HYRIMOZ
These highlights do not include all the information needed to use HYRIMOZ safely and effectively. See full prescribing information for HYRIMOZ. HYRIMOZ (adalimumab-adaz) injection, for subcutaneous useInitial U.S. Approval: 2018HYRIMOZ (adalimumab-adaz) is biosimilar* to HUMIRA (adalimumab)
3e303a4a-980b-4f2a-9d03-786928758637
HUMAN PRESCRIPTION DRUG LABEL
Jun 15, 2023
Cordavis Limited
DUNS: 986134209
Products 8
Detailed information about drug products covered under this FDA approval, including NDC codes, dosage forms, ingredients, and administration routes.
adalimumab-adaz
Product Details
FDA regulatory identification and product classification information
FDA Identifiers
Product Classification
Product Specifications
INGREDIENTS (7)
adalimumab-adaz
Product Details
FDA regulatory identification and product classification information
FDA Identifiers
Product Classification
Product Specifications
adalimumab-adaz
Product Details
FDA regulatory identification and product classification information
FDA Identifiers
Product Classification
Product Specifications
INGREDIENTS (9)
adalimumab-adaz
Product Details
FDA regulatory identification and product classification information
FDA Identifiers
Product Classification
Product Specifications
INGREDIENTS (7)
adalimumab-adaz
Product Details
FDA regulatory identification and product classification information
FDA Identifiers
Product Classification
Product Specifications
INGREDIENTS (9)
adalimumab-adaz
Product Details
FDA regulatory identification and product classification information
FDA Identifiers
Product Classification
Product Specifications
INGREDIENTS (7)
adalimumab-adaz
Product Details
FDA regulatory identification and product classification information
FDA Identifiers
Product Classification
Product Specifications
INGREDIENTS (7)
adalimumab-adaz
Product Details
FDA regulatory identification and product classification information
FDA Identifiers
Product Classification
Product Specifications
INGREDIENTS (7)
Drug Labeling Information
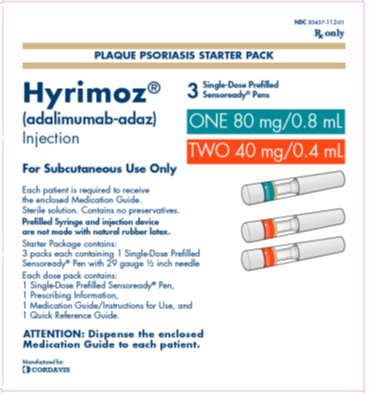
PACKAGE LABEL.PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL
PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL
NDC 83457-112-01
Rx only
PLAQUE PSORIASIS OR UVEITIS STARTER PACK
Hyrimoz**®**
(adalimumab-adaz)
Injection
ONE 80 mg/0.8 mL
TWO 40 mg/0.4 mL
For Subcutaneous Use Only
3Single-Dose Prefilled Sensoready®** Pens**
Each patient is required to receive the enclosed Medication Guide.
Sterile solution. Contains no preservatives.
Prefilled Syringe and injection device are not made with natural rubber latex.
Starter Package contains:
3 packs each containing 1 Single-Dose Prefilled
Sensoready**®** Pen with 29 gauge ½ inch needle
Each dose pack contains:
1 Single-Dose Prefilled Sensoready**®** Pen,
1 Prescribing Information,
1 Medication Guide/Instructions for Use, and
1 Quick Reference Guide.
ATTENTION: Dispense the enclosed Medication Guide to each patient.
INDICATIONS & USAGE SECTION
1 INDICATIONS AND USAGE
1.1 Rheumatoid Arthritis
HYRIMOZ is indicated for reducing signs and symptoms, inducing major clinical response, inhibiting the progression of structural damage, and improving physical function in adult patients with moderately to severely active rheumatoid arthritis. HYRIMOZ can be used alone or in combination with methotrexate or other non-biologic disease-modifying anti-rheumatic drugs (DMARDs).
1.2 Juvenile Idiopathic Arthritis
HYRIMOZ is indicated for reducing signs and symptoms of moderately to severely active polyarticular juvenile idiopathic arthritis in patients 2 years of age and older. HYRIMOZ can be used alone or in combination with methotrexate.
1.3 Psoriatic Arthritis
HYRIMOZ is indicated for reducing signs and symptoms, inhibiting the progression of structural damage, and improving physical function in adult patients with active psoriatic arthritis. HYRIMOZ can be used alone or in combination with non-biologic DMARDs.
1.4 Ankylosing Spondylitis
HYRIMOZ is indicated for reducing signs and symptoms in adult patients with active ankylosing spondylitis.
1.5 Crohn’s Disease
HYRIMOZ is indicated for the treatment of moderately to severely active Crohn’s disease in adults and pediatric patients 6 years of age and older.
1.6 Ulcerative Colitis
HYRIMOZ is indicated for the treatment of moderately to severely active ulcerative colitis in adult patients.
Limitations of Use:
The effectiveness of adalimumab products has not been established in patients who have lost response to or were intolerant to TNF-blockers [see Clinical Studies (14.7)].
1.7 Plaque Psoriasis
HYRIMOZ is indicated for the treatment of adult patients with moderate to severe chronic plaque psoriasis who are candidates for systemic therapy or phototherapy, and when other systemic therapies are medically less appropriate. HYRIMOZ should only be administered to patients who will be closely monitored and have regular follow-up visits with a physician [see Warnings and Precautions (5)].
1.8 Hidradenitis Suppurativa
HYRIMOZ is indicated for the treatment of moderate to severe hidradenitis suppurativa in adult patients.
1.9 Uveitis
HYRIMOZ is indicated for the treatment of non-infectious intermediate, posterior, and panuveitis in adult patients.
HYRIMOZ is a tumor necrosis factor (TNF)-blocker indicated for:
•
**Rheumatoid Arthritis (RA)****(1.1)****:** reducing signs and symptoms, inducing major clinical response, inhibiting the progression of structural damage, and improving physical function in adult patients with moderately to severely active RA.
•
**Juvenile Idiopathic Arthritis (JIA)****(1.2)****:** reducing signs and symptoms of moderately to severely active polyarticular JIA in patients 2 years of age and older.
•
**Psoriatic Arthritis (PsA)****(1.3)****:** reducing signs and symptoms, inhibiting the progression of structural damage, and improving physical function in adult patients with active PsA.
•
**Ankylosing Spondylitis (AS)****(1.4)****:** reducing signs and symptoms in adult patients with active AS.
•
**Crohn’s Disease (CD)****(1.5)****:** treatment of moderately to severely active Crohn’s disease in adults and pediatric patients 6 years of age and older.
