Registrants1
Companies and organizations registered with the FDA for this drug approval, including their contact information and regulatory details.
791119022
Manufacturing Establishments1
FDA-registered manufacturing facilities and establishments involved in the production, packaging, or distribution of this drug product.
Preferred Pharmaceuticals Inc.
Preferred Pharmaceuticals Inc.
791119022
Products1
Detailed information about drug products covered under this FDA approval, including NDC codes, dosage forms, ingredients, and administration routes.
Cephalexin
Product Details
Drug Labeling Information
Complete FDA-approved labeling information including indications, dosage, warnings, contraindications, and other essential prescribing details.
PACKAGE LABEL.PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL
PACKAGE LABEL- PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL - 500 mg
NDC 68788-8538
** Rx only**
** Cephalexin**
** Capsules, USP**
** 500 mg**
** AUROBINDO**
Repackaged By: Preferred Pharmaceuticals Inc.

DESCRIPTION SECTION
11 DESCRIPTION
Cephalexin capsules, USP is a semisynthetic cephalosporin antibacterial drug intended for oral administration. It is 7-(D-α-Amino-α- phenylacetamido)-3-methyl-3-cephem-4-carboxylic acid monohydrate. Cephalexin has the molecular formula C16H17N3O4S•H2O and the molecular weight is 365.41.
Cephalexin has the following structural formula:
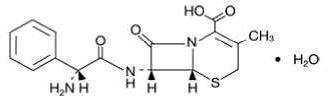
Each capsule contains cephalexin monohydrate equivalent to 250 mg or 500 mg of cephalexin. The capsules also contain the following inactive ingredients: microcrystalline cellulose, croscarmellose sodium, D&C Yellow No. 10, FD&C Blue No. 1, FD&C Yellow No. 6, gelatin, magnesium stearate, titanium dioxide, and sodium lauryl sulfate.
DOSAGE & ADMINISTRATION SECTION
Highlight:
Adults and patients at least 15 years of age
The usual dose is 250 mg every 6 hours, but a dose of 500 mg every 12 hours may be administered (2.1)
Pediatric
patients (over 1
year of age)•
Otitis media: 75 to 100 mg/kg in equally divided doses every 6 hours (2.2)•
All other indications: 25 to 50 mg/kg given in equally divided doses (2.2)•
In severe infections: 50 to 100 mg/kg may be administered in equally divided doses (2.2)•
Duration of therapy ranges from 7 to 14 days depending on the infection type and severity. (2)•
Dosage adjustment is required in patients with severe and end stage renal disease (ESRD) defined as creatinine clearance below 30 mL/min. (2.3)2 DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
2.1 Adults and Pediatric Patients at Least 15 Years of Age
The usual dose of oral cephalexin capsules is 250 mg every 6 hours, but a dose of 500 mg every 12 hours may be administered. Treatment is administered for 7 to 14 days.
For more severe infections larger doses of oral cephalexin capsules may be needed, up to 4 grams daily in two to four equally divided doses.
2.2 Pediatric Patients (over 1 year of age)
The recommended total daily dose of oral cephalexin capsules for pediatric patients is 25 to 50 mg/kg given in equally divided doses for 7 to 14 days. In the treatment of β-hemolytic streptococcal infections, duration of at least 10 days is recommended. In severe infections, a total daily dose of 50 to 100 mg/kg may be administered in equally divided doses.
For the treatment of otitis media, the recommended daily dose is 75 to 100 mg/kg given in equally divided doses.
2.3 Dosage Adjustments in Adult and Pediatric Patients at Least 15 Years of
Age with Renal Impairment
Administer the following dosing regimens for cephalexin capsules to patients with renal impairment [see Warnings and Precautions (5.4) and Use in Specific Populations (8.6)].
Table 1. Recommended Dose Regimen for Patients with Renal Impairment
*There is insufficient information to make dose adjustment recommendations in patients on hemodialysis.
