RYBELSUS
These highlights do not include all the information needed to use safely and effectively. See full prescribing information for . Initial U.S. Approval: 2017
27f15fac-7d98-4114-a2ec-92494a91da98
HUMAN PRESCRIPTION DRUG LABEL
Jan 24, 2024
Novo Nordisk
DUNS: 622920320
Products 3
Detailed information about drug products covered under this FDA approval, including NDC codes, dosage forms, ingredients, and administration routes.
Oral Semaglutide
Product Details
FDA regulatory identification and product classification information
FDA Identifiers
Product Classification
Product Specifications
INGREDIENTS (5)
Oral Semaglutide
Product Details
FDA regulatory identification and product classification information
FDA Identifiers
Product Classification
Product Specifications
INGREDIENTS (5)
Oral Semaglutide
Product Details
FDA regulatory identification and product classification information
FDA Identifiers
Product Classification
Product Specifications
INGREDIENTS (5)
Drug Labeling Information
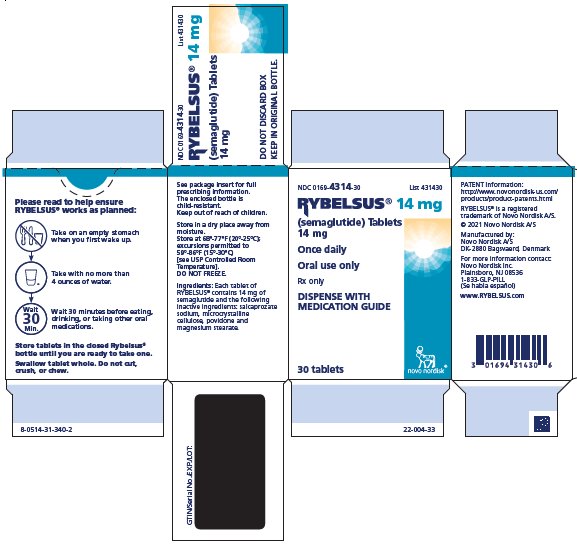
PACKAGE LABEL.PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL
PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL – 14 mg Bottle
NDC 0169-4314-30List 431430
RYBELSUS**®**** 14 mg**
(semaglutide) Tablets
14 mg
Once daily
Oral use only
Rx only
DISPENSE WITH MEDICATION GUIDE
30 tablets
Boxed Warning section
WARNING: RISK OF THYROID C-CELL TUMORS
INDICATIONS & USAGE SECTION
1 INDICATIONS AND USAGE
RYBELSUS is indicated as an adjunct to diet and exercise to improve glycemic control in adults with type 2 diabetes mellitus.
Limitations of Use
•
RYBELSUS has not been studied in patients with a history of pancreatitis. Consider other antidiabetic therapies in patients with a history of pancreatitis [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2)].
•
RYBELSUS is not indicated for use in patients with type 1 diabetes mellitus.
RYBELSUS is a glucagon-like peptide-1 (GLP-1) receptor agonist indicated as an adjunct to diet and exercise to improve glycemic control in adults with type 2 diabetes mellitus (1).
Limitations of Use
•
Has not been studied in patients with a history of pancreatitis (1, 5.2).
•
Not for treatment of type 1 diabetes mellitus (1).
CONTRAINDICATIONS SECTION
4 CONTRAINDICATIONS
RYBELSUS is contraindicated in patients with:
•
A personal or family history of medullary thyroid carcinoma (MTC) or in patients with Multiple Endocrine Neoplasia syndrome type 2 (MEN 2) [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)].
•
A prior serious hypersensitivity reaction to semaglutide or to any of the excipients in RYBELSUS. Serious hypersensitivity reactions including anaphylaxis and angioedema have been reported with RYBELSUS [see Warnings and Precautions (5.6)].
•
Personal or family history of medullary thyroid carcinoma or in patients with Multiple Endocrine Neoplasia syndrome type 2 (4).
•
Prior serious hypersensitivity reaction to semaglutide or any of the excipients in RYBELSUS (4).
ADVERSE REACTIONS SECTION
6 ADVERSE REACTIONS
The following serious adverse reactions are described below or elsewhere in the prescribing information:
•
Risk of Thyroid C-cell Tumors [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)]
•
Pancreatitis [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2)]
•
Diabetic Retinopathy Complications [see Warnings and Precautions (5.3)]
•
Hypoglycemia with Concomitant Use of Insulin Secretagogues or Insulin [see Warnings and Precautions (5.4)]
•
Acute Kidney Injury [see Warnings and Precautions (5.5)]
•
Hypersensitivity [see Warnings and Precautions (5.6)]
•
Acute Gallbladder Disease [see Warnings and Precautions (5.7)]
6.1 Clinical Trials Experience
Because clinical trials are conducted under widely varying conditions, adverse reaction rates observed in the clinical trials of a drug cannot be directly compared to rates in the clinical trials of another drug and may not reflect the rates observed in practice.
Pool of Placebo-Controlled Trials
The data inTable 1 are derived from 2 placebo-controlled trials in adult patients with type 2 diabetes [see Clinical Studies (14)]. These data reflect exposure of 1071 patients to RYBELSUS with a mean duration of exposure of 41.8 weeks. The mean age of patients was 58 years, 3.9% were 75 years or older and 52% were male. In these trials, 63% were White, 6% were Black or African American, and 27% were Asian; 19% identified as Hispanic or Latino ethnicity. At baseline, patients had type 2 diabetes for an average of 9.4 years and had a mean HbA1c of 8.1%. At baseline, 20.1% of the population reported retinopathy. Baseline estimated renal function was normal (eGFR ≥90 mL/min/1.73m2) in 66.2%, mildly impaired (eGFR 60 to 90 mL/min/1.73m2) in 32.4% and moderately impaired (eGFR 30 to 60 mL/min/1.73m2) in 1.4% of patients.
Pool of Placebo- and Active-Controlled Trials
The occurrence of adverse reactions was also evaluated in a larger pool of adult patients with type 2 diabetes participating in 9 placebo- and active- controlled trials [see Clinical Studies (14)]. In this pool, 4116 patients with type 2 diabetes were treated with RYBELSUS for a mean duration of 59.8 weeks. The mean age of patients was 58 years, 5% were 75 years or older and 55% were male. In these trials, 65% were White, 6% were Black or African American, and 24% were Asian; 15% identified as Hispanic or Latino ethnicity. At baseline, patients had type 2 diabetes for an average of 8.8 years and had a mean HbA1c of 8.2%. At baseline, 16.6% of the population reported retinopathy. Baseline estimated renal function was normal (eGFR ≥90 mL/min/1.73m2) in 65.9%, mildly impaired (eGFR 60 to 90 mL/min/1.73m2) in 28.5%, and moderately impaired (eGFR 30 to 60 mL/min/1.73m2) in 5.4% of the patients.
Common Adverse Reactions
Table 1 shows common adverse reactions, excluding hypoglycemia, associated with the use of RYBELSUS in adult patients with type 2 diabetes in the pool of placebo-controlled trials. These adverse reactions occurred more commonly on RYBELSUS than on placebo and occurred in at least 5% of patients treated with RYBELSUS.
Table 1. Adverse Reactions in Placebo-Controlled Trials Reported in ≥5% of RYBELSUS-Treated Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus
|
Adverse Reaction |
Placebo (N=362) % |
RYBELSUS 7 mg (N=356) % |
RYBELSUS 14 mg (N=356) % |
|
Nausea |
6 |
11 |
20 |
|
Abdominal Pain |
4 |
10 |
11 |
|
Diarrhea |
4 |
9 |
10 |
|
Decreased appetite |
1 |
6 |
9 |
|
Vomiting |
3 |
6 |
8 |
|
Constipation |
2 |
6 |
5 |
In the pool of placebo- and active-controlled trials, the types and frequency of common adverse reactions, excluding hypoglycemia, were similar to those listed inTable 1.
Gastrointestinal Adverse Reactions
In the pool of placebo-controlled trials, gastrointestinal adverse reactions occurred more frequently among patients receiving RYBELSUS than placebo (placebo 21%, RYBELSUS 7 mg 32%, RYBELSUS 14 mg 41%). The majority of reports of nausea, vomiting, and/or diarrhea occurred during dose escalation. More patients receiving RYBELSUS 7 mg (4%) and RYBELSUS 14 mg (8%) discontinued treatment due to gastrointestinal adverse reactions than patients receiving placebo (1%).