•
**Ulcerative Colitis (UC) (****1.6****):** treatment of moderately to severely active ulcerative colitis in adult patients.
Limitations of Use: Effectiveness has not been established in patients who have lost response to or were intolerant to TNF blockers.
•
**Plaque Psoriasis (Ps) (****1.7****):** treatment of adult patients with moderate to severe chronic plaque psoriasis who are candidates for systemic therapy or phototherapy, and when other systemic therapies are medically less appropriate.
•
**Hidradenitis Suppurativa (HS) (****1.8****)**: treatment of moderate to severe hidradenitis suppurativa in adult patients.
•
**Uveitis (UV) (****1.9****)**: treatment of non-infectious intermediate, posterior, and panuveitis in adult patients.
WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS SECTION
5 WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS
5.1 Serious Infections
Patients treated with adalimumab products, including HYRIMOZ, are at increased risk for developing serious infections involving various organ systems and sites that may lead to hospitalization or death. Opportunistic infections due to bacterial, mycobacterial, invasive fungal, viral, parasitic, or other opportunistic pathogens including aspergillosis, blastomycosis, candidiasis, coccidioidomycosis, histoplasmosis, legionellosis, listeriosis, pneumocystosis and tuberculosis have been reported with TNF blockers. Patients have frequently presented with disseminated rather than localized disease.
The concomitant use of a TNF blocker and abatacept or anakinra was associated with a higher risk of serious infections in patients with rheumatoid arthritis (RA); therefore, the concomitant use of HYRIMOZ and these biologic products is not recommended in the treatment of patients with RA [see Warnings and Precautions (5.7, 5.11) and Drug Interactions (7.2)].
Treatment with HYRIMOZ should not be initiated in patients with an active infection, including localized infections. Patients 65 years of age and older, patients with co-morbid conditions and/or patients taking concomitant immunosuppressants (such as corticosteroids or methotrexate), may be at greater risk of infection. Consider the risks and benefits of treatment prior to initiating therapy in patients:
•
with chronic or recurrent infection;
•
who have been exposed to tuberculosis;
•
with a history of an opportunistic infection;
•
who have resided or traveled in areas of endemic tuberculosis or endemic mycoses, such as histoplasmosis, coccidioidomycosis, or blastomycosis; or
•
with underlying conditions that may predispose them to infection.
Tuberculosis
Cases of reactivation of tuberculosis and new onset tuberculosis infections have been reported in patients receiving adalimumab products, including patients who have previously received treatment for latent or active tuberculosis. Reports included cases of pulmonary and extrapulmonary (i.e., disseminated) tuberculosis. Evaluate patients for tuberculosis risk factors and test for latent infection prior to initiating HYRIMOZ and periodically during therapy.
Treatment of latent tuberculosis infection prior to therapy with TNF blocking agents has been shown to reduce the risk of tuberculosis reactivation during therapy. Prior to initiating HYRIMOZ, assess if treatment for latent tuberculosis is needed; and consider an induration of ≥ 5 mm a positive tuberculin skin test result, even for patients previously vaccinated with Bacille Calmette-Guerin (BCG).
Consider anti-tuberculosis therapy prior to initiation of HYRIMOZ in patients with a past history of latent or active tuberculosis in whom an adequate course of treatment cannot be confirmed, and for patients with a negative test for latent tuberculosis but having risk factors for tuberculosis infection. Despite prophylactic treatment for tuberculosis, cases of reactivated tuberculosis have occurred in patients treated with adalimumab products. Consultation with a physician with expertise in the treatment of tuberculosis is recommended to aid in the decision whether initiating anti-tuberculosis therapy is appropriate for an individual patient.
Strongly consider tuberculosis in the differential diagnosis in patients who develop a new infection during HYRIMOZ treatment, especially in patients who have previously or recently traveled to countries with a high prevalence of tuberculosis, or who have had close contact with a person with active tuberculosis.
Monitoring
Closely monitor patients for the development of signs and symptoms of infection during and after treatment with HYRIMOZ, including the development of tuberculosis in patients who tested negative for latent tuberculosis infection prior to initiating therapy. Tests for latent tuberculosis infection may also be falsely negative while on therapy with HYRIMOZ.
Discontinue HYRIMOZ if a patient develops a serious infection or sepsis. For a patient who develops a new infection during treatment with HYRIMOZ, closely monitor them, perform a prompt and complete diagnostic workup appropriate for an immunocompromised patient, and initiate appropriate antimicrobial therapy.
Invasive Fungal Infections
If patients develop a serious systemic illness and they reside or travel in regions where mycoses are endemic, consider invasive fungal infection in the differential diagnosis. Antigen and antibody testing for histoplasmosis may be negative in some patients with active infection. Consider appropriate empiric antifungal therapy, taking into account both the risk for severe fungal infection and the risks of antifungal therapy, while a diagnostic workup is being performed. To aid in the management of such patients, consider consultation with a physician with expertise in the diagnosis and treatment of invasive fungal infections.
5.2 Malignancies
Consider the risks and benefits of TNF-blocker treatment including HYRIMOZ prior to initiating therapy in patients with a known malignancy other than a successfully treated non-melanoma skin cancer (NMSC) or when considering continuing a TNF-blocker in patients who develop a malignancy.
Malignancies in Adults
In the controlled portions of clinical trials of some TNF-blockers, including adalimumab products, more cases of malignancies have been observed among TNF- blocker-treated adult patients compared to control-treated adult patients. During the controlled portions of 39 global adalimumab clinical trials in adult patients with rheumatoid arthritis (RA), psoriatic arthritis (PsA), ankylosing spondylitis (AS), Crohn’s disease (CD), ulcerative colitis (UC), plaque psoriasis (Ps), hidradenitis suppurativa (HS) and uveitis (UV), malignancies, other than non-melanoma (basal cell and squamous cell) skin cancer, were observed at a rate (95% confidence interval) of 0.7 (0.48, 1.03) per 100 patient-years among 7973 adalimumab-treated patients versus a rate of 0.7 (0.41, 1.17) per 100 patient-years among 4848 control-treated patients (median duration of treatment of 4 months for adalimumab-treated patients and 4 months for control-treated patients). In 52 global controlled and uncontrolled clinical trials of adalimumab in adult patients with RA, PsA, AS, CD, UC, Ps, HS and UV, the most frequently observed malignancies, other than lymphoma and NMSC, were breast, colon, prostate, lung, and melanoma. The malignancies in adalimumab-treated patients in the controlled and uncontrolled portions of the studies were similar in type and number to what would be expected in the general U.S. population according to the SEER database (adjusted for age, gender, and race).1
In controlled trials of other TNF blockers in adult patients at higher risk for malignancies (i.e., patients with COPD with a significant smoking history and cyclophosphamide-treated patients with Wegener’s granulomatosis), a greater portion of malignancies occurred in the TNF blocker group compared to the control group.
