CEFIXIME
These highlights do not include all the information needed to use CEFIXIME safely and effectively. See full prescribing information for CEFIXIME. CEFIXIME for oral suspension, 100 mg/5 mLCEFIXIME for oral suspension, 200 mg/5 mLCEFIXIME capsules, 400 mgFor oral administration Initial U.S. Approval: 1986
6d68dbd9-7d75-4ff1-91db-79ff8ae879ec
HUMAN PRESCRIPTION DRUG LABEL
Jul 11, 2025
Lupin Pharmaceuticals, Inc.
DUNS: 089153071
Products 4
Detailed information about drug products covered under this FDA approval, including NDC codes, dosage forms, ingredients, and administration routes.
CEFIXIME
Product Details
FDA regulatory identification and product classification information
FDA Identifiers
Product Classification
Product Specifications
INGREDIENTS (6)
CEFIXIME
Product Details
FDA regulatory identification and product classification information
FDA Identifiers
Product Classification
Product Specifications
INGREDIENTS (14)
CEFIXIME
Product Details
FDA regulatory identification and product classification information
FDA Identifiers
Product Classification
Product Specifications
INGREDIENTS (14)
CEFIXIME
Product Details
FDA regulatory identification and product classification information
FDA Identifiers
Product Classification
Product Specifications
INGREDIENTS (6)
Drug Labeling Information
PACKAGE LABEL.PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL
PACKAGE LABEL.PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL
CEFIXIME FOR ORAL SUSPENSION USP
100 mg/5 mL
Rx only
NDC 68180-405-01: Bottle of 50 mL

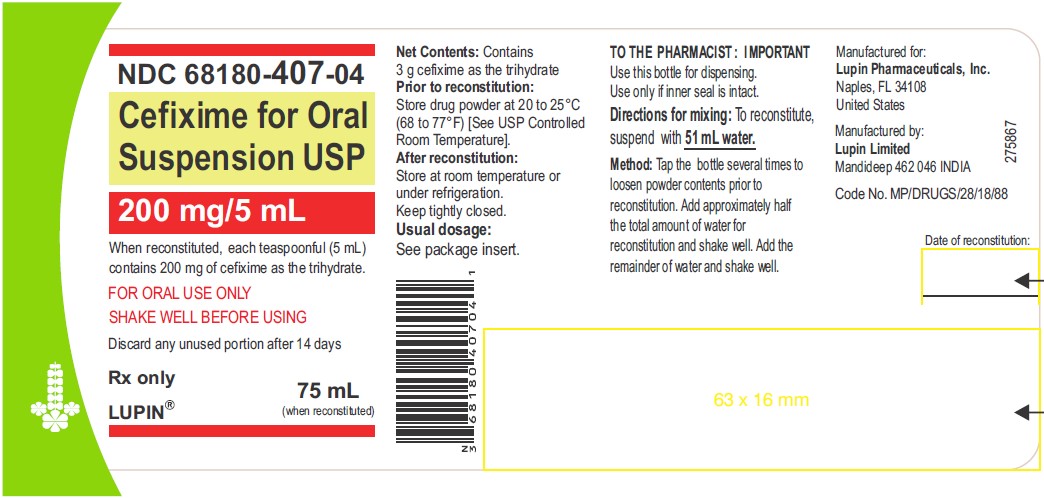
CEFIXIME FOR ORAL SUSPENSION USP
200 mg/5 mL
Rx only
NDC 68180-407-03: Bottle of 50 mL
NDC 68180-407-04: Bottle of 75 mL

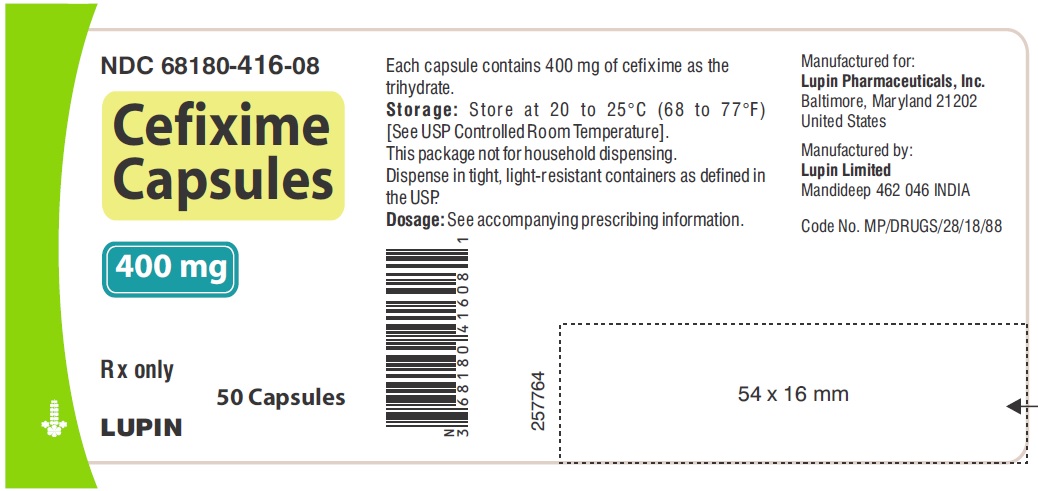
CEFIXIME CAPSULES
400 mg
Rx only
NDC 68180-416-08 - Bottle of 50 capsules
CEFIXIME CAPSULES
400 mg
Rx only
NDC 68180-416-11 - Blister
Unit dose Package of 10 (1 blister of 10 capsules)

CEFIXIME CAPSULES
400 mg
Rx only
NDC 68180-416-11 - Carton

CEFIXIME CAPSULES
400 mg
Rx only
NDC 68180-423-08 - Bottle of 50 capsules

CEFIXIME CAPSULES
400 mg
Rx only
NDC 68180-423-11 - Blister
Unit dose Package of 10 (1 blister of 10 capsules)

CEFIXIME CAPSULES
400 mg
Rx only
NDC 68180-423-11 - Carton

INDICATIONS & USAGE SECTION
1 INDICATIONS AND USAGE
1.1 Uncomplicated Urinary Tract Infections
Cefixime for oral suspension and cefixime capsule is indicated in the treatment of adults and pediatric patients six months of age or older with uncomplicated urinary tract infections caused by susceptible isolates of Escherichia coli and Proteus mirabilis.