In addition to the reactions inTable 1, the following gastrointestinal adverse reactions with a frequency of <5% were associated with RYBELSUS (frequencies listed, respectively, as placebo; 7 mg; 14 mg): abdominal distension (1%, 2%, 3%), dyspepsia (0.6%, 3%, 0.6%), eructation (0%, 0.6%, 2%), flatulence (0%, 2%, 1%), gastroesophageal reflux disease (0.3%, 2%, 2%), and gastritis (0.8%, 2%, 2%).
Other Adverse Reactions
Pancreatitis
In the pool of placebo- and active-controlled trials with RYBELSUS, pancreatitis was reported as a serious adverse event in 6 RYBELSUS-treated patients (0.1 events per 100 patient years) versus 1 in comparator-treated patients (<0.1 events per 100 patient years).
Diabetic Retinopathy Complications
In the pool of placebo- and active-controlled trials with RYBELSUS, patients reported diabetic retinopathy related adverse reactions during the trial (4.2% with RYBELSUS and 3.8% with comparator).
Hypoglycemia
Table 2 summarizes the incidence of hypoglycemia by various definitions in the placebo-controlled trials.
Table 2. Hypoglycemia Adverse Reactions in Placebo-Controlled Trials In Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus
|
Placebo |
RYBELSUS 7 mg |
RYBELSUS 14 mg | |
|
Monotherapy | |||
|
N=178 |
N=175 |
N=175 |
|
0% |
1% |
0% |
|
Plasma glucose <54 mg/dL |
1% |
0% |
0% |
|
Add-on to metformin and/or sulfonylurea, basal insulin alone or metformin in combination with basal insulin in patients with moderate renal impairment | |||
|
N=161 |
- |
N=163 |
|
0% |
|
0% |
|
Plasma glucose <54 mg/dL |
3% |
|
6% |
|
Add-on to insulin with or without metformin | |||
|
N=184 |
N=181 |
N=181 |
|
1% |
0% |
1% |
|
Plasma glucose <54 mg/dL |
32% |
26% |
30% |
- “Severe” hypoglycemia adverse reactions are episodes requiring the assistance of another person.
Hypoglycemia was more frequent when RYBELSUS was used in combination with insulin secretagogues (e.g., sulfonylureas) or insulin.
Increases in Amylase and Lipase
In placebo-controlled trials, patients exposed to RYBELSUS 7 mg and 14 mg had a mean increase from baseline in amylase of 10% and 13%, respectively, and lipase of 30% and 34%, respectively. These changes were not observed in placebo-treated patients.
Cholelithiasis
In placebo-controlled trials, cholelithiasis was reported in 1% of patients treated with RYBELSUS 7 mg. Cholelithiasis was not reported in RYBELSUS 14 mg or placebo-treated patients.
Increases in Heart Rate
In placebo-controlled trials, RYBELSUS 7 mg and 14 mg resulted in a mean increase in heart rate of 1 to 3 beats per minute. There was no change in heart rate in placebo-treated patients.
6.2 Postmarketing Experience
The following adverse reactions have been reported during post-approval use of semaglutide, the active ingredient of RYBELSUS. Because these reactions are reported voluntarily from a population of uncertain size, it is not always possible to reliably estimate their frequency or establish a causal relationship to drug exposure.
Gastrointestinal: ileus
Hypersensitivity: anaphylaxis, angioedema, rash, urticaria
Hepatobiliary: cholecystitis, cholelithiasis requiring cholecystectomy
Nervous system disorders:dizziness, dysgeusia
Most common adverse reactions (incidence ≥5%) are nausea, abdominal pain, diarrhea, decreased appetite, vomiting and constipation (6.1).
**To report SUSPECTED ADVERSE REACTIONS, contactNovo Nordisk Inc., at 1-833-457-7455 or FDA at 1-800-FDA-1088 or **www.fda.gov/medwatch.
DRUG INTERACTIONS SECTION
7 DRUG INTERACTIONS
7.1 Concomitant Use with an Insulin Secretagogue (e.g., Sulfonylurea) or
with Insulin
RYBELSUS stimulates insulin release in the presence of elevated blood glucose concentrations. Patients receiving RYBELSUS in combination with an insulin secretagogue (e.g., sulfonylurea) or insulin may have an increased risk of hypoglycemia, including severe hypoglycemia.
When initiating RYBELSUS, consider reducing the dose of concomitantly administered insulin secretagogue (such as sulfonylureas) or insulin to reduce the risk of hypoglycemia [see Warnings and Precautions (5.4), Adverse Reactions (6.1)].
7.2 Oral Medications
RYBELSUS causes a delay of gastric emptying, and thereby has the potential to impact the absorption of other oral medications. Levothyroxine exposure was increased 33% (90% CI: 125-142) when administered with RYBELSUS in a drug interaction study [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)].
When coadministering oral medications instruct patients to closely follow RYBELSUS administration instructions. Consider increased clinical or laboratory monitoring for medications that have a narrow therapeutic index or that require clinical monitoring [see Dosage and Administration (2)].
Oral Medications: RYBELSUS delays gastric emptying. Instruct patients to closely follow RYBELSUS administration instructions (7.2).
DOSAGE FORMS & STRENGTHS SECTION
3 DOSAGE FORMS AND STRENGTHS
RYBELSUS tablets are available as:
•
3 mg: white to light yellow, oval shaped debossed with “3” on one side and “novo” on the other side.
•
7 mg: white to light yellow, oval shaped debossed with “7” on one side and “novo” on the other side.
•
14 mg: white to light yellow, oval shaped debossed with “14” on one side and “novo” on the other side.
Tablets: 3 mg, 7 mg and 14 mg (3).
OVERDOSAGE SECTION
10 OVERDOSAGE
In the event of overdose, appropriate supportive treatment should be initiated according to the patient’s clinical signs and symptoms. A prolonged period of observation and treatment for these symptoms may be necessary, taking into account the long half-life of RYBELSUS of approximately 1 week.
CLINICAL STUDIES SECTION
14 CLINICAL STUDIES
14.1 Overview of Clinical Studies
RYBELSUS has been studied as monotherapy and in combination with metformin, sulfonylureas, sodium-glucose co-transporter-2 (SGLT-2) inhibitors, insulins, and thiazolidinediones in patients with type 2 diabetes. The efficacy of RYBELSUS was compared with placebo, empagliflozin, sitagliptin, and liraglutide. RYBELSUS has also been studied in patients with type 2 diabetes with mild and moderate renal impairment.
In patients with type 2 diabetes, RYBELSUS produced clinically significant reduction from baseline in HbA1c compared with placebo.
The efficacy of RYBELSUS was not impacted by baseline age, gender, race, ethnicity, BMI, body weight, diabetes duration and level of renal impairment.
14.2 Monotherapy Use of RYBELSUS in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus
In a 26-week double-blind trial (NCT02906930), 703 adult patients with type 2 diabetes inadequately controlled with diet and exercise were randomized to RYBELSUS 3 mg, RYBELSUS 7 mg or RYBELSUS 14 mg once daily or placebo. Patients had a mean age of 55 years and 51% were men. The mean duration of type 2 diabetes was 3.5 years, and the mean BMI was 32 kg/m2. Overall, 75% were White, 5% were Black or African American, and 17% were Asian; 26% identified as Hispanic or Latino ethnicity.
Monotherapy with RYBELSUS 7 mg and RYBELSUS 14 mg once daily for 26 weeks resulted in a statistically significant reduction in HbA1c compared with placebo (seeTable 3).
