of starting treatment at 10 mg daily in MDS
|
If baseline is at least 100,000/mcL | |
|
When Platelets |
Recommended Course |
|
Fall below 50,000/mcL |
Interrupt lenalidomide capsules treatment |
|
Return to at least 50,000/mcL |
Resume lenalidomide capsules at 5 mg daily |
|
If baseline is below 100,000/mcL | |
|
When Platelets |
Recommended Course |
|
Fall to 50% of the baseline value |
Interrupt lenalidomide capsules treatment |
|
If baseline is at least 60,000/mcL and returns to at least 50,000/mcL |
Resume lenalidomide capsules at 5 mg daily |
|
If baseline is below 60,000/mcL and returns to at least 30,000/mcL |
Resume lenalidomide capsules at 5 mg daily |
If thrombocytopenia develops AFTER 4 weeks of starting treatment at 10 mg daily in MDS
|
When Platelets |
Recommended Course |
|
Fall below 30,000/mcL or below 50,000/mcL with platelet transfusions |
Interrupt lenalidomide capsules treatment |
|
Return to at least 30,000/mcL (without hemostatic failure) |
Resume lenalidomide capsules at 5 mg daily |
Patients who experience thrombocytopenia at 5 mg daily should have their dosage adjusted as follows:
If thrombocytopenia develops during treatment at 5 mg daily in MDS
|
When Platelets |
Recommended Course |
|
Fall below 30,000/mcL or below 50,000/mcL with platelet transfusions |
Interrupt lenalidomide capsules treatment |
|
Return to at least 30,000/mcL (without hemostatic failure) |
Resume lenalidomide capsules at 2.5 mg daily |
Patients who are dosed initially at 10 mg and experience neutropenia should have their dosage adjusted as follows:
Absolute Neutrophil counts (ANC)
If neutropenia develops WITHIN 4 weeks of starting treatment at 10 mg daily in MDS
|
If baseline ANC isat least1,000/mcL | |
|
When Neutrophils |
Recommended Course |
|
Fall below 750/mcL |
Interrupt lenalidomide capsules treatment |
|
Return to at least 1,000/mcL |
Resume lenalidomide capsules at 5 mg daily |
|
If baseline ANC is below 1,000/mcL | |
|
When Neutrophils |
Recommended Course |
|
Fall below 500/mcL |
Interrupt lenalidomide capsules treatment |
|
Return to at least 500/mcL |
Resume lenalidomide capsules at 5 mg daily |
If neutropenia develops AFTER 4 weeks of starting treatment at 10 mg daily in MDS
|
When Neutrophils |
Recommended Course |
|
Fall below 500/mcL for at least 7 days or below 500/mcL |
Interrupt lenalidomide capsules treatment |
|
Return to at least 500/mcL |
Resume lenalidomide capsules at 5 mg daily |
Patients who experience neutropenia at 5 mg daily should have their dosage adjusted as follows:
If neutropenia develops during treatment at 5 mg daily in MDS
|
When Neutrophils |
Recommended Course |
|
Fall below 500/mcL for at least 7 days or below 500/mcL |
Interrupt lenalidomide capsules treatment |
|
Return to at least 500/mcL |
Resume lenalidomide capsules at 2.5 mg daily |
2.3 Recommended Dosage for Mantle Cell Lymphoma
The recommended starting dose of lenalidomide capsules is 25 mg/day orally on Days 1 to 21 of repeated 28-day cycles for relapsed or refractory mantle cell lymphoma. Treatment should be continued until disease progression or unacceptable toxicity.
Treatment is continued, modified or discontinued based upon clinical and laboratory findings.
Dose Adjustments for Hematologic Toxicities During MCL Treatment
Dose modification guidelines as summarized below are recommended to manage Grade 3 or 4 neutropenia or thrombocytopenia or other Grade 3 or 4 toxicities considered to be related to lenalidomide capsules.
Platelet counts
Thrombocytopenia during treatment in MCL
|
When Platelets |
Recommended Course |
|
Fall below 50,000/mcL |
Interrupt lenalidomide capsules treatment and follow CBC weekly |
|
Return to at least 50,000/mcL |
Resume lenalidomide capsules at 5 mg less than the previous dose. Do not dose below 5 mg daily |
Absolute Neutrophil counts (ANC)
Neutropenia during treatment in MCL
|
When Neutrophils |
Recommended Course |
|
Fall below 1,000/mcL for at least 7 days OR Falls below 1,000/mcL with an associated temperature at least 38.5°C OR Falls below 500/mcL |
Interrupt lenalidomide capsules treatment and follow CBC weekly |
|
Return to at least 1,000/mcL |
Resume lenalidomide capsules at 5 mg less than the previous dose. Do not dose below 5 mg daily |
2.5 Dosage Modifications for Non-Hematologic Adverse Reactions
For non-hematologic Grade 3/4 toxicities judged to be related to lenalidomide capsules, hold treatment and restart at the physician's discretion at next lower dose level when toxicity has resolved to Grade 2 or below.