Non-Melanoma Skin Cancer
During the controlled portions of 39 global adalimumab clinical trials in adult patients with RA, PsA, AS, CD, UC, Ps, HS and UV, the rate (95% confidence interval) of NMSC was 0.8 (0.52, 1.09) per 100 patient-years among adalimumab-treated patients and 0.2 (0.10, 0.59) per 100 patient-years among control-treated patients. Examine all patients, and in particular patients with a medical history of prior prolonged immunosuppressant therapy or psoriasis patients with a history of PUVA treatment for the presence of NMSC prior to and during treatment with HYRIMOZ.
Lymphoma and Leukemia
In the controlled portions of clinical trials of all the TNF-blockers in adults, more cases of lymphoma have been observed among TNF-blocker-treated patients compared to control-treated patients. In the controlled portions of 39 global adalimumab clinical trials in adult patients with RA, PsA, AS, CD, UC, Ps, HS and UV, 2 lymphomas occurred among 7973 adalimumab-treated patients versus 1 among 4848 control-treated patients. In 52 global controlled and uncontrolled clinical trials of adalimumab in adult patients with RA, PsA, AS, CD, UC, Ps, HS and UV with a median duration of approximately 0.7 years, including 24,605 patients and over 40,215 patient-years of adalimumab, the observed rate of lymphomas was approximately 0.11 per 100 patient-years. This is approximately 3-fold higher than expected in the general U.S. population according to the SEER database (adjusted for age, gender, and race).1 Rates of lymphoma in clinical trials of adalimumab cannot be compared to rates of lymphoma in clinical trials of other TNF blockers and may not predict the rates observed in a broader patient population. Patients with RA and other chronic inflammatory diseases, particularly those with highly active disease and/or chronic exposure to immunosuppressant therapies, may be at a higher risk (up to several fold) than the general population for the development of lymphoma, even in the absence of TNF blockers. Post-marketing cases of acute and chronic leukemia have been reported in association with TNF-blocker use in RA and other indications. Even in the absence of TNF-blocker therapy, patients with RA may be at a higher risk (approximately 2-fold) than the general population for the development of leukemia.
Malignancies in Pediatric Patients and Young Adults
Malignancies, some fatal, have been reported among children, adolescents, and young adults who received treatment with TNF-blockers (initiation of therapy ≤ 18 years of age), of which HYRIMOZ is a member. Approximately half the cases were lymphomas, including Hodgkin's and non-Hodgkin's lymphoma. The other cases represented a variety of different malignancies and included rare malignancies usually associated with immunosuppression and malignancies that are not usually observed in children and adolescents. The malignancies occurred after a median of 30 months of therapy (range 1 to 84 months). Most of the patients were receiving concomitant immunosuppressants. These cases were reported post-marketing and are derived from a variety of sources including registries and spontaneous postmarketing reports.
Postmarketing cases of hepatosplenic T-cell lymphoma (HSTCL), a rare type of T-cell lymphoma, have been reported in patients treated with TNF blockers including adalimumab products. These cases have had a very aggressive disease course and have been fatal. The majority of reported TNF blocker cases have occurred in patients with Crohn's disease or ulcerative colitis and the majority were in adolescent and young adult males. Almost all of these patients had received treatment with the immunosuppressants azathioprine or 6-mercaptopurine (6–MP) concomitantly with a TNF blocker at or prior to diagnosis. It is uncertain whether the occurrence of HSTCL is related to use of a TNF blocker or a TNF blocker in combination with these other immunosuppressants. The potential risk with the combination of azathioprine or 6-mercaptopurine and HYRIMOZ should be carefully considered.
5.3 Hypersensitivity Reactions
Anaphylaxis and angioneurotic edema have been reported following administration of adalimumab products. If an anaphylactic or other serious allergic reaction occurs, immediately discontinue administration of HYRIMOZ and institute appropriate therapy. In clinical trials of adalimumab, hypersensitivity reactions (e.g., rash, anaphylactoid reaction, fixed drug reaction, non-specified drug reaction, urticaria) have been observed.
5.4 Hepatitis B Virus Reactivation
Use of TNF blockers, including HYRIMOZ, may increase the risk of reactivation of hepatitis B virus (HBV) in patients who are chronic carriers of this virus. In some instances, HBV reactivation occurring in conjunction with TNF blocker therapy has been fatal. The majority of these reports have occurred in patients concomitantly receiving other medications that suppress the immune system, which may also contribute to HBV reactivation. Evaluate patients at risk for HBV infection for prior evidence of HBV infection before initiating TNF blocker therapy. Exercise caution in prescribing TNF blockers for patients identified as carriers of HBV. Adequate data are not available on the safety or efficacy of treating patients who are carriers of HBV with anti-viral therapy in conjunction with TNF blocker therapy to prevent HBV reactivation. For patients who are carriers of HBV and require treatment with TNF blockers, closely monitor such patients for clinical and laboratory signs of active HBV infection throughout therapy and for several months following termination of therapy. In patients who develop HBV reactivation, stop HYRIMOZ and initiate effective anti-viral therapy with appropriate supportive treatment. The safety of resuming TNF blocker therapy after HBV reactivation is controlled is not known. Therefore, exercise caution when considering resumption of HYRIMOZ therapy in this situation and monitor patients closely.
5.5 Neurologic Reactions
Use of TNF blocking agents, including adalimumab products, has been associated with rare cases of new onset or exacerbation of clinical symptoms and/or radiographic evidence of central nervous system demyelinating disease, including multiple sclerosis (MS) and optic neuritis, and peripheral demyelinating disease, including Guillain-Barré syndrome. Exercise caution in considering the use of HYRIMOZ in patients with preexisting or recent-onset central or peripheral nervous system demyelinating disorders; discontinuation of HYRIMOZ should be considered if any of these disorders develop. There is a known association between intermediate uveitis and central demyelinating disorders.
5.6 Hematological Reactions
Rare reports of pancytopenia including aplastic anemia have been reported with TNF blocking agents. Adverse reactions of the hematologic system, including medically significant cytopenia (e.g., thrombocytopenia, leukopenia) have been infrequently reported with adalimumab products. The causal relationship of these reports to adalimumab products remains unclear. Advise all patients to seek immediate medical attention if they develop signs and symptoms suggestive of blood dyscrasias or infection (e.g., persistent fever, bruising, bleeding, pallor) while on HYRIMOZ. Consider discontinuation of HYRIMOZ therapy in patients with confirmed significant hematologic abnormalities.
