Trospium Chloride
These highlights do not include all the information needed to use Trospium Chloride Tablets safely and effectively. See full prescribing information for Trospium Chloride Tablets. TROSPIUM chloride tablets, USP for oral use Initial U.S. Approval:2004
1523cb4c-3a52-6c18-e063-6394a90a396f
HUMAN PRESCRIPTION DRUG LABEL
Apr 2, 2024
Aphena Pharma Solutions - Tennessee, LLC
DUNS: 128385585
Products 1
Detailed information about drug products covered under this FDA approval, including NDC codes, dosage forms, ingredients, and administration routes.
Trospium Chloride
Product Details
FDA regulatory identification and product classification information
FDA Identifiers
Product Classification
Product Specifications
INGREDIENTS (16)
Drug Labeling Information
PACKAGE LABEL.PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL
PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL - 20mg
NDC 71610-812 - Trospium Chloride, USP 20mg Tablets - Rx Only

INDICATIONS & USAGE SECTION
1 INDICATIONS AND USAGE
Trospium chloride tablets are a muscarinic antagonist indicated for the treatment of overactive bladder (OAB) with symptoms of urge urinary incontinence, urgency, and urinary frequency.
Trospium chloride tablets are a muscarinic antagonist indicated for the treatment of overactive bladder (OAB) with symptoms of urge urinary incontinence, urgency, and urinary frequency. ( 1)
CONTRAINDICATIONS SECTION
4 CONTRAINDICATIONS
Trospium chloride tablets are contraindicated in patients with:
- urinary retention
- gastric retention
- uncontrolled narrow-angle glaucoma.
- known hypersensitivity to the drug or its ingredients. Angioedema, rash and anaphylactic reaction have been reported.
Trospium chloride tablets are contraindicated in
- patients with urinary retention, gastric retention, or uncontrolled narrow-angle glaucoma, and in patients who are at risk for these conditions ( 4)
- patients with known hypersensitivity ( 4)
WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS SECTION
5 WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS
5.1 Risk of Urinary Retention
Trospium chloride tablets should be administered with caution to patients with clinically significant bladder outflow obstruction because of the risk of urinary retention [ see Contraindications ( 4) ].
5.2 Angioedema
Angioedema of the face, lips, tongue, and/or larynx has been reported with trospium chloride, the active ingredient in trospium chloride tablets. In one case, angioedema occurred after the first dose of trospium chloride. Angioedema associated with upper airway swelling may be life threatening. If involvement of the tongue, hypopharynx, or larynx occurs, trospium chloride should be promptly discontinued and appropriate therapy and/or measures necessary to ensure a patent airway should be promptly provided.
5.3 Decreased Gastrointestinal Motility
Trospium should be administered with caution to patients with gastrointestinal obstructive disorders because of the risk of gastric retention [ see Contraindications ( 4) ]. Trospium chloride, like other antimuscarinic agents, may decrease gastrointestinal motility and should be used with caution in patients with conditions such as ulcerative colitis, intestinal atony and myasthenia gravis.
5.4 Controlled Narrow-angle Glaucoma
In patients being treated for narrow-angle glaucoma, trospium chloride should only be used if the potential benefits outweigh the risks and in that circumstance only with careful monitoring [ see Contraindications ( 4) ].
5.5 Central Nervous System Effects
Trospium chloride is associated with anticholinergic central nervous system (CNS) effects [ see Adverse Reactions ( 6.2) ]. A variety of CNS anticholinergic effects have been reported, including dizziness, confusion, hallucinations and somnolence. Patients should be monitored for signs of anticholinergic CNS effects, particularly after beginning treatment or increasing the dose. Advise patients not to drive or operate heavy machinery until they know how trospium chloride affects them. If a patient experiences anticholinergic CNS effects, dose reduction or drug discontinuation should be considered.
5.6 Anticholinergic Adverse Reactions in Patients with Moderate Renal
Impairment
Trospium is substantially excreted by the kidney. The effects of moderate renal impairment on systemic exposure are not known but systemic exposure is likely increased. Therefore, anticholinergic adverse reactions (including dry mouth, constipation, dyspepsia, urinary tract infection, and urinary retention) are expected to be greater in patients with moderate renal impairment [ see Dosage and Administration ( 2), and Use in Specific Populations ( 8.6) ].
- Trospium chloride tablets should be administered with caution to patients with clinically significant bladder outflow obstruction or gastrointestinal obstructive disorders due to risk of urinary or gastric retention. ( 5.1, 5.3)
- Angioedema of the face, lips, tongue and/or larynx has been reported with trospium chloride. ( 5.2)
- In patients with controlled narrow angle glaucoma trospium chloride should be used only with careful monitoring. ( 5.4)
- Central Nervous System Effects: Somnolence has been reported with trospium chloride. Advise patients not to drive or operate heavy machinery until they know how trospium chloride affects them. ( 5.5)
- Trospium is substantially excreted by the kidney. The effects of moderate renal impairment on systemic exposure are not known but systemic exposure is likely increased. Therefore, the risk of anticholinergic adverse reactions is expected to be greater in patients with moderate renal impairment. ( 5.6)
ADVERSE REACTIONS SECTION
6 ADVERSE REACTIONS
6.1 Clinical Trials Experience
Because clinical trials are conducted under widely varying conditions, the adverse reaction rates observed in the clinical trials of a drug cannot be directly compared to rates in the clinical trials of another drug and may not reflect the rates observed in clinical practice.
The safety of trospium chloride was evaluated in controlled clinical trials in a total of 2975 patients, who were treated with trospium chloride (N=1673), placebo (N=1056) or active control medications (N=246). Of this total, 1181 patients participated in two, 12-week, U.S., efficacy and safety studies and a 9-month open-label extension. Of this total, 591 patients received trospium chloride tablets 20 mg twice daily. In all controlled trials combined, 232 and 208 patients received treatment with trospium chloride for at least 24 and 52 weeks, respectively.