1.2 Otitis Media
Cefixime for oral suspension and cefixime capsule is indicated in the treatment of adults and pediatric patients six months of age or older with otitis media caused by susceptible isolates of Haemophilus influenzae, Moraxella catarrhalis, and Streptococcus pyogenes. (Efficacy for Streptococcus pyogenes in this organ system was studied in fewer than 10 infections.)
Note: For patients with otitis media caused by Streptococcus pneumoniae, overall response was approximately 10% lower for cefixime than for the comparator [see Clinical Studies (14)].
1.3 Pharyngitis and Tonsillitis
Cefixime for oral suspension and cefixime capsule is indicated in the treatment of adults and pediatric patients six months of age or older with pharyngitis and tonsillitis caused by susceptible isolates of Streptococcus pyogenes. (Note: Penicillin is the usual drug of choice in the treatment of Streptococcus pyogenes infections. Cefixime for oral suspension and cefixime capsule is generally effective in the eradication of Streptococcus pyogenes from the nasopharynx; however, data establishing the efficacy of cefixime for oral suspension and cefixime capsule in the subsequent prevention of rheumatic fever is not available.)
1.4 Acute Exacerbations of Chronic Bronchitis
Cefixime for oral suspension and cefixime capsule is indicated in the treatment of adults and pediatric patients six months of age or older with acute exacerbations of chronic bronchitis caused by susceptible isolates of Streptococcus pneumoniae and Haemophilus influenzae.
1.5 Uncomplicated Gonorrhea (cervical/urethral)
Cefixime for oral suspension and cefixime capsule is indicated in the treatment of adults and pediatric patients six months of age or older with uncomplicated gonorrhea (cervical/urethral) caused by susceptible isolates of Neisseria gonorrhoeae (penicillinase-and non-penicillinase-producing isolates).
1.6 Usage to Reduce Development of Drug-Resistant Bacteria
To reduce the development of drug resistant bacteria and maintain the effectiveness of cefixime and other antibacterial drugs, cefixime for oral suspension and cefixime capsule should be used only to treat infections that are proven or strongly suspected to be caused by susceptible bacteria. When culture and susceptibility information are available, they should be considered in selecting or modifying antimicrobial therapy. In the absence of such data, local epidemiology and susceptibility patterns may contribute to the empiric selection of therapy.
Cefixime is a cephalosporin antibacterial drug indicated in the treatment of adults and pediatric patients six months and older with the following infections:
- Uncomplicated Urinary Tract Infections (1.1)
- Otitis Media (1.2)
- Pharyngitis and Tonsillitis (1.3)
- Acute Exacerbations of Chronic Bronchitis (1.4)
- Uncomplicated Gonorrhea (cervical/urethral) (1.5)
Usage to Reduce Development of Drug-Resistant Bacteria
To reduce the development of drug-resistant bacteria and maintain the effectiveness of cefixime and other antibacterial drugs, cefixime for oral suspension and cefixime capsules should be used only to treat infections that are proven or strongly suspected to be caused by bacteria. (1.6)
WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS SECTION
5 WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS
5.1 Hypersensitivity Reactions
Anaphylactic/anaphylactoid reactions (including shock and fatalities) have been reported with the use of cefixime.
Before therapy with cefixime is instituted, careful inquiry should be made to determine whether the patient has had previous hypersensitivity reactions to cephalosporins, penicillins, or other drugs. If this product is to be given to penicillin-sensitive patients, caution should be exercised because cross hypersensitivity among beta-lactam antibacterial drugs has been clearly documented and may occur in up to 10% of patients with a history of penicillin allergy. If an allergic reaction to cefixime occurs, discontinue the drug.
5.2 Clostridioides difficile-Associated Diarrhea
Clostridium difficile-associated diarrhea (CDAD) has been reported with use of nearly all antibacterial agents, including cefixime, and may range in severity from mild diarrhea to fatal colitis. Treatment with antibacterial agents alters the normal flora of the colon leading to overgrowth of C. difficile.
C. difficile produces toxins A and B which contribute to the development of CDAD. Hypertoxin producing isolates of C. difficile cause increased morbidity and mortality, as these infections can be refractory to antimicrobial therapy and may require colectomy. CDAD must be considered in all patients who present with diarrhea following antibacterial drug use. Careful medical history is necessary since CDAD has been reported to occur over two months after the administration of antibacterial agents.