5.7 Increased Risk of Infection When Used with Anakinra
Concurrent use of anakinra (an interleukin-1 antagonist) and another TNF- blocker, was associated with a greater proportion of serious infections and neutropenia and no added benefit compared with the TNF-blocker alone in patients with RA. Therefore, the combination of HYRIMOZ and anakinra is not recommended [see Drug Interactions (7.2)].
5.8 Heart Failure
Cases of worsening congestive heart failure (CHF) and new onset CHF have been reported with TNF blockers. Cases of worsening CHF have also been observed with adalimumab products. Adalimumab products have not been formally studied in patients with CHF; however, in clinical trials of another TNF blocker, a higher rate of serious CHF-related adverse reactions was observed. Exercise caution when using HYRIMOZ in patients who have heart failure and monitor them carefully.
5.9 Autoimmunity
Treatment with adalimumab products may result in the formation of autoantibodies and, rarely, in the development of a lupus-like syndrome. If a patient develops symptoms suggestive of a lupus-like syndrome following treatment with HYRIMOZ, discontinue treatment [see Adverse Reactions (6.1)].
5.10 Immunizations
In a placebo-controlled clinical trial of patients with RA, no difference was detected in anti-pneumococcal antibody response between adalimumab and placebo treatment groups when the pneumococcal polysaccharide vaccine and influenza vaccine were administered concurrently with adalimumab. Similar proportions of patients developed protective levels of anti-influenza antibodies between adalimumab and placebo treatment groups; however, titers in aggregate to influenza antigens were moderately lower in patients receiving adalimumab. The clinical significance of this is unknown. Patients on HYRIMOZ may receive concurrent vaccinations, except for live vaccines. No data are available on the secondary transmission of infection by live vaccines in patients receiving adalimumab products.
It is recommended that pediatric patients, if possible, be brought up to date with all immunizations in agreement with current immunization guidelines prior to initiating HYRIMOZ therapy. Patients on HYRIMOZ may receive concurrent vaccinations, except for live vaccines.
The safety of administering live or live-attenuated vaccines in infants exposed to adalimumab products in utero is unknown. Risks and benefits should be considered prior to vaccinating (live or live-attenuated) exposed infants [see Use in Specific Populations (8.1, 8.4)].
5.11 Increased Risk of Infection When Used with Abatacept
In controlled trials, the concurrent administration of TNF-blockers and abatacept was associated with a greater proportion of serious infections than the use of a TNF-blocker alone; the combination therapy, compared to the use of a TNF-blocker alone, has not demonstrated improved clinical benefit in the treatment of RA. Therefore, the combination of abatacept with TNF-blockers including HYRIMOZ is not recommended [see Drug Interactions (7.2)].
•
Serious infections: Do not start HYRIMOZ during an active infection. If an infection develops, monitor carefully, and stop HYRIMOZ if infection becomes serious (5.1)
•
Invasive fungal infections: For patients who develop a systemic illness on HYRIMOZ, consider empiric antifungal therapy for those who reside or travel to regions where mycoses are endemic (5.1)
•
Malignancies: Incidence of malignancies was greater in adalimumab-treated patients than in controls (5.2)
•
Anaphylaxis or serious hypersensitivity reactions may occur (5.3)
•
Hepatitis B virus reactivation: Monitor HBV carriers during and several months after therapy. If reactivation occurs, stop HYRIMOZ and begin anti-viral therapy (5.4)
•
Demyelinating disease: Exacerbation or new onset, may occur (5.5)
•
Cytopenias, pancytopenia: Advise patients to seek immediate medical attention if symptoms develop, and consider stopping HYRIMOZ (5.6)
•
Heart failure: Worsening or new onset, may occur (5.8)
•
Lupus-like syndrome: Stop HYRIMOZ if syndrome develops (5.9)
DRUG INTERACTIONS SECTION
7 DRUG INTERACTIONS
7.1 Methotrexate
Adalimumab has been studied in rheumatoid arthritis (RA) patients taking concomitant methotrexate (MTX). Although MTX reduced the apparent adalimumab clearance, the data do not suggest the need for dose adjustment of either HYRIMOZ or MTX [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)].
7.2 Biological Products
In clinical studies in patients with RA, an increased risk of serious infections has been observed with the combination of TNF-blockers with anakinra or abatacept, with no added benefit; therefore, use of HYRIMOZ with abatacept or anakinra is not recommended in patients with RA [see Warnings and Precautions (5.7, 5.11)]. A higher rate of serious infections has also been observed in patients with RA treated with rituximab who received subsequent treatment with a TNF-blocker. There is insufficient information regarding the concomitant use of HYRIMOZ and other biologic products for the treatment of RA, PsA, AS, CD, UC, Ps, HS and UV. Concomitant administration of HYRIMOZ with other biologic DMARDS (e.g., anakinra and abatacept) or other TNF-blockers is not recommended based upon the possible increased risk for infections and other potential pharmacological interactions.
7.3 Live Vaccines
Avoid the use of live vaccines with HYRIMOZ [see Warnings and Precautions (5.10)].
7.4 Cytochrome P450 Substrates
The formation of CYP450 enzymes may be suppressed by increased concentrations of cytokines (e.g., TNFα, IL-6) during chronic inflammation. It is possible for products that antagonize cytokine activity, such as adalimumab products, to influence the formation of CYP450 enzymes. Upon initiation or discontinuation of HYRIMOZ in patients being treated with CYP450 substrates with a narrow therapeutic index, monitoring of the effect (e.g., warfarin) or drug concentration (e.g., cyclosporine or theophylline) is recommended and the individual dose of the drug product may be adjusted as needed.
•
Abatacept: Increased risk of serious infection (5.1, 5.11, 7.2)
•
Anakinra: Increased risk of serious infection (5.1, 5.7, 7.2)
•
Live vaccines: Avoid use with HYRIMOZ (5.10, 7.3)
*****Biosimilar means that the biological product is approved based on data demonstrating that it is highly similar to an FDA-approved biological product, known as a reference product, and that there are no clinically meaningful differences between the biosimilar product and the reference product. Biosimilarity of HYRIMOZ has been demonstrated for the condition(s) of use (e.g. indication(s), dosing regimen(s)), strength(s), dosage form(s), and route(s) of administration described in its Full Prescribing Information.