In all placebo-controlled trials combined, the incidence of serious adverse events was 2.9% among patients receiving trospium chloride tablets 20 mg twice daily and 1.5% among patients receiving placebo. Table 1 lists adverse reactions from the combined 12-week U.S. safety and efficacy trials were reported by at least 1% of patients, and were reported more frequently in the trospium chloride group than in the placebo group.
The two most common adverse reactions reported by patients receiving trospium chloride tablets 20 mg twice daily were dry mouth and constipation. The single most frequently reported adverse reaction for trospium chloride tablets, dry mouth, occurred in 20.1% of trospium chloride treated patients and 5.8% of patients receiving placebo. In the two U.S. studies, dry mouth led to discontinuation in 1.9% of patients treated with trospium chloride tablets 20 mg twice daily. For the patients who reported dry mouth, most had their first occurrence of the event within the first month of treatment.
Table 1. Incidence (%) of adverse reactions with trospium chloride, reported in greater than or equal to 1% of all patients treated with trospium chloride tablets and more frequent with trospium chloride tablets (20 mg twice daily) than placebo in Studies 1 and 2 combined|
Adverse Reaction |
Placebo |
Trospium Chloride Tablets 20 mg |
|
Gastrointestinal Disorders | ||
|
Dry mouth |
34 (5.8) |
119 (20.1) |
|
Constipation |
27 (4.6) |
57 (9.6) |
|
Abdominal pain upper |
7 (1.2) |
9 (1.5) |
|
Constipation aggravated |
5 (0.8) |
8 (1.4) |
|
Dyspepsia |
2 (0.3) |
7 (1.2) |
|
Flatulence |
5 (0.8) |
7 (1.2) |
|
Nervous System Disorders | ||
|
Headache |
12 (2.0) |
25 (4.2) |
|
General Disorders | ||
|
Fatigue |
8 (1.4) |
11 (1.9) |
|
Renal and Urinary Disorders | ||
|
Urinary retention |
2 (0.3) |
7 (1.2) |
|
Eye Disorders | ||
|
Dry eyes |
2 (0.3) |
7 (1.2) |
Other adverse reactions from the U.S., placebo-controlled trials, occurring in greater than or equal to 0.5% and less than 1.0% of patients treated with trospium chloride, and more common with trospium chloride than placebo are: tachycardia, vision blurred, abdominal distension, vomiting, dysgeusia, dry throat, and dry skin.
During controlled clinical studies, one adverse reaction of angioneurotic edema was reported.
6.2 Post-marketing Experience
The following adverse reactions have been identified during post-approval use of trospium chloride. Because these reactions are reported voluntarily from a population of uncertain size, it is not always possible to reliably estimate their frequency or establish a causal relationship to drug exposure.
Gastrointestinal – gastritis; Cardiovascular – palpitations, supraventricular tachycardia, chest pain, syncope, "hypertensive crisis"; Immunological – Stevens-Johnson syndrome, anaphylactic reaction, angioedema; Nervous System – dizziness, confusion, vision abnormal, hallucinations, somnolence and delirium; Musculoskeletal – rhabdomyolysis; General – rash.
The most common adverse reactions (greater than or equal to 1%) with trospium chloride are dry mouth (20.1%), constipation (9.6%), and headache (4.2%). ( 6.1)
To report SUSPECTED ADVERSE REACTIONS, contact Avet Pharmaceuticals Inc. at 1-866-901-DRUG (3784) or FDA at 1-800-FDA-1088 or www.fda.gov/medwatch.
DRUG INTERACTIONS SECTION
7 DRUG INTERACTIONS
7.1 Digoxin
Concomitant use of trospium chloride and digoxin did not affect the pharmacokinetics of either drug [ see Clinical Pharmacology ( 12.3) ].
7.2 Drugs Eliminated by Active Tubular Secretion
Although demonstrated in a drug-drug interaction study not to affect the pharmacokinetics of digoxin, trospium chloride has the potential for pharmacokinetic interactions with other drugs that are eliminated by active tubular secretion (e.g., procainamide, pancuronium, morphine, vancomycin, and tenofovir). Coadministration of trospium chloride with these drugs may increase the serum concentration of trospium chloride and/or the coadministered drug due to competition for this elimination pathway. Careful patient monitoring is recommended in patients receiving such drugs [ see Clinical Pharmacology ( 12.3) ].
7.3 Antimuscarinic Agents
The concomitant use of trospium chloride with other antimuscarinic agents that produce dry mouth, constipation, and other anticholinergic pharmacological effects may increase the frequency and/or severity of such effects. Trospium chloride may potentially alter the absorption of some concomitantly administered drugs due to anticholinergic effects on gastrointestinal motility.
7.4 Metformin
Co-administration of 500 mg metformin immediate release tablets twice daily with SANCTURA XR ®+(trospium chloride 60 mg extended release capsules) reduced the steady-state systemic exposure of trospium by approximately 29% for mean AUC 0-24and by 34% for mean C max[ see Clinical Pharmacology ( 12.3) ].
- Concomitant use with digoxin did not affect the pharmacokinetics of either drug. ( 7.1)
- Some drugs which are actively secreted by the kidney may interact with trospium chloride by competing for renal tubular secretion. ( 7.2)
- Concomitant use with metformin immediate release tablets reduced exposure and peak concentration of trospium. ( 7.4)
RECENT MAJOR CHANGES SECTION
RECENT MAJOR CHANGES
Warnings and Precautions, Central Nervous System Effects ( 5.5) 07/2012
Warnings and Precautions, Central Nervous System Effects ( 5.5) 07/2012
DOSAGE & ADMINISTRATION SECTION
2 DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
The recommended dose is 20 mg twice daily. Trospium chloride tablets should be dosed at least one hour before meals or given on an empty stomach.
