VOTRIENT
These highlights do not include all the information needed to use VOTRIENT safely and effectively. See full prescribing information for VOTRIENT. VOTRIENT (pazopanib) tablets, for oral useInitial U.S. Approval: 2009
eeaaaf38-fb86-4d9f-a19d-0f61daac2fd7
HUMAN PRESCRIPTION DRUG LABEL
Jan 25, 2024
Novartis Pharmaceuticals Corporation
DUNS: 002147023
Products 2
Detailed information about drug products covered under this FDA approval, including NDC codes, dosage forms, ingredients, and administration routes.
pazopanib hydrochloride
Product Details
FDA regulatory identification and product classification information
FDA Identifiers
Product Classification
Product Specifications
INGREDIENTS (10)
pazopanib hydrochloride
Product Details
FDA regulatory identification and product classification information
FDA Identifiers
Product Classification
Product Specifications
INGREDIENTS (10)
Drug Labeling Information
PACKAGE LABEL.PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL
PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL
NDC 0078-1077-66
Votrient®
(pazopanib)
Tablets
200 mg
120 Tablets
Rx only
Each tablet contains 216.7 mg of
pazopanib hydrochloride, equivalent
to 200 mg of pazopanib free base.
Dispense with Medication Guide
attached or provided separately.
NOVARTIS

BOXED WARNING SECTION
WARNING: HEPATOTOXICITY
INDICATIONS & USAGE SECTION
1 INDICATIONS AND USAGE
1.1 Renal Cell Carcinoma
VOTRIENT® is indicated for the treatment of adults with advanced renal cell carcinoma (RCC).
1.2 Soft Tissue Sarcoma
VOTRIENT is indicated for the treatment of adults with advanced soft tissue sarcoma (STS) who have received prior chemotherapy.
Limitations of Use: The efficacy of VOTRIENT for the treatment of patients with adipocytic STS or gastrointestinal stromal tumors has not been demonstrated.
VOTRIENT is a kinase inhibitor indicated for the treatment of adults with:
- advanced renal cell carcinoma (RCC). (1.1)
- advanced soft tissue sarcoma (STS) who have received prior chemotherapy. (1.2)
Limitations of Use: The efficacy of VOTRIENT for the treatment of patients with adipocytic soft tissue sarcoma or gastrointestinal stromal tumors has not been demonstrated.
CONTRAINDICATIONS SECTION
4 CONTRAINDICATIONS
None.
None. (4)
ADVERSE REACTIONS SECTION
6 ADVERSE REACTIONS
The following clinically significant adverse reactions are elsewhere in the labeling:
- Hepatic Toxicity [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)]
- QT Prolongation and Torsades de Pointes [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2)]
- Cardiac Dysfunction [see Warnings and Precautions (5.3)]
- Hemorrhagic Events [see Warnings and Precautions (5.4)]
- Arterial Thromboembolic Events [see Warnings and Precautions (5.5)]
- Venous Thromboembolic Events [see Warnings and Precautions (5.6)]
- Thrombotic Microangiopathy (TMA) [see Warnings and Precautions (5.7)]
- Gastrointestinal Perforation and Fistula [see Warnings and Precautions (5.8)]
- Interstitial Lung Disease (ILD)/Pneumonitis [see Warnings and Precautions (5.9)]
- Posterior Reversible Encephalopathy Syndrome (PRES) [see Warnings and Precautions (5.10)]
- Hypertension [see Warnings and Precautions (5.11)]
- Hypothyroidism [see Warnings and Precautions (5.13)]
- Proteinuria [see Warnings and Precautions (5.14)]
- Tumor Lysis Syndrome [see Warnings and Precautions (5.15)]
- Infection [see Warnings and Precautions (5.16)]
6.1 Clinical Trials Experience
Because clinical trials are conducted under widely varying conditions, adverse reaction rates observed in the clinical trials of a drug cannot be directly compared with rates in the clinical trials of another drug and may not reflect the rates observed in practice.
The data described in the WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS section reflect exposure of 977 patients who received VOTRIENT as a single agent, including 586 VOTRIENT- treated patients with RCC. With a median duration of treatment of 7.4 months (range, 0.1 to 27.6) in these 977 patients, the most common adverse reactions (≥ 20%) in these 586 patients were diarrhea, hypertension, hair color change, nausea, fatigue, anorexia, and vomiting.
The data described in the WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS also reflects exposure of 382 patients with advanced soft tissue sarcoma who received VOTRIENT as a single agent, with a median duration of treatment of 3.6 months (range, 0 to 53). The most common adverse reactions (≥ 20%) in these 382 patients were fatigue, diarrhea, nausea, decreased weight, hypertension, decreased appetite, vomiting, tumor pain, hair color changes, musculoskeletal pain, headache, dysgeusia, dyspnea, and skin hypopigmentation.
Renal Cell Carcinoma
The safety of VOTRIENT was evaluated in 290 patients with RCC who participated in VEG105192, a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial [see Clinical Studies (14.1)]. The median duration of treatment was 7.4 months (range, 0 to 23) for patients who received VOTRIENT.
Forty-two percent of patients on VOTRIENT required a dose interruption and 36% required a dose reduction.
Table 3 presents adverse reactions in VEG105192.
Table 3. Adverse Reactions (≥ 10%) in Patients with RCC Who Received VOTRIENT in VEG105192|
Abbreviation: RCC, renal cell carcinoma. | ||||||
|
VOTRIENT |
Placebo | |||||
|
All Gradesa |
Grade 3 |
Grade 4 |
All Gradesa |
Grade 3 |
Grade 4 | |
|
Adverse reactions |
% |
% |
% |
% |
% |
% |
|
Diarrhea |
52 |
3 |
< 1 |
9 |
< 1 |
0 |
|
Hypertension |
40 |
4 |
0 |
10 |
< 1 |
0 |
|
Hair color changes |
38 |
< 1 |
0 |
3 |
0 |
0 |
|
Nausea |
26 |
< 1 |
0 |
9 |
0 |
0 |
|
Anorexia |
22 |
2 |
0 |
10 |
< 1 |
0 |
|
Vomiting |
21 |
2 |
< 1 |
8 |
2 |
0 |
|
Fatigue |
19 |
2 |
0 |
8 |
1 |
1 |
|
Asthenia |
14 |
3 |
0 |
8 |
0 |
0 |
|
Abdominal pain |
11 |
2 |
0 |
1 |
0 |
0 |
|
Headache |
10 |
0 |
0 |
5 |
0 |
0 |
Other adverse reactions observed more commonly in patients treated with VOTRIENT than placebo and that occurred in < 10% (any grade) were alopecia (8% versus < 1%), chest pain (5% versus 1%), dysgeusia (8% versus < 1%), dyspepsia (5% versus < 1%), dysphonia (4% versus < 1%), facial edema (1% versus 0%), palmar-plantar erythrodysesthesia (6% versus < 1%), proteinuria (9% versus 0%), rash (8% versus 3%), skin depigmentation (3% versus 0%), and weight decreased (9% versus 3%).
Table 4 presents the laboratory abnormalities in VEG105192.