Permanently discontinue lenalidomide capsules for angioedema, anaphylaxis, Grade 4 rash, skin exfoliation, bullae, or any other severe dermatologic reactions [see Warnings and Precautions (5.9, 5.15)].
2.6 Recommended Dosage for Patients with Renal Impairment
The recommendations for dosing patients with renal impairment are shown in the following table [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)].
Table 3: Dose Adjustments for Patients with Renal Impairment|
Renal Function (Cockcroft-Gault) |
Dose in Lenalidomide Capsules Combination Therapy for MM and MCL |
Dose in Lenalidomide Capsules for MDS |
|
CLcr 30 to 60 mL/min |
10 mg once daily |
5 mg once daily |
|
CLcr below 30 mL/min (not requiring dialysis) |
15 mg every other day |
2.5 mg once daily |
|
CLcr below 30 mL/min (requiring dialysis) |
5 mg once daily. On dialysis days, administer the dose following dialysis. |
2.5 mg once daily. On dialysis days, administer the dose following dialysis. |
Lenalidomide Capsules Combination Therapy for MM: For CLcr of 30 to 60 mL/min, consider escalating the dose to 15 mg after 2 cycles if the patient tolerates the 10 mg dose of lenalidomide without dose-limiting toxicity.
Lenalidomide Capsules Therapy for MCL and MDS: Base subsequent lenalidomide capsules dose increase or decrease on individual patient treatment tolerance [see Dosage and Administration (2.1 to 2.3)].
2.7 Administration
Advise patients to take lenalidomide capsules orally at about the same time each day, either with or without food. Advise patients to swallow lenalidomide capsules whole with water and not to open, break, or chew them.
DOSAGE FORMS & STRENGTHS SECTION
Highlight: Capsules: 2.5 mg and 20 mg (3).
3 DOSAGE FORMS AND STRENGTHS
Capsules:
- 2.5 mg white capsules printed with “NAT” on cap and “2.5mg” on body of the capsule in black ink.
- 20 mg green/blue capsules printed with “NAT” on cap and “20 mg” on body of the capsule in black ink.
CONTRAINDICATIONS SECTION
Highlight: * Pregnancy (Boxed Warning, 4.1, 5.1, 8.1).
- Demonstrated severe hypersensitivity to lenalidomide (4.2, 5.9, 5.15).
4 CONTRAINDICATIONS
4.1 Pregnancy
Lenalidomide capsules can cause fetal harm when administered to a pregnant female. Limb abnormalities were seen in the offspring of monkeys that were dosed with lenalidomide during organogenesis. This effect was seen at all doses tested. Due to the results of this developmental monkey study, and lenalidomide’s structural similarities to thalidomide, a known human teratogen, lenalidomide is contraindicated in females who are pregnant [see Boxed Warning]. If this drug is used during pregnancy or if the patient becomes pregnant while taking this drug, the patient should be apprised of the potential risk to a fetus [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1, 5.2), Use in Special Populations (8.1, 8.3)].
4.2 Severe Hypersensitivity Reactions
Lenalidomide capsules are contraindicated in patients who have demonstrated severe hypersensitivity (e.g., angioedema, Stevens-Johnson syndrome, toxic epidermal necrolysis) to lenalidomide [see Warnings and Precautions (5.9, 5.15)].
BOXED WARNING SECTION
WARNING: EMBRYO-FETAL TOXICITY, HEMATOLOGIC TOXICITY, and VENOUS and
ARTERIAL THROMBOEMBOLISM
OVERDOSAGE SECTION
10 OVERDOSAGE
There is no specific experience in the management of lenalidomide overdose in patients with MM, MDS, or MCL. In dose-ranging studies in healthy subjects, some were exposed to up to 200 mg (administered 100 mg BID) and in single-dose studies, some subjects were exposed to up to 400 mg. Pruritus, urticaria, rash, and elevated liver transaminases were the primary reported AEs. In clinical trials, the dose-limiting toxicity was neutropenia and thrombocytopenia.