Dosage modification is recommended in the following patient populations:
- For patients with severe renal impairment (creatinine clearance less than 30 mL/min), the recommended dose is 20 mg once daily at bedtime [ see Warnings and Precautions ( 5.5), Use in Specific Populations ( 8.6), and Clinical Pharmacology ( 12.3) ].
- In geriatric patients greater than or equal to 75 years of age, dose may be titrated down to 20 mg once daily based upon tolerability [ see Use in Specific Populations ( 8.5) ].
- The recommended dose of trospium chloride tablet is one 20 mg tablet twice daily. Trospium chloride tablets should be dosed with water on an empty stomach, at least one hour before a meal. ( 2)
- For patients with severe renal impairment (creatinine clearance less than 30 mL/min), the recommended dose is 20 mg once daily at bedtime. ( 2)
- In geriatric patients greater than or equal to 75 years of age, dose may be titrated down to 20 mg once daily based upon tolerability. ( 2)
DOSAGE FORMS & STRENGTHS SECTION
3 DOSAGE FORMS AND STRENGTHS
Trospium chloride tablets are supplied as 20 mg tablets (round, white to off white, film coated tablets. Imprinted "HP" with black ink on one side and "530" on the reverse side).
- 20 mg tablets. ( 3)
USE IN SPECIFIC POPULATIONS SECTION
8 USE IN SPECIFIC POPULATIONS
8.1 Pregnancy
Teratogenic Effects
**Pregnancy Category C:**There are no adequate and well-controlled studies of trospium chloride in pregnant women. Trospium chloride should be used during pregnancy only if the potential benefit to the patient outweighs the risk to the patient and fetus. Women who become pregnant during trospium chloride treatment are encouraged to contact their physician.
Risk Summary
Based on animal data, trospium chloride is predicted to have a low probability of increased risk of adverse developmental outcomes, above background risk. Adverse developmental findings were not observed to correlate with dose in rats or in rabbits. No increased risk above background was observed in rats and rabbits treated at an exposure approximately equivalent to the maximal recommended human dose (MRHD) of 40 mg.
Animal Data
In a rat embryo/fetal development study, pregnant rats received doses of trospium chloride up to 200 mg/kg/day, from implantation to closure of the fetal hard palate, with maternal systemic exposures corresponding to approximately nine times the exposure of women treated at the MRHD of 40 mg, based on AUC. No malformations or fetal toxicity were observed.
The offspring of female rats exposed orally, pre- and post-natally, to trospium chloride up to 200 mg/kg/day showed no increased developmental toxicity over background in surviving pups. However, maternal toxicity (death, irregular breathing, increased excitability) was observed at 200 mg/kg/day. A no-effect level for maternal and pup toxicity (survival to Day 4) was 20 mg/kg/day, an exposure approximately equivalent to the maximal recommended human dose (MRHD) of 40 mg.
In a rabbit embryo/fetal development study, pregnant rabbits received doses of trospium chloride up to 200 mg/kg/day, from implantation to closure of the fetal hard palate. At 200 mg/kg/day, maternal systemic exposures corresponded to approximately 16 times the exposure of women treated at the MRHD of 40 mg, based on AUC. However, one fetus in each of the three treated dose groups (0.3 to 16 times exposures at the MRHD) demonstrated multiple malformations, including umbilical hernia and skeletal malformations. A maternal no-effect level was set at 20 mg/kg/day, at an exposure approximately equivalent to the maximal recommended human dose (MRHD) of 40 mg, due to clinical signs (reduced feces, hunched posture, diarrhea) observed in a pharmacokinetic study at 200 mg/kg/day.
8.2 Labor and Delivery
The effect of trospium chloride tablets on labor and delivery is unknown.
8.3 Nursing Mothers
Trospium chloride (2 mg/kg orally and 50 mcg/kg intravenously) was excreted, to a limited extent (less than 1%), into the milk of lactating rats (primarily as parent compound). It is not known whether this drug is excreted in human milk. Because many drugs are excreted in human milk, trospium chloride should be used during lactation only if the potential benefit justifies the potential risk to the newborn.
8.4 Pediatric Use
The safety and effectiveness of trospium chloride in pediatric patients have not been established.
8.5 Geriatric Use
Of the 591 patients with overactive bladder who received treatment with trospium chloride in the two U.S., placebo-controlled, efficacy and safety studies, 249 patients (42%) were 65 years of age and older. Eighty-eight trospium chloride treated patients (15%) were greater than or equal to 75 years of age.
In these 2 studies, the incidence of commonly reported anticholinergic adverse reactions in patients treated with trospium chloride (including dry mouth, constipation, dyspepsia, urinary tract infection, and urinary retention) was higher in patients 75 years of age and older as compared to younger patients. This effect may be related to an enhanced sensitivity to anticholinergic agents in this patient population [ see Clinical Pharmacology ( 12.3) ]. Therefore, based upon tolerability, the dose frequency of trospium chloride may be reduced to 20 mg once daily in patients 75 years of age and older.
8.6 Renal Impairment
Severe renal impairment (creatinine clearance less than 30 mL/minute) significantly altered the disposition of trospium chloride. A 4.2-fold and 1.8-fold increase in mean AUC (0-∞)and C max, respectively, and the appearance of an additional elimination phase with a long half-life (~33 hr) were detected in patients with severe renal impairment compared with nearly age- matched subjects with creatinine clearance equal to or higher than 80 mL/min. The different pharmacokinetic behavior of trospium chloride in patients with severe renal impairment necessitates adjustment of dosage frequency [ see Dosage and Administration ( 2) ]. The pharmacokinetics of trospium have not been studied in patients with creatinine clearance ranging from 30-80 mL/min.