Table 4. Select Laboratory Abnormalities (> 10%) in Patients with RCC Who Received VOTRIENT with a Difference Between Arms of ≥ 5% Compared to Placebo in VEG105192|
Abbreviations: ALT, alanine aminotransferase; AST, aspartate aminotransferase;
RCC, renal cell carcinoma. | ||||||
|
VOTRIENT |
Placebo | |||||
|
All Gradesa |
Grade 3 |
Grade 4 |
All Gradesa |
Grade 3 |
Grade 4 | |
|
Parameters |
% |
% |
% |
% |
% |
% |
|
Chemistry | ||||||
|
ALT increased |
53 |
10 |
2 |
22 |
1 |
0 |
|
AST increased |
53 |
7 |
< 1 |
19 |
< 1 |
0 |
|
Glucose increased |
41 |
< 1 |
0 |
33 |
1 |
0 |
|
Total bilirubin increased |
36 |
3 |
< 1 |
10 |
1 |
< 1 |
|
Phosphorus decreased |
34 |
4 |
0 |
11 |
0 |
0 |
|
Sodium decreased |
31 |
4 |
1 |
24 |
4 |
0 |
|
Magnesium decreased |
26 |
< 1 |
1 |
14 |
0 |
0 |
|
Glucose decreased |
17 |
0 |
< 1 |
3 |
0 |
0 |
|
Hematologic | ||||||
|
Leukopenia |
37 |
0 |
0 |
6 |
0 |
0 |
|
Neutropenia |
34 |
1 |
< 1 |
6 |
0 |
0 |
|
Thrombocytopenia |
32 |
< 1 |
< 1 |
5 |
0 |
< 1 |
|
Lymphocytopenia |
31 |
4 |
< 1 |
24 |
1 |
0 |
Additional adverse reactions from other clinical trials in patients with RCC who received VOTRIENT include arthralgia and muscle spasms.
Soft Tissue Sarcoma
The safety of VOTRIENT was evaluated in 240 patients who participated in VEG110727, a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial [see Clinical Studies (14.2)]. The median duration of treatment was 4.5 months (range, 0 to 24) for patients who received VOTRIENT.
Fifty-eight percent of patients on VOTRIENT required a dose interruption and 38% required a dose reduction. Seventeen percent of patients who received VOTRIENT discontinued therapy due to adverse reactions.
Table 5 presents the adverse reactions in VEG110727.
Table 5. Adverse Reactions (≥ 10%) in Patients with STS Who Received VOTRIENT in VEG110727|
Abbreviation: STS, soft tissue sarcoma. | ||||||
|
VOTRIENT |
Placebo | |||||
|
All Gradesa |
Grade 3 |
Grade 4 |
All Gradesa |
Grade 3 |
Grade 4 | |
|
Adverse reactions |
% |
% |
% |
% |
% |
% |
|
Fatigue |
65 |
13 |
1 |
48 |
4 |
1 |
|
Diarrhea |
59 |
5 |
0 |
15 |
1 |
0 |
|
Nausea |
56 |
3 |
0 |
22 |
2 |
0 |
|
Weight decreased |
48 |
4 |
0 |
15 |
0 |
0 |
|
Hypertension |
42 |
7 |
0 |
6 |
0 |
0 |
|
Appetite decreased |
40 |
6 |
0 |
19 |
0 |
0 |
|
Hair color changes |
39 |
0 |
0 |
2 |
0 |
0 |
|
Vomiting |
33 |
3 |
0 |
11 |
1 |
0 |
|
Tumor pain |
29 |
8 |
0 |
21 |
7 |
2 |
|
Dysgeusia |
28 |
0 |
0 |
3 |
0 |
0 |
|
Headache |
23 |
1 |
0 |
8 |
0 |
0 |
|
Musculoskeletal pain |
23 |
2 |
0 |
20 |
2 |
0 |
|
Myalgia |
23 |
2 |
0 |
9 |
0 |
0 |
|
Gastrointestinal pain |
23 |
3 |
0 |
9 |
4 |
0 |
|
Dyspnea |
20 |
5 |
< 1 |
17 |
5 |
1 |
|
Exfoliative rash |
18 |
< 1 |
0 |
9 |
0 |
0 |
|
Cough |
17 |
< 1 |
0 |
12 |
< 1 |
0 |
|
Peripheral edema |
14 |
2 |
0 |
9 |
2 |
0 |
|
Mucositis |
12 |
2 |
0 |
2 |
0 |
0 |
|
Alopecia |
12 |
0 |
0 |
1 |
0 |
0 |
|
Dizziness |
11 |
1 |
0 |
4 |
0 |
0 |
|
Skin disorderb |
11 |
2 |
0 |
1 |
0 |
0 |
|
Skin hypopigmentation |
11 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
|
Stomatitis |
11 |
< 1 |
0 |
3 |
0 |
0 |
|
Chest pain |
10 |
2 |
0 |
6 |
0 |
0 |
Other adverse reactions observed more commonly in patients treated with VOTRIENT that occurred in ≥ 5% of patients and at an incidence of more than 2% difference from placebo included insomnia (9% versus 6%), hypothyroidism (8% versus 0%), dysphonia (8% versus 2%), epistaxis (8% versus 2%), left ventricular dysfunction (8% versus 4%), dyspepsia (7% versus 2%), dry skin (6% versus < 1%), chills (5% versus 1%), vision blurred (5% versus 2%), and nail disorder (5% versus 0%).
Table 6 presents the laboratory abnormalities in VEG110727.
Table 6. Select Laboratory Abnormalities (> 10%) in Patients with STS Who Received VOTRIENT with a Difference Between Arms of ≥ 5% Compared to Placebo in VEG110727|
Abbreviations: ALT, alanine aminotransferase; AST, aspartate aminotransferase;
STS, soft tissue sarcoma. | ||||||
|
VOTRIENT |
Placebo | |||||
|
All Gradesa |
Grade 3 |
Grade 4 |
All Gradesa |
Grade 3 |
Grade 4 | |
|
Parameters |
% |
% |
% |
% |
% |
% |
|
Chemistry | ||||||
|
AST increased |
51 |
5 |
3 |
22 |
2 |
0 |
|
ALT increased |
46 |
8 |
2 |
18 |
2 |
1 |
|
Glucose increased |
45 |
< 1 |
0 |
35 |
2 |
0 |
|
Albumin decreased |
34 |
1 |
0 |
21 |
0 |
0 |
|
Alkaline phosphatase increased |
32 |
3 |
0 |
23 |
1 |
0 |
|
Sodium decreased |
31 |
4 |
0 |
20 |
3 |
0 |
|
Total bilirubin increased |
29 |
1 |
0 |
7 |
2 |
0 |
|
Potassium increased |
16 |
1 |
0 |
11 |
0 |
0 |
|
Hematologic | ||||||
|
Leukopenia |
44 |
1 |
0 |
15 |
0 |
0 |
|
Lymphocytopenia |
43 |
10 |
0 |
36 |
9 |
2 |
|
Thrombocytopenia |
36 |
3 |
1 |
6 |
0 |
0 |
|
Neutropenia |
33 |
4 |
0 |
7 |
0 |
0 |
Other Clinically Relevant Adverse Reactions
Lipase Elevations
In a single-arm RCC trial (VEG102616), elevated lipase was observed for 27% of 181 patients with available laboratory data. Elevated lipase as an adverse reaction was reported for 4% of 225 patients, including 2.7% (6/225) with Grade 3 and 0.4% (1/225) with Grade 4. In the RCC trials, clinical pancreatitis was observed in < 1% of 586 patients.
Pneumothorax
Two of 290 patients (0.7%) treated with VOTRIENT in the randomized RCC trial (VEG105192) and 8 of 240 patients (3.3%) treated with VOTRIENT in the randomized STS trial (VEG110727) developed a pneumothorax.
Bradycardia
In the randomized RCC trial (VEG105192), bradycardia based on vital signs (< 60 beats per minute) was observed in 19% of 280 patients treated with VOTRIENT. Bradycardia was reported as an adverse reaction in 2% of 290 patients.
In the randomized STS trial (VEG110727), bradycardia based on vital signs (< 60 beats per minute) was observed in 19% of 238 patients treated with VOTRIENT. Bradycardia was reported as an adverse reaction in 2% of 240 patients.
Adverse Reactions in East Asian Patients
In an analysis of pooled clinical trial data (N = 1938) with VOTRIENT, Grade 3 and Grade 4 neutropenia (12% versus 2%), thrombocytopenia (6% versus < 1%) and palmar-plantar erythrodysesthesia (6% versus 2%) were observed more frequently in patients of East Asian descent than in patients of non-East Asian descent.