Table 3. Results at Week 26 in a Trial of RYBELSUS as Monotherapy in Adult Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus Inadequately Controlled with Diet and Exercise
|
Placebo |
RYBELSUS 7 mg |
RYBELSUS 14 mg | |
|
Intent-to-Treat (ITT) Population (N)a |
178 |
175 |
175 |
|
HbA1c (%) | |||
|
7.9 |
8.0 |
8.0 |
|
-0.3 |
-1.2 |
-1.4 |
|
−0.9 [−1.1; −0.6]c |
−1.1 [−1.3; −0.9]c | |
|
Patients (%) achieving HbA1c <7% |
31 |
69 |
77 |
|
FPG (mg/dL) | |||
|
160 |
162 |
158 |
|
-3 |
-28 |
-33 |
a The intent-to-treat population includes all randomized patients. At week 26, the primary HbA1c endpoint was missing for 5.6%, 8.6% and 8.6% of patients randomized to placebo, RYBELSUS 7 mg and RYBELSUS 14 mg, respectively. Missing data were imputed by a pattern mixture model using multiple imputation (MI). Pattern was defined by randomized treatment and treatment status at week 26. During the trial, additional anti-diabetic medication was initiated as an add on to randomized treatment by 15%, 2% and 1% of patients randomized to placebo, RYBELSUS 7 mg and RYBELSUS 14 mg, respectively.
b Estimated using an ANCOVA model based on data irrespectively of discontinuation of trial product or initiation of rescue medication adjusted for baseline value and region.
c p<0.001 (unadjusted 2-sided) for superiority, controlled for multiplicity.
The mean baseline body weight was 88.6 kg, 89.0 kg and 88.1 kg in the placebo, RYBELSUS 7 mg, and RYBELSUS 14 mg arms, respectively. The mean changes from baseline to week 26 were -1.4 kg, -2.3 kg and -3.7 kg in the placebo, RYBELSUS 7 mg, and RYBELSUS 14 mg arms, respectively. The difference from placebo (95% CI) for RYBELSUS 7 mg was -0.9 kg (-1.9, 0.1) and for RYBELSUS 14 mg was -2.3 kg (-3.1, -1.5).
14.3 Combination Therapy Use of RYBELSUS in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes
Mellitus
Combination with Metformin
In a 26-week trial (NCT02863328), 822 adult patients with type 2 diabetes were randomized to RYBELSUS 14 mg once daily or empagliflozin 25 mg once daily, all in combination with metformin. Patients had a mean age of 58 years and 50% were men. The mean duration of type 2 diabetes was 7.4 years, and the mean BMI was 33 kg/m2. Overall, 86% were White, 7% were Black or African American, and 6% were Asian; 24% identified as Hispanic or Latino ethnicity.
Treatment with RYBELSUS 14 mg once daily for 26 weeks resulted in a statistically significant reduction in HbA1c compared to empagliflozin 25 mg once daily (seeTable 4).
Table 4. Results at Week 26 in a Trial of RYBELSUS Compared to Empagliflozin in Adult Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus in Combination with Metformin
|
RYBELSUS 14 mg |
Empagliflozin 25 mg | |
|
Intent-to-Treat (ITT) Population (N)a |
411 |
410 |
|
HbA1c (%) | ||
|
8.1 |
8.1 |
|
-1.3 |
-0.9 |
|
-0.4 [-0.6, -0.3]c | |
|
Patients (%) achieving HbA1c <7% |
67 |
40 |
|
FPG (mg/dL) | ||
|
172 |
174 |
|
-36 |
-36 |
a The intent-to-treat population includes all randomized patients. At week 26, the primary HbA1c endpoint was missing for 4.6% and 3.7% of patients randomized to RYBELSUS 14 mg and empagliflozin 25 mg, respectively. Missing data were imputed by a pattern mixture model using multiple imputation (MI). Pattern was defined by randomized treatment and treatment status at week 26. During the trial, additional anti-diabetic medication was initiated as an add on to randomized treatment by 1.9% and 1.2% of patients randomized to RYBELSUS 14 mg and empagliflozin 25 mg, respectively.
b Estimated using an ANCOVA based on data irrespectively of discontinuation of trial product or initiation of rescue medication adjusted for baseline value and region.
c p<0.001 (unadjusted 2-sided) for superiority, controlled for multiplicity.
The mean baseline body weight was 91.9 kg and 91.3 kg in the RYBELSUS 14 mg and empagliflozin 25 mg arms, respectively. The mean changes from baseline to week 26 were -3.8 kg and -3.7 kg in the RYBELSUS 14 mg and empagliflozin 25 mg arms, respectively. The difference from empagliflozin (95% CI) for RYBELSUS 14 mg was -0.1 kg (-0.7, 0.5).
Combination with Metformin or Metformin with Sulfonylurea
In a 26-week, double-blind trial (NCT02607865), 1864 adult patients with type 2 diabetes on metformin alone or metformin with sulfonylurea were randomized to RYBELSUS 3 mg, RYBELSUS 7 mg, RYBELSUS 14 mg or sitagliptin 100 mg once daily. Patients had a mean age of 58 years and 53% were men. The mean duration of type 2 diabetes was 8.6 years, and the mean BMI was 32 kg/m2. Overall, 71% were White, 9% were Black or African American, and 13% were Asian; 17% identified as Hispanic or Latino ethnicity.
Treatment with RYBELSUS 7 mg and RYBELSUS 14 mg once daily for 26 weeks resulted in a statistically significant reduction in HbA1c compared to sitagliptin 100 mg once daily (seeTable 5).
Table 5. Results at Week 26 in a Trial of RYBELSUS Compared to Sitagliptin 100 mg Once Daily in Adult Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus in Combination with Metformin or Metformin with Sulfonylurea
|
RYBELSUS 7 mg |
RYBELSUS 14 mg |
** Sitagliptin** 100 mg | |
|
Intent-to-Treat (ITT) Population (N)a |
465 |
465 |
467 |
|
HbA1c (%) | |||
|
8.4 |
8.3 |
8.3 |
|
-1.0 |
-1.3 |
-0.8 |
|
-0.3 [-0.4; -0.1]c |
-0.5 [-0.6; -0.4]c | |
|
Patients (%) achieving HbA1c <7% |
44 |
56 |
32 |
|
FPG (mg/dL) | |||
|
170 |
168 |
172 |
|
-21 |
-31 |
-15 |
a The intent-to-treat population includes all randomized patients. At week 26, the primary HbA1c endpoint was missing for 5.8%, 6.2% and 4.5% of patients randomized to RYBELSUS 7 mg, RYBELSUS 14 mg and sitagliptin 100 mg, respectively. Missing values were imputed by a pattern mixture model using multiple imputation (MI). Pattern was defined by randomized treatment and treatment status at week 26. During the trial, additional anti-diabetic medication was initiated as an add on to randomized treatment by 2.4%, 1.1% and 2.8% of patients randomized to RYBELSUS 7 mg, RYBELSUS 14 mg and sitagliptin 100 mg, respectively.
b Estimated using an ANCOVA based on data irrespectively of discontinuation of trial product or initiation of rescue medication adjusted for baseline value, background medication and region.
c p<0.001 (unadjusted 2-sided) for superiority, controlled for multiplicity.
The mean baseline body weight was 91.3 kg, 91.2 kg and 90.9 kg in the RYBELSUS 7 mg, RYBELSUS 14 mg and sitagliptin 100 mg arms, respectively. The mean changes from baseline to week 26 were -2.2 kg, -3.1 kg and -0.6 kg in the RYBELSUS 7 mg, RYBELSUS 14 mg and sitagliptin 100 mg arms, respectively. The difference from sitagliptin (95% CI) for RYBELSUS 7 mg was -1.6 kg (-2.0, -1.1) and RYBELSUS 14 mg was -2.5 kg (-3.0, -2.0).
Combination with Metformin or Metformin with SGLT-2 Inhibitors
In a 26-week, double-blind, double-dummy trial (NCT02863419), 711 adult patients with type 2 diabetes on metformin alone or metformin with SGLT-2 inhibitors were randomized to RYBELSUS 14 mg once daily, liraglutide 1.8 mg s.c. injection once daily or placebo. Patients had a mean age of 56 years and 52% were men. The mean duration of type 2 diabetes was 7.6 years, and the mean BMI was 33 kg/m2. Overall, 73% were White, 4% were Black or African American, and 13% were Asian; 6% identified as Hispanic or Latino ethnicity.
Treatment with RYBELSUS 14 mg once daily for 26 weeks resulted in statistically significant reductions in HbA1c compared to placebo. Treatment with RYBELSUS 14 mg once daily for 26 weeks resulted in non-inferior reductions in HbA1c compared to liraglutide 1.8 mg (seeTable 6).
