POLIVY
These highlights do not include all the information needed to use POLIVY safely and effectively. See full prescribing information for POLIVY. POLIVY (polatuzumab vedotin-piiq) for injection, for intravenous use Initial U.S. Approval: 2019
20a16ab2-f338-4abb-9dcd-254bd949a2bc
HUMAN PRESCRIPTION DRUG LABEL
Apr 2, 2024
Genentech, Inc.
DUNS: 080129000
Products 2
Detailed information about drug products covered under this FDA approval, including NDC codes, dosage forms, ingredients, and administration routes.
polatuzumab vedotin
Product Details
FDA regulatory identification and product classification information
FDA Identifiers
Product Classification
Product Specifications
INGREDIENTS (5)
polatuzumab vedotin
Product Details
FDA regulatory identification and product classification information
FDA Identifiers
Product Classification
Product Specifications
INGREDIENTS (5)
Drug Labeling Information
PACKAGE LABEL.PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL
PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL - 30 mg Vial Carton
NDC 50242-103-01
Polivy®
(polatuzumab vedotin-piiq)
For Injection
30 mg per vial
For Intravenous Infusion Only.
Reconstitute and Dilute
prior to administration.
Single-Dose Vial.
Discard unused portion.
CAUTION: Hazardous Agent
Rx only
1 vial
Genentech
11008718

INDICATIONS & USAGE SECTION
1 INDICATIONS AND USAGE
1.1 Previously Untreated DLBCL, NOS or HGBL
POLIVY in combination with a rituximab product, cyclophosphamide, doxorubicin, and prednisone (R-CHP) is indicated for the treatment of adult patients who have previously untreated diffuse large B-cell lymphoma (DLBCL), not otherwise specified (NOS) or high-grade B-cell lymphoma (HGBL) and who have an International Prognostic Index score of 2 or greater.
1.2 Relapsed or Refractory DLBCL, NOS
POLIVY in combination with bendamustine and a rituximab product is indicated for the treatment of adult patients with relapsed or refractory DLBCL, NOS, after at least two prior therapies.
POLIVY is a CD79b-directed antibody and microtubule inhibitor conjugate indicated:
- in combination with a rituximab product, cyclophosphamide, doxorubicin, and prednisone (R-CHP) for the treatment of adult patients who have previously untreated diffuse large B-cell lymphoma (DLBCL), not otherwise specified (NOS) or high-grade B-cell lymphoma (HGBL) and who have an International Prognostic Index score of 2 or greater. (1.1)
- in combination with bendamustine and a rituximab product for the treatment of adult patients with relapsed or refractory DLBCL, NOS, after at least two prior therapies. (1.2)
CONTRAINDICATIONS SECTION
4 CONTRAINDICATIONS
None.
None. (4)
ADVERSE REACTIONS SECTION
6 ADVERSE REACTIONS
The following clinically significant adverse reactions are discussed in greater detail in other sections of the label:
- Peripheral Neuropathy [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)]
- Infusion-Related Reactions [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2)]
- Myelosuppression [see Warnings and Precautions (5.3)]
- Serious and Opportunistic Infections [see Warnings and Precautions (5.4)]
- Progressive Multifocal Leukoencephalopathy [see Warnings and Precautions (5.5)]
- Tumor Lysis Syndrome [see Warnings and Precautions (5.6)]
- Hepatotoxicity [see Warnings and Precautions (5.7)]
6.1 Clinical Trials Experience
Because clinical trials are conducted under widely varying conditions, adverse reaction rates observed in the clinical trials of a drug cannot be directly compared with rates in the clinical trials of another drug and may not reflect the rates observed in practice.
The safety data described below reflect exposure to POLIVY 1.8 mg/kg in 480 patients with large B-cell lymphoma (LBCL), including those with previously untreated LBCL (POLARIX) and relapsed or refractory DLBCL (GO29365).
Previously Untreated DLBCL, NOS or HGBL
GO39942 (POLARIX)
The safety of POLIVY in combination with R-CHP chemoimmunotherapy was evaluated in POLARIX, a randomized double-blind, placebo-controlled, multicenter study of 873 patients with previously untreated large B-cell lymphoma, 435 of whom received POLIVY plus R-CHP [see Clinical Studies (14.1)].
Patients were randomized 1:1 to receive POLIVY plus R-CHP or to receive R-CHOP for six 21-day cycles followed by two additional cycles of rituximab alone in both arms. Granulocyte colony-stimulating factor (G-CSF) primary prophylaxis was required and administered to 90% of patients in the POLIVY plus R-CHP arm and 93% of patients in the R-CHOP arm. Following premedication with an antihistamine and antipyretic, POLIVY was administered intravenously at 1.8 mg/kg on Day 1 of Cycles 1–6. R-CHP was administered starting on Day 1 of Cycles 1–6. Rituximab monotherapy was administered on Day 1 of Cycles 7–8 [see Clinical Studies (14.1)].
The trial required an absolute neutrophil count ≥1,000/µL, platelet count ≥75,000/µL, creatinine clearance (CLcr) ≥40 mL/min, hepatic transaminases ≤2.5 times the upper limit of normal (ULN), and bilirubin <1.5 times ULN, unless abnormalities were from the underlying disease. The trial excluded patients having age >80, ECOG performance status above 2, known central nervous system (CNS) lymphoma, and Grade 2 or higher peripheral neuropathy.
