Not Applicable
These highlights do not include all the information needed to use OMEPRAZOLE AND SODIUM BICARBONATE CAPSULES safely and effectively. See full prescribing information for OMEPRAZOLE AND SODIUM BICARBONATE CAPSULES.OMEPRAZOLE and SODIUM BICARBONATE capsules, for oral useInitial U.S. Approval: 2004
f77428fd-1744-4b3f-bd9c-b7fde46a211a
HUMAN PRESCRIPTION DRUG LABEL
Jul 13, 2017
Sterling Knight Pharmaceuticals LLC
DUNS: 079556942
Products 1
Detailed information about drug products covered under this FDA approval, including NDC codes, dosage forms, ingredients, and administration routes.
omeprazole sodium bicarbonate
Product Details
FDA regulatory identification and product classification information
FDA Identifiers
Product Classification
Product Specifications
INGREDIENTS (9)
Drug Labeling Information
RECENT MAJOR CHANGES SECTION
CLINICAL STUDIES SECTION
14 CLINICAL STUDIES
14.1 Duodenal Ulcer Disease
Active Duodenal Ulcer – In a multicenter, double-blind, placebo controlled study of 147 patients with endoscopically documented duodenal ulcer, the percentage of patients healed (per protocol) at 2 and 4 weeks was significantly higher with omeprazole 20 mg once a day than with placebo (p ≤ 0.01). (See Table 6)
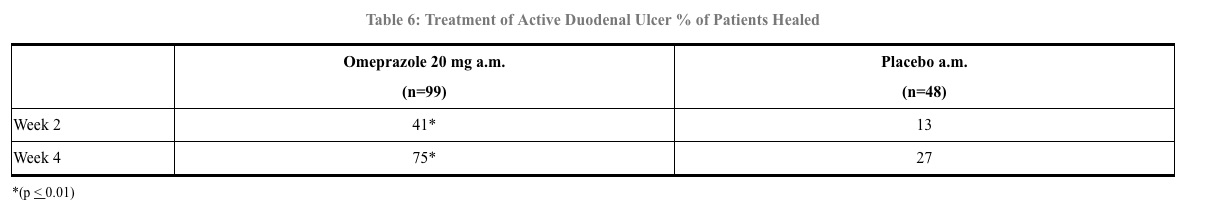
Complete daytime and nighttime pain relief occurred significantly faster (p ≤ 0.01) in patients treated with omeprazole 20 mg than in patients treated with placebo. At the end of the study, significantly more patients who had received omeprazole had complete relief of daytime pain (p ≤ 0.05) and nighttime pain (p ≤ 0.01).
In a multicenter, double-blind study of 293 patients with endoscopically documented duodenal ulcer, the percentage of patients healed (per protocol) at 4 weeks was significantly higher with omeprazole 20 mg once a day than with ranitidine 150 mg b.i.d. (p < 0.01). (See Table 7)
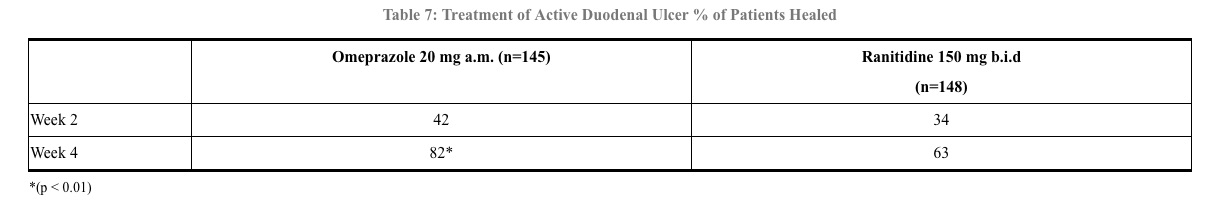
Healing occurred significantly faster in patients treated with omeprazole than in those treated with ranitidine 150 mg b.i.d. (p < 0.01).