Table 6. Results at Week 26 in a Trial of RYBELSUS Compared to Liraglutide and Placebo in Adult Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus in Combination with Metformin or Metformin with SGLT-2i
|
Placebo |
Liraglutide 1.8 mg |
RYBELSUS 14 mg | |
|
Intent-to-Treat (ITT) Population (N)a |
142 |
284 |
285 |
|
HbA1c (%) | |||
|
7.9 |
8.0 |
8.0 |
|
-0.2 |
-1.1 |
-1. 2 |
|
-1.1 [-1.2; -0.9]c | ||
|
-0.1 [-0.3; 0.0] | ||
|
Patients (%) achieving HbA1c <7% |
14 |
62 |
68 |
|
FPG (mg/dL) | |||
|
167 |
168 |
167 |
|
-7 |
-34 |
-36 |
a The intent-to-treat population includes all randomized patients. At week 26, the primary HbA1c endpoint was missing for 5.6%, 4.2% and 2.5% of patients randomized to placebo, liraglutide 1.8 mg and RYBELSUS 14 mg, respectively. Missing values were imputed by a pattern mixture model using multiple imputation (MI). Pattern was defined by randomized treatment and treatment status at week 26. During the trial, additional anti-diabetic medication was initiated as an add on to randomized treatment by 7.7%, 3.2% and 3.5% of patients randomized to placebo, liraglutide 1.8 mg and RYBELSUS 14 mg respectively.
b Estimated using an ANCOVA based on data irrespectively of discontinuation of trial product or initiation of rescue medication adjusted for baseline value, background medication and region.
c p<0.001 (unadjusted 2-sided) for superiority, controlled for multiplicity.
The mean baseline body weight was 93.2 kg, 95.5 kg and 92.9 kg in the placebo, liraglutide 1.8 mg, and RYBELSUS 14 mg arms, respectively. The mean changes from baseline to week 26 were -0.5 kg, -3.1 kg and -4.4 kg in the placebo, liraglutide 1.8 mg, and RYBELSUS 14 mg arms, respectively. The difference from placebo (95% CI) for RYBELSUS 14 mg was -3.8 kg (-4.7, -3.0). The difference from liraglutide 1.8 mg for RYBELSUS 14 mg was -1.2 (-1.9, -0.6).
Combination in patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus and Moderate Renal Impairment with Metformin alone, Sulfonylurea alone, Basal Insulin alone, or Metformin in Combination with either Sulfonylurea or Basal Insulin
In a 26-week, double-blind trial (NCT02827708), 324 adult patients with moderate renal impairment (eGFRCKD-EPI 30−59 mL/min/1.73m2) were randomized to RYBELSUS 14 mg or placebo once daily. RYBELSUS was added to the patient’s stable pre-trial antidiabetic regimen. The insulin dose was reduced by 20% at randomization for patients on basal insulin. Dose reduction of insulin and sulfonylurea was allowed in case of hypoglycemia; up titration of insulin was allowed but not beyond the pre-trial dose.
Patients had a mean age of 70 years and 48% were men. The mean duration of type 2 diabetes was 14 years, and the mean BMI was 32 kg/m2. Overall, 96% were White, 4% were Black or African American, and 0.3% were Asian; 6.5% identified as Hispanic or Latino ethnicity. 39.5% of patients had an eGFR value of 30 to 44 mL/min/1.73m2.
Treatment with RYBELSUS 14 mg once daily for 26 weeks resulted in a statistically significant reduction in HbA1c from baseline compared to placebo (seeTable 7).
Table 7. Results at Week 26 in a Trial of RYBELSUS Compared to Placebo in Patients with Moderate Renal Impairment
|
Placebo |
RYBELSUS 14 mg | |
|
Intent-to-Treat (ITT) Population (N)a |
161 |
163 |
|
HbA1c (%) | ||
|
7.9 |
8.0 |
|
-0.2 |
-1.0 |
|
-0.8 [-1.0; -0.6]c | |
|
Patients (%) achieving HbA1c <7% |
23 |
58 |
|
FPG (mg/dL) | ||
|
164 |
164 |
|
-7 |
-28 |
a The intent-to-treat population includes all randomized patients including patients on rescue medication. At week 26, the primary HbA1c endpoint was missing for 3.7% and 5.5% of patients randomized to placebo and RYBELSUS 14 mg, respectively. Missing values were imputed by a pattern mixture model using multiple imputation (MI). Pattern was defined by randomized treatment and treatment status at week 26. During the trial, additional anti-diabetic medication was initiated as an add on to randomized treatment by 10% and 4.3% of patients randomized to placebo and RYBELSUS 14 mg, respectively.
b Estimated using an ANCOVA based on data irrespectively of discontinuation of trial product or initiation of rescue medication adjusted for baseline value, background medication, renal status and region.
c p<0.001 (unadjusted 2-sided) for superiority, controlled for multiplicity.
The mean baseline body weight was 90.4 kg and 91.3 kg in the placebo and RYBELSUS 14 mg arms, respectively. The mean changes from baseline to week 26 were -0.9 kg and -3.4 kg in the placebo and RYBELSUS 14 mg arms, respectively. The difference from placebo (95% CI) for RYBELSUS 14 mg was -2.5 kg (-3.2, -1.8).
Combination with Insulin with or without Metformin
In a 26-week double blind trial (NCT03021187), 731 adult patients with type 2 diabetes inadequately controlled on insulin (basal, basal/bolus or premixed) with or without metformin, were randomized to RYBELSUS 3 mg, 7 mg and 14 mg once daily or placebo once daily. All patients reduced their insulin dose by 20% at randomization to reduce the risk of hypoglycemia. Patients were allowed to increase the insulin dose only up to the starting insulin dose prior to randomization.
Patients had a mean age of 61 years and 54% were men. The mean duration of type 2 diabetes was 15 years, and the mean BMI was 31 kg/m2. Overall, 51% were White, 7% were Black or African American, and 36% were Asian; 13% identified as Hispanic or Latino ethnicity.
Treatment with RYBELSUS 7 mg and 14 mg once daily for 26 weeks resulted in a statistically significant reduction in HbA1c from baseline compared to placebo once daily (seeTable 8).
Table 8. Results at Week 26 in a Trial of RYBELSUS Compared to Placebo in Adult Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus in Combination with Insulin alone or with Metformin
|
Placebo |
RYBELSUS 7 mg |
RYBELSUS 14 mg | |
|
Intent-to-Treat (ITT) Population (N)a |
184 |
182 |
181 |
|
HbA1c (%) | |||
|
8.2 |
8.2 |
8.2 |
|
-0.1 |
-0.9 |
-1.3 |
|
-0.9 [-1.1; -0.7]c |
-1.2 [-1.4; -1.0]c | |
|
Patients (%) achieving HbA1c <7% |
7 |
43 |
58 |
|
FPG (mg/dL) | |||
|
150 |
153 |
150 |
|
5 |
-20 |
-24 |
a The intent-to-treat population includes all randomized patients. At week 26, the primary HbA1c endpoint was missing for 4.3%, 4.4%, and 4.4% of patients randomized to placebo, RYBELSUS 7 mg and RYBELSUS 14 mg, respectively. Missing values were imputed by a pattern mixture model using multiple imputation (MI). Pattern was defined by randomized treatment and treatment status at week 26. During the trial, additional anti-diabetic medication was initiated as an add on to randomized treatment by 4.9%, 1.1 % and 2.2% of patients randomized to placebo, RYBELSUS 7 mg and RYBELSUS 14 mg, respectively.
b Estimated using an ANCOVA based on data irrespectively of discontinuation of trial product or initiation of rescue medication adjusted for baseline value, background medication and region.
c p<0.001 (unadjusted 2-sided) for superiority, controlled for multiplicity.
The mean baseline body weight was 86.0 kg, 87.1 kg and 84.6 kg in the placebo, RYBELSUS 7 mg, and RYBELSUS 14 mg arms, respectively. The mean changes from baseline to week 26 were -0.4 kg, -2.4 kg and -3.7 kg in the placebo, RYBELSUS 7 mg, and RYBELSUS 14 mg arms, respectively. The difference from placebo (95% CI) for RYBELSUS 7 mg was -2.0 kg (-3.0, -1.0), and for RYBELSUS 14 mg was -3.3 kg (-4.2, -2.3).