If CDAD is suspected or confirmed, ongoing antibacterial drug use not directed against C. difficile may need to be discontinued. Appropriate fluid and electrolyte management, protein supplementation, antibacterial drug treatment of C. difficile, and surgical evaluation should be instituted as clinically indicated.
5.3 Dose Adjustment in Renal Impairment
The dose of cefixime should be adjusted in patients with renal impairment as well as those undergoing continuous ambulatory peritoneal dialysis (CAPD) and hemodialysis (HD). Patients on dialysis should be monitored carefully [see Dosage and Administration (2)].
5.4 Coagulation Effects
Cephalosporins, including cefixime, may be associated with a fall in prothrombin activity. Those at risk include patients with renal or hepatic impairment, or poor nutritional state, as well as patients receiving a protracted course of antimicrobial therapy, and patients previously stabilized on anticoagulant therapy. Prothrombin time should be monitored in patients at risk and exogenous vitamin K administered as indicated.
5.5 Development of Drug-Resistant Bacteria
Prescribing cefixime in the absence of a proven or strongly suspected bacterial infection is unlikely to provide benefit to the patient and increases the risk of the development of drug-resistant bacteria.
- Hypersensitivity reactions including shock and fatalities have been reported with cefixime. Discontinue use if a reaction occurs. (5.1)
- Clostridiodes difficile-Associated Diarrhea: Evaluate if diarrhea occurs. (5.2)
ADVERSE REACTIONS SECTION
6 ADVERSE REACTIONS
6.1 Clinical Trials Experience
Because clinical trials are conducted under widely varying conditions, adverse reaction rates observed in the clinical trials of a drug cannot be directly compared to rates in the clinical trials of another drug and may not reflect the rates observed in practice.
The most commonly seen adverse reactions in U.S. trials of the tablet formulation were gastrointestinal events, which were reported in 30% of adult patients on either the twice daily or the once daily regimen. Five percent (5%) of patients in the U.S. clinical trials discontinued therapy because of drug-related adverse reactions. Individual adverse reactions included diarrhea 16%, loose or frequent stools 6%, abdominal pain 3%, nausea 7%, dyspepsia 3%, and flatulence 4%. The incidence of gastrointestinal adverse reactions, including diarrhea and loose stools, in pediatric patients receiving the suspension was comparable to the incidence seen in adult patients receiving tablets.
6.2 Post-marketing Experience
The following adverse reactions have been reported following the post-approval use of cefixime. Incidence rates were less than 1 in 50 (less than 2%).
Gastrointestinal
Several cases of documented pseudomembranous colitis were identified in clinical trials. The onset of pseudomembranous colitis symptoms may occur during or after therapy.
Hypersensitivity Reactions
Anaphylactic/anaphylactoid reactions (including shock and fatalities), skin rashes, urticaria, drug fever, pruritus, angioedema, and facial edema. Erythema multiforme, Stevens-Johnson syndrome, and serum sickness-like reactions have been reported.
Hepatic
Transient elevations in SGPT, SGOT, alkaline phosphatase, hepatitis, jaundice.
Renal
Transient elevations in BUN or creatinine, acute renal failure.
Central Nervous System
Headaches, dizziness, seizures.
Hemic and Lymphatic System
Transient thrombocytopenia, leukopenia, neutropenia, prolongation in prothrombin time, elevated LDH, pancytopenia, agranulocytosis, and eosinophilia.
Abnormal Laboratory Tests
Hyperbilirubinemia.
Other Adverse Reactions
Genital pruritus, vaginitis, candidiasis, toxic epidermal necrolysis.
Adverse Reactions Reported for Cephalosporin-class Drugs
Allergic reactions, superinfection, renal dysfunction, toxic nephropathy, hepatic dysfunction including cholestasis, aplastic anemia, hemolytic anemia, hemorrhage, and colitis.
Several cephalosporins have been implicated in triggering seizures, particularly in patients with renal impairment when the dosage was not reduced [see Dosage and Administration (2) and Overdosage (10)]. If seizures associated with drug therapy occur, the drug should be discontinued. Anticonvulsant therapy can be given if clinically indicated.
Most common adverse reactions are gastrointestinal such as diarrhea (16%), nausea (7%), loose stools (6%), abdominal pain (3%), dyspepsia (3%), and vomiting. (6)
To report SUSPECTED ADVERSE REACTIONS, contact Lupin Pharmaceuticals, Inc. at 1-800-399-2561 or FDA at 1-800-FDA-1088 or****www.fda.gov/medwatch.
DRUG INTERACTIONS SECTION
7 DRUG INTERACTIONS
7.1 Carbamazepine
Elevated carbamazepine levels have been reported in postmarketing experience when cefixime is administered concomitantly. Drug monitoring may be of assistance in detecting alterations in carbamazepine plasma concentrations.
7.2 Warfarin and Anticoagulants
Increased prothrombin time, with or without clinical bleeding, has been reported when cefixime is administered concomitantly.
7.3 Drug/Laboratory Test Interactions
A false-positive reaction for ketones in the urine may occur with tests using nitroprusside but not with those using nitroferricyanide.