INFORMATION FOR PATIENTS SECTION
17 PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATION
Advise the patient to read the FDA-approved Patient labeling (Medication Guide)
Embryo-Fetal Toxicity
Advise patients that lenalidomide capsules are contraindicated in pregnancy [see Boxed Warning and Contraindications (4.1)]. Lenalidomide is a thalidomide analogue and can cause serious birth defects or death to a developing baby [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1) and Use in Specific Populations (8.1)].
-
Advise females of reproductive potential that they must avoid pregnancy while taking lenalidomide capsules and for at least 4 weeks after completing therapy.
-
Initiate lenalidomide capsules treatment in females of reproductive potential only following a negative pregnancy test.
-
Advise females of reproductive potential of the importance of monthly pregnancy tests and the need to use 2 different forms of contraception including at least 1 highly effective form, simultaneously during lenalidomide capsules therapy, during dose interruption and for 4 weeks after she has completely finished taking lenalidomide capsules. Highly effective forms of contraception other than tubal ligation include IUD and hormonal (birth control pills, injections, patch or implants) and a partner’s vasectomy. Additional effective contraceptive methods include latex or synthetic condom, diaphragm and cervical cap.
-
Instruct patient to immediately stop taking lenalidomide capsules and contact her healthcare provider if she becomes pregnant while taking this drug, if she misses her menstrual period, or experiences unusual menstrual bleeding, if she stops taking birth control, or if she thinks FOR ANY REASON that she may be pregnant.
-
Advise patient that if her healthcare provider is not available, she should call the REMS Call Center at
1‐888‐423‐5436 [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1) and Use in Specific Populations (8.3)]. -
Advise males to always use a latex or synthetic condom during any sexual contact with females of reproductive potential while taking lenalidomide capsules and for up to 4 weeks after discontinuing lenalidomide capsules, even if they have undergone a successful vasectomy.
-
Advise male patients taking lenalidomide capsules that they must not donate sperm and for up to 4 weeks after discontinuation of lenalidomide capsules [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1) and Use in Specific Populations (8.3)].
-
All patients must be instructed to not donate blood while taking lenalidomide capsules, during dose interruptions and for 4 weeks following discontinuation of lenalidomide capsules [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)].
Lenalidomide REMS program
Because of the risk of embryo-fetal toxicity, lenalidomide capsules are only available through a restricted program called the Lenalidomide REMS program [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2)].
- Patients must sign a Patient-Physician agreement form and comply with the requirements to receive lenalidomide capsules. In particular, females of reproductive potential must comply with the pregnancy testing, contraception requirements and participate in monthly telephone surveys. Males must comply with the contraception requirements [see Use in Specific Populations (8.3)].
- Lenalidomide capsules are available only from pharmacies that are certified in Lenalidomide REMS program. Provide patients with the telephone number and website for information on how to obtain the product.
Pregnancy Exposure Registry
Inform females there is a Pregnancy Exposure Registry that monitors pregnancy outcomes in females exposed to lenalidomide capsules during pregnancy and that they can contact the Pregnancy Exposure Registry by calling 1‐888‐423‐5436 [see Use in Specific Populations (8.1)].
Hematologic Toxicity
Inform patients that lenalidomide capsules are associated with significant neutropenia and thrombocytopenia [see Boxed Warning and Warnings and Precautions (5.3)].
Venous and Arterial Thromboembolism
Inform patients of the risk of thrombosis including DVT, PE, MI, and stroke and to report immediately any signs and symptoms suggestive of these events for evaluation [see Boxed Warning and Warnings and Precautions (5.4)].
Increased Mortality in Patients with CLL
Inform patients that lenalidomide capsules had increased mortality in patients with CLL and serious adverse cardiovascular reactions, including atrial fibrillation, myocardial infarction, and cardiac failure [see Warnings and Precautions (5.5)].
Second Primary Malignancies
Inform patients of the potential risk of developing second primary malignancies during treatment with lenalidomide capsules [see Warnings and Precautions (5.6)].
Hepatotoxicity
Inform patients of the risk of hepatotoxicity, including hepatic failure and death, and to report any signs and symptoms associated with this event to their healthcare provider for evaluation [see Warnings and Precautions (5.8)].
Severe Cutaneous Reactions
Inform patients of the potential risk for severe skin reactions such as SJS, TEN, and DRESS and report any signs and symptoms associated with these reactions to their healthcare provider for evaluation. Patients with a prior history of Grade 4 rash associated with thalidomide treatment should not receive lenalidomide capsules [see Warnings and Precautions (5.9)].