14.4 Cardiovascular Outcomes Trial in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes
Mellitus and Cardiovascular Disease
PIONEER 6 (NCT02692716) was a multi-center, multi-national, placebo- controlled, double-blind trial. In this trial, 3,183 adult patients with inadequately controlled type 2 diabetes and atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease were randomized to RYBELSUS 14 mg once daily or placebo for a median observation time of 16 months. The trial compared the risk of a major adverse cardiovascular event (MACE) between RYBELSUS 14 mg and placebo when these were added to and used concomitantly with standard of care treatments for diabetes and cardiovascular disease. The primary endpoint, MACE, was the time to first occurrence of a three-part composite outcome which included cardiovascular death, non-fatal myocardial infarction and non-fatal stroke.
Patients eligible to enter the trial were 50 years of age or older and had established, stable, cardiovascular, cerebrovascular, peripheral artery disease, chronic kidney disease or NYHA class II and III heart failure or were 60 years of age or older and had other specified risk factors for cardiovascular disease. In total, 1,797 patients (56.5%) had established cardiovascular disease without chronic kidney disease, 354 patients (11.1%) had chronic kidney disease only, and 544 patients (17.1%) had both cardiovascular disease and kidney disease; 488 patients (15.3%) had cardiovascular risk factors without established cardiovascular disease or chronic kidney disease. The mean age at baseline was 66 years, and 68% were men. The mean duration of diabetes was 14.9 years, and mean BMI was 32 kg/m2. Overall, 72% were White, 6% were Black or African American, and 20% were Asian; 16% identified as Hispanic or Latino ethnicity. Concomitant diseases of patients in this trial included, but were not limited to, heart failure (12%), history of ischemic stroke (8%) and history of a myocardial infarction (36%). In total, 99.7% of the patients completed the trial and the vital status was known at the end of the trial for 100%.
For the primary analysis, a Cox proportional hazards model was used to test for non-inferiority of RYBELSUS 14 mg to placebo for time to first MACE using a risk margin of 1.3. Type-1 error was controlled across multiple tests using a hierarchical testing strategy. Non‑inferiority to placebo was established, with a hazard ratio equal to 0.79 (95% CI: 0.57, 1.11) over the median observation time of 16-months. The proportion of patients who experienced at least one MACE was 3.8% (61/1591) for RYBELSUS 14 mg and 4.8% (76/1592) for placebo.
DESCRIPTION SECTION
11 DESCRIPTION
RYBELSUS tablets, for oral use, contain semaglutide, a GLP-1 receptor agonist. The peptide backbone is produced by yeast fermentation. The main protraction mechanism of semaglutide is albumin binding, facilitated by modification of position 26 lysine with a hydrophilic spacer and a C18 fatty di-acid. Furthermore, semaglutide is modified in position 8 to provide stabilization against degradation by the enzyme dipeptidyl-peptidase 4 (DPP-4). A minor modification was made in position 34 to ensure the attachment of only one fatty di-acid. The molecular formula is C187H291N45O59 and the molecular weight is 4113.58 g/mol.
Structural formula:
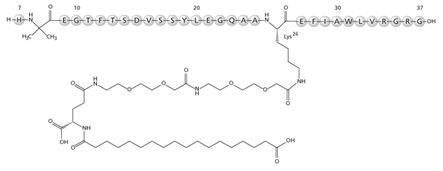
Semaglutide is a white to almost white hygroscopic powder. Each tablet of RYBELSUS contains 3 mg, 7 mg or 14 mg of semaglutide and the following inactive ingredients: magnesium stearate, microcrystalline cellulose, povidone and salcaprozate sodium (SNAC).
SPL MEDGUIDE SECTION
Medication Guide
|
Medication Guide RYBELSUS**®**** (reb-EL-sus)** (semaglutide) tablets, for oral use | ||
|
Read this Medication Guide before you start using RYBELSUS and each time you get a refill. There may be new information. This information does not take the place of talking to your healthcare provider about your medical condition or your treatment. | ||
|
What is the most important information I should know about RYBELSUS? RYBELSUS** may cause serious side effects, including:** • • | ||
|
What is RYBELSUS? RYBELSUS is a prescription medicine used along with diet and exercise to improve blood sugar (glucose) in adults with type 2 diabetes. • • It is not known if RYBELSUS is safe and effective for use in children under 18 years of age. | ||
|
Do not use RYBELSUS if: • • o o o o o | ||
|
Before using RYBELSUS, tell your healthcare provider if you have any other medical conditions, including if you: • • • • Tell your healthcare provider about all the medicines you take, including prescription and over-the-counter medicines, vitamins, and herbal supplements. RYBELSUS may affect the way some medicines work and some medicines may affect the way RYBELSUS works. Before using RYBELSUS, talk to your healthcare provider about low blood sugar and how to manage it. Tell your healthcare provider if you are taking other medicines to treat diabetes, including insulin or sulfonylureas. Know the medicines you take. Keep a list of them to show your healthcare provider and pharmacist when you get a new medicine. | ||
|
How should I take RYBELSUS? • • • • • • Your dose of RYBELSUS and other diabetes medicines may need to change because of: change in level of physical activity or exercise, weight gain or loss, increased stress, illness, change in diet, fever, trauma, infection, surgery or because of other medicines you take. | ||
|
What are the possible side effects of RYBELSUS? RYBELSUS may cause serious side effects, including: • • • • | ||
|
o |
o |
o |
|
o |
o |
o |
|
o |
o |
o |
|
o |
o |
o |
|
• • o o o o o • | ||
|
o |
o | |
|
o |
o | |
|
The most common side effects of RYBELSUS may include nausea, stomach (abdominal) pain, diarrhea, decreased appetite, vomiting and constipation. Nausea, vomiting and diarrhea are most common when you first start RYBELSUS. Talk to your healthcare provider about any side effect that bothers you or does not go away. These are not all the possible side effects of RYBELSUS. Call your doctor for medical advice about side effects. You may report side effects to FDA at 1‑800‑FDA‑1088. | ||
|
How should I store RYBELSUS? • • • • | ||
|
General information about the safe and effective use of RYBELSUS. Medicines are sometimes prescribed for purposes other than those listed in a Medication Guide. Do not use RYBELSUS for a condition for which it was not prescribed. Do not give RYBELSUS to other people, even if they have the same symptoms that you have. It may harm them. You can ask your pharmacist or healthcare provider for information about RYBELSUS that is written for health professionals. | ||
|
What are the ingredients in RYBELSUS? Active Ingredient: semaglutide **Inactive Ingredients:**magnesium stearate, microcrystalline cellulose, povidone and salcaprozate sodium (SNAC). | ||
|
Manufactured by: Novo Nordisk A/S, DK-2880 Bagsvaerd, Denmark RYBELSUS® is a registered trademark of Novo Nordisk A/S. PATENT Information: http://www.novonordisk-us.com/products/product- patents.html © 2023 Novo Nordisk For more information, go to www.RYBELSUS.com or call 1-833-GLP-PILL. |
This Medication Guide has been approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration. Revised: 01/2023
DOSAGE & ADMINISTRATION SECTION
2 DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
2.1 Important Administration Instructions
•
Instruct patients to take RYBELSUS at least 30 minutes before the first food, beverage, or other oral medications of the day with no more than 4 ounces of plain water only [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)]. Waiting less than 30 minutes, or taking RYBELSUS with food, beverages (other than plain water) or other oral medications will lessen the effect of RYBELSUS by decreasing its absorption. Waiting more than 30 minutes to eat may increase the absorption of RYBELSUS.
•
Swallow tablets whole. Do not split, crush, or chew tablets.
2.2 Recommended Dosage
•
Start RYBELSUS with 3 mg once daily for 30 days. The 3 mg dosage is intended for treatment initiation and is not effective for glycemic control.
•
After 30 days on the 3 mg dosage, increase the dosage to 7 mg once daily.
•
The dosage may be increased to 14 mg once daily if additional glycemic control is needed after at least 30 days on the 7 mg dosage.
•
Taking two 7 mg RYBELSUS tablets to achieve a 14 mg dosage is not recommended.
•
If a dose is missed, the missed dose should be skipped, and the next dose should be taken the following day.
2.3 Switching Patients between OZEMPIC and RYBELSUS
•
Patients treated with RYBELSUS 14 mg daily can be transitioned to OZEMPIC subcutaneous injection 0.5 mg once weekly. Patients can start OZEMPIC the day after their last dose of RYBELSUS.