Trospium is known to be substantially excreted by the kidney, and the risk of adverse reactions may be greater in patients with impaired renal function.
8.7 Hepatic Impairment
There is no information regarding the effect of severe hepatic impairment on exposure to trospium chloride. In a study of patients with mild and with moderate hepatic impairment, given 40 mg of immediate-release trospium chloride, mean C maxincreased 12% and 63%, respectively, and mean AUC (0-∞)decreased 5% and 15%, respectively, compared to healthy subjects. The clinical significance of these findings is unknown. Caution should be used when administering trospium chloride to patients with moderate and severe hepatic impairment.
- The safety and effectiveness of trospium chloride in pediatric patients have not been established. ( 8.4)
OVERDOSAGE SECTION
10 OVERDOSAGE
Overdosage with antimuscarinic agents, including trospium chloride, can result in severe antimuscarinic effects. Supportive treatment should be provided according to symptoms. In the event of overdosage, electrocardiographic monitoring is recommended.
A 7-month-old baby experienced tachycardia and mydriasis after administration of a single dose of trospium 10 mg given by a sibling. The baby's weight was reported as 5 kg. Following admission into the hospital and about 1 hour after ingestion of the trospium, medicinal charcoal was administered for detoxification. While hospitalized, the baby experienced mydriasis and tachycardia up to 230 beats per minute. Therapeutic intervention was not deemed necessary. The baby was discharged as completely recovered the following day.
DESCRIPTION SECTION
11 DESCRIPTION
Trospium chloride is a quaternary ammonium compound with the chemical name of Spiro [8-azoniabicyclo[3.2.1]octane-8,1'-pyrrolidinium], 3-[(hydroxydiphenylacetyl)oxy]-, chloride, (1α, 3β, 5α). The empirical formula of trospium chloride is C 25H 30ClNO 3and its molecular weight is 427.96. The structural formula of trospium chloride is represented below:
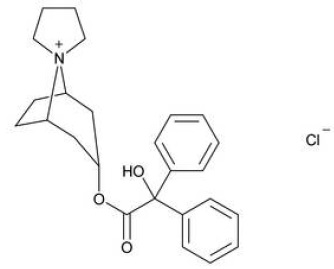
Trospium chloride is a white or almost white, crystalline powder. The compound is very soluble in water.
Each trospium chloride tablet intended for oral administration contains 20 mg of trospium chloride, a muscarinic antagonist, for oral administration. Each trospium chloride tablet also contains the following inactive ingredients: black iron oxide, confectioners' sugar, croscarmellose sodium, hypromellose, lactose monohydrate, magnesium stearate, microcrystalline cellulose, polyethylene glycol, povidone, propylene glycol, shellac, silicon dioxide, talc and titanium dioxide.
Product meets USP Dissolution Test 2.
HOW SUPPLIED SECTION
16 HOW SUPPLIED/STORAGE AND HANDLING
Trospium Chloride Tablets USP, 20 mg intended for oral administration are round, white to off-white, film coated tablets. Imprinted "HP" with black ink on one side and "530" on the reverse side. They are supplied as follows:
Bottle of 60 tablets, NDC 0904-7059-52
Store at 20 oto 25 oC (68 oto 77 oF) [see USP Controlled Room Temperature].
Dispense in a tight, light-resistant container as defined in the USP using a child-resistant closure. Keep container tightly closed
SPL UNCLASSIFIED SECTION
REPACKAGING INFORMATION
Please reference the HOW SUPPLIED section listed above for a description of individual drug products listed below. This drug product has been received by Aphena Pharma Solutions - Tennessee, LLC in a manufacturer or distributor packaged configuration and repackaged in full compliance with all applicable cGMP regulations. The package configurations available from Aphena are listed below:
20mg
NDC 71610-812-87, Bottles of 2400 Tablets
Store between 20°-25°C (68°-77°F). See USP Controlled Room Temperature. Dispense in a tight light-resistant container as defined by USP. Keep this and all drugs out of the reach of children.
Repackaged by:

Cookeville, TN 38506
20240402AMH
CLINICAL STUDIES SECTION
14 CLINICAL STUDIES
Trospium chloride was evaluated for the treatment of patients with overactive bladder who had symptoms of urinary frequency, urgency, and urge incontinence in two U.S. 12-week, placebo-controlled studies and one 9-month open label extension.