The administration of cefixime may result in a false positive reaction for glucose in the urine when using glucose tests based on the Benedict's solution or Fehling's solution. It is recommended that glucose tests based on enzymatic glucose oxidase reactions be used. A false positive direct Coombs test has been reported during treatment with other cephalosporins; therefore, it should be recognized that a positive Coombs test may be due to the drug.
- Elevated carbamazepine levels have been reported in postmarketing experience when cefixime is administered concomitantly. (7.1)
- Increased prothrombin time, with or without clinical bleeding, has been reported when cefixime is administered concomitantly with warfarin and anticoagulants. (7.2)
CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY SECTION
12 CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY
12.1 Mechanism of Action
Cefixime is a semisynthetic cephalosporin antibacterial drug [see Microbiology (12.4)].
12.3 Pharmacokinetics
Cefixime tablets and cefixime for oral suspension, given orally, are about 40% to 50% absorbed whether administered with or without food; however, time to maximal absorption is increased approximately 0.8 hours when administered with food. A single 200 mg tablet of cefixime produces an average peak serum concentration of approximately 2 mcg/mL (range 1 to 4 mcg/mL); a single 400 mg tablet produces an average peak concentration of approximately 3.7 mcg/mL (range 1.3 to 7.7 mcg/mL). The cefixime oral suspension produces average peak concentrations approximately 25% to 50% higher than the tablets, when tested in normal adult volunteers. Two hundred and 400 mg doses of cefixime oral suspension produce average peak concentrations of 3 mcg/mL (range 1 to 4.5 mcg/mL) and 4.6 mcg/mL (range 1.9 to 7.7 mcg/mL), respectively, when tested in normal adult volunteers. The area under the time versus concentration curve (AUC) is greater by approximately 10% to 25% with the cefixime for oral suspension than with the tablet after doses of 100 to 400 mg, when tested in normal adult volunteers. This increased absorption should be taken into consideration if the cefixime for oral suspension is to be substituted for the tablet. Because of the lack of bioequivalence, cefixime tablets should not be substituted for cefixime for oral suspension in the treatment of otitis media [see Dosage and Administration (2)]. Cross-over studies of tablet versus suspension have not been performed in children.
The 400 mg cefixime capsule is bioequivalent to the 400 mg cefixime tablet under fasting conditions. However, food reduces the absorption following administration of the capsule by approximately 15% based on AUC and 25% based on Cmax.
Peak serum concentrations occur between 2 and 6 hours following oral administration of a single 200 mg tablet, a single 400 mg cefixime tablet or 400 mg of cefixime for oral suspension. Peak serum concentrations occur between 2 and 5 hours following a single administration of 200 mg of cefixime for oral suspension. Peak serum concentrations occur between 3 and 8 hours following oral administration of a single 400 mg cefixime capsule.
Distribution
Serum protein binding is concentration independent with a bound fraction of approximately 65%. In a multiple dose study conducted with a research formulation which is less bioavailable than the cefixime tablet or cefixime for oral suspension, there was little accumulation of drug in serum or urine after dosing for 14 days. Adequate data on CSF levels of cefixime are not available.
Elimination
Metabolism and Excretion
There is no evidence of metabolism of cefixime in vivo. Approximately 50% of the absorbed dose is excreted unchanged in the urine in 24 hours. In animal studies, it was noted that cefixime is also excreted in the bile in excess of 10% of the administered dose. The serum half-life of cefixime in healthy subjects is independent of dosage form and averages 3 to 4 hours but may range up to 9 hours in some normal volunteers.
Specific Populations
Geriatric Patients**:**Average AUCs at steady state in elderly patients are approximately 40% higher than average AUCs in other healthy adults. Differences in the pharmacokinetic parameters between 12 young and 12 elderly subjects who received 400 mg of cefixime once daily for 5 days are summarized as follows:
Table 4. Pharmacokinetic Parameters for Cefixime in Both Young and Elderly Subjects|
** Pharmacokinetic**** Parameters**** (mean**** ±**** SD)**** for**** Cefixime**** in**** Both**** Young**** &**** Elderly**** Subjects** | ||
|
** Pharmacokinetic**** parameter** |
** Young** |
** Elderly** |
|
Cmax (mg/L) |
4.74 ± 1.43 |
5.68 ± 1.83 |
|
Tmax (h) * |
3.9 ± 0.3 |
4.3 ± 0.6 |
|
AUC (mg.h/L) * |
34.9 ± 12.2 |
49.5 ± 19.1 |
|
T½ (h) * |
3.5 ± 0.6 |
4.2 ± 0.4 |
|
Cave (mg/L)* |
1.42 ±0.50 |
1.99 ± 0.75 |
|
*Difference between age groups was significant. (p<0.05) |
However, these increases were not clinically significant [see Dosage and Administration (2)].
**Patients with Renal Impairment:**In subjects with moderate impairment of renal function (20 to 40 mL/min creatinine clearance), the average serum half- life of cefixime is prolonged to 6.4 hours. In severe renal impairment (5 to 20 mL/min creatinine clearance), the half-life increased to an average of 11.5 hours. The drug is not cleared significantly from the blood by hemodialysis or peritoneal dialysis. However, a study indicated that with doses of 400 mg of cefixime, patients undergoing hemodialysis have similar blood profiles as subjects with creatinine clearances of 21 to 60 mL/min.