•
Patients treated with once weekly OZEMPIC 0.5 mg subcutaneous injection can be transitioned to RYBELSUS 7 mg or 14 mg. Patients can start RYBELSUS up to 7 days after their last injection of OZEMPIC. There is no equivalent dose of RYBELSUS for OZEMPIC 1 mg.
•
Instruct patients to take RYBELSUS at least 30 minutes before the first food, beverage, or other oral medications of the day with no more than 4 ounces of plain water only. Waiting less than 30 minutes, or taking with food, beverages (other than plain water) or other oral medications will lessen the effect of RYBELSUS. Waiting more than 30 minutes to eat may increase the absorption of RYBELSUS (2.1).
•
Swallow tablets whole. Do not split, crush, or chew tablets (2.1).
•
Start RYBELSUS with 3 mg once daily for 30 days. After 30 days on the 3 mg dosage, increase the dosage to 7 mg once daily (2.2).
•
Dosage may be increased to 14 mg once daily if additional glycemic control is needed after at least 30 days on the 7 mg dosage (2.2).
•
See the Full Prescribing Information for instructions on switching between OZEMPIC® and RYBELSUS (2.3).
USE IN SPECIFIC POPULATIONS SECTION
8 USE IN SPECIFIC POPULATIONS
8.1 Pregnancy
Risk Summary
Available data with RYBELSUS use in pregnant women are insufficient to evaluate for a drug-associated risk of major birth defects, miscarriage or other adverse maternal or fetal outcomes. There are clinical considerations regarding the risks of poorly controlled diabetes in pregnancy (see Clinical Considerations). Based on animal reproduction studies, there may be potential risks to the fetus from exposure to RYBELSUS during pregnancy. RYBELSUS should be used during pregnancy only if the potential benefit justifies the potential risk to the fetus.
In pregnant rats administered semaglutide during organogenesis, embryofetal mortality, structural abnormalities and alterations to growth occurred at maternal exposures below the maximum recommended human dose (MRHD) based on AUC. In rabbits and cynomolgus monkeys administered semaglutide during organogenesis, early pregnancy losses and structural abnormalities were observed at exposure below the MRHD (rabbit) and ≥10-fold the MRHD (monkey). These findings coincided with a marked maternal body weight loss in both animal species (see Data).
The estimated background risk of major birth defects is 6 to 10% in women with pre-gestational diabetes with an HbA1c >7 and has been reported to be as high as 20 to 25% in women with a HbA1c >10. In the U.S. general population, the estimated background risk of major birth defects and miscarriage in clinically recognized pregnancies is 2 to 4% and 15 to 20%, respectively.
Clinical Considerations
Disease associated maternal and fetal risk
Poorly controlled diabetes during pregnancy increases the maternal risk for diabetic ketoacidosis, pre- eclampsia, spontaneous abortions, preterm delivery, and delivery complications. Poorly controlled diabetes increases the fetal risk for major birth defects, stillbirth, and macrosomia related morbidity.
Data
Animal Data
In a combined fertility and embryofetal development study in rats, subcutaneous doses of 0.01, 0.03 and 0.09 mg/kg/day (0.2-, 0.7-, and 2.1-fold the MRHD) were administered to males for 4 weeks prior to and throughout mating and to females for 2 weeks prior to mating, and throughout organogenesis to Gestation Day 17. In parental animals, pharmacologically mediated reductions in body weight gain and food consumption were observed at all dose levels. In the offspring, reduced growth and fetuses with visceral (heart blood vessels) and skeletal (cranial bones, vertebra, ribs) abnormalities were observed at the human exposure.
In an embryofetal development study in pregnant rabbits, subcutaneous doses of 0.0010, 0.0025 or 0.0075 mg/kg/day (0.06-, 0.6-, and 4.4-fold the MRHD) were administered throughout organogenesis from Gestation Day 6 to 19. Pharmacologically mediated reductions in maternal body weight gain and food consumption were observed at all dose levels. Early pregnancy losses and increased incidences of minor visceral (kidney, liver) and skeletal (sternebra) fetal abnormalities were observed at ≥0.0025 mg/kg/day, at clinically relevant exposures.
In an embryofetal development study in pregnant cynomolgus monkeys, subcutaneous doses of 0.015, 0.075, and 0.15 mg/kg twice weekly (1.9-, 9.9-, and 29-fold the MRHD) were administered throughout organogenesis, from Gestation Day 16 to 50. Pharmacologically mediated, marked initial maternal body weight loss and reductions in body weight gain and food consumption coincided with the occurrence of sporadic abnormalities (vertebra, sternebra, ribs) at ≥0.075 mg/kg twice weekly (>9X human exposure).
In a pre- and postnatal development study in pregnant cynomolgus monkeys, subcutaneous doses of 0.015, 0.075, and 0.15 mg/kg twice weekly (1.3-, 6.4-, and 14-fold the MRHD) were administered from Gestation Day 16 to 140. Pharmacologically mediated marked initial maternal body weight loss and reductions in body weight gain and food consumption coincided with an increase in early pregnancy losses and led to delivery of slightly smaller offspring at ≥0.075 mg/kg twice weekly (>6X human exposure).
Salcaprozate sodium (SNAC), an absorption enhancer in RYBELSUS, crosses the placenta and reaches fetal tissues in rats. In a pre- and postnatal development study in pregnant Sprague Dawley rats, SNAC was administered orally at 1,000 mg/kg/day (exposure levels were not measured) on Gestation Day 7 through lactation day 20. An increase in gestation length, an increase in the number of stillbirths and a decrease in pup viability were observed.
8.2 Lactation
Risk Summary
There are no data on the presence of semaglutide in human milk, the effects on the breastfed infant, or the effects on milk production. Semaglutide was present in the milk of lactating rats. SNAC and/or its metabolites concentrated in the milk of lactating rats. When a substance is present in animal milk, it is likely that the substance will be present in human milk (see Data). There are no data on the presence of SNAC in human milk. Since the activity of UGT2B7, an enzyme involved in SNAC clearance, is lower in infants compared to adults, higher SNAC plasma levels may occur in neonates and infants. Because of the unknown potential for serious adverse reactions in the breastfed infant due to the possible accumulation of SNAC from breastfeeding and because there are alternative formulations of semaglutide that can be used during lactation, advise patients that breastfeeding is not recommended during treatment with RYBELSUS.
Data
In lactating rats, semaglutide was detected in milk at levels 3- to 12-fold lower than in maternal plasma. SNAC and/or its metabolites were detected in milk of lactating rats following a single maternal administration on lactation day 10. Mean levels of SNAC and/or its metabolites in milk were approximately 2- to 12-fold higher than in maternal plasma.
8.3 Females and Males of Reproductive Potential
Discontinue RYBELSUS in women at least 2 months before a planned pregnancy due to the long washout period for semaglutide [see Use in Specific Populations (8.1)].
8.4 Pediatric Use
The safety and effectiveness of RYBELSUS have not been established in pediatric patients.
8.5 Geriatric Use
In the pool of glycemic control trials, 1229 (30%) RYBELSUS-treated patients were 65 years of age and over and 199 (5%) RYBELSUS-treated patients were 75 years of age and over [see Clinical Studies (14)]. In PIONEER 6, the cardiovascular outcomes trial, 891 (56%) RYBELSUS-treated patients were 65 years of age and over and 200 (13%) RYBELSUS-treated patients were 75 years of age and over.
No overall differences in safety or effectiveness for RYBELSUS have been observed between patients 65 years of age and older and younger adult patients.
8.6 Renal Impairment
The safety and effectiveness of RYBELSUS was evaluated in a 26-week clinical study that included 324 patients with moderate renal impairment (eGFR 30 to 59 mL/min/1.73m2) [see Clinical Studies (14.1)]. In patients with renal impairment including end-stage renal disease (ESRD), no clinically relevant change in semaglutide pharmacokinetics (PK) was observed [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)].
No dose adjustment of RYBELSUS is recommended for patients with renal impairment.
8.7 Hepatic Impairment
In a study in subjects with different degrees of hepatic impairment, no clinically relevant change in semaglutide pharmacokinetics (PK) was observed [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)].
No dose adjustment of RYBELSUS is recommended for patients with hepatic impairment.