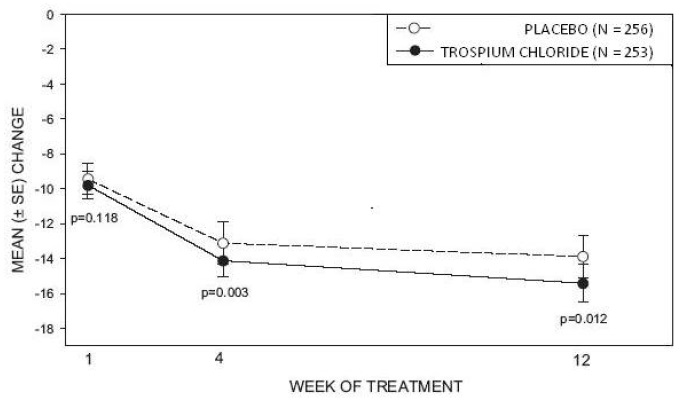
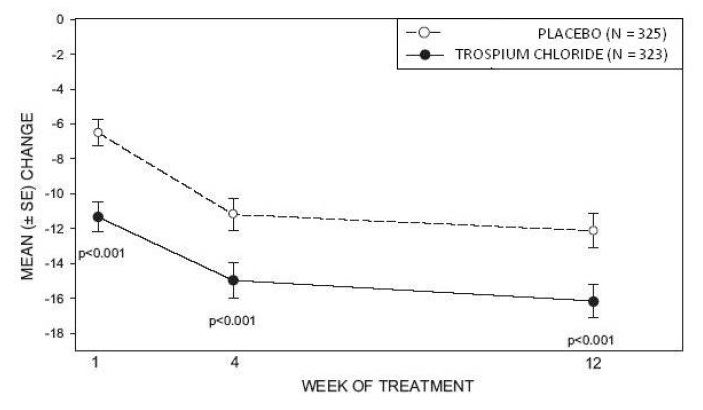
Study 1was a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled, parallel-group study in 523 patients. A total of 262 patients received trospium chloride tablets 20 mg twice daily and 261 patients received placebo. The majority of patients were Caucasian (85%) and female (74%) with a mean age of 61 years (range: 21 to 90 years). Entry criteria required that patients have urge or mixed incontinence (with a predominance of urge), urge incontinence episodes of at least 7 per week, and greater than 70 micturitions per week. The patient's medical history and urinary diary during the treatment-free baseline confirmed the diagnosis. Reductions in urinary frequency, urge incontinence episodes and urinary void volume for placebo and trospium chloride treatment groups are summarized in Table 3 and Figures 2 and 3.
Table 3. Mean (SE) change from baseline to end of treatment (Week 12 or last observation carried forward) for urinary frequency, urge incontinence episodes, and void volume in Study 1|
Efficacy endpoint |
Placebo N=256 |
Trospium Chloride N=253 |
P-value |
|
*Urinary frequency/24 hours**a, |
12.9 |
12.7 |
<0.001 |
|
*Urge incontinence episodes/week**b, |
30.1 |
27.3 |
0.012 |
|
**Urinary void volume/toilet void (mL)**a,c |
156.6 |
155.1 |
<0.001 |
|
aTreatment differences assessed by analysis of variance for ITT:LOCF data set. |
Figure 2 – Mean Change from Baseline in Urinary Frequency/24 Hours, by Visit: Study 1
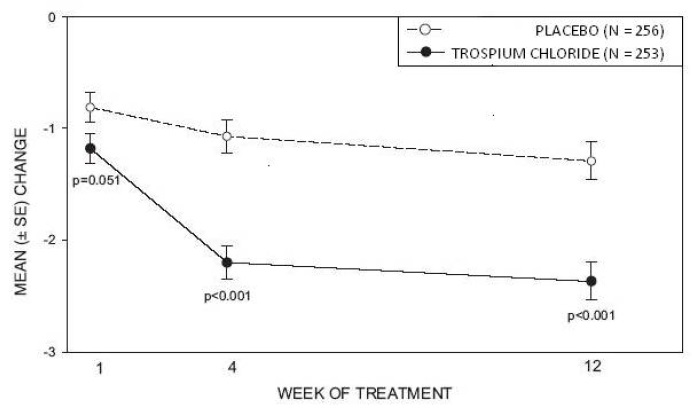
Figure 3 – Mean Change from Baseline in Urge Incontinence/Week, by Visit: Study 1
Study 2was nearly identical in design to Study 1. A total of 329 patients received trospium chloride tablets 20 mg twice daily and 329 patients received placebo. The majority of patients were Caucasian (88%) and female (82%) with a mean age of 61 years (range: 19 to 94 years). Entry criteria were identical to Study 1. Reductions in urinary frequency, urge incontinence episodes, and urinary void volume for placebo and trospium chloride treatment groups are summarized in Table 4 and Figures 4 and 5.
Table 4. Mean (SE) change from baseline to end of treatment (Week 12 or last observation carried forward) for urinary frequency, urge incontinence episodes, and void volume in Study 2|
Efficacy endpoint |
Placebo N=325 |
Trospium |
P-value |
|
*Urinary frequency/24 hours**a, |
13.2 |
12.9 |
<0.001 |
|
*Urge incontinence episodes/week**b, |
27.3 |
26.9 |
<0.001 |
|
**Urinary void volume/toilet void (mL)**a,c |
154.6 |
154.8 |
<0.001 |
|
a Treatment differences assessed by analysis of variance for ITT:LOCF data
set.
|
Figure 4 – Mean Change from Baseline in Urinary Frequency/24 Hours, by Visit: Study 2
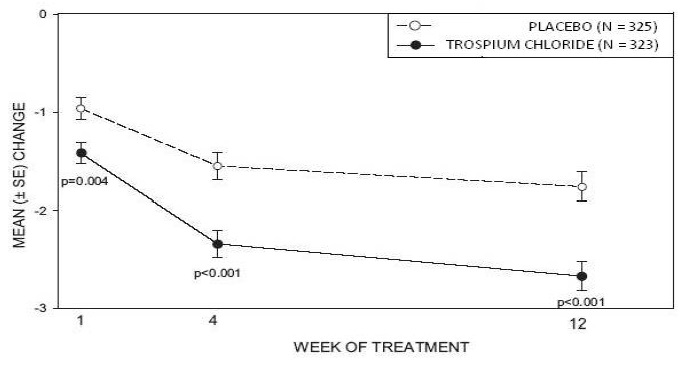
Figure 5 – Mean Change from Baseline in Urge Incontinence/Week, by Visit: Study 2
CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY SECTION
12 CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY
12.1 Mechanism of Action
Trospium chloride is a muscarinic antagonist.