Renal function
Dose regimen recommendation
Creatinine clearance > 60 mL/min
No dose adjustment
Creatinine clearance 30 to 59 mL/min
No dose adjustment; maximum daily dose should not exceed 1g
Creatinine clearance 15 to 29 mL/min
250 mg, every 8 hours or every 12 hours
Creatinine clearance 5 to 14 mL/min not yet on dialysis*
250 mg, every 24 hours
Creatinine clearance 1 to 4 mL/min not yet on dialysis*
250 mg, every 48 hours or every 60 hours
DOSAGE FORMS & STRENGTHS SECTION
Highlight: Capsules: 250 mg and 500 mg (3)
3 DOSAGE FORMS AND STRENGTHS
250 mg capsules: Dark green opaque/white size “2” hard gelatin capsule filled with off white granular powder and imprinted with “A 42” on dark green opaque cap and “250 mg” on white body with black ink.
500 mg capsules: Dark green opaque/light green opaque size “0” hard gelatin capsule filled with off white granular powder and imprinted with “A 43” on dark green opaque cap and “500 mg” on light green opaque body with black ink.
CONTRAINDICATIONS SECTION
Highlight: Patients with known hypersensitivity to cephalexin or other members of the cephalosporin class of antibacterial drugs. (4)
4 CONTRAINDICATIONS
Cephalexin capsules are contraindicated in patients with known hypersensitivity to cephalexin or other members of the cephalosporin class of antibacterial drugs.
WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS SECTION
Highlight: •
Serious hypersensitivity (anaphylactic) reactions: Prior to use, inquire regarding history of hypersensitivity to beta-lactam antibacterial drugs. Discontinue the drug if signs or symptoms of an allergic reaction occur and institute supportive measures. (5.1)•
Clostridium difficile-associated diarrhea (CDAD): Evaluate if diarrhea occurs. (5.2)•
Direct Coombs’ Test Seroconversion: If anemia develops during or after cephalexin therapy, evaluate for drug-induced hemolytic anemia. (5.3)•
Seizure Potential: Use lower dose in patients with renal impairment. (5.4)5 WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS
5.1 Hypersensitivity Reactions
Allergic reactions in the form of rash, urticaria, angioedema, anaphylaxis, erythema multiforme, Stevens-Johnson syndrome, or toxic epidermal necrolysis have been reported with the use of cephalexin. Before therapy with cephalexin is instituted, inquire whether the patient has a history of hypersensitivity reactions to cephalexin, cephalosporins, penicillins, or other drugs. Cross- hypersensitivity among beta-lactam antibacterial drugs may occur in up to 10% of patients with a history of penicillin allergy.
If an allergic reaction to cephalexin occurs, discontinue the drug and institute appropriate treatment.
5.2 Clostridium difficile-Associated Diarrhea
Clostridium difficile**-**associated diarrhea (CDAD) has been reported with use of nearly all antibacterial agents, including cephalexin, and may range in severity from mild diarrhea to fatal colitis. Treatment with antibacterial agents alters the normal flora of the colon leading to overgrowth of C. difficile.
C. difficile produces toxins A and B, which contribute to the development of CDAD. Hypertoxin-producing strains of C. difficile cause increased morbidity and mortality, as these infections can be refractory to antimicrobial therapy and may require colectomy. CDAD must be considered in all patients who present with diarrhea following antibiotic use. Careful medical history is necessary since CDAD has been reported to occur over two months after the administration of antibacterial agents.
If CDAD is suspected or confirmed, ongoing antibiotic use not directed against C. difficile may need to be discontinued. Appropriate fluid and electrolyte management, protein supplementation, antibiotic treatment of C. difficile, and surgical evaluation should be instituted as clinically indicated.
5.3 Direct Coombs’ Test Seroconversion
Positive direct Coombs’ tests have been reported during treatment with the cephalosporin antibacterial drugs including cephalexin. Acute intravascular hemolysis induced by cephalexin therapy has been reported. If anemia develops during or after cephalexin therapy, perform a diagnostic work-up for drug- induced hemolytic anemia, discontinue cephalexin and institute appropriate therapy.