Tumor Lysis Syndrome
Inform patients of the potential risk of tumor lysis syndrome and to report any signs and symptoms associated with this event to their healthcare provider for evaluation [see Warnings and Precautions (5.10)].
Tumor Flare Reaction
Inform patients of the potential risk of tumor flare reaction and to report any signs and symptoms associated with this event to their healthcare provider for evaluation [see Warnings and Precautions (5.11)].
Early Mortality in Patients with MCL
Inform patients with MCL of the potential for early death [see Warnings and Precautions (5.14)].
Hypersensitivity
Inform patients of the potential for severe hypersensitivity reactions such as angioedema and anaphylaxis to lenalidomide capsules. Instruct patients to contact their healthcare provider right away for signs and symptoms of these reactions. Advise patients to seek emergency medical attention for signs or symptoms of severe hypersensitivity reactions [see Warnings and Precautions (5.15)].
Dosing Instructions
Inform patients how to take lenalidomide capsules [see Dosage and Administration (2)]
- Lenalidomide capsules should be taken once daily at about the same time each day,
- Lenalidomide capsules may be taken either with or without food.
- The capsules should not be opened, broken, or chewed. Lenalidomide capsules should be swallowed whole with water.
- Instruct patients that if they miss a dose of lenalidomide capsules, they may still take it up to 12 hours after the time they would normally take it. If more than 12 hours have elapsed, they should be instructed to skip the dose for that day. The next day, they should take lenalidomide capsules at the usual time. Warn patients to not take 2 doses to make up for the one that they missed.
Manufactured In India By:
Natco Pharma Limited
****Kothur - 509 228, India
Manufactured For:
Teva Pharmaceuticals
****Parsippany, NJ 07054
Iss. 5/2022
SPL MEDGUIDE SECTION
MEDICATION GUIDE
|
LENALIDOMIDE (len" a lid' oh mide) Capsules | ||
|
What is the most important information I should know about lenalidomide capsules? Before you begin taking lenalidomide capsules, you must read and agree to all of the instructions in the Lenalidomide REMS program. Before prescribing lenalidomide capsules, your healthcare provider will explain the Lenalidomide REMS program to you and have you sign the Patient-Physician Agreement Form. Lenalidomide capsules may cause serious side effects including: *Possible birth defects (deformed babies) or death of an unborn baby. Females who are pregnant or who plan to become pregnant must not take lenalidomide capsules. Lenalidomide is similar to the medicine thalidomide. We know thalidomide can cause severe life-threatening birth defects. Lenalidomide capsules have not been tested in pregnant females. Lenalidomide capsules have harmed unborn animals in animal testing. Females must not get pregnant:
Females who can become pregnant:
If you become pregnant while taking lenalidomide capsules, stop taking it right away and call your healthcare provider. If your healthcare provider is not available, you can call the REMS Call Center at 1‐888‐423‐5436. Healthcare providers and patients should report all cases of pregnancy to:
There is a pregnancy exposure registry that monitors the outcomes of females who take lenalidomide capsules during pregnancy, or if their male partner takes lenalidomide capsules and they are exposed during pregnancy. You can enroll in this registry by calling the Lenalidomide REMS program at the phone number listed above. Lenalidomide can pass into human semen:
Men, if your female partner becomes pregnant, you should call your healthcare provider right away. *Low white blood cells (neutropenia) and low platelets (thrombocytopenia). Lenalidomide capsules cause low white blood cells and low platelets in most people. You may need a blood transfusion or certain medicines if your blood counts drop too low. Your healthcare provider should check your blood counts often especially during the first several months of treatment with lenalidomide capsules, and then at least monthly. Tell your healthcare provider if you develop any bleeding or bruising, during treatment with lenalidomide capsules. *Blood clots. Blood clots in the arteries, veins, and lungs happen more often in people who take lenalidomide capsules. This risk is even higher for people with multiple myeloma who take the medicine dexamethasone with lenalidomide capsules. Heart attacks and strokes also happen more often in people who take lenalidomide capsules with dexamethasone. To reduce this increased risk, most people who take lenalidomide capsules will also take a blood thinner medicine. Before taking lenalidomide capsules, tell your healthcare provider:
| ||
|
What are lenalidomide capsules? Lenalidomide capsules are a prescription medicine, used to treat adults with:
Lenalidomide capsules should not be used to treat people who have chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL) unless they are participants in a controlled clinical trial. It is not known if lenalidomide capsules are safe and effective in children. | ||
|
Who should not take lenalidomide capsules? Do not take lenalidomide capsules if you: *are pregnant, plan to become pregnant, or become pregnant**during treatment with lenalidomide capsules.**See “What is the most important information I should know about lenalidomide capsules?” *****are allergic to lenalidomide or any of the ingredients in lenalidomide capsules. See the end of this Medication Guide for a complete list of ingredients in lenalidomide capsules. | ||
|
What should I tell my healthcare provider before taking lenalidomide capsules? Before you take lenalidomide capsules, tell your healthcare provider about all of your medical conditions, including if you:
Tell your healthcare provider about all the medicines you take, including prescription and over-the-counter medicines, vitamins, and herbal supplements. Lenalidomide capsules and other medicines may affect each other, causing serious side effects. Talk with your healthcare provider before taking any new medicines. Know the medicines you take. Keep a list of them to show your healthcare provider and pharmacist. | ||
|
How should I take lenalidomide capsules?