Trospium chloride antagonizes the effect of acetylcholine on muscarinic receptors in cholinergically innervated organs including the bladder. Its parasympatholytic action reduces the tonus of smooth muscle in the bladder.
Receptor assays showed that trospium chloride has negligible affinity for nicotinic receptors as compared to muscarinic receptors at concentrations obtained from therapeutic doses.
12.2 Pharmacodynamics
Placebo-controlled studies employing urodynamic variables were conducted in patients with conditions characterized by involuntary detrusor contractions. The results demonstrate that trospium chloride increases maximum cystometric bladder capacity and volume at first detrusor contraction.
Electrophysiology
The effect of 20 mg twice daily and up to 100 mg twice daily of trospium chloride on QT interval was evaluated in a single-blind, randomized, placebo and active (moxifloxacin 400 mg once daily) controlled 5 day parallel trial in 170 male and female healthy volunteer subjects aged 18 to 45 years. The QT interval was measured over a 24-hour period at steady state. The 100 mg twice daily dose of trospium chloride was chosen because this achieves the C maxexpected in severe renal impairment. Trospium chloride was not associated with an increase in individual corrected (QTcI) or Fridericia corrected (QTcF) QT interval at any time during steady state measurement, while moxifloxacin was associated with a 6.4 msec increase in QTcF.
In this study, asymptomatic, non-specific T wave inversions were observed more often in subjects receiving trospium chloride than in subjects receiving moxifloxacin or placebo following five days of treatment. This finding was not observed during routine safety monitoring in 2 other placebo-controlled clinical trials in 591 trospium chloride treated overactive bladder patients [ see Clinical Studies ( 14) ]. The clinical significance of T wave inversion in this study is unknown. Trospium chloride is associated with an increase in heart rate that correlates with increasing plasma concentrations. In the study described above, trospium chloride demonstrated a mean increase in heart rate compared to placebo of 9.1 bpm for the 20 mg dose and of 18 bpm for the 100 mg dose. In the two U.S. placebo-controlled trials in patients with overactive bladder, the mean increase in heart rate compared to placebo in Study 1 was observed to be 3 bpm and in Study 2 was 4 bpm.
12.3 Pharmacokinetics
Absorption:After oral administration, less than 10% of the dose is absorbed. Mean absolute bioavailability of a 20 mg dose is 9.6% (range: 4 to 16.1%). Peak plasma concentrations (C max) occur between 5 to 6 hours post-dose. Mean C maxincreases greater than dose-proportionally; a 3-fold and 4-fold increase in C maxwas observed for dose increases from 20 mg to 40 mg and from 20 mg to 60 mg, respectively. AUC exhibits dose linearity for single doses up to 60 mg. Trospium chloride exhibits diurnal variability in exposure with a decrease in C maxand AUC of up to 59% and 33%, respectively, for evening relative to morning doses.
Effect of Food:Administration with a high (50%) fat-content meal resulted in reduced absorption, with AUC and C maxvalues 70 to 80% lower than those obtained when trospium chloride was administered while fasting. Therefore, it is recommended that trospium chloride should be taken at least one hour prior to meals or on an empty stomach [ see Dosage and Administration ( 2) ].
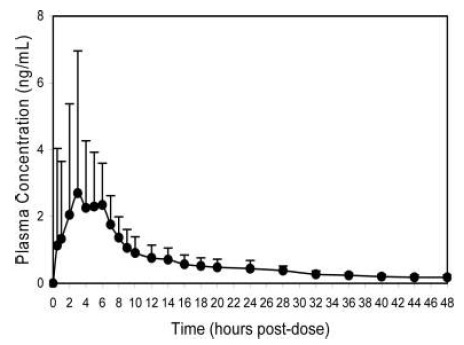
A summary of mean (± standard deviation) pharmacokinetic parameters for a single 20 mg dose of trospium chloride tablets is provided in Table 2.
Table 2. Mean (± SD) Pharmacokinetic Parameter Estimates for a Single Dose of Trospium Chloride Tablets in Healthy Volunteers|
C****max(ng/mL) |
AUC****0-∞(ng/mL•hr) |
T****max(hr) |
t****½(hr) |
|
3.5 ± 4.0 |
36.4 ± 21.8 |
5.3 ± 1.2 |
18.3 ± 3.2 |
The mean plasma concentration-time (+ SD) profile for trospium chloride is shown in Figure 1.
Figure 1 - Mean (+ SD) Concentration-Time Profile for a Single 20 mg Oral Dose of Trospium Chloride Tablets in Healthy Volunteers
Distribution: Protein binding ranged from 50 to 85% when concentration levels of trospium chloride (0.5 to 50 ng/mL) were incubated with human serum in vitro.
The 3H-trospium chloride ratio of plasma to whole blood was 1.6:1. This ratio indicates that the majority of 3H-trospium chloride is distributed in plasma.
The apparent volume of distribution for a 20 mg oral dose is 395 (± 140) liters.
Metabolism:The metabolic pathway of trospium in humans has not been fully defined. Of the 10% of the dose absorbed, metabolites account for approximately 40% of the excreted dose following oral administration. The major metabolic pathway is hypothesized as ester hydrolysis with subsequent conjugation of benzylic acid to form azoniaspironortropanol with glucuronic acid. Cytochrome P450 (CYP) is not expected to contribute significantly to the elimination of trospium. Data taken from in vitrohuman liver microsomes investigating the inhibitory effect of trospium on seven CYP isoenzyme substrates (CYP1A2, 2A6, 2C9, 2C19, 2D6, 2E1, and 3A4) suggest a lack of inhibition at clinically relevant concentrations.
Excretion:The plasma half-life for trospium chloride following oral administration is approximately 20 hours. After oral administration of an immediate-release formulation of 14C-trospium chloride, the majority of the dose (85.2%) was recovered in feces and a smaller amount (5.8% of the dose) was recovered in urine; 60% of the radioactivity excreted in urine was unchanged trospium.