6.2 Postmarketing Experience
The following adverse reactions have been identified during post-approval use of VOTRIENT. Because these reactions are reported voluntarily from a population of uncertain size, it is not always possible to reliably estimate the frequency or establish a causal relationship to drug exposure.
Blood and Lymphatic System Disorders: Polycythemia
Eye Disorders: Retinal detachment/tear
Gastrointestinal Disorders: Pancreatitis
Metabolic and Nutrition Disorder: Tumor lysis syndrome (including fatal cases)
Vascular Disorders: Arterial (including aortic) aneurysms, dissections, and rupture (including fatal cases)
- The most common adverse reactions in patients with RCC (≥ 20%) are diarrhea, hypertension, hair color changes (depigmentation), nausea, anorexia, and vomiting. (6.1)
- The most common adverse reactions in patients with STS (≥ 20%) are fatigue, diarrhea, nausea, decreased weight, hypertension, decreased appetite, vomiting, tumor pain, hair color changes, musculoskeletal pain, headache, dysgeusia, dyspnea, and skin hypopigmentation. (6.1)
To report SUSPECTED ADVERSE REACTIONS, contact Novartis Pharmaceuticals Corporation at 1-888-669-6682 or FDA at 1-800-FDA-1088 or www.fda.gov/medwatch.
DOSAGE & ADMINISTRATION SECTION
2 DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
2.1 Recommended Dosage
The recommended dosage of VOTRIENT is 800 mg (four 200 mg tablets) orally once daily without food (at least 1 hour before or 2 hours after a meal) until disease progression or unacceptable toxicity [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)]. The dosage should be modified for hepatic impairment and in patients taking certain concomitant drugs [see Dosage and Administration (2.3, 2.4)].
Swallow tablets whole. Do not crush tablets due to the potential for increased rate of absorption, which may affect systemic exposure [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)].
If a dose is missed, it should not be taken if it is < 12 hours until the next dose.
2.2 Dosage Modifications for Adverse Reactions
Table 1 summarizes the recommended dose reductions.
Table 1. Recommended Dose Reductions of VOTRIENT for Adverse Reactions|
Dose reduction |
For renal cell carcinoma |
For soft tissue sarcoma |
|
First |
400 mg orally once daily |
600 mg orally once daily |
|
Second |
200 mg orally once daily |
400 mg orally once daily |
Permanently discontinue VOTRIENT in patients unable to tolerate the second dose reduction.
Table 2 summarizes the recommended dosage modifications for adverse reactions.
Table 2. Recommended Dosage Modifications of VOTRIENT for Adverse Reactions|
Abbreviations: ALT, alanine aminotransferase; ULN, upper limit of normal. | ||
|
Adverse reaction |
Severity****a |
Dosage modification |
|
Hepatic Toxicity [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)] |
Isolated ALT elevations between 3 × ULN and 8 × ULN |
Continue and monitor liver function weekly until ALT returns to Grade 1 or baseline. |
|
Isolated ALT elevations of > 8 × ULN |
Withhold until improvement to Grade 1 or baseline. If the potential benefit for resuming treatment with VOTRIENT is considered to outweigh the risk for hepatotoxicity, then resume at a reduced dose of no more than 400 mg once daily and measure serum liver tests weekly for 8 weeks. Permanently discontinue if ALT elevations > 3 × ULN recur despite dose reduction(s). | |
|
ALT elevations > 3 × ULN occur concurrently with |
Permanently discontinue and continue to monitor until resolution. Patients with only a mild, indirect (unconjugated) hyperbilirubinemia, known as Gilbert’s syndrome, and ALT elevations > 3 × ULN should be managed per the recommendations outlined for isolated ALT elevations. | |
|
Left Ventricular Systolic Dysfunction [see Warnings and Precautions (5.3)] |
Symptomatic or Grade 3 |
Withhold until improvement to Grade < 3. Resume treatment based on medical judgement. |
|
Grade 4 |
Permanently discontinue. | |
|
Hemorrhagic Events [see Warnings and Precautions (5.4)] |
Grade 2 |
Withhold until improvement to Grade ≤ 1. Resume at reduced dose (see Table 1). Permanently discontinue if Grade 2 recurs after dose interruption and reduction. |
|
Grade 3 or 4 |
Permanently discontinue. | |
|
Arterial Thromboembolic Events [see Warnings and Precautions (5.5)] |
Any grade |
Permanently discontinue. |
|
Venous Thromboembolic Events [see Warnings and Precautions (5.6)] |
Grade 3 |
Withhold VOTRIENT and resume at same dose if managed with appropriate therapy for at least one week. |
|
Grade 4 |
Permanently discontinue. | |
|
Thrombotic Microangiopathy [see Warnings and Precautions (5.7)] |
Any grade |
Permanently discontinue. |
|
Gastrointestinal Perforation [see Warnings and Precautions (5.8)] |
Any grade |
Permanently discontinue. |
|
Gastrointestinal Fistula [see Warnings and Precautions (5.8)] |
Grade 2 or 3 |
Withhold and resume based on medical judgement. |
|
Grade 4 |
Permanently discontinue. | |
|
Interstitial Lung Disease / Pneumonitis [see Warnings and Precautions (5.9)] |
Any grade |
Permanently discontinue. |
|
Posterior Reversible Encephalopathy Syndrome [see Warnings and Precautions (5.10)] |
Any grade |
Permanently discontinue. |
|
Hypertension [see Warnings and Precautions (5.11)] |
Grade 2 or 3 |
Reduce dose (see Table 1) and initiate or adjust anti-hypertensive therapy. Permanently discontinue if hypertension remains Grade 3 despite dose reduction(s) and adjustment of anti-hypertensive therapy. |
|
Grade 4 or hypertensive crisis |
Permanently discontinue. | |
|
Proteinuria [see Warnings and Precautions (5.14)] |
24-hour urine protein ≥ 3 grams |
Withhold until improvement to Grade ≤ 1. Resume at a reduced dose (see Table 1). Permanently discontinue if 24-hour urine protein ≥ 3 grams does not improve or recurs despite dose reductions. |
|
Confirmed nephrotic syndrome |
Permanently discontinue. |
2.3 Dosage Modifications for Hepatic Impairment
Moderate and Severe Hepatic Impairment
In patients with moderate hepatic impairment [total bilirubin > 1.5 to 3 × upper limit of normal (ULN) and any alanine aminotransferase (ALT) value], consider alternatives to VOTRIENT. If VOTRIENT is used in patients with moderate hepatic impairment, reduce the VOTRIENT dose to 200 mg orally once daily.
VOTRIENT is not recommended in patients with severe hepatic impairment (total bilirubin > 3 × ULN and any ALT value) [see Use in Specific Populations (8.7)].
2.4 Dosage Modifications for Drug Interactions
Strong CYP3A4 Inhibitors
Avoid concomitant use of strong CYP3A4 inhibitors by use of an alternate concomitant medication with no or minimal potential to inhibit CYP3A4. If coadministration of a strong CYP3A4 inhibitor is warranted, reduce the dose of VOTRIENT to 400 mg [see Drug Interactions (7.1)].
Strong CYP3A4 Inducers
Avoid concomitant use of strong CYP3A4 inducers by use of an alternate concomitant medication with no or minimal enzyme induction potential. VOTRIENT is not recommended in patients who cannot avoid chronic use of strong CYP3A4 inducers [see Drug Interactions (7.1)].
Gastric Acid-Reducing Agents
Avoid concomitant use of gastric acid-reducing agents. If concomitant use of a gastric acid-reducing agent cannot be avoided, consider short-acting antacid in place of proton pump inhibitors (PPIs) and H2-receptor antagonists. Separate short-acting antacid and VOTRIENT dosing by several hours [see Drug Interactions (7.4), Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)].