12.4 Microbiology
Mechanism of Action
As with other cephalosporins, the bactericidal action of cefixime results from inhibition of cell wall synthesis. Cefixime is stable in the presence of certain beta-lactamase enzymes. As a result, certain organisms resistant to penicillins and some cephalosporins due to the presence of beta-lactamases may be susceptible to cefixime.
Resistance
Resistance to cefixime in isolates of Haemophilus influenzae and Neisseria gonorrhoeae is most often associated with alterations in penicillin-binding proteins (PBPs). Cefixime may have limited activity against Enterobacteriaceae producing extended spectrum beta-lactamases (ESBLs). Pseudomonas species, Enterococcus species, strains of Group D streptococci, Listeria monocytogenes, most strains of staphylococci (including methicillin-resistant strains), most strains of Enterobacter species, most strains of Bacteroides fragilis, and most strains of Clostridium species are resistant to cefixime.
Antimicrobial Activity
Cefixime has been shown to be active against most isolates of the following microorganisms, both in vitro and in clinical infections [see Indications and Usage (1)].
Gram-positive Bacteria
Streptococcus pneumoniae
Streptococcus pyogenes
Gram-negative Bacteria
Escherichia coli
Haemophilus influenzae
Moraxella catarrhalis
Neisseria gonorrhoeae
Proteus mirabilis
The following in vitro data are available, but their clinical significance is unknown. At least 90 percent of the following bacteria exhibit an in vitro minimum inhibitory concentration (MIC) less than or equal to the susceptible breakpoint for cefixime against isolates of similar genus or organism group. However, the efficacy of cefixime in treating clinical infections caused by these bacteria has not been established in adequate and well-controlled clinical trials.
Gram-positive Bacteria
Streptococcus agalactiae
Gram-negative Bacteria
Citrobacter amalonaticus
Citrobacter diversus
Haemophilus parainfluenzae
Klebsiella oxytoca
Klebsiella pneumoniae
Pasteurella multocida
Proteus vulgaris
Providencia species
Salmonella species
Serratia marcescens
Shigella species
Susceptibility Testing
For specific information regarding susceptibility test interpretive criteria and associated test methods and quality control standards recognized by FDA for this drug, please see: https://www.fda.gov/STIC.
NONCLINICAL TOXICOLOGY SECTION
13 NONCLINICAL TOXICOLOGY
13.1 Carcinogenesis, Mutagenesis, Impairment of Fertility
Lifetime studies in animals to evaluate carcinogenic potential have not been conducted. Cefixime did not cause point mutations in bacteria or mammalian cells, DNA damage, or chromosome damage in vitro and did not exhibit clastogenic potential in vivo in the mouse micronucleus test. In the fertility and reproductive performance study in rats, no difference between control and drug-treated animals was detected in mating behavior, pregnancy rate, or litter parameters (determined at sacrifice on day 13 of pregnancy) at oral doses up to 1000 mg/kg/day (25 times the adult therapeutic dose) administered to males (for 68 days prior to pairing and during the cohabitation period) and females (for 14 days before pairing to weaning).
REFERENCES SECTION
15 REFERENCES
- Halperin-Walega, E. Batra VK, Tonelli AP, Barr A, Yacobi A. 'Disposition of Cefixime in the Pregnant and Lactating Rat. Transfer to the Fetus and Nursing Pup'. Drug Metabolism and Disposition. 1988:16(1): pp130–134.
USE IN SPECIFIC POPULATIONS SECTION
8 USE IN SPECIFIC POPULATIONS
8.1 Pregnancy
Risk Summary
Available data from published observational studies, case series, and case reports over several decades with cephalosporin use, including cefixime, in pregnant women have not established drug-associated risks of major birth defects, miscarriage, or adverse maternal or fetal outcomes (see Data). Reproduction studies have been performed in mice and rats at doses equivalent to 40 and 80 times, respectively, the adult human recommended dose and have revealed no evidence of harm to the fetus due to cefixime (see Data).
The background risk of major birth defects and miscarriage for the indicated population is unknown. All pregnancies have a background risk of birth defect, loss, or other adverse outcomes. In the U.S. general population, the estimated background risks of major birth defects and miscarriage in clinically recognized pregnancies is 2% to 4% and 15% to 20%, respectively.
Clinical Considerations
Disease-Associated Maternal and/or Embryo/Fetal Risk
Maternal gonorrhea may be associated with preterm birth, low neonatal birth weight, chorioamnionitis, intrauterine growth restriction, small for gestational age and premature rupture of membranes. Perinatal transmission of gonorrhea to the offspring can result in infant blindness, joint infections, and bloodstream infections.
Data
Human Data
While available studies cannot definitively establish the absence of risk, published data from prospective cohort studies, case series, and case reports over several decades have not identified a consistent association with cephalosporin use, including cefixime, during pregnancy, and major birth defects, miscarriage, or other adverse maternal or fetal outcomes. Available studies have methodological limitations, including small sample size, retrospective data collection, and inconsistent comparator groups.