The mean renal clearance for trospium (29.07 L/hour) is 4-fold higher than average glomerular filtration rate, indicating that active tubular secretion is a major route of elimination for trospium. There may be competition for elimination with other compounds that are also renally eliminated [ see Drug Interactions ( 7.2) ].
Drug Interactions
Digoxin:Concomitant use of 20 mg trospium chloride immediate release tablets twice daily at steady state and a single dose of 0.5 mg digoxin in a crossover study with 40 male and female subjects did not affect the pharmacokinetics of either drug.
Metformin:A drug interaction study was conducted in which SANCTURA XR ®+60 [an extended release form of trospium chloride capsules, 60 mg] once daily was co- administered with Glucophage ®++(metformin hydrochloride) 500 mg twice daily under steady-state conditions in 44 healthy subjects. Co-administration of 500 mg metformin immediate release tablets twice daily reduced the steady-state systemic exposure of trospium by approximately 29% for mean AUC 0-24and by 34% for mean C max. The effect of decrease in trospium exposure on the efficacy of SANCTURA XR ®+[an extended release form of trospium chloride capsules, 60 mg] is unknown. The steady-state pharmacokinetics of metformin were comparable when administered with or without 60 mg SANCTURA XR ®+[an extended release form of trospium chloride capsules, 60 mg] once daily under fasted condition. The effect of metformin at higher doses on trospium PK is unknown.
Specific Populations
Age:Age did not appear to significantly affect the pharmacokinetics of trospium chloride, however, increased anticholinergic side effects unrelated to drug exposure were observed in patients greater than or equal to 75 years of age [ see Use in Specific Populations ( 8.5) ].
Pediatric:The pharmacokinetics of trospium chloride were not evaluated in pediatric patients.
Race:Pharmacokinetic differences due to race have not been studied.
Gender:Studies comparing the pharmacokinetics in different genders had conflicting results. When a single 40 mg trospium chloride tablets dose was administered to 16 elderly subjects, exposure was 45% lower in elderly females compared to elderly males. When 20 mg trospium chloride tablets was dosed twice daily for 4 days to 6 elderly males and 6 elderly females (60 to 75 years), AUC and C maxwere 26% and 68% higher, respectively, in females without hormone replacement therapy than in males.
Renal Impairment:In a clinical pharmacokinetic study where a single dose of 40 mg immediate release trospium chloride was administered to 12 healthy males and 12 males with severe renal impairment, severe renal impairment (creatinine clearance less than 30 mL/minute) significantly altered the disposition of trospium chloride. A 4.2-fold and 1.8-fold increase in mean AUC (0-∞)and C max, respectively, and the appearance of an additional elimination phase with a long half-life (~33 hours vs. 18 hours) were detected in patients with severe renal impairment compared with nearly age-matched subjects with creatinine clearance equal to or higher than 80 mL/min. The different pharmacokinetic behavior of trospium chloride in patients with severe renal impairment necessitates adjustment of dosage frequency [ see Dosage and Administration ( 2) ]. The pharmacokinetics of trospium have not been studied in patients with creatinine clearance ranging from 30 to 80 mL/min.
Hepatic Impairment:In a clinical pharmacokinetic study in patients with mild (Child-Pugh score 5 to 6) and with moderate (Child-Pugh score 7 to 8) hepatic impairment, given a single dose of 40 mg immediate-release trospium chloride, mean C maxincreased 12% and 63%, respectively, and mean AUC (0-∞)decreased 5% and 15%, respectively, compared to healthy subjects. There is no information regarding the effect of severe hepatic impairment on exposure to trospium chloride.
NONCLINICAL TOXICOLOGY SECTION
13 NONCLINICAL TOXICOLOGY
13.1 Carcinogenesis, Mutagenesis, Impairment of Fertility
Carcinogenesis:Carcinogenicity studies with trospium chloride were conducted in mice and rats for 78 weeks and 104 weeks, respectively, at maximally tolerated doses. No evidence of a carcinogenic effect was found in either mice or rats administered up to 200 mg/kg/day, approximately 9 times the expected clinical exposure levels at the maximum recommended human dose (MRHD) of 40 mg.
Mutagenesis:Trospium chloride was not mutagenic nor genotoxic in tests in vitroin bacteria (Ames test) and mammalian cells (L5178Y mouse lymphoma and CHO cells) or in vivoin the rat micronucleus test.
Impairment of Fertility:No evidence of impaired fertility was observed in rats administered doses up to 200 mg/kg/day (about 16 times the expected clinical exposure at the MRHD, based on AUC).
INFORMATION FOR PATIENTS SECTION
17 PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATION
"See FDA-approved Patient Labeling (Patient Information)"
17.1 Angioedema
Patients should be informed that trospium chloride, the active ingredient in trospium chloride tablets, may produce angioedema which could result in life- threatening airway obstruction. Patients should be advised to promptly discontinue trospium chloride tablets and seek immediate medical attention if they experience edema of the tongue, edema of the laryngopharynx, or difficulty breathing.
17.2 When Not to Use
Prior to treatment, patients should fully understand the risks and benefits of trospium chloride. In particular, patients should be informed not to take trospium chloride tablets if they:
- have urinary retention;
- gastric retention;
- uncontrolled narrow-angle glaucoma;
- are allergic to any component of trospium chloride tablets.
17.3 Administration
Patients should be instructed regarding the recommended dosing and administration of trospium chloride tablets:
- Take one trospium chloride tablet twice daily with water.
- Take trospium chloride tablets on an empty stomach or at least 1 hour before a meal.