5.4 Seizure Potential
Several cephalosporins have been implicated in triggering seizures, particularly in patients with renal impairment when the dosage was not reduced. If seizures occur, discontinue cephalexin. Anticonvulsant therapy can be given if clinically indicated.
5.5 Prolonged Prothrombin Time
Cephalosporins may be associated with prolonged prothrombin time. Those at risk include patients with renal or hepatic impairment, or poor nutritional state, as well as patients receiving a protracted course of antibacterial therapy, and patients receiving anticoagulant therapy. Monitor prothrombin time in patients at risk and manage as indicated.
5.6 Development of Drug-Resistant Bacteria
Prescribing cephalexin in the absence of a proven or strongly suspected bacterial infection is unlikely to provide benefit to the patient and increases the risk of the development of drug-resistant bacteria.
Prolonged use of cephalexin may result in the overgrowth of nonsusceptible organisms. Careful observation of the patient is essential. If superinfection occurs during therapy, appropriate measures should be taken.
USE IN SPECIFIC POPULATIONS SECTION
Highlight: •
Renal Impairment: Monitor patients longer for toxicity and drug interactions due to delayed clearance. (8.6)8 USE IN SPECIFIC POPULATIONS
8.1 Pregnancy
Risk Summary
Available data from published epidemiologic studies and pharmacovigilance case reports over several decades with cephalosporin use, including cephalexin use in pregnant women have not established drug-associated risks of major birth defects, miscarriage, or adverse maternal or fetal outcomes (see Data).
Animal reproduction studies with mice and rats using oral doses of cephalexin that are 0.6- and 1.2-times the maximum recommended human dose (MRHD) based on body surface area during organogenesis revealed no evidence of harm to the fetus (see Data).
The estimated background risk of major birth defects and miscarriage for the indicated population is unknown. All pregnancies have a background risk of birth defect, loss, or other adverse outcomes. In the U.S. general population, the estimated background risk of major birth defects and miscarriage in clinically recognized pregnancies is 2% to 4% and 15% to 20%, respectively.
Data
Human Data
While available studies cannot definitively establish the absence of risk, published data from epidemiologic studies and postmarketing case reports over several decades have not identified a consistent association with cephalosporin use, including cephalexin, during pregnancy, and major birth defects, miscarriage, or other adverse maternal or fetal outcomes. Available studies have methodologic limitations, including small sample size, retrospective data collection, and inconsistent comparator groups.
Animal Data
In animal reproduction studies, pregnant mice and rats administered oral cephalexin doses of 250 or 500 mg/kg/day (approximately 0.6 and 1.2 times the MRHD) based on body surface area, respectively during the period of organogenesis showed no adverse effects on embryofetal development.
In a pre-and post-natal developmental toxicity study, pregnant rats that received oral doses of 250 or 500 mg/kg/day of cephalexin from Day 15 of pregnancy to litter Day 21 showed no adverse effects on parturition, litter size, or growth of offspring.
8.2 Lactation
Risk Summary
Data from a published clinical lactation study reports that cephalexin is present in human milk. The Relative Infant Dose (RID) is considered to be <1% of the maternal weight adjusted dose. There are no data on the effects of cephalexin on the breastfed child or on milk production.
The development of health benefits of breastfeeding should be considered along with the mother’s clinical need for cephalexin and any potential adverse effects on the breastfed child from cephalexin or from the underlying maternal condition.
8.4 Pediatric Use
The safety and effectiveness of cephalexin in pediatric patients was established in clinical trials for the dosages described in the dosage and administration section [see Dosage and Administration (2.2)].
8.5 Geriatric Use
Of the 701 subjects in 3 published clinical studies of cephalexin, 433 (62%) were 65 and over. No overall differences in safety or effectiveness were observed between these subjects and younger subjects, and other reported clinical experience has not identified differences in responses between the elderly and younger patients.