| ||
|
What should I avoid while taking lenalidomide capsules?
| ||
|
What are the possible side effects of lenalidomide capsules? Lenalidomide capsules can cause serious side effects, including:
| ||
|
| |
|
*Severe skin reactions and severe allergic reactions can happen with lenalidomide capsules and may cause death. Call your healthcare provider right away if you develop any of the following signs or symptoms during treatment with lenalidomide capsules: | ||
|
|
|
|
Get emergency medical help right away if you develop any of the following signs or symptoms during treatment with lenalidomide capsules: | ||
|
| |
|
*Tumor lysis syndrome (TLS). TLS is caused by the fast breakdown of cancer cells. TLS can cause kidney failure and the need for dialysis treatment, abnormal heart rhythm, seizure and sometimes death. Your healthcare provider may do blood tests to check you for TLS. ***Worsening of your tumor (tumor flare reaction)**can happen with lenalidomide capsules and may cause death. Tell your healthcare provider if you get any of these symptoms of tumor flare reaction during treatment with lenalidomide capsules: tender swollen lymph nodes, low grade fever, pain, or rash. Your healthcare provider may tell you to decrease your dose, temporarily stop or permanently stop taking lenalidomide capsules if you develop certain serious side effects during treatment with lenalidomide capsules. *Thyroid problems. Your healthcare provider may check your thyroid function before you start taking lenalidomide capsules and during treatment with lenalidomide capsules. *Risk of Early Death in MCL. In people who have Mantle Cell Lymphoma (MCL), there may be a risk of dying sooner (early death) when taking lenalidomide capsules. Talk with your healthcare provider about any concerns and possible risk factors. The most common side effects of lenalidomide capsules include: | ||
|
|
|
|
These are not all the possible side effects of lenalidomide capsules. Call your doctor for medical advice about side effects. You may report side effects to the FDA at 1-800-FDA-1088. | ||
|
How should I store lenalidomide capsules?
Keep lenalidomide capsules and all medicines out of the reach of children. | ||
|
General information about the safe and effective use of lenalidomide capsules. Medicines are sometimes prescribed for purposes other than those listed in a Medication Guide. Do not take lenalidomide capsules for conditions for which they were not prescribed. Do not give lenalidomide capsules to other people, even if they have the same symptoms you have. It may harm them and may cause birth defects. If you would like more information, talk with your healthcare provider. You can ask your healthcare provider or pharmacist for information about lenalidomide capsules that is written for health professionals. | ||
|
What are the ingredients in lenalidomide capsules? Active ingredient: lenalidomide Inactive ingredients: anhydrous lactose. The capsule shell ingredients common for both strengths are gelatin and titanium dioxide. Additionally, the 20 mg capsule contains FD&C Blue #1, FD&C Yellow #6 and iron oxide yellow. Each capsule is printed with black ink, which includes black iron oxide, potassium hydroxide, propylene glycol, shellac, and strong ammonia solution. Manufactured In India By:Natco Pharma Limited, Kothur - 509 228, India For more information, call 1-888-838-2872 or go to www.lenalidomiderems.com. |
This Medication Guide has been approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration. Iss. 5/2022
REFERENCES SECTION
15 REFERENCES
- OSHA Hazardous Drugs. OSHA [Accessed on 29 January 2013, from http://www.osha.gov/SLTC/hazardousdrugs/index.html]