In a foreign multinational randomized, double-blind study of 105 patients with endoscopically documented duodenal ulcer, 40 mg and 20 mg of omeprazole were compared to 150 mg b.i.d. of ranitidine at 2, 4 and 8 weeks. At 2 and 4 weeks both doses of omeprazole were statistically superior (per protocol) to ranitidine, but 40 mg was not superior to 20 mg of omeprazole, and at 8 weeks there was no significant difference between any of the active drugs. (See Table 8)
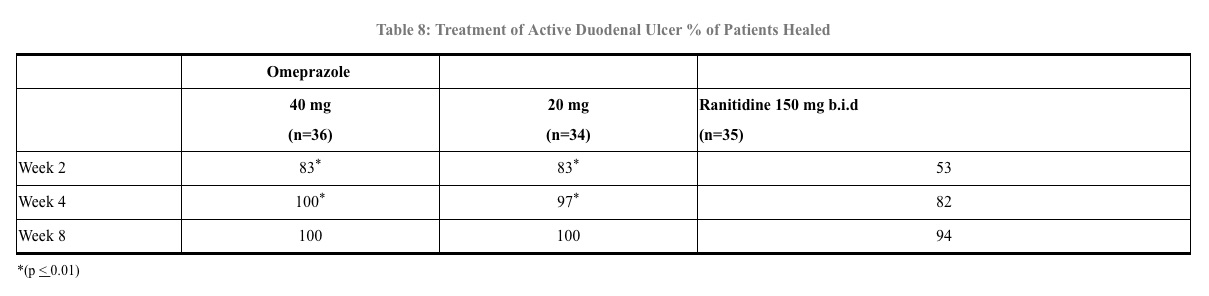
14.2 Gastric Ulcer
In a U.S. multicenter, double-blind study of omeprazole 40 mg once a day, 20 mg once a day, and placebo in 520 patients with endoscopically diagnosed gastric ulcer, the following results were obtained. (See Table 9)
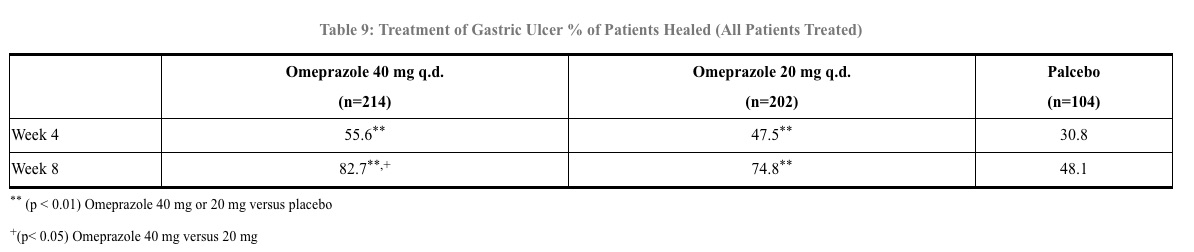
For the stratified groups of patients with ulcer size less than or equal to 1 cm, no difference in healing rates between 40 mg and 20 mg was detected at either 4 or 8 weeks. For patients with ulcer size greater than 1 cm, 40 mg was significantly more effective than 20 mg at 8 weeks.
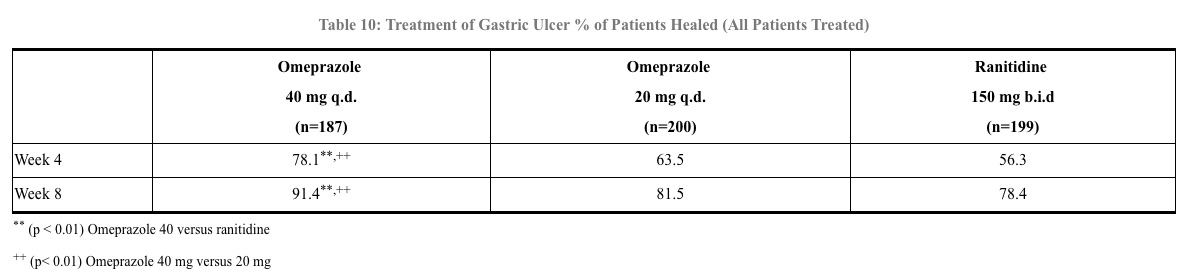
In a foreign, multinational, double-blind study of 602 patients with endoscopically diagnosed gastric ulcer, omeprazole 40 mg once a day, 20 mg once a day, and ranitidine 150 mg twice a day were evaluated. (See Table 10)
14.3 Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease (GERD)
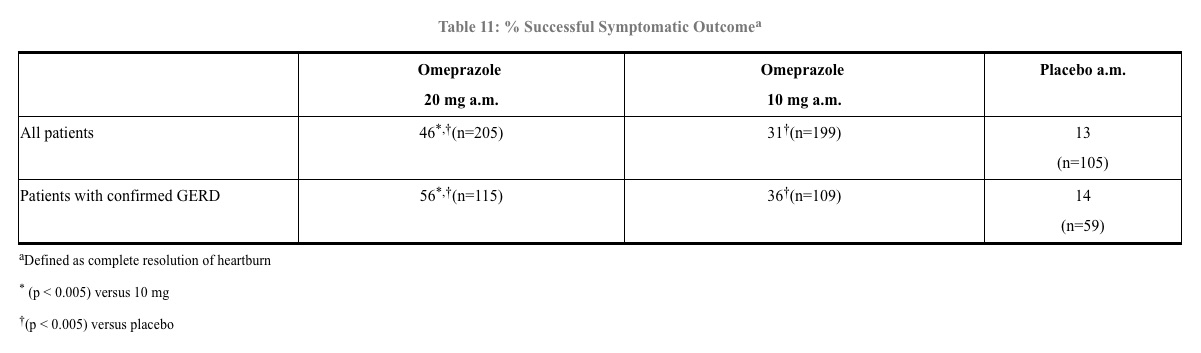
Symptomatic GERD - A placebo controlled study was conducted in Scandinavia to compare the efficacy of omeprazole 20 mg or 10 mg once daily for up to 4 weeks in the treatment of heartburn and other symptoms in GERD patients without erosive esophagitis. Results are shown in Table 11.