USE IN SPECIFIC POPULATIONS SECTION
8 USE IN SPECIFIC POPULATIONS
8.1 Pregnancy
Risk Summary
Available studies with use of adalimumab during pregnancy do not reliably establish an association between adalimumab and major birth defects. Clinical data are available from the Organization of Teratology Information Specialists (OTIS)/MotherToBaby Pregnancy Registry in pregnant women with rheumatoid arthritis (RA) or Crohn’s disease (CD) treated with adalimumab. Registry results showed a rate of 10% for major birth defects with first trimester use of adalimumab in pregnant women with RA or CD and a rate of 7.5% for major birth defects in the disease-matched comparison cohort. The lack of pattern of major birth defects is reassuring and differences between exposure groups may have impacted the occurrence of birth defects (see Data).
Adalimumab is actively transferred across the placenta during the third trimester of pregnancy and may affect immune response in the in-utero exposed infant (see Clinical Considerations). In an embryo-fetal perinatal development study conducted in cynomolgus monkeys, no fetal harm or malformations were observed with intravenous administration of adalimumab during organogenesis and later in gestation, at doses that produced exposures up to approximately 373 times the maximum recommended human dose (MRHD) of 40 mg subcutaneous without methotrexate (see Data).
The estimated background risk of major birth defects and miscarriage for the indicated populations is unknown. All pregnancies have a background risk of birth defect, loss, or other adverse outcomes. In the U.S. general population, the estimated background risk of major birth defects and miscarriage in clinically recognized pregnancies is 2-4% and 15-20%, respectively.
Clinical Considerations
Disease-associated maternal and embryo/fetal risk
Published data suggest that the risk of adverse pregnancy outcomes in women with RA or inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) is associated with increased disease activity. Adverse pregnancy outcomes include preterm delivery (before 37 weeks of gestation), low birth weight (less than 2500 g) infants, and small for gestational age at birth.
Fetal/Neonatal Adverse Reactions
Monoclonal antibodies are increasingly transported across the placenta as pregnancy progresses, with the largest amount transferred during the third trimester (see Data). Risks and benefits should be considered prior to administering live or live-attenuated vaccines to infants exposed to adalimumab products in utero [see Use in Specific Populations (8.4)].
Data
Human Data
A prospective cohort pregnancy exposure registry conducted by OTIS/MotherToBaby in the U.S. and Canada between 2004 and 2016 compared the risk of major birth defects in live-born infants of 221 women (69 RA, 152 CD) treated with adalimumab during the first trimester and 106 women (74 RA, 32 CD) not treated with adalimumab.
The proportion of major birth defects among live-born infants in the adalimumab-treated and untreated cohorts was 10% (8.7% RA, 10.5% CD) and 7.5% (6.8% RA, 9.4% CD), respectively. The lack of pattern of major birth defects is reassuring and differences between exposure groups may have impacted the occurrence of birth defects. This study cannot reliably establish whether there is an association between adalimumab and major birth defects because of methodological limitations of the registry, including small sample size, the voluntary nature of the study, and the non-randomized design.
In an independent clinical study conducted in ten pregnant women with IBD treated with adalimumab, adalimumab concentrations were measured in maternal serum as well as in cord blood (n=10) and infant serum (n=8) on the day of birth. The last dose of adalimumab was given between 1 and 56 days prior to delivery. Adalimumab concentrations were 0.16 to 19.7 mcg/mL in cord blood, 4.28 to 17.7 mcg/mL in infant serum, and 0 to 16.1 mcg/mL in maternal serum. In all but 1 case, the cord blood concentration of adalimumab was higher than the maternal serum concentration, suggesting adalimumab actively crosses the placenta. In addition, one infant had serum concentrations at each of the following: 6 weeks (1.94 mcg/mL), 7 weeks (1.31 mcg/mL), 8 weeks (0.93 mcg/mL), and 11 weeks (0.53 mcg/mL), suggesting adalimumab can be detected in the serum of infants exposed in utero for at least 3 months from birth.
Animal Data
In an embryo-fetal perinatal development study, pregnant cynomolgus monkeys received adalimumab from gestation days 20 to 97 at doses that produced exposures up to 373 times that achieved with the MRHD without methotrexate (on an AUC basis with maternal IV doses up to 100 mg/kg/week). Adalimumab did not elicit harm to the fetuses or malformations.
8.2 Lactation
Risk Summary
Limited data from case reports in the published literature describe the presence of adalimumab in human milk at infant doses of 0.1% to 1% of the maternal serum concentration. Published data suggest that the systemic exposure to a breastfed infant is expected to be low because adalimumab is a large molecule and is degraded in the gastrointestinal tract. However, the effects of local exposure in the gastrointestinal tract are unknown. There are no reports of adverse effects of adalimumab products on the breastfed infant and no effects on milk production. The developmental and health benefits of breastfeeding should be considered along with the mother’s clinical need for HYRIMOZ and any potential adverse effects on the breastfed child from HYRIMOZ or from the underlying maternal condition.
8.4 Pediatric Use
The safety and effectiveness of HYRIMOZ have been established for:
•
reducing signs and symptoms of moderately to severely active polyarticular JIA in pediatric patients 2 years of age and older.
•
the treatment of moderately to severely active Crohn’s Disease in pediatric patients 6 years of age and older.
Pediatric assessments for HYRIMOZ demonstrate that HYRIMOZ is safe and effective for pediatric patients in indications for which HUMIRA (adalimumab) is approved. However, HYRIMOZ is not approved for such indications due to marketing exclusivity for HUMIRA (adalimumab).
Due to their inhibition of TNFα, adalimumab products administered during pregnancy could affect immune response in the in utero-exposed newborn and infant. Data from eight infants exposed to adalimumab in utero suggest adalimumab crosses the placenta [see Use in Specific Populations (8.1)]. The clinical significance of elevated adalimumab concentrations in infants is unknown. The safety of administering live or live-attenuated vaccines in exposed infants is unknown. Risks and benefits should be considered prior to vaccinating (live or live-attenuated) exposed infants.
Post-marketing cases of lymphoma, including hepatosplenic T-cell lymphoma and other malignancies, some fatal, have been reported among children, adolescents, and young adults who received treatment with TNF-blockers including adalimumab products [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2)].
Juvenile Idiopathic Arthritis
In Study JIA-I, adalimumab was shown to reduce signs and symptoms of active polyarticular JIA in patients 4 to 17 years of age [see Clinical Studies (14.2)]. In Study JIA-II, the safety profile for patients 2 to <4 years of age was similar to the safety profile for patients 4 to 17 years of age with polyarticular JIA [see Adverse Reactions (6.1)]. Adalimumab products have not been studied in patients with polyarticular JIA less than 2 years of age or in patients with a weight below 10 kg.
The safety of adalimumab in patients in the polyarticular JIA trials was generally similar to that observed in adults with certain exceptions [see Adverse Reactions (6.1)].