Animal Data
The results of embryo-fetal development studies in mice and rats show that cefixime, at doses up to 3200 mg/kg/day administered during the period of organogenesis did not adversely affect development. In these studies, in mice and rats, cefixime did not affect postnatal development or reproductive capacity of the F1 generation or fetal development of the F2 generation. In an embryo-fetal development study in rabbits, cefixime at doses of 3.2, 10 or 32 mg/kg given daily during the period of organogenesis (gestation days 6 through 18) resulted in abortions and/or maternal deaths at doses > 10 mg/kg (typically associated with the administration of antibiotics in this species), but no malformations were reported at lower doses. A pre- and post-natal development study of cefixime at oral doses up to 3200 mg/kg/day in rats demonstrated no effect on the duration of pregnancy, process of parturition, development and viability of offspring, or reproductive capacity of the F1 generation and development of their fetuses (F2).
8.2 Lactation
Risk Summary
There are no available data on the presence of cefixime in human milk, the effects on the breast-fed infant, or the effects on milk production. Cefixime is present in animal milk (see Data). When a drug is present in animal milk, it is likely the drug will be present in human milk. The developmental and health benefits of breastfeeding should be considered along with the mother's clinical need for cefixime and any potential adverse effects on the breast-fed infant from cefixime or from the mother's underlying condition.
Data
In a study on disposition of cefixime in pregnant and lactating rats, continuous intra-peritoneal infusion of 2.54 mg/kg/day of 14C-cefixime from days 10 to 14 postpartum resulted in steady state plasma concentrations of radioactivity in the dams that were 70 times greater than in their nursing pups.
After 102 hours of drug infusion, total radioactivity in the body of the pups, including the stomach and intestinal contents, was 1.5% of the 14C-cefixime estimated to be in the mother's body at steady state.1
8.4 Pediatric Use
The safety and effectiveness of cefixime have been established in pediatric patients 6 months of age and older. Safety and effectiveness of cefixime in pediatric patients younger than 6 months of age have not been established. The incidence of gastrointestinal adverse reactions, including diarrhea and loose stools, in the pediatric patients receiving the cefixime for oral suspension, was comparable to the incidence seen in adult patients receiving tablets.
8.5 Geriatric Use
Clinical studies did not include sufficient numbers of subjects aged 65 and older to determine whether they respond differently than younger subjects. Other reported clinical experience has not identified differences in responses between the elderly and younger patients. A pharmacokinetic study in the elderly detected differences in pharmacokinetic parameters [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)]. These differences were small and do not indicate a need for dosage adjustment of cefixime in the elderly.
8.6 Renal Impairment
The dose of cefixime should be adjusted in patients with renal impairment as well as those undergoing continuous ambulatory peritoneal dialysis (CAPD) and hemodialysis (HD). Patients on dialysis should be monitored carefully [see Dosage and Administration (2.3)].
- Pediatric Use: Efficacy and safety in pediatric patients younger than 6 months of age have not been established. (8.4)
- Geriatric Use: Clinical studies did not include sufficient numbers of subjects aged 65 and older to determine whether they respond differently than younger subjects. Other reported clinical experience has not identified differences in responses between the elderly and younger patients. (8.5)
- Renal Impairment: Cefixime may be administered in the presence of impaired renal function. Dose adjustment is required in patients whose creatinine clearance is less than 60 mL/min. (8.6)
DESCRIPTION SECTION
11 DESCRIPTION
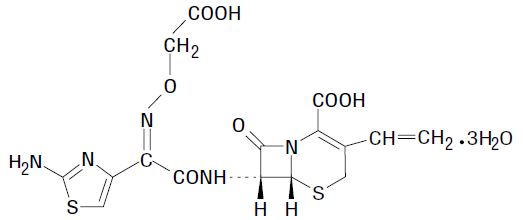
Cefixime is a semisynthetic, cephalosporin antibacterial for oral administration. Chemically, it is (6R,7R)-7-[2-(2-Amino-4-thiazolyl)glyoxylamido]-8-oxo-3-vinyl-5-thia-1-azabicyclo [4.2.0] oct-2-ene-2-carboxylic acid, 72-(Z)-[O-(carboxy methyl) oxime] trihydrate.
Molecular weight = 507.50 as the trihydrate. Chemical Formula is C16H15N5O7S2.3H2O
The structural formula for cefixime is:
Inactive ingredients contained in the cefixime powder for oral suspension USP are colloidal silicon dioxide, sodium benzoate, strawberry flavor, sucrose, and xanthan gum.
Inactive ingredients contained in the cefixime capsules 400 mg are colloidal silicon dioxide, croscarmellose sodium, low substituted hydroxy propyl cellulose, magnesium stearate, and mannitol. The capsule shell contains the following inactive ingredients: ferric oxide black, ferric oxide red, gelatin, potassium hydroxide, propylene glycol, shellac, sodium lauryl sulfate, and titanium dioxide.
DOSAGE & ADMINISTRATION SECTION
2 DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
2.1 Adults
The recommended dose of cefixime is 400 mg daily. This may be given as a 400 mg capsule daily. For the treatment of uncomplicated cervical/urethral gonococcal infections, a single oral dose of 400 mg is recommended. The capsule may be administered without regard to food.
In the treatment of infections due to Streptococcus pyogenes, a therapeutic dosage of cefixime should be administered for at least 10 days.
2.2 Pediatric Patients (6 months or older)
The recommended dose is 8 mg/kg/day of the cefixime for suspension. This may be administered as a single daily dose or may be given in two divided doses, as 4 mg/kg every 12 hours.