- Recommended Dosage: 800 mg orally once daily without food (at least 1 hour before or 2 hours after a meal). (2.1)
- Moderate Hepatic Impairment: 200 mg orally once daily. (2.2)
DOSAGE FORMS & STRENGTHS SECTION
3 DOSAGE FORMS AND STRENGTHS
Tablets: 200 mg, modified capsule-shaped, gray or pink, film-coated with ‘GS JT’ debossed on one side.
Tablets: 200 mg (3)
CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY SECTION
12 CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY
12.1 Mechanism of Action
Pazopanib is a multi-tyrosine kinase inhibitor of vascular endothelial growth factor receptor (VEGFR)-1, VEGFR-2, VEGFR-3, platelet-derived growth factor receptor (PDGFR)-α and -β, fibroblast growth factor receptor (FGFR)-1 and -3, cytokine receptor (Kit), interleukin-2 receptor-inducible T-cell kinase (Itk), lymphocyte-specific protein tyrosine kinase (Lck), and transmembrane glycoprotein receptor tyrosine kinase (c-Fms). In vitro, pazopanib inhibited ligand-induced autophosphorylation of VEGFR-2, Kit, and PDGFR-β receptors. In vivo, pazopanib inhibited VEGF-induced VEGFR-2 phosphorylation in mouse lungs, angiogenesis in a mouse model, and the growth of some human tumor xenografts in mice.
12.2 Pharmacodynamics
Increases in blood pressure have been observed and are related to steady-state trough plasma pazopanib concentrations.
Cardiac Electrophysiology
The QT prolongation potential of pazopanib was assessed in a randomized, blinded, parallel trial (N = 96) using moxifloxacin as a positive control. VOTRIENT 800 mg orally under fasting conditions was administered on Days 2 to 8 and 1,600 mg was administered on Day 9 after a meal in order to increase exposure to pazopanib and its metabolites. No large changes (i.e., > 20 msec) in QTc interval following exposure to pazopanib were detected in this QT trial. The trial was not able to exclude small changes (< 10 msec) in QTc interval, because assay sensitivity below this threshold (< 10 msec) was not established in this trial [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2)].
12.3 Pharmacokinetics
The recommended dosage of 800 mg once daily results in mean AUC of 1,037 mcg•h/mL and Cmax of 58.1 mcg/mL. There was no consistent increase in AUC or Cmax at pazopanib doses above 800 mg.
Administration of a single 400-mg crushed tablet increased AUC0-72h by 46% and Cmax by approximately 2-fold and decreased Tmax by approximately 2 hours compared with administration of the whole tablet [see Dosage and Administration (2.1)].
Absorption
The median time to achieve peak concentrations was 2 to 4 hours after a dose.
Effect of Food
Systemic exposure to pazopanib is increased when administered with food. Administration of pazopanib with a high-fat (approximately 50% fat) or low-fat (approximately 5% fat) meal results in an approximately 2-fold increase in AUC and Cmax.
Distribution
Binding of pazopanib to human plasma protein in vivo was > 99% with no concentration dependence over the range of 10 to 100 mcg/mL. In vitro studies suggest that pazopanib is a substrate for P-gp and BCRP.
Elimination
Pazopanib has a mean half-life of 31 hours after administration of the recommended dose of 800 mg.
Metabolism
In vitro studies demonstrated that pazopanib is metabolized by CYP3A4 with a minor contribution from CYP1A2 and CYP2C8.
Excretion
Elimination is primarily via feces with renal elimination accounting for < 4% of the administered dose.
Specific Populations
Patients with Hepatic Impairment
Table 7 presents a comparison of the median steady-state Cmax and the median AUC0-24h values for patients with normal, mild, moderate and severe hepatic impairment.
The median steady-state of pazopanib Cmax and AUC0-24h after a once-daily dose of 800 mg in patients with mild impairment were in a similar range as the median steady-state Cmax and median AUC0-24h in patients with no hepatic impairment.
The maximum tolerated pazopanib dose in patients with moderate hepatic impairment was 200 mg once daily. The median steady-state Cmax and the median AUC0-24h were approximately 43% and 29%, respectively, of the corresponding median values after administration of 800 mg once daily in patients with no hepatic impairment.
The median steady-state Cmax and the median AUC0-24h were approximately 18% and 15%, respectively, of the corresponding median values after administration of 800 mg once daily in patients with no hepatic impairment.
Table 7. Pharmacokinetic Parameters of Pazopanib in Patients with Hepatic Impairment|
Abbreviations: ALT, alanine aminotransferase; AUC, area under the curve; Cmax, maximum concentration; ULN, upper limit of normal. | ||||
|
No hepatic impairment |
Mild hepatic impairment |
Moderate hepatic impairment |
Severe hepatic impairment | |
|
Dose |
800 mg once daily |
800 mg once daily |
200 mg once daily |
200 mg once daily |
|
Median steady-state Cmax (range) mcg/mL |
52 |
34 |
22 |
9.4 |
|
Median AUC0-24h (range) mcg•h/mL |
888 |
774 |
257 |
131 |
Drug Interactions Studies
Clinical Studies
Strong CYP3A4 Inhibitor: Coadministration of multiple doses of oral VOTRIENT 400 mg with multiple doses of oral ketoconazole 400 mg (strong CYP3A4/P-gp inhibitor) resulted in a 1.7-fold increase in the AUC0-24h and a 1.5-fold increase in the Cmax of pazopanib [see Dosage and Administration (2.4), Drug Interactions (7.1)].
Weak CYP3A4 Inhibitor: Coadministration of 1,500 mg lapatinib, a substrate and weak inhibitor of CYP3A4, P-gp, and BCRP, with VOTRIENT 800 mg resulted in an approximately 50% to 60% increase in mean pazopanib AUC0-24h and Cmax.
CYP1A2, CYP2C9 and CYP2C19 Substrates: Clinical studies, using VOTRIENT 800 mg once daily, have demonstrated that pazopanib does not have a clinically relevant effect on the pharmacokinetics of caffeine (CYP1A2 probe substrate), warfarin (CYP2C9 probe substrate), or omeprazole (CYP2C19 probe substrate) in patients with cancer.
CYP3A4, CYP2D6, and CYP2C8 Substrates: Coadministration of VOTRIENT resulted in an increase of approximately 30% in the mean AUC and Cmax of midazolam (CYP3A4 probe substrate) and increases of 33% to 64% in the ratio of dextromethorphan to dextrorphan concentrations in the urine after oral administration of dextromethorphan (CYP2D6 probe substrate). Coadministration of VOTRIENT 800 mg once daily and paclitaxel 80 mg/m2 (CYP3A4 and CYP2C8 substrate) once weekly resulted in a mean increase of 26% and 31% in paclitaxel AUC and Cmax, respectively [see Drug Interactions (7.2)].
Gastric Acid-Reducing Agents: Coadministration of VOTRIENT with esomeprazole, a PPI, decreased the exposure of pazopanib by approximately 40% (AUC and Cmax) [see Dosage and Administration (2.4), Drug Interactions (7.4)].
In Vitro Studies
In vitro studies with human liver microsomes showed that pazopanib inhibited the activities of CYP enzymes 1A2, 3A4, 2B6, 2C8, 2C9, 2C19, 2D6, and 2E1. Potential induction of human CYP3A4 was demonstrated in an in vitro human pregnane X receptor (PXR) assay.
In vitro studies also showed that pazopanib inhibits UGT1A1 and organic anion- transporting polypeptide (OATP1B1) with IC50s of 1.2 and 0.79 μM, respectively.