The safety and effectiveness of HYRIMOZ have not been established in pediatric patients with JIA less than 2 years of age.
Pediatric Crohn’s Disease
The safety and effectiveness of HYRIMOZ for the treatment of moderately to severely active Crohn’s disease have been established in pediatric patients 6 years of age and older. Use of HYRIMOZ for this indication is supported by evidence from adequate and well-controlled studies in adults with additional data from a randomized, double-blind, 52-week clinical study of two dose concentrations of adalimumab in 192 pediatric patients (6 years to 17 years of age) [see Adverse Reactions (6.1), Clinical Pharmacology (12.2, 12.3), Clinical Studies (14.6)]. The adverse reaction profile in patients 6 years to 17 years of age was similar to adults.
The safety and effectiveness of HYRIMOZ have not been established in pediatric patients with Crohn’s disease less than 6 years of age.
8.5 Geriatric Use
A total of 519 RA patients 65 years of age and older, including 107 patients 75 years of age and older, received adalimumab in clinical studies RA-I through IV. No overall difference in effectiveness was observed between these patients and younger patients. The frequency of serious infection and malignancy among adalimumab treated patients 65 years of age and older was higher than for those less than 65 years of age. Consider the benefits and risks of HYRIMOZ in patients 65 years of age and older. In patients treated with HYRIMOZ, closely monitor for the development of infection or malignancy [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1, 5.2)].
DESCRIPTION SECTION
11 DESCRIPTION
Adalimumab-adaz is a tumor necrosis factor blocker. Adalimumab-adaz is a recombinant human IgG1 monoclonal antibody with human derived heavy and light chain variable regions and human IgG1:k constant regions. Adalimumab-adaz is produced by recombinant DNA technology in a Chinese hamster ovary cell expression system and is purified by a process that includes specific viral inactivation and removal steps. It consists of 1330 amino acids and has a molecular weight of approximately 148 kilodaltons.
HYRIMOZ (adalimumab-adaz) injection is supplied as a sterile, preservative- free solution for subcutaneous administration. The drug product is supplied as either a single-dose, prefilled pen (Sensoready Pen), as a single-dose, prefilled 1 mL glass syringe with needle guard and add-on finger flange or as a single-dose, prefilled 1 mL glass syringe. Enclosed within the Pen is a single-dose, 1 mL prefilled glass syringe. The solution of HYRIMOZ is clear, colorless or slightly yellowish, with a pH of about 5.2.
Each 80 mg/0.8 mL prefilled Sensoready Pen or prefilled syringe with BD UltraSafe PassiveTM Needle Guard delivers 0.8 mL (80 mg) of drug product. Each 0.8 mL of HYRIMOZ contains adalimumab-adaz (80 mg), adipic acid (1.75 mg), mannitol (33.6 mg), polysorbate 80 (0.32 mg), and Water for Injection, USP. Hydrochloric acid and sodium hydroxide are added as necessary to adjust pH.
Each 40 mg/0.4 mL prefilled Sensoready Pen or prefilled syringe with BD UltraSafe PassiveTM Needle Guard delivers 0.4 mL (40 mg) of drug product. Each 0.4 mL of HYRIMOZ contains adalimumab-adaz (40 mg), adipic acid (0.88 mg), mannitol (16.8 mg), polysorbate 80 (0.16 mg) and Water for Injection, USP. Hydrochloric acid and sodium hydroxide are added as necessary to adjust pH.
Each 40 mg/0.8 mL prefilled Sensoready Pen or prefilled syringe with BD UltraSafe PassiveTM Needle Guard delivers 0.8 mL (40 mg) of drug product. Each 0.8 mL of HYRIMOZ contains adalimumab-adaz (40 mg), adipic acid (2.69 mg), citric acid monohydrate (0.206 mg), mannitol (9.6 mg), polysorbate 80 (0.8 mg), sodium chloride (4.93 mg), and Water for Injection, USP. Hydrochloric acid and sodium hydroxide are added as necessary to adjust pH.
Each 20 mg/0.4 mL prefilled syringe with BD UltraSafe PassiveTM Needle Guard delivers 0.4 mL (20 mg) of drug product. Each 0.4 mL of HYRIMOZ contains adalimumab-adaz (20 mg), adipic acid (1.34 mg), citric acid monohydrate (0.103 mg), mannitol (4.8 mg), polysorbate 80 (0.4 mg), sodium chloride (2.46 mg), and Water for Injection, USP. Hydrochloric acid and sodium hydroxide are added as necessary to adjust pH.
Each 20 mg/0.2 mL prefilled syringe delivers 0.2 mL (20 mg) of drug product. Each 0.2 mL of HYRIMOZ contains adalimumab-adaz (20 mg), adipic acid (0.44 mg), mannitol (8.4 mg), polysorbate 80 (0.08 mg) and Water for Injection, USP. Hydrochloric acid and sodium hydroxide are added as necessary to adjust pH.
Each 10 mg/0.1 mL prefilled syringe delivers 0.1 mL (10 mg) of drug product. Each 0.1 mL of HYRIMOZ contains adalimumab-adaz (10 mg), adipic acid (0.22 mg), mannitol (4.2 mg), polysorbate 80 (0.04 mg) and Water for Injection, USP. Hydrochloric acid and sodium hydroxide are added as necessary to adjust pH.
Each 10 mg/0.2 mL prefilled syringe delivers 0.2 mL (10 mg) of drug product. Each 0.2 mL of HYRIMOZ contains adalimumab-adaz (10 mg), adipic acid (0.67 mg), citric acid monohydrate (0.051 mg), mannitol (2.4 mg), polysorbate 80 (0.2 mg), sodium chloride (1.23 mg), and Water for Injection, USP. Hydrochloric acid and sodium hydroxide are added as necessary to adjust pH.
HOW SUPPLIED SECTION
16 HOW SUPPLIED/STORAGE AND HANDLING
HYRIMOZ single-dose prefilled Sensoready Pen, HYRIMOZ single-dose prefilled syringe with BD UltraSafe Passive™ Needle Guard and add-on finger flange and HYRIMOZ single-dose prefilled syringe.