17.4 Adverse Reactions
Patients should be informed that the most common side effects with trospium chloride tablets are dry mouth and constipation and that other less common side effects include trouble emptying the bladder, blurred vision, and heat prostration. Because anticholinergics, such as trospium chloride, may produce dizziness or blurred vision, patients should be advised to exercise caution in decisions to engage in potentially dangerous activities until the drug's effects have been determined. Patients should be informed that alcohol may enhance the drowsiness caused by anticholinergic agents.
+SANCUTURA XR ®is a registered trademark by Allergan Inc. for Trospium Chloride Extended-Release Capsules, 60 mg.
++Glucophage ®is a registered trade mark by Bristol Meyers Squibb for Metformin Hydrochloride Tablets.
Distributed by:
Avet Pharmaceuticals Inc.
East Brunswick, NJ 08816
1.866.901.DRUG (3784)
Distributed By:
MAJOR® PHARMACEUTICALS
17177 N Laurel Park Dr., Suite 233
Livonia, MI 48152
Revised: 06/2020
Patient Information Leaflet
Trospium (TROSE-pee-um) Chloride Tablets, USP
Read the Patient Information that comes with trospium chloride tablets before you start taking it and each time you get a refill. There may be new information. This leaflet does not take the place of talking with your doctor about your medical condition or your treatment.
What is trospium chloride tablets?
Trospium chloride tablets are a prescription medicine used to treat adults with overactive bladder who have the following symptoms:
- a strong need to urinate right away;
- leaking or wetting accidents due to a strong need to urinate right away;
- a need to urinate often.
Who should not take trospium chloride tablets?
Do not take trospium chloride tablets if you:
- have trouble emptying your bladder;
- have delayed or slow emptying of your stomach;
- have an eye problem called "uncontrolled narrow-angle glaucoma";
- are allergic to trospium chloride tablets or any of its ingredients. See the end of this leaflet for a complete list of ingredients.
Trospium chloride tablets has not been studied in children under the age of 18 years.
What should I tell my doctor before starting trospium chloride tablets?
Tell your doctor about all of your medical conditions including if you:
- have any stomach or intestinal problems or problems with constipation;
- have trouble emptying your bladder or have a weak urine stream;
- have an eye problem called narrow-angle glaucoma;
- have kidney problems;
- have liver problems;
- are pregnant or planning to become pregnant. It is not known if trospium chloride can harm your unborn baby.
- are breastfeeding. It is not known if trospium chloride passes into breast milk and if it can harm your baby. You should talk to your doctor about the best way to feed your baby if you are taking trospium chloride tablets.
Tell your doctor about all the medicines you take including prescription and nonprescription medicines, vitamins and herbal supplements. Trospium chloride tablets and certain other medicines can interact and make some side effects worse. Trospium chloride tablets can affect how other medicines are handled by the body.
Know all the medicines you take. Keep a list of them with you to show your doctor and pharmacist each time you get a new medicine.
How should I take trospium chloride tablets?
Take trospium chloride tablets exactly as prescribed.
- Take one trospium chloride tablet twice daily with water.
- Take trospium chloride tablets on an empty stomach or at least 1 hour before a meal.
- If you take too much trospium chloride, call your local Poison Control Center or go to an emergency room right away.
What are the possible side effects of trospium chloride tablets?
Trospium chloride tablets may cause allergic reactions that may be serious. Symptoms of a serious allergic reaction may include swelling of the face, lips, throat or tongue. If you experience these symptoms, you should stop taking trospium chloride tablets and get emergency medical help right away.
The most common side effects with trospium chloride tablets are:
- dry mouth;
- constipation;
- headache.
Trospium chloride tablets may cause other less common side effects, including:
- trouble emptying the bladder;
- blurred vision; and drowsiness. Do not drive or operate heavy machinery until you know how trospium chloride tablets affects you. Alcohol can worsen the drowsiness caused by drugs such as trospium chloride.
- heat prostration. Due to decreased sweating, heat prostration can occur when drugs such as trospium chloride are used in a hot environment.
Tell your doctor if you have any side effects that bother you or that do not go away.
These are not all possible side effects of trospium chloride. For more information, ask your doctor, healthcare professional or pharmacist.
How should I store trospium chloride tablets?
- Keep trospium chloride tablet and all other medicines out of the reach of children.
- Store trospium chloride tablet at room temperature, 68° to 77°F (20° to 25°C).
- Safely dispose of trospium chloride tablets that are out of date or that you no longer need.
General information about trospium chloride tablets
Medicines are sometimes prescribed for conditions that are not mentioned in patient information leaflets. Do not use trospium chloride tablet for a condition for which it was not prescribed. Do not give trospium chloride tablet to other people, even if they have the same symptoms you have. It may harm them.
This leaflet summarizes the most important information about trospium chloride tablets. If you would like more information, talk with your doctor. You can ask your doctor or pharmacist for information about trospium chloride tablets that is written for health professionals. You can also call Avet at 1-866-901-DRUG (3784).
What are the ingredients in trospium chloride tablets?
Active Ingredient: trospium chloride.
Inactive Ingredients: black iron oxide, confectioners' sugar, croscarmellose sodium, hypromellose, lactose monohydrate, magnesium stearate, microcrystalline cellulose, polyethylene glycol, povidone, propylene glycol, shellac, silicon dioxide, talc and titanium dioxide.
Dispense with Patient Information available at: www.avetpharma.com/product
Distributed by:
Avet Pharmaceuticals Inc.
East Brunswick, NJ 08816
1.866.901.DRUG (3784)
51U000000240US05
Distributed By:
MAJOR® PHARMACEUTICALS
17177 N Laurel Park Dr., Suite 233
Livonia, MI 48152
Revised: 06/2020