12.5 Pharmacogenomics
Pazopanib can increase serum total bilirubin levels [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)]. In vitro studies showed that pazopanib inhibits UGT1A1, which glucuronidates bilirubin for elimination. A pooled pharmacogenetic analysis of 236 white patients who received VOTRIENT showed that the (TA)7/(TA)7 genotype (UGT1A1*28/*28) (underlying genetic susceptibility to Gilbert’s syndrome) was associated with a statistically significant increase in the incidence of hyperbilirubinemia relative to the (TA)6/(TA)6 and (TA)6/(TA)7 genotypes.
In a pooled pharmacogenetic analysis of data from 31 clinical studies of pazopanib administered as either monotherapy or in combination with other agents, ALT > 3 × ULN (Grade 2) occurred in 32% (42/133) of HLA-B57:01 allele carriers and in 19% (397/2101) of non-carriers and ALT > 5 × ULN (Grade 3) occurred in 19% (25/133) of HLA-B57:01 allele carriers and in 10% (213/2101) of non-carriers. In this dataset, 6% (133/2234) of the patients carried the HLA-B*57:01 allele [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)].
OVERDOSAGE SECTION
10 OVERDOSAGE
Dose-limiting toxicity (Grade 3 fatigue) and Grade 3 hypertension were each observed in 1 of 3 patients dosed at 2,000 mg daily (2.5 times the recommended dose) and 1,000 mg daily (1.25 times the recommended dose), respectively.
Provide general supportive measures to manage an overdose. Hemodialysis is not expected to enhance the elimination of VOTRIENT because pazopanib is not significantly renally excreted and is highly bound to plasma proteins.
DESCRIPTION SECTION
11 DESCRIPTION
Pazopanib is a kinase inhibitor. Pazopanib is presented as the hydrochloride salt, with the chemical name 5-[[4-[(2,3-dimethyl-2H-indazol-6-yl)methylamino]-2-pyrimidinyl]amino]-2-methylbenzenesulfonamide monohydrochloride. It has the molecular formula C21H23N7O2S•HCl and a molecular weight of 473.99 g/mol. Pazopanib hydrochloride has the following chemical structure:

Pazopanib hydrochloride is a white to slightly yellow solid. It is very slightly soluble at pH 1 and practically insoluble above pH 4 in aqueous media.
VOTRIENT tablets are for oral use. Each 200-mg tablet of VOTRIENT contains 200 mg of pazopanib equivalent to 216.7 mg of pazopanib hydrochloride. The inactive ingredients of VOTRIENT are:Tablet Core: magnesium stearate, microcrystalline cellulose, povidone, and sodium starch glycolate. Coating: Gray or pink film-coat: hypromellose, iron oxide black, macrogol/polyethylene glycol 400 (PEG 400), polysorbate 80, and titanium dioxide.
CLINICAL STUDIES SECTION
14 CLINICAL STUDIES
14.1 Renal Cell Carcinoma
The efficacy of VOTRIENT was evaluated in VEG105192, a randomized, double- blind, placebo-controlled, multicenter trial (NCT00387764). Patients with locally advanced and/or metastatic RCC who had received either no prior therapy or one prior cytokine-based systemic therapy were randomized (2:1) to receive VOTRIENT 800 mg once daily or placebo once daily. Eligible subjects were stratified according to the following 3 stratification factors: baseline ECOG performance status 0 versus 1; prior nephrectomy yes versus no; and prior systemic therapy for advanced RCC: treatment-naïve versus one prior cytokine- based therapy. The major efficacy outcome measure was progression-free survival (PFS). Additional outcome measures were overall survival (OS), overall response rate (ORR), and duration of response.
Of the total of 435 patients enrolled in this trial, 233 patients had no prior systemic therapy (treatment-naïve subgroup) and 202 patients received one prior IL-2 or INFα-based therapy (cytokine-pretreated subgroup). The baseline demographic and disease characteristics were balanced between the arms receiving VOTRIENT and placebo. The majority of patients were male (71%) with a median age of 59 years. Eighty-six percent of patients were white, 14% were Asian, and < 1% were other. Forty-two percent were ECOG performance status 0 and 58% were ECOG performance status 1. All patients had clear cell histology (90%) or predominantly clear cell histology (10%). Approximately 50% of all patients had 3 or more organs involved with metastatic disease. The most common metastatic sites at baseline were lung (74%), lymph nodes (56%), bone (27%), and liver (25%).
A similar proportion of patients in each arm were treatment-naïve and cytokine-pretreated (see Table 8). In the cytokine-pretreated subgroup, the majority (75%) had received interferon-based treatment. Similar proportions of patients in each arm had prior nephrectomy (89% and 88% for VOTRIENT and placebo, respectively).
The analysis of the primary endpoint PFS was based on disease assessment by independent radiological review in the entire trial population. Efficacy results are presented in Table 8 and Figure 1.
Table 8. Efficacy Results in RCC Patients by Independent Assessment in VEG105192|
Abbreviations: CI, confidence interval; CR, complete response; HR, hazard
ratio; ITT, intent-to-treat; PFS, progression-free survival; PR, partial
response; RCC, renal cell carcinoma. | |||
|
HR | |||
|
Endpoint/Trial population |
VOTRIENT |
Placebo |
(95% CI) |
|
PFS | |||
|
Overall ITT |
N = 290 |
N = 145 | |
|
Median (months) |
9.2 |
4.2 |
0.46a |
|
Treatment-naïve subgroup |
N = 155 (53%) |
N = 78 (54%) | |
|
Median (months) |
11.1 |
2.8 |
0.40 |
|
Cytokine pre-treated subgroup |
N = 135 (47%) |
N = 67 (46%) | |
|
Median (months) |
7.4 |
4.2 |
0.54 |
|
Response rate (CR + PR) |
N = 290 |
N = 145 | |
|
% (95% CI) |
30 (25.1, 35.6) |
3 (0.5, 6.4) |
– |
|
Duration of response | |||
|
Median (weeks) (95% CI) |
58.7 (52.1, 68.1) |
–b |
Figure 1. Kaplan-Meier Curve for Progression-free Survival in RCC by Independent Assessment for the Overall Population (Treatment-naïve and Cytokine Pre-treated Populations) in VEG105192
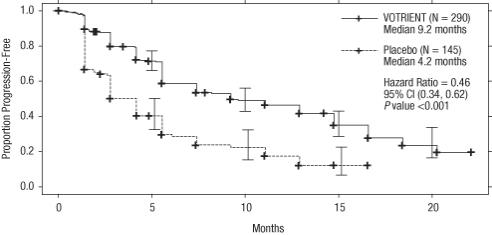
At the protocol-specified final analysis of OS, the median OS was 22.9 months for patients randomized to VOTRIENT and 20.5 months for the placebo arm [HR = 0.91 (95% CI: 0.71, 1.16)]. The median OS for the placebo arm includes 79 patients (54%) who discontinued placebo treatment because of disease progression and crossed over to treatment with VOTRIENT. In the placebo arm, 95 (66%) patients received at least one systemic anticancer treatment after progression compared with 88 (30%) patients randomized to VOTRIENT.
14.2 Soft Tissue Sarcoma
The efficacy of VOTRIENT was evaluated in VEG110727, a randomized, double- blind, placebo-controlled, multicenter trial (NCT00753688). Patients with metastatic STS who had received prior chemotherapy, including anthracycline treatment, or were unsuited for such therapy, were randomized (2:1) to receive VOTRIENT 800 mg once daily or placebo. Patients with gastrointestinal stromal tumors (GIST) or adipocytic sarcoma were excluded from the trial. Randomization was stratified by the factors of WHO performance status (WHO PS) 0 or 1 at baseline and the number of lines of prior systemic therapy for advanced disease (0 or 1 versus 2+). The major efficacy outcome measure was PFS assessed by independent radiological review. Additional outcome measures were OS, ORR, and duration of response.