•
Pregnancy: May cause fetal harm (8.1).
•
Lactation: Breastfeeding not recommended (8.2).
•
Females and Males of Reproductive Potential: Discontinue RYBELSUS in women at least 2 months before a planned pregnancy due to the long washout period for semaglutide (8.3).
CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY SECTION
12 CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY
12.1 Mechanism of Action
Semaglutide is a GLP-1 analogue with 94% sequence homology to human GLP-1. Semaglutide acts as a GLP-1 receptor agonist that selectively binds to and activates the GLP-1 receptor, the target for native GLP-1.
GLP-1 is a physiological hormone that has multiple actions on glucose, mediated by the GLP-1 receptors.
The principal mechanism of protraction resulting in the long half-life of semaglutide is albumin binding, which results in decreased renal clearance and protection from metabolic degradation. Furthermore, semaglutide is stabilized against degradation by the DPP-4 enzyme.
Semaglutide reduces blood glucose through a mechanism where it stimulates insulin secretion and lowers glucagon secretion, both in a glucose-dependent manner. Thus, when blood glucose is high, insulin secretion is stimulated and glucagon secretion is inhibited. The mechanism of blood glucose lowering also involves a minor delay in gastric emptying in the early postprandial phase.
12.2 Pharmacodynamics
All pharmacodynamic evaluations were performed after 12 weeks of treatment (including dose escalation) at steady state semaglutide injection 1 mg.
Fasting and Postprandial Glucose
Semaglutide reduces fasting and postprandial glucose concentrations. In patients with type 2 diabetes, treatment with semaglutide injection 1 mg resulted in reductions in glucose in terms of absolute change from baseline and relative reduction compared to placebo of 29 mg/dL (22%) for fasting glucose, 74 mg/dL (36%) for 2-hour postprandial glucose, and 30 mg/dL (22%) for mean 24-hour glucose concentration.
Insulin Secretion
Both first- and second-phase insulin secretion are increased in patients with type 2 diabetes treated with semaglutide compared with placebo.
Glucagon Secretion
Semaglutide lowers the fasting and postprandial glucagon concentrations.
Glucose dependent insulin and glucagon secretion
Semaglutide lowers high blood glucose concentrations by stimulating insulin secretion and lowering glucagon secretion in a glucose-dependent manner.
During induced hypoglycemia, semaglutide did not alter the counter regulatory responses of increased glucagon compared to placebo and did not impair the decrease of C-peptide in patients with type 2 diabetes.
Gastric emptying
Semaglutide causes a delay of early postprandial gastric emptying, thereby reducing the rate at which glucose appears in the circulation postprandially.
Cardiac electrophysiology (QTc)
The effect of subcutaneously administered semaglutide on cardiac repolarization was tested in a thorough QTc trial. At an average exposure level 4-fold higher than that of the maximum recommended dose of RYBELSUS, semaglutide does not prolong QTc intervals to any clinically relevant extent.
12.3 Pharmacokinetics
Absorption
Semaglutide is co-formulated with salcaprozate sodium which facilitates the absorption of semaglutide after oral administration. The absorption of semaglutide predominantly occurs in the stomach.
Population pharmacokinetics (PK) estimated semaglutide exposure to increase in a dose-proportional manner. In patients with type 2 diabetes, the mean population-PK estimated steady-state concentrations following once daily oral administration of 7 and 14 mg semaglutide were approximately 6.7 nmol/L and 14.6 nmol/L, respectively.
Following oral administration, maximum concentration of semaglutide is reached 1-hour post-dose. Steady-state exposure is achieved following 4 to 5 weeks administration.
Population-PK estimated absolute bioavailability of semaglutide to be approximately 0.4% to 1%, following oral administration.
Distribution
The estimated volume of distribution of semaglutide following oral administration in healthy subjects is approximately 8 L. Semaglutide is extensively bound to plasma albumin (>99%).
Elimination
With an elimination half-life of approximately 1 week, semaglutide is present in the circulation for about 5 weeks after the last dose. The clearance of semaglutide following oral administration in healthy subjects is approximately 0.04 L/h.
Metabolism
The primary route of elimination for semaglutide is metabolism following proteolytic cleavage of the peptide backbone and sequential beta-oxidation of the fatty acid side chain.
Excretion
The primary excretion routes of semaglutide-related material are via the urine and feces. Approximately 3% of the absorbed dose is excreted in the urine as intact semaglutide.
Specific Populations
Based on a population pharmacokinetic analysis, age, sex, race, ethnicity, upper GI disease, and renal impairment do not have a clinically meaningful effect on the pharmacokinetics of semaglutide. The exposure of semaglutide decreases with an increase in body weight. However, RYBELSUS doses of 7 mg and 14 mg provide adequate systemic exposure over the body weight range of 40 to 188 kg evaluated in the clinical trials. The effects of intrinsic factors on the pharmacokinetics of semaglutide are shown inFigure 1.
Figure 1. Impact of intrinsic factors on semaglutide exposure

Semaglutide exposure (Cavg) relative to reference subject profile: White, non- Hispanic or Latino female aged 18-64 years, with body weight of 85 kg, without upper GI disease or renal impairment, dosed 14 mg. Body weight categories (56 and 129 kg) represent the 5% and 95% percentiles in the dataset.
Abbreviations: Cavg: average semaglutide concentration, GI: gastrointestinal, CI: confidence interval
Patients with Renal impairment - Renal impairment does not impact the pharmacokinetics of semaglutide in a clinically relevant manner. This was shown in a study with 10 consecutive days of once daily oral doses of semaglutide in patients with different degrees of renal impairment (mild, moderate, severe, end staged renal disease) compared with subjects with normal renal function. This was also shown for subjects with both type 2 diabetes and renal impairment based on data from clinical studies (Figure 1).
Patients with Hepatic impairment - Hepatic impairment does not have any impact on the exposure of semaglutide. The pharmacokinetics of semaglutide were evaluated in patients with different degrees of hepatic impairment (mild, moderate, severe) compared with subjects with normal hepatic function in a study with 10 consecutive days of once daily oral doses of semaglutide.
Patients with disease in the upper GI tract - Upper GI disease (chronic gastritis and/or gastroesophageal reflux disease) does not impact semaglutide pharmacokinetics in a clinically relevant manner. This was shown in a study in patients with type 2 diabetes with or without upper GI disease dosed for 10 consecutive days with once daily oral doses of semaglutide.
Pediatric Patients - Semaglutide has not been studied in pediatric patients.
Drug Interaction Studies
In vitro studies have shown very low potential for semaglutide to inhibit or induce CYP enzymes, and to inhibit drug transporters.
The delay of gastric emptying with semaglutide may influence the absorption of concomitantly administered oral medicinal products. Trials were conducted to study the potential effect of semaglutide on the absorption of oral medications taken with semaglutide administered orally at steady-state exposure.
No clinically relevant drug-drug interaction with semaglutide (Figure 2) was observed based on the evaluated medications. Total exposure (AUC) of thyroxine (adjusted for endogenous levels) was increased by 33% following administration of a single dose of levothyroxine 600 mcg concurrently administered with semaglutide. Maximum exposure (Cmax) was unchanged [see Drug Interactions (7.2)].
Figure 2. Impact of semaglutide on the exposure of treatment with other oral medications
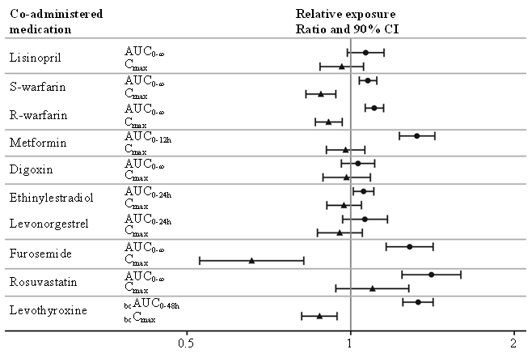
Relative exposure in terms of AUC and Cmax for each medication when given with semaglutide compared to without semaglutide. Metformin and oral contraceptive drug (ethinylestradiol/levonorgestrel) were assessed at steady state. Effect on levothyroxine is measured as baseline corrected total T4 (thyroxine) concentration. Lisinopril, warfarin (S-warfarin/R-warfarin), digoxin, furosemide, rosuvastatin and levothyroxine were assessed after a single dose.