HYRIMOZ (adalimumab-adaz) injection is supplied as a preservative-free, sterile, clear and colorless or slightly yellowish solution for subcutaneous administration. The following packaging configurations are available.
|
80 mg/0.8 mL single-dose prefilled Sensoready Pen with a fixed 29 gauge, ½ inch needle |
Carton of 2 |
NDC 83457-107-01 |
|
80 mg/0.8 mL single-dose prefilled Sensoready Pen with a fixed 29 gauge, ½ inch needle |
Crohn’s disease and Ulcerative colitis or Hidradenitis Suppurativa Starter Package Carton of 3 |
NDC 83457-113-01 |
|
80 mg/0.8 mL and 40 mg/0.4 mL single-dose prefilled Sensoready Pens with fixed 29 gauge, ½ inch needle each |
Plaque Psoriasis or Uveitis Starter Package Carton of 3 (1x 80 mg/0.8 mL, 2x 40 mg/0.4 mL) |
NDC 83457-112-01 |
|
80 mg/0.8 mL and 40 mg/0.4 mL single-dose prefilled Sensoready Pens with fixed 29 gauge, ½ inch needle each |
Crohn’s Disease, Ulcerative Colitis or Hidradenitis Suppurativa Starter Package Carton of 4 (3x 80 mg/0.8 mL, 1x 40 mg/0.4 mL) |
NDC 83457-116-01 |
|
80 mg/0.8 mL single-dose prefilled syringe with a fixed 29 gauge, ½ inch needle and with BD UltraSafe Passive™ Needle Guard |
Carton of 2 |
NDC 83457-106-01 |
|
80 mg/0.8 mL single-dose prefilled syringe with a fixed 29 gauge, ½ inch needle and with BD UltraSafe Passive™ Needle Guard |
Starter Pack for Pediatric Crohn’s Disease Carton of 3 |
NDC 83457-115-01 |
|
80 mg/0.8 mL and 40 mg/0.4 mL single-dose prefilled syringe with a fixed 29 gauge, ½ inch needle and with BD UltraSafe Passive™ Needle Guard |
Starter Pack for Pediatric Crohn’s Disease Carton of 2 |
NDC 83457-114-01 |
|
40 mg/0.4 mL single-dose prefilled syringe with a fixed 29 gauge, ½ inch needle and with BD UltraSafe Passive™ Needle Guard |
Carton of 2 |
NDC 83457-101-01 |
|
40 mg/0.4 mL single-dose prefilled Sensoready Pen with a fixed 29 gauge, ½ inch needle |
Carton of 2 |
NDC 83457-100-01 |
|
40 mg/0.4 mL single-dose prefilled Sensoready Pen with a fixed 29 gauge, ½ inch needle |
Carton of 4 |
NDC 83457-105-01 |
|
40 mg/0.8 mL single-dose prefilled syringe with a fixed 29 gauge, ½ inch needle and with BD UltraSafe Passive™ Needle Guard |
Carton of 2 |
NDC 83457-103-01 |
|
40 mg/0.8 mL single-dose prefilled Sensoready Pen with a fixed 29 gauge, ½ inch needle |
Carton of 2 |
NDC 83457-102-01 |
|
20 mg/0.2 mL single-dose prefilled syringe with a fixed 29 gauge, ½ inch needle |
Carton of 2 |
NDC 83457-108-01 |
|
20 mg/0.4 mL single-dose prefilled syringe with a fixed 29 gauge, ½ inch needle and with BD UltraSafe Passive™ Needle Guard |
Carton of 2 |
NDC 83457-109-01 |
|
10 mg/0.1 mL single-dose prefilled syringe with a fixed 29 gauge, ½ inch needle |
Carton of 2 |
NDC 83457-110-01 |
|
10 mg/0.2 mL single-dose prefilled syringe with a fixed 29 gauge, ½ inch needle |
Carton of 1 |
NDC 83457-111-01 |
Prefilled syringes and injection devices are not made with natural rubber latex.
Storage and Handling
Do not use beyond the expiration date on the container. HYRIMOZ must be refrigerated at 36°F to 46°F (2°C to 8°C). DO NOT FREEZE. Do not use if frozen even if it has been thawed.
Store in original carton until time of administration to protect from light.
Do not store HYRIMOZ in extreme heat or cold.
HYRIMOZ single-dose prefilled syringe with BD UltraSafe Passive™ Needle Guard (20 mg/0.4 mL, 40 mg/0.8 mL) and HYRIMOZ single-dose prefilled Sensoready Pen (40 mg/0.8 mL):
If needed, for example when traveling, HYRIMOZ may be stored at room temperature up to a maximum of 77°F (25°C) for a period of up to 21 days, with protection from light. HYRIMOZ should be discarded if not used within the 21-day period. Record the date when HYRIMOZ is first removed from the refrigerator in the spaces provided on the carton.
HYRIMOZ single-dose prefilled syringe with BD UltraSafe Passive™ Needle Guard (40 mg/0.4 mL, 80 mg/0.8 mL), HYRIMOZ single-dose prefilled Sensoready Pen (40 mg/0.4 mL, 80 mg/0.8 mL) and HYRIMOZ single-dose prefilled syringe (10 mg/0.1 mL, 20 mg/0.2 mL):
If needed, for example when traveling, HYRIMOZ may be stored at room temperature up to a maximum of 77°F (25°C) for a period of up to 14 days, with protection from light. HYRIMOZ should be discarded if not used within the 14-day period. Record the date when HYRIMOZ is first removed from the refrigerator in the spaces provided on the carton.
HYRIMOZ single-dose prefilled syringe – 10 mg/0.2 mL:
If needed, for example when traveling, HYRIMOZ may be stored at room temperature up to a maximum of 77°F (25°C) for a period of up to 21 days, with protection from light. HYRIMOZ should be discarded if not used within the 21-day period. Record the date when HYRIMOZ is first removed from the refrigerator in the spaces provided on the carton.
DOSAGE & ADMINISTRATION SECTION
2 DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
2.1 Rheumatoid Arthritis, Psoriatic Arthritis, and Ankylosing Spondylitis
The recommended subcutaneous dosage of HYRIMOZ for adult patients with rheumatoid arthritis (RA), psoriatic arthritis (PsA), or ankylosing spondylitis (AS) is 40 mg administered every other week. Methotrexate (MTX), other non-biologic DMARDS, glucocorticoids, nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), and/or analgesics may be continued during treatment with HYRIMOZ. In the treatment of RA, some patients not taking concomitant MTX may derive additional benefit from increasing the dosage of HYRIMOZ to 40 mg every week or 80 mg every other week.
2.2 Juvenile Idiopathic Arthritis
The recommended subcutaneous dosage of HYRIMOZ for patients 2 years of age and older with polyarticular juvenile idiopathic arthritis (JIA) is based on weight as shown below. MTX, glucocorticoids, NSAIDs, and/or analgesics may be continued during treatment with HYRIMOZ.
|
Pediatric Weight |
Recommended Dosage |
|
10 kg (22 lbs) to less than 15 kg (33 lbs) |
10 mg every other week |
|
15 kg (33 lbs) to less than 30 kg (66 lbs) |
20 mg every other week |
|
30 kg (66 lbs) and greater |
40 mg every other week |
Adalimumab products have not been studied in patients with polyarticular JIA less than 2 years of age or in patients with a weight below 10 kg.