The majority of patients were female (59%) with a median age of 55 years. Seventy-two percent of patients were white, 22% were Asian, and 6% were other. Forty-three percent of patients had leiomyosarcoma, 10% had synovial sarcoma, and 47% had other soft tissue sarcomas. Fifty-six percent of patients had received 2 or more lines of prior systemic therapy and 44% had received 0 or 1 lines of prior systemic therapy.
Efficacy results are presented in Table 9 and Figure 2.
Table 9. Efficacy Results in STS Patients by Independent Assessment in VEG110727|
Abbreviations: CI, confidence interval; CR, complete response; HR, hazard
ratio; ITT, intent-to-treat; PFS, progression-free survival; PR, partial
response; STS, soft tissue sarcoma. | |||
|
HR | |||
|
Endpoint/Trial population |
VOTRIENT |
Placebo |
(95% CI) |
|
PFS | |||
|
Overall ITT |
N = 246 |
N = 123 |
0.35a |
|
Median (months) |
4.6 |
1.6 |
(0.26, 0.48) |
|
Leiomyosarcoma subgroup |
N = 109 |
N = 49 |
0.37 |
|
Median (months) |
4.6 |
1.9 |
(0.23, 0.60) |
|
Synovial sarcoma subgroup |
N = 25 |
N = 13 |
0.43 |
|
Median (months) |
4.1 |
0.9 |
(0.19, 0.98) |
|
‘Other soft tissue sarcoma’ subgroup |
N = 112 |
N = 61 |
0.39 |
|
Median (months) |
4.6 |
1.0 |
(0.25, 0.60) |
|
Response rate (CR + PR) | |||
|
% (95% CI) |
4 (2.3, 7.9)b |
0 (0.0, 3.0) |
– |
|
Duration of response | |||
|
Median (months) (95% CI) |
9.0 (3.9, 9.2) |
Figure 2. Kaplan-Meier Curve for Progression-free Survival in STS by Independent Assessment for the Overall Population in VEG110727
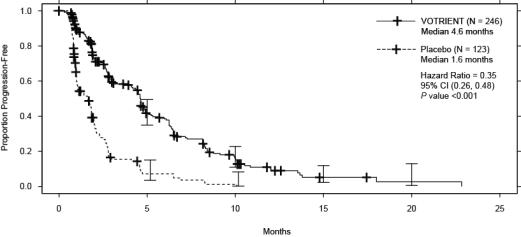
At the protocol-specified final analysis of OS, the median OS was 12.6 months for patients randomized to VOTRIENT and 10.7 months for the placebo arm [HR = 0.87 (95% CI: 0.67, 1.12)].
HOW SUPPLIED SECTION
16 HOW SUPPLIED/STORAGE AND HANDLING
VOTRIENT 200 mg tablets are supplied as modified capsule-shaped, gray or pink, film-coated with ‘GS JT’ debossed on one side and are available in:
- Bottles of 120 tablets: NDC 0078-0670-66 (gray tablets), NDC 0078-1077-66 (pink tablets)
Store at 20°C to 25°C (68°F to 77°F), excursions permitted between 15°C and 30°C (59°F and 86°F) [see USP Controlled Room Temperature].
INFORMATION FOR PATIENTS SECTION
17 PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATION
Advise the patient to read the FDA-approved patient labeling (Medication Guide).
-
Hepatic Toxicity: Inform patients that periodic laboratory testing will be performed. Advise patients to report signs and symptoms of liver dysfunction to their healthcare provider right away [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)].
-
QT Prolongation and Torsades de Pointes: Inform patients that ECG monitoring may be performed. Advise patients to inform their physicians of concomitant medications [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2)].
-
Interstitial Lung Disease/Pneumonitis: Advise patients to report pulmonary signs or symptoms indicative of interstitial lung disease (ILD) or pneumonitis [see Warnings and Precautions (5.9)].
-
Cardiac Dysfunction: Advise patients to report hypertension or signs and symptoms of congestive heart failure [see Warnings and Precautions (5.3)].
-
Hemorrhagic Events: Advise patients to report unusual bleeding [see Warnings and Precautions (5.4)].
-
Arterial Thromboembolic Events: Advise patients to report signs or symptoms of an arterial thrombosis [see Warnings and Precautions (5.5)].
-
Pneumothorax and Venous Thromboembolic Events: Advise patients to report new onset of dyspnea, chest pain, or localized limb edema [see Warnings and Precautions (5.6), Adverse Reactions (6.1)].
-
Posterior Reversible Encephalopathy Syndrome: Advise patients to inform their doctor if they have worsening of neurological function consistent with PRES (headache, seizure, lethargy, confusion, blindness, and other visual and neurologic disturbances) [see Warnings and Precautions (5.10)].
-
Hypertension: Advise patients to monitor blood pressure early in the course of therapy and frequently thereafter and report increases of blood pressure or symptoms, such as blurred vision, confusion, severe headache, or nausea and vomiting [see Warnings and Precautions (5.11)].
-
Gastrointestinal Perforation and Fistula: Advise patients to report signs and symptoms of a GI perforation or fistula [see Warnings and Precautions (5.8)].
-
Risk of Impaired Wound Healing: Advise patients that VOTRIENT may impair wound healing. Advise patients to inform their healthcare provider of any scheduled surgical procedure [see Warnings and Precautions (5.12)].
-
Hypothyroidism and Proteinuria: Inform patients that thyroid function testing and urinalysis will be performed during treatment [see Warnings and Precautions (5.13, 5.14)].
-
Tumor Lysis Syndrome: Advise patients to contact their healthcare provider promptly to report any signs and symptoms of TLS, such as abnormal heart rhythm, seizure, confusion, muscle cramps or spasms, or a decrease in urine output [see Warnings and Precautions (5.15)].
-
Infection: Advise patients to promptly report any signs or symptoms of infection [see Warnings and Precautions (5.16)].
-
Embryo-Fetal Toxicity: Advise female patients to inform their healthcare provider of a known or suspected pregnancy during treatment with VOTRIENT. Inform female patients of the risk to a fetus and the potential loss of the pregnancy [see Warnings and Precautions (5.19), Use in Specific Populations (8.1)].
Advise females of reproductive potential to use effective contraception during treatment and for at least 2 weeks after the last dose of VOTRIENT. Advise male patients with female partners of reproductive potential to use condoms during treatment with VOTRIENT and for at least 2 weeks after the last dose [see Warnings and Precautions (5.19), Use in Specific Populations (8.3)]. -
Lactation: Advise women not to breastfeed during treatment with VOTRIENT and for 2 weeks after the last dose [see Use in Specific Populations (8.2)].
-
Infertility: Advise males and females of reproductive potential that VOTRIENT may impair fertility [see Use in Specific Populations (8.3)].
-
Gastrointestinal Adverse Reactions: Advise patients on how to manage nausea, vomiting, and diarrhea and to notify their healthcare provider if moderate-to-severe vomiting or diarrhea occurs or if there is a decrease in oral intake [see Adverse Reactions (6.1)].
-
Depigmentation: Advise patients that depigmentation of the hair or skin may occur during treatment with VOTRIENT [see Adverse Reactions (6.1)].
-
Drug Interactions: Advise patients to inform their healthcare providers of all concomitant medications, vitamins, or dietary and herbal supplements [see Drug Interactions (7)].
-
Dosage and Administration: Advise patients to take VOTRIENT without food (at least 1 hour before or 2 hours after a meal) [see Dosage and Administration (2.1)].
Distributed by:
Novartis Pharmaceuticals Corporation
East Hanover, New Jersey 07936
© Novartis
T2024-07
SPL MEDGUIDE SECTION
|
This Medication Guide has been approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration. |
Revised: December 2021 |
|
MEDICATION GUIDE | |
|
What is the most important information I should know about VOTRIENT? | |
|
○ yellowing of your skin or the whites of your eyes (jaundice) |
○ loss of appetite |
|
○ dark urine |
○ pain on the right side of your stomach area (abdomen) |
|
○ tiredness |
○ bruise easily |
|
○ nausea or vomiting | |
|
Your healthcare provider may need to prescribe a lower dose of VOTRIENT for you or tell you to stop taking VOTRIENT if you develop liver problems during treatment. | |
|
What is VOTRIENT?