Abbreviations: AUC: area under the curve, Cmax: maximum concentration, CI: confidence interval
No clinically relevant change in semaglutide exposure was observed when taken with omeprazole.
12.6 Immunogenicity
The observed incidence of anti-drug antibodies is highly dependent on the sensitivity and specificity of the assay. Differences in assay methods preclude meaningful comparisons of the incidence of anti-drug antibodies in the studies described below with the incidence of anti-drug antibodies in other studies, including those of semaglutide or of other semaglutide products.
During the 26- to 78-week treatment periods in 5 clinical trials [see Clinical Studies (14.2), (14.3)] and 1 clinical trial in Japanese adults with type 2 diabetes mellitus, 14/2924 (0.5%) of RYBELSUS-treated patients developed anti- semaglutide antibodies. Of these 14 RYBELSUS-treated patients, 7 patients (0.2% of the total RYBELSUS-treated study population) developed antibodies that cross-reacted with native GLP-1. No identified clinically significant effect of anti-semaglutide antibodies on pharmacokinetics of RYBELSUS was observed. There is insufficient information to characterize the effects of anti-semaglutide antibodies on pharmacodynamics, safety, or effectiveness of semaglutide.
NONCLINICAL TOXICOLOGY SECTION
13 NONCLINICAL TOXICOLOGY
13.1 Carcinogenesis, Mutagenesis, Impairment of Fertility
In a 2-year carcinogenicity study in CD-1 mice, subcutaneous doses of 0.3, 1 and 3 mg/kg/day [9-, 33- and 113-fold the maximum recommended human dose (MRHD) of RYBELSUS 14 mg, based on AUC] were administered to the males, and 0.1, 0.3 and 1 mg/kg/day (3-, 9-, and 33-fold MRHD) were administered to the females. A statistically significant increase in thyroid C-cell adenomas and a numerical increase in C-cell carcinomas were observed in males and females at all dose levels (>3X human exposure).
In a 2-year carcinogenicity study in Sprague Dawley rats, subcutaneous doses of 0.0025, 0.01, 0.025 and 0.1 mg/kg/day were administered (below quantification, 0.8-, 1.8- and 11-fold the exposure at the MRHD). A statistically significant increase in thyroid C-cell adenomas was observed in males and females at all dose levels, and a statistically significant increase in thyroid C-cell carcinomas was observed in males at ≥0.01 mg/kg/day, at clinically relevant exposures.
Human relevance of thyroid C-cell tumors in rats is unknown and could not be determined by clinical studies or nonclinical studies [see Boxed Warning, Warnings and Precautions (5.1)].
Semaglutide was not mutagenic or clastogenic in a standard battery of genotoxicity tests (bacterial mutagenicity (Ames), human lymphocyte chromosome aberration, rat bone marrow micronucleus).
In a combined fertility and embryo-fetal development study in rats, subcutaneous doses of 0.01, 0.03 and 0.09 mg/kg/day (0.2-, 0.7- and 2.1-fold the MRHD) were administered to male and female rats. Males were dosed for 4 weeks prior to mating, and females were dosed for 2 weeks prior to mating and throughout organogenesis until Gestation Day 17. No effects were observed on male fertility. In females, an increase in estrus cycle length was observed at all dose levels, together with a small reduction in numbers of corpora lutea at ≥0.03 mg/kg/day. These effects were likely an adaptive response secondary to the pharmacological effect of semaglutide on food consumption and body weight.
13.2 Animal Toxicology and/or Pharmacology
Increase in lactate levels and decrease in glucose levels in the plasma and cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) were observed in mechanistic studies with SNAC in rats. Small but statistically significant increases in lactate levels (up to 2-fold) were observed in a few animals at approximately the clinical exposure. At higher exposures these findings were associated with moderate to marked adverse clinical signs (lethargy, abnormal respiration, ataxia, and reduced activity, body tone and reflexes) and marked decreases in plasma and CSF glucose levels. These findings are consistent with inhibition of cellular respiration and lead to mortality at SNAC concentrations ≥100-times the clinical Cmax.
HOW SUPPLIED SECTION
16 HOW SUPPLIED/STORAGE AND HANDLING
How Supplied
RYBELSUS tablets are available as follows:
|
Tablet Strength |
Description |
Package Configuration |
NDC No. |
|
3 mg |
White to light yellow, oval shaped debossed with “3” on one side and “novo” on the other side |
Bottle of 30 tablets |
0169-4303-30 |
|
7 mg |
White to light yellow, oval shaped debossed with “7” on one side and “novo” on the other side |
Bottle of 30 tablets |
0169-4307-30 |
|
14 mg |
White to light yellow, oval shaped debossed with “14” on one side and “novo” on the other side |
Bottle of 30 tablets |
0169-4314-30 |
Storage and Handling
Store at 68° to 77°F (20° to 25°C); excursions permitted to 59° to 86°F (15° to 30°C) [see USP Controlled Room Temperature]. Store and dispense in the original bottle.
Store tablet in the original bottle until use to protect tablets from moisture. Store product in a dry place away from moisture.
INFORMATION FOR PATIENTS SECTION
17 PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATION
Advise the patient to read the FDA-approved patient labeling (Medication Guide).
Risk of Thyroid C-cell Tumors
Inform patients that semaglutide causes thyroid C-cell tumors in rodents and that the human relevance of this finding has not been determined. Counsel patients to report symptoms of thyroid tumors (e.g., a lump in the neck, hoarseness, dysphagia, or dyspnea) to their physician [see Boxed Warning, Warnings and Precautions (5.1)].
Pancreatitis
Inform patients of the potential risk for pancreatitis. Instruct patients to discontinue RYBELSUS promptly and contact their physician if pancreatitis is suspected (severe abdominal pain that may radiate to the back, and which may or may not be accompanied by vomiting) [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2)].
Diabetic Retinopathy Complications
Inform patients to contact their physician if changes in vision are experienced during treatment with RYBELSUS [see Warnings and Precautions (5.3)].
Hypoglycemia with Concomitant Use of Insulin Secretagogues or Insulin
Inform patients that the risk of hypoglycemia is increased when RYBELSUS is used with an insulin secretagogue (such as a sulfonylurea) or insulin. Educate patients on the signs and symptoms of hypoglycemia [see Warnings and Precautions (5.4)].
Dehydration and Renal Failure
Advise patients treated with RYBELSUS of the potential risk of dehydration due to gastrointestinal adverse reactions and take precautions to avoid fluid depletion. Inform patients of the potential risk for worsening renal function and explain the associated signs and symptoms of renal impairment, as well as the possibility of dialysis as a medical intervention if renal failure occurs [see Warnings and Precautions (5.5)].
Hypersensitivity Reactions
Inform patients that serious hypersensitivity reactions have been reported during postmarketing use of RYBELSUS. Advise patients on the symptoms of hypersensitivity reactions and instruct them to stop taking RYBELSUS and seek medical advice promptly if such symptoms occur [see Warnings and Precautions (5.6)].
Acute Gallbladder Disease
Inform patients of the potential risk for cholelithiasis or cholecystitis. Instruct patients to contact their physician if cholelithiasis or cholecystitis is suspected for appropriate clinical follow-up [see Warnings and Precautions (5.7)].
Pregnancy
Advise a pregnant woman of the potential risk to a fetus. Advise women to inform their healthcare provider if they are pregnant or intend to become pregnant [see Use in Specific Populations (8.1), (8.3)].
Lactation
Advise females not to breastfeed during treatment with RYBELSUS [see Use in Specific Populations (8.2)].
Females and Males of Reproductive Potential
Discontinue RYBELSUS at least 2 months before a planned pregnancy due to the long washout period for semaglutide [see Use in Specific Populations (8.3)].
Manufactured by:
Novo Nordisk A/S
DK-2880 Bagsvaerd
Denmark
For information about RYBELSUS contact:
Novo Nordisk Inc.
800 Scudders Mill Road
Plainsboro, NJ 08536
1-833-457-7455
Version: 6
RYBELSUS ® and OZEMPIC® are registered trademarks of Novo Nordisk A/S.
PATENT INFORMATION: https://www.novonordisk-us.com/products/product- patents.html
© 2024 Novo Nordisk