Note: A suggested dose has been determined for each pediatric weight range. Refer to Table 1. Ensure all orders that specify a dose in milliliters include a concentration, because cefixime for oral suspension is available in two different concentrations (100 mg/5 mL and 200 mg/5 mL).
Table1. Suggested doses for pediatric patients|
** PEDIATRIC**** DOSAGE**** CHART** | |||
|
** Cefixime**** for oral**** s**** uspension** | |||
|
** 100**** mg/5**** mL** |
** 200**** mg/5**** mL** | ||
|
** Patient**** Weight** |
** Dose/Day** |
** Dose/Day** |
** Dose/Day** |
|
5 to 7.5 |
50 |
2.5 |
-- |
|
7.6 to 10 |
80 |
4 |
2 |
|
10.1 to 12.5 |
100 |
5 |
2.5 |
|
12.6 to 20.5 |
150 |
7.5 |
4 |
|
20.6 to 28 |
200 |
10 |
5 |
|
28.1 to 33 |
250 |
12.5 |
6 |
|
33.1 to 40 |
300 |
15 |
7.5 |
|
40.1 to 45 |
350 |
17.5 |
9 |
|
45.1 or greater |
400 |
20 |
10 |
Pediatric patients weighing more than 45 kg or older than 12 years should be treated with the recommended adult dose.
Otitis media should be treated with cefixime for oral suspension. Clinical trials of otitis media were conducted with the suspension, and the suspension results in higher peak blood levels than the tablet when administered at the same dose.
Therefore, the cefixime tablet or cefixime capsule should not be substituted for the cefixime for oral suspension in the treatment of otitis media [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)].
In the treatment of infections due to Streptococcus pyogenes, a therapeutic dosage of cefixime should be administered for at least 10 days.
2.3 Renal Impairment
Cefixime may be administered in the presence of impaired renal function. Normal dose and schedule may be employed in patients with creatinine clearances of 60 mL/min or greater. Refer to Table 2 for dose adjustments for adults with renal impairment. Neither hemodialysis nor peritoneal dialysis removes significant amounts of drug from the body.
Table2. Doses for Adults with Renal Impairment|
** Renal**** Dysfunction** |
** Cefixime**** for**** Oral**** Suspension** | |
|
Creatinine Clearance (mL/min) |
** 100**** mg/5**** mL** |
** 200**** mg/5**** mL** |
|
Dose/Day (mL) |
Dose/Day (mL) | |
|
60 or greater |
Normal dose |
Normal dose |
|
21 to 59* |
13 |
6.5 |
|
20 or less |
8.6 |
4.4 |
|
*The preferred concentrations of oral suspension to use are 200 mg/5 mL for patients with this renal dysfunction |
2.4 Reconstitution Directions for Cefixime for Oral Suspension
Table 3. Reconstitution Direction for Cefixime for Oral Suspension|
** Strength** |
** Bottle**** Size** |
** Reconstitution**** Directions** |
|
200 mg/5 mL |
75 mL |
To reconstitute, suspend with51**** mL**** water . Method: Tap the bottle several times to loosen powder contents prior to reconstitution. Add approximately half the total amount of water for reconstitution and shake well. Add the remainder of water and shake well. |
|
100 mg/5 mL and 200 mg/5 mL |
50 mL |
To reconstitute, suspend with34**** mL**** water . Method: Tap the bottle several times to loosen powder contents prior to reconstitution. Add approximately half the total amount of water for reconstitution and shake well. Add the remainder of water and shake well. |
After reconstitution, the suspension may be kept for 14 days either at room temperature, or under refrigeration, without significant loss of potency. Keep tightly closed. Shake well before using. Discard unused portion after 14 days.
- Adults: 400 mg daily (2.1)
- Pediatric patients (6 months and older): 8 mg/kg/day (2.2)
DOSAGE FORMS & STRENGTHS SECTION
3 DOSAGE FORMS AND STRENGTHS
Cefixime for oral suspension USP is available for oral administration in a powder for oral suspension, when reconstituted, provides either 100 mg/5 mL or 200 mg/5 mL of cefixime as trihydrate. The powder has an off white to pale yellow color and is strawberry flavored.
Cefixime capsule is available for oral administration as capsules which provide 400 mg of cefixime as trihydrate. These are size "0" capsules with pink opaque cap and pink opaque body, imprinted with "LU" on the cap and "U43" on the body in black ink. Capsules contain white to yellowish white granular powder.
- Oral Suspension: 100 mg/5 mL and 200 mg/5 mL (3)
- Capsules: 400mg (3)
CLINICAL STUDIES SECTION
14 CLINICAL STUDIES
Comparative clinical trials of otitis media were conducted in nearly 400 pediatric patients between the ages of 6 months to 10 years. Streptococcus pneumoniae was isolated from 47% of the patients, Haemophilus influenzae from 34%, Moraxella catarrhalis from 15% and S. pyogenes from 4%.
The overall response rate of Streptococcus pneumoniae to cefixime was approximately 10% lower and that of Haemophilus influenzae or Moraxella catarrhalis approximately 7% higher (12% when beta-lactamase positive isolates of H. influenzae are included) than the response rates of these organisms to the active control drugs.