It is not known if VOTRIENT is effective in treating certain soft tissue
sarcomas or certain gastrointestinal tumors. | |
|
What should I tell my healthcare provider before taking VOTRIENT?
Tell your healthcare provider about all the medicines you take, including prescription and over-the-counter medicines, vitamins, and herbal supplements. VOTRIENT may affect the way other medicines work and other medicines may affect how VOTRIENT works. | |
|
Especially, tell your healthcare provider if you:
| |
|
○ certain antibiotics (used to treat infections) |
○ certain medicines used to treat depression |
|
○ certain medicines used to treat HIV-1 |
○ medicines used to treat irregular heartbeats |
Ask your healthcare provider if you are not sure if your medicine is one that
is listed above. | |
|
How should I take VOTRIENT?
| |
|
What are the possible side effects of VOTRIENT?
*irregular or fast heartbeat or fainting ***heart failure.**This is a condition where your heart does not pump as well as it should and may cause you to have shortness of breath. *bleeding problems. These bleeding problems may be severe and cause death. *heart attack or stroke. Heart attack and stroke can happen with VOTRIENT and may cause death. *blood clots. Blood clots may form in a vein, especially in your legs (deep vein thrombosis or DVT). Pieces of a blood clot may travel to your lungs (pulmonary embolism). This may be life-threatening and cause death. *Thrombotic microangiopathy (TMA), including thrombotic thrombocytopenia purpura (TTP) and hemolytic uremic syndrome (HUS). TMA is a condition involving blood clots that can happen while taking VOTRIENT. TMA is accompanied by a decrease in red blood cells and cells that are involved in clotting. TMA may harm organs, such as the brain and kidneys. tear in your stomach or intestinal wall (perforation) or an abnormal connection between two parts of your gastrointestinal tract (fistula).*** *lung problems. VOTRIENT may cause lung problems that may lead to death. Tell your healthcare provider right away if you get a cough that will not go away or shortness of breath. *Posterior Reversible Encephalopathy Syndrome (PRES). PRES is a condition that can happen while taking VOTRIENT that may cause death. *high blood pressure. High blood pressure can happen with VOTRIENT, including a sudden and severe rise in blood pressure which may be life-threatening. These blood pressure increases usually happen in the first several months of treatment. Your blood pressure should be well controlled before you start taking VOTRIENT. Your healthcare provider should begin checking your blood pressure within 1 week of you starting VOTRIENT and often during treatment to make sure that your blood pressure is well controlled. *thyroid problems. Your healthcare provider should check you for this during treatment with VOTRIENT. *Tumor lysis syndrome (TLS). TLS is a condition that can happen during treatment with VOTRIENT that may cause death. TLS is caused by a fast breakdown of cancer cells. Your healthcare provider may do a blood test to check you for TLS. Call your healthcare provider or get emergency medical help right away if you develop any of these symptoms during treatment with VOTRIENT: irregular heartbeat, seizures, confusion, muscle cramps or spasms, or a decrease in urine output. *protein in your urine. Your healthcare provider will check you for this problem. If there is too much protein in your urine, your healthcare provider may tell you to stop taking VOTRIENT. *serious infections.Serious infections can happen with VOTRIENT and can cause death. *collapsed lung (pneumothorax). A collapsed lung can happen with VOTRIENT. Air may get trapped in the space between your lung and chest wall. This may cause you to have shortness of breath. | |
|
Call your healthcare provider right away if you have any of the symptoms
listed above. | |
|
|
|
Other common side effects in people with advanced soft tissue sarcoma who take VOTRIENT include: | |
|
|
|
These are not all the possible side effects of VOTRIENT. Call your doctor for medical advice about side effects. You may report side effects to FDA at 1-800-FDA-1088. | |
|
How should I store VOTRIENT tablets? | |
|
General information about the safe and effective use of VOTRIENT. | |
|
What are the ingredients in VOTRIENT? Distributed by: Novartis Pharmaceuticals Corporation, East Hanover, New Jersey
07936 © Novartis |
T2021-161
USE IN SPECIFIC POPULATIONS SECTION
8 USE IN SPECIFIC POPULATIONS
8.1 Pregnancy
Risk Summary
Based on animal reproduction studies and its mechanism of action [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.1)], VOTRIENT can cause fetal harm when administered to a pregnant woman. There are no available data on VOTRIENT use in pregnant women to evaluate for a drug-associated risk. In animal developmental and reproductive toxicology studies, oral administration of pazopanib to pregnant rats and rabbits throughout organogenesis resulted in teratogenicity, and abortion at systemic exposures lower than that observed at the MRHD of 800 mg/day (based on AUC) (see Data). Advise pregnant women of the potential risk to a fetus.
The estimated background risk of major birth defects and miscarriage for the indicated population is unknown. All pregnancies have a background risk of birth defect, loss or other adverse outcomes. In the U.S. general population, the estimated background risk of major birth defects in clinically recognized pregnancies and miscarriage is 2% to 4% and 15% to 20%, respectively.
Data
Animal Data
In a female fertility and early embryonic development study, female rats were administered oral pazopanib at least 15 days prior to mating and for 6 days after mating, which resulted in increased pre-implantation loss and early resorptions at dosages greater than or equal to 30 mg/kg/day (approximately 0.4-fold the AUC at the MRHD of 800 mg/day). Total litter resorption was seen at 300 mg/kg/day (approximately 0.8-fold the AUC at the MRHD of 800 mg/day). Postimplantation loss, embryolethality, and decreased fetal body weights were noted in females administered doses greater than or equal to 10 mg/kg/day (approximately 0.3-fold the AUC at the MRHD of 800 mg/day).
In embryo-fetal developmental toxicity studies in rats and rabbits, oral pazopanib was administered to pregnant animals during organogenesis. In rats, dose levels of greater than or equal to 3 mg/kg/day (approximately 0.1-fold the AUC at the MRHD of 800 mg/day) resulted in teratogenic effects, including cardiovascular malformations (retroesophageal subclavian artery, missing innominate artery, changes in the aortic arch), incomplete or absent ossification, increases in postimplantation loss, embryolethality and reduced fetal body weight. In rabbits, maternal toxicity, increased postimplantation loss and abortion were observed at doses greater than or equal to 30 mg/kg/day (approximately 0.007-fold the AUC at the MRHD of 800 mg/day). In addition, severe maternal body weight loss and 100% litter loss were observed at doses greater than or equal to 100 mg/kg/day (0.02-fold the AUC at the MRHD of 800 mg/day), while fetal weight was reduced at doses greater than or equal to 3 mg/kg/day (AUC not calculated).
8.2 Lactation
Risk Summary
There is no data on the presence of pazopanib or its metabolites in human milk or their effects on the breastfed infant or milk production. Because of the potential for serious adverse reactions in breastfed infants, advise women not to breastfeed during treatment with VOTRIENT and for 2 weeks after the final dose.
8.3 Females and Males of Reproductive Potential
VOTRIENT can cause fetal harm when administered to a pregnant woman [see Use in Specific Populations (8.1)].
Pregnancy Testing
Verify pregnancy status of females of reproductive potential prior to starting treatment with VOTRIENT.
Contraception
Females
Advise females of reproductive potential to use effective contraception during treatment with VOTRIENT and for at least 2 weeks after the last dose.
Males
Advise males (including those who have had vasectomies) with female partners of reproductive potential to use condoms during treatment with VOTRIENT and for at least 2 weeks after the last dose.