Erosive Esophagitis - In a U.S. multicenter double-blind placebo controlled study of 40 mg or 20 mg of omeprazole delayed release capsules in patients with symptoms of GERD and endoscopically diagnosed erosive esophagitis of grade 2 or above, the percentage healing rates (per protocol) were as shown in Table 12.
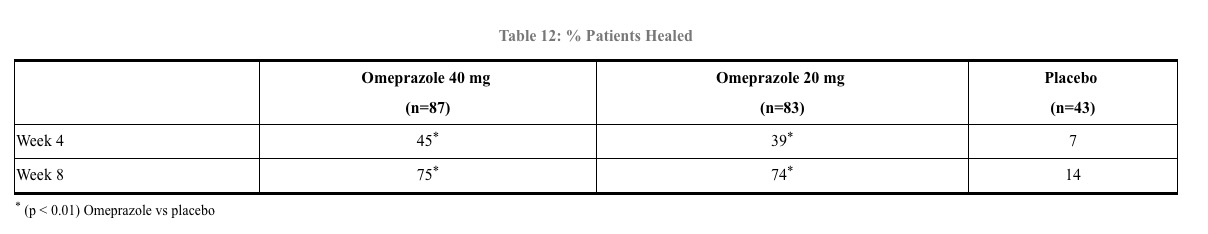
In this study, the 40-mg dose was not superior to the 20-mg dose of omeprazole in the percentage healing rate. Other controlled clinical trials have also shown that omeprazole is effective in severe GERD. In comparisons with histamine H2-receptor antagonists in patients with erosive esophagitis, grade 2 or above, omeprazole in a dose of 20 mg was significantly more effective than the active controls. Complete daytime and nighttime heartburn relief occurred significantly faster (p < 0.01) in patients treated with omeprazole than in those taking placebo or histamine H2-receptor antagonists.
In this and five other controlled GERD studies, significantly more patients taking 20 mg omeprazole (84%) reported complete relief of GERD symptoms than patients receiving placebo (12%).
14.4 Long Term Maintenance Treatment of Erosive Esophagitis
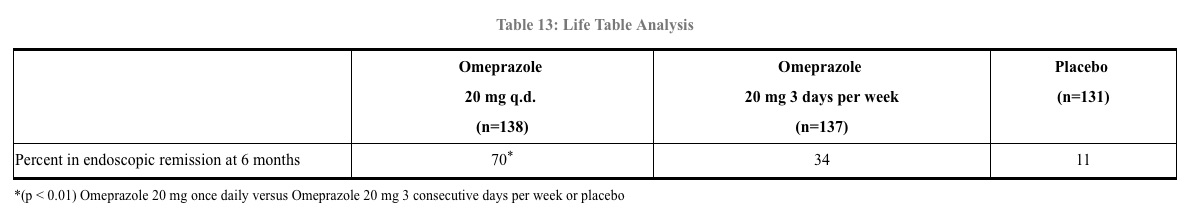
In a U.S. double-blind, randomized, multicenter, placebo controlled study; two dose regimens of omeprazole were studied in patients with endoscopically confirmed healed esophagitis. Results to determine maintenance of healing of erosive esophagitis are shown in Table 13.
In an international, multicenter, double-blind study, omeprazole 20 mg daily and 10 mg daily were compared to ranitidine 150 mg twice daily in patients with endoscopically confirmed healed esophagitis. Table 14 provides the results of this study for maintenance of healing of erosive esophagitis.
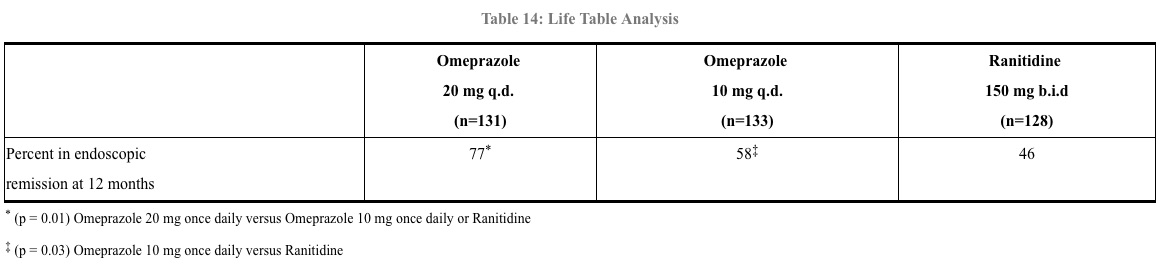
In patients who initially had grades 3 or 4 erosive esophagitis, for maintenance after healing 20 mg daily of omeprazole was effective, while 10 mg did not demonstrate effectiveness.