2.3 Crohn’s Disease
Adults
The recommended subcutaneous dosage of HYRIMOZ for adult patients with Crohn’s disease (CD) is 160 mg initially on Day 1 (given in one day or split over two consecutive days), followed by 80 mg two weeks later (Day 15). Two weeks later (Day 29) begin a dosage of 40 mg every other week. Aminosalicylates and/or corticosteroids may be continued during treatment with HYRIMOZ. Azathioprine, 6-mercaptopurine (6-MP) [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2)] or MTX may be continued during treatment with HYRIMOZ if necessary.
Pediatrics
The recommended subcutaneous dosage of HYRIMOZ for pediatric patients 6 years of age and older with Crohn’s disease (CD) is based on body weight as shown below:
|
Pediatric Weight |
Recommended Dosage | |
|
Days 1 through 15 |
Starting on Day 29 | |
|
17 kg (37 lbs) to less than 40 kg (88 lbs) |
Day 1: 80 mg Day 15: 40 mg |
20 mg every other week |
|
40 kg (88 lbs) and greater |
Day 1: 160 mg (single dose or split over two consecutive days) Day 15: 80 mg |
40 mg every other week |
2.4 Ulcerative Colitis
Adults
The recommended subcutaneous dosage of HYRIMOZ for adult patients with ulcerative colitis is 160 mg initially on Day 1 (given in one day or split over two consecutive days), followed by 80 mg two weeks later (Day 15). Two weeks later (Day 29) continue with a dosage of 40 mg every other week.
Discontinue HYRIMOZ in adult patients without evidence of clinical remission by eight weeks (Day 57) of therapy. Aminosalicylates and/or corticosteroids may be continued during treatment with HYRIMOZ. Azathioprine and 6-mercaptopurine (6-MP) [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2)] may be continued during treatment with HYRIMOZ if necessary.
2.5 Plaque Psoriasis or Adult Uveitis
The recommended subcutaneous dosage of HYRIMOZ for adult patients with plaque psoriasis (Ps) or Uveitis (UV) is an initial dose of 80 mg, followed by 40 mg given every other week starting one week after the initial dose. The use of adalimumab products in moderate to severe chronic Ps beyond one year has not been evaluated in controlled clinical studies.
2.6 Hidradenitis Suppurativa
Adults
The recommended subcutaneous dosage of HYRIMOZ for adult patients with hidradenitis suppurativa (HS) is an initial dose of 160 mg (given in one day or split over two consecutive days), followed by 80 mg two weeks later (Day 15). Begin 40 mg weekly or 80 mg every other week dosing two weeks later (Day 29).
2.7 Monitoring to Assess Safety
Prior to initiating HYRIMOZ and periodically during therapy, evaluate patients for active tuberculosis and test for latent infection [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)].
2.8 General Considerations for Administration
HYRIMOZ is intended for use under the guidance and supervision of a physician. A patient may self-inject HYRIMOZ or a caregiver may inject HYRIMOZ using either the HYRIMOZ single-dose prefilled Sensoready Pen or the HYRIMOZ single- dose prefilled syringe if a physician determines that it is appropriate, and with medical follow-up, as necessary, after proper training in subcutaneous injection technique.
You may leave HYRIMOZ at room temperature for about 15 to 30 minutes before injecting. Do not remove the cap while allowing it to reach room temperature. Carefully inspect the solution in the HYRIMOZ single-dose prefilled Sensoready Pen or HYRIMOZ single-dose prefilled syringe for particulate matter and discoloration prior to subcutaneous administration. The solution should be clear, colorless or slightly yellowish. Do not use a prefilled syringe or prefilled Sensoready Pen if the solution is cloudy, discolored, or has flakes or particles in it. HYRIMOZ does not contain preservatives; therefore, discard unused portions of drug remaining from the syringe.
Instruct patients using the HYRIMOZ single-dose prefilled Sensoready Pen and the HYRIMOZ single-dose prefilled syringe to inject the full amount according to the directions provided in the Instructions for Use [see Instructions for Use].
Injections should occur at separate sites in the thigh or abdomen. Rotate injection sites and do not give injections into areas where the skin is tender, bruised, red or hard.
If a dose is missed, administer the dose as soon as possible. Thereafter, resume dosing at the regular scheduled time.
•
Administer by subcutaneous injection (2)
Rheumatoid Arthritis, Psoriatic Arthritis, Ankylosing Spondylitis (2.1):
•
Adults: 40 mg every other week.
•
Some patients with RA not receiving methotrexate may benefit from increasing the dosage to 40 mg every week or 80 mg every other week.
Juvenile Idiopathic Arthritis**(2.2)****:**
|
Pediatric Weight 2 Years of Age and Older |
Recommended Dosage |
|
10 kg (22 lbs) to less than 15 kg (33 lbs) |
10 mg every other week |
|
15 kg (33 lbs) to less than 30 kg (66 lbs) |
20 mg every other week |
|
30 kg (66 lbs) and greater |
40 mg every other week |
Crohn's Disease**(2.3****):**
•
Adults: 160 mg on Day 1 (given in one day or split over two consecutive days); 80 mg on Day 15; and 40 mg
every other week starting on Day 29.
•
Pediatric Patients 6 Years of Age and Older:
|
Pediatric Weight |
Recommended Dosage | |
|
Days 1 and 15 |
| |
|
17 kg (37 lbs) to less than 40 kg (88 lbs) |
Day 1: 80 mg Day 15: 40 mg |
20 mg every other week |
|
40 kg (88 lbs) and greater |
Day 1: 160 mg (single dose or split over two consecutive days) Day 15: 80 mg |
40 mg every other week |
Ulcerative Colitis**(2.4****):**
•
Adults: 160 mg on Day 1 (given in one day or split over two consecutive days), 80 mg on Day 15 and 40 mg every other week starting on Day 29.
Discontinue in patients without evidence of clinical remission by eight weeks (Day 57).
Plaque Psoriasis or Adult Uveitis (2.5):
•
Adults: 80 mg initial dose, followed by 40 mg every other week starting one week after initial dose.
Hidradenitis Suppurativa (2.6):
•
Adults:
o
Day 1: 160 mg (given in one day or split over two consecutive days)
o
Day 15: 80 mg
o
Day 29 and subsequent doses: 40 mg every week or 80 mg every other week.