Infertility
Based on findings from animal studies, VOTRIENT may impair fertility in females and males of reproductive potential while receiving treatment [see Nonclinical Toxicology (13.1)].
8.4 Pediatric Use
The safety and effectiveness of VOTRIENT in pediatric patients have not been established.
VOTRIENT is not indicated for use in pediatric patients [see Warnings and Precautions (5.18)]. Based on its mechanism of action, pazopanib may have severe effects on organ growth and maturation during early postnatal development. Administration of pazopanib to juvenile rats < 21 days old resulted in toxicity to the lungs, liver, heart, and kidney and in death at doses significantly lower than the clinically recommended dose or doses tolerated in older animals (see Juvenile Animal Toxicity Data).
The safety and efficacy of VOTRIENT or an unapproved pazopanib formulation were investigated but not established in two open-label studies: a study in 37 pediatric patients 2 to < 17 years with recurrent or refractory solid tumors [NCT00929903] and a study in 46 pediatric patients 1 year to < 17 years with refractory solid tumors, including sarcoma [NCT01956669]. Meaningful anti- tumor activity was not observed in these studies.
Juvenile Animal Toxicity Data
In rats, weaning occurs at Day 21 postpartum which approximately equates to a human pediatric age of 2 years. In a juvenile animal toxicology study performed in rats, when animals were dosed from Day 9 through Day 14 postpartum (pre-weaning), pazopanib caused abnormal organ growth/maturation in the kidney, lung, liver, and heart at approximately 0.1-fold the AUC in adults at the MRHD of 800 mg/day of VOTRIENT. At approximately 0.4-fold the AUC in adults at the MRHD of 800 mg/day, pazopanib administration resulted in mortality.
In repeat-dose toxicology studies in rats, including 4-week, 13-week, and 26-week administration, toxicities in bone, teeth, and nail beds were observed at doses greater than or equal to 3 mg/kg/day (approximately 0.07-fold the AUC at the MRHD of 800 mg/day). Doses of 300 mg/kg/day (approximately 0.8-fold the AUC at the MRHD of 800 mg/day) were not tolerated in 13- and 26-week studies and animals required dose reductions due to body weight loss and morbidity. Hypertrophy of epiphyseal growth plates, nail abnormalities (including broken, overgrown, or absent nails) and tooth abnormalities in growing incisor teeth (including excessively long, brittle, broken, and missing teeth, and dentine and enamel degeneration and thinning) were observed in rats at doses greater than or equal to 30 mg/kg/day (approximately 0.35-fold the AUC at the MRHD of 800 mg/day) at 26 weeks, with the onset of tooth and nail bed alterations noted clinically after 4 to 6 weeks. Similar findings were noted in repeat- dose studies in juvenile rats dosed with pazopanib beginning Day 21 postpartum (post-weaning). In the post-weaning animals, the occurrence of changes in teeth and bones occurred earlier and with greater severity than in older animals. There was evidence of tooth degeneration and decreased bone growth at doses greater than or equal to 30 mg/kg (approximately 0.1- to 0.2-fold the AUC at the MRHD of 800 mg/day). Pazopanib exposure in juvenile rats was lower than that seen at the same dose levels in adult animals, based on comparative AUC values. At pazopanib doses approximately 0.5- to 0.7-fold the AUC at the MRHD of 800 mg/day, decreased bone growth in juvenile rats persisted even after the end of the dosing period. Finally, despite lower pazopanib exposures than those reported in adult animals or adult humans, juvenile animals administered 300 mg/kg/dose pazopanib required dose reduction within 4 weeks of dosing initiation due to significant toxicity, although adult animals could tolerate this same dose for at least 3 times as long [see Warnings and Precautions (5.18)].
8.5 Geriatric Use
In pooled clinical trials with VOTRIENT, 30% of 2080 patients were aged ≥ 65 years. More patients ≥ 65 years had ALT elevations > 3 × ULN compared to patients < 65 years (23% versus 18%) [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)].
In the RCC trials, 33% of 586 patients were aged ≥ 65 years. No overall differences in safety or effectiveness of VOTRIENT were observed between these patients and younger patients.
In the STS trials, 24% of 382 patients were aged ≥ 65 years. Patients aged ≥ 65 years had a higher incidence of Grade 3 or 4 fatigue (19% versus 12% for patients aged < 65 years), hypertension (10% versus 6%), decreased appetite (11% versus 2%), ALT elevations (3% versus 2%) and AST elevations (4% versus 1%). In the randomized STS trial (VEG110727), no overall differences in effectiveness of VOTRIENT were observed between patients aged ≥ 65 years and younger patients.
8.6 Renal Impairment
No dose adjustment is recommended for patients with renal impairment. VOTRIENT has not been studied in patients with severe renal impairment or in patients undergoing peritoneal dialysis or hemodialysis.
8.7 Hepatic Impairment
No dose adjustment is required in patients with mild hepatic impairment (either total bilirubin ≤ ULN and ALT > ULN or bilirubin > 1 to 1.5 × ULN and any ALT value). VOTRIENT is not recommended in patients with moderate (total bilirubin > 1.5 to 3 × ULN and any ALT value) and severe (total bilirubin > 3 × ULN and any ALT value) hepatic impairment [see Dosage and Administration (2.3), Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)].
- Lactation: Advise not to breastfeed. (8.2)
NONCLINICAL TOXICOLOGY SECTION
13 NONCLINICAL TOXICOLOGY
13.1 Carcinogenesis, Mutagenesis, Impairment of Fertility
The carcinogenic potential of pazopanib was evaluated in CD-1 mice, and Sprague-Dawley rats. Administration of pazopanib to mice for 2 years did not result in increased incidence of neoplasms at doses up to 100 mg/kg/day (approximately 1.4-fold the AUC at the MRHD of 800 mg/day). Administration of pazopanib to rats for 2 years resulted in findings of duodenal adenocarcinoma in males at 30 mg/kg/day (approximately 0.3-fold the AUC at the MRHD of 800 mg/day) and in females at greater than or equal to 10 mg/kg/day (approximately 0.3-fold the AUC at the MRHD of 800 mg/day). The human relevance of these neoplastic findings is unclear.
Pazopanib did not induce mutations in the microbial mutagenesis (Ames) assay and was not clastogenic in both the in vitro cytogenetic assay using primary human lymphocytes and in the in vivo rat micronucleus assay.
In an oral female fertility and early embryonic development study, female rats were administered pazopanib at least 15 days prior to mating, and for 6 days after mating. Pazopanib did affect fertility in female rats. Reduced fertility, including increased pre-implantation loss and early resorptions, were noted at dosages greater than or equal to 30 mg/kg/day (approximately 0.4-fold the AUC at the MRHD of 800 mg/day). Decreased corpora lutea and increased cysts were noted in mice given greater than or equal to 100 mg/kg/day for 13 weeks and ovarian atrophy was noted in rats given greater than or equal to 300 mg/kg/day for 26 weeks (approximately 1.3 and 0.85-fold the AUC at the MRHD of 800 mg/day). Decreased corpora lutea was also noted in monkeys given 500 mg/kg/day for up to 34 weeks (approximately 0.4-fold the AUC at the MRHD of 800 mg/day).
Pazopanib did not affect mating or fertility in male rats. However, there were reductions in sperm production rates and testicular sperm concentrations at doses greater than or equal to 3 mg/kg/day, epididymal sperm concentrations at doses greater than or equal to 30 mg/kg/day, and sperm motility at greater than or equal to 100 mg/kg/day following 15 weeks of dosing. Following 15 and 26 weeks of dosing, there were decreased testicular and epididymal weights at doses of greater than or equal to 30 mg/kg/day (approximately 0.35-fold the AUC at the MRHD of 800 mg/day); atrophy and degeneration of the testes with aspermia, hypospermia, and cribiform change in the epididymis was also observed at this dose in the 6-month toxicity studies in male rats.