In these studies, patients were randomized and treated with either cefixime at dose regimens of 4 mg/kg twice a day or 8 mg/kg once a day, or with a comparator. Sixty-nine to 70% of the patients in each group had resolution of signs and symptoms of otitis media when evaluated 2 to 4 weeks post-treatment, but persistent effusion was found in 15% of the patients. When evaluated at the completion of therapy, 17% of patients receiving cefixime and 14% of patients receiving effective comparative drugs (18% including those patients who had Haemophilus influenzae resistant to the control drug and who received the control antibacterial drug) were considered to be treatment failures. By the 2 to 4 week follow-up, a total of 30%-31% of patients had evidence of either treatment failure or recurrent disease.
Table 5. Bacteriological Outcome of Otitis Media|
(a) Number eradicated/number isolated. | |||
|
(b) An additional 20 beta-lactamase positive isolates of Haemophilus influenzae were isolated, but were excluded from this analysis because they were resistant to the control antibacterial drug. In nineteen of these, the clinical course could be assessed and a favorable outcome occurred in 10. When these cases are included in the overall bacteriological evaluation of therapy with the control drugs, 140/185 (76%) of pathogens were considered to be eradicated. | |||
|
** Bacteriological**** Outcome**** of**** Otitis**** Media**** at**** Two**** to**** Four**** Weeks**** Post-Therapy**** Based**** on**** Repeat**** Middle**** Ear**** Fluid**** Culture**** or**** Extrapolation**** from**** Clinical**** Outcome** | |||
|
** Organism** |
** Cefixime(a)** |
** Cefixime(a)** |
** Control(a)** |
|
Streptococcuspneumoniae |
48/70 (69%) |
18/22 (82%) |
82/100 (82%) |
|
Haemophilus influenzae beta-lactamase negative |
24/34 (71%) |
13/17 (76%) |
23/34 (68%) |
|
Haemophilus influenzae beta-lactamase positive |
17/22 (77%) |
9/12 (75%) |
1/1 (b) |
|
Moraxellacatarrhalis |
26/31 (84%) |
5/5 |
18/24 (75%) |
|
S.pyogenes |
5/5 |
3/3 |
6/7 |
|
All Isolates |
120/162 (74%) |
48/59 (81%) |
130/166 (78%) |
HOW SUPPLIED SECTION
16 HOW SUPPLIED/STORAGE AND HANDLING
Cefixime for oral suspension USP, 100 mg/5 mL is an off-white to pale yellow colored powder. After reconstituted as directed, each 5 mL of reconstituted suspension contains 100 mg of cefixime as the trihydrate and is supplied as follows:
NDC 68180-405-01 - 50 mL Bottle
Prior to reconstitution**: Store drug powder at 20°C to 25°C (68°F to 77°F) [See USP Controlled Room Temperature].**
After reconstitution**: Store at room temperature or under refrigeration.**
Keep tightly closed.
Cefixime for oral suspension USP, 200 mg/5 mL is an off-white to pale yellow colored powder. After reconstituted as directed, each 5 mL of reconstituted suspension contains 200 mg of cefixime as the trihydrate and is supplied as follows:
NDC 68180-407-03 - 50 mL Bottle
NDC 68180-407-04 - 75 mL Bottle
Prior to reconstitution**: Store drug powder at 20°C to 25°C (68°F to 77°F) [See USP Controlled Room Temperature].**
After reconstitution**: Store at room temperature or under refrigeration.**
Keep tightly closed.
Cefixime capsules, 400 mg is size "0" capsule with pink opaque cap and pink opaque body, imprinted with "LU" on cap and "U43" on body in black ink, containing white to yellowish white granular powder containing 400 mg of cefixime as the trihydrate and is supplied as follows:
NDC 68180-423-08 - Bottle of 50 capsules
NDC 68180-423-11 - Unit dose Package of 10 (1 blister of 10 capsules)
Store at 20**°C to 25°C (68°F to 77°F) [See USP Controlled Temperature].**
INFORMATION FOR PATIENTS SECTION
17 PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATION
Development of Drug Resistance Bacteria
Patients should be counseled that antibacterial drugs, including cefixime, should only be used to treat bacterial infections. They do not treat viral infections (e.g., the common cold). When cefixime is prescribed to treat a bacterial infection, patients should be told that although it is common to feel better early in the course of therapy, the medication should be taken exactly as directed. Skipping doses or not completing the full course of therapy may: (1) decrease the effectiveness of the immediate treatment and (2) increase the likelihood that bacteria will develop resistance and will not be treatable by cefixime or other antibacterial drugs in the future.
Diarrhea
Advise patients that diarrhea is a common problem caused by antibacterial drugs, including cefixime which usually ends when the antibacterial drug is discontinued. Sometimes after starting treatment with antibacterial drugs, patients can develop watery and bloody stools (with or without stomach cramps and fever) even as late as two or more months after having taken the last dose of the antibacterial drug. If this occurs, patients should contact their physician as soon as possible.
LUPIN and the
 are registered trademarks of Lupin Pharmaceuticals, Inc.
are registered trademarks of Lupin Pharmaceuticals, Inc.
Manufactured for:
Lupin Pharmaceuticals, Inc.
Naples, FL 34108
United States
Manufactured by:
Lupin Limited
Mandideep 462 046
INDIA
Revised: July 2025 ID#: 280709