This drug is substantially excreted by the kidney, and the risk of toxic reactions to this drug may be greater in patients with impaired renal function. Because elderly patients are more likely to have decreased renal function, care should be taken in dose selection [see Warnings and Precautions (5.4)].
8.6 Renal Impairment
Cephalexin should be administered with careful monitoring in the presence of renal impairment (creatinine clearance < 30 mL/min, with or without dialysis). Under such conditions, careful clinical observation and laboratory studies renal function monitoring should be conducted because safe dosage may be lower than that usually recommended [see Dosage and Administration (2.3)]. Monitor patients longer for toxicity and drug interactions due to delayed clearance.
OVERDOSAGE SECTION
10 OVERDOSAGE
Symptoms of oral overdose may include nausea, vomiting, epigastric distress, diarrhea, and hematuria. In the event of an overdose, institute general supportive measures.
Forced diuresis, peritoneal dialysis, hemodialysis, or charcoal hemoperfusion have not been established as beneficial for an overdose of cephalexin.
NONCLINICAL TOXICOLOGY SECTION
13 NONCLINICAL TOXICOLOGY
13.1 Carcinogenesis, Mutagenesis, Impairment of Fertility
Lifetime studies in animals have not been performed to evaluate the carcinogenic potential of cephalexin. Tests to determine the mutagenic potential of cephalexin have not been performed. In male and female rats, fertility and reproductive performance were not affected by cephalexin oral doses up to 1.5 times the highest recommended human dose based upon body surface area.
INFORMATION FOR PATIENTS SECTION
17 PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATION
Allergic Reactions
Advise patients that allergic reactions, including serious allergic reactions, could occur and that serious reactions require immediate treatment. Ask the patient about any previous hypersensitivity reactions to cephalexin, other beta-lactams (including cephalosporins) or other allergens (5.1)
Diarrhea
Advise patients that diarrhea is a common problem caused by antibacterial drugs and usually resolves when the drug is discontinued. Sometimes, frequent watery or bloody diarrhea may occur and may be a sign of a more serious intestinal infection. If severe watery or bloody diarrhea develops, advise patients to contact their healthcare provider.
Antibacterial Resistance
Counsel patients that antibacterial drugs including cephalexin, should only be used to treat bacterial infections. They do not treat viral infections (e.g., the common cold). When cephalexin is prescribed to treat a bacterial infection, tell patients that although it is common to feel better early in the course of therapy, the medication should be taken exactly as directed. Skipping doses or not completing the full course of therapy may (1) decrease the effectiveness of the immediate treatment and (2) increase the likelihood that bacteria will develop resistance and will not be treatable by cephalexin or other antibacterial drugs in the future.
Distributed by:
Aurobindo Pharma USA, Inc.
279 Princeton-Hightstown Road
East Windsor, NJ 08520Manufactured by:
Aurobindo Pharma Limited
Hyderabad-500 032, IndiaRevised: 10/2021
Repackaged By: Preferred Pharmaceuticals Inc.
HOW SUPPLIED SECTION
16 HOW SUPPLIED/STORAGE AND HANDLING
Cephalexin capsules, USP are available in:
500 mg Capsule
Dark green opaque/light green opaque size “0” hard gelatin capsule filled with off white granular powder and imprinted with “A 43” on dark green opaque cap and “500 mg” on light green opaque body with black ink.
Bottles of 6 NDC 68788-8538-5
Bottles of 12 NDC 68788-8538-1
Bottles of 14 NDC 68788-8538-9
Bottles of 20 NDC 68788-8538-2
Bottles of 21 NDC 68788-8538-7
Bottles of 28 NDC 68788-8538-8
Bottles of 30 NDC 68788-8538-3
Bottles of 40 NDC 68788-8538-4
Bottles of 60 NDC 68788-8538-6
Store at 20° to 25°C (68° to 77°F); excursions permitted to 15° to 30°C (59° to 86°F) [see USP Controlled Room Temperature].
Dispense in a tight, light-resistant container.