The median age was 65 years overall (range: 19 to 80 years); 54% of patients were male; 53% were White, 19% were Asian, 2%, Black or African American, and 5% were Hispanic or Latino.
In the POLIVY plus R-CHP group, 92% of patients received 6 cycles of POLIVY, and 94% completed 6 cycles of combination therapy.
Serious adverse reactions occurred in 34% of patients who received POLIVY plus R-CHP, including febrile neutropenia and pneumonia in ≥5% of recipients. Fatal adverse reactions occurred in 3% of recipients of POLIVY plus R-CHP within 90 days of last treatment, primarily from infection including pneumonia (0.9%) and sepsis (0.2%).
Adverse reactions led to dose reduction of POLIVY in 6% of patients, mainly from peripheral neuropathy. Adverse reactions lead to dose interruption of POLIVY in 18% of patients, most commonly from pneumonia and neutropenia, and permanent discontinuation of POLIVY in 4.4% of patients.
Table 6 summarizes adverse reactions in POLARIX. In recipients of POLIVY plus R-CHP, adverse reactions in ≥20% of patients, excluding laboratory abnormalities, were peripheral neuropathy, nausea, fatigue, diarrhea, constipation, alopecia, and mucositis. New or worsening Grade 3 to 4 laboratory abnormalities in ≥10% of patients were lymphopenia, neutropenia, hyperuricemia, and anemia.
Table 6 Select Adverse Reactions Occurring in ≥10% of Patients Treated with POLIVY Plus R-CHP in POLARIX|
Adverse Reactions by Body System |
POLIVY + R-CHP |
R-CHOP | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
All Grades, |
Grade 3–4, |
All Grades, |
Grade 3–4, | |
|
The table includes a combination of grouped and ungrouped terms. Events were graded using NCI CTCAE version 4.0. | ||||
Þ ß à è ð | ||||
|
Blood and Lymphatic System Disorders* | ||||
|
Lymphopenia |
80 |
44 |
77 |
44 |
|
Anemia |
68 |
14 |
67 |
11 |
|
Neutropenia |
60 |
39 |
60 |
42 |
|
Thrombocytopenia |
32 |
8 |
33 |
6 |
|
Febrile neutropenia† |
15 |
15 |
9 |
9 |
|
Investigations* | ||||
|
Creatinine increased |
66 |
0.7 |
64 |
0.9 |
|
Aspartate aminotransferase increased |
26 |
0.7 |
23 |
1.1 |
|
Alanine aminotransferase increased |
25 |
1.4 |
27 |
0.5 |
|
Alkaline phosphatase increased |
23 |
0 |
22 |
0.5 |
|
Uric acid increased |
19 |
18 |
17 |
16 |
|
Weight decreased |
13 |
0.9 |
12 |
0.2 |
|
Nervous System Disorders | ||||
|
Peripheral neuropathy‡,§ |
53 |
1.6 |
54 |
1.1 |
|
Altered taste |
14 |
0 |
16 |
0 |
|
Headache |
13 |
0.2 |
14 |
0.9 |
|
Gastrointestinal Disorders | ||||
|
Nausea |
42 |
1.1 |
37 |
0.5 |
|
Diarrhea |
31 |
3.9 |
20 |
1.8 |
|
Constipation |
29 |
1.1 |
29 |
0.2 |
|
Mucositis¶ |
22 |
1.4 |
19 |
0.5 |
|
Abdominal pain# |
16 |
1.1 |
14 |
1.6 |
|
Vomiting |
15 |
1.1 |
14 |
0.7 |
|
General Disorders | ||||
|
Fatigue |
37 |
2.5 |
38 |
3.0 |
|
Pyrexia |
16 |
1.4 |
13 |
0 |
|
EdemaÞ |
14 |
0.5 |
11 |
0.2 |
|
Infusion-related reactionß |
13 |
1.1 |
16 |
1.6 |
|
Skin and Subcutaneous Tissue Disorders | ||||
|
Alopecia |
24 |
0 |
24 |
0.2 |
|
Rashà |
13 |
0.7 |
11 |
0 |
|
Musculoskeletal Disorders | ||||
|
Musculoskeletal painè |
19 |
0.5 |
21 |
1.8 |
|
Infections | ||||
|
Upper respiratory tract infectionð |
17 |
0.5 |
16 |
0.5 |
|
Metabolism and Nutrition Disorders | ||||
|
Decreased appetite |
17 |
1.1 |
14 |
0.7 |
|
Respiratory Disorders | ||||
|
Cough |
15 |
0 |
14 |
0 |
|
Dyspnea |
13 |
0.9 |
10 |
0.9 |
Other clinically relevant adverse reactions in <10% of recipients of POLIVY plus R-CHP included:
*Infections: pneumonia, herpesvirus infection, sepsis, cytomegalovirus infection *Metabolic disorders: tumor lysis syndrome *Renal disorders: renal insufficiency *Respiratory disorders: pneumonitis
Relapsed or Refractory DLBCL, NOS
GO29365
The data described in this section reflect exposure to POLIVY in Study GO29365, a multicenter clinical trial for adult patients with relapsed or refractory B-cell lymphomas [see Clinical Studies (14.2)]. In patients with relapsed or refractory DLBCL, the trial included a single-arm safety evaluation of POLIVY in combination with bendamustine and a rituximab product (BR) (n = 6), followed by an open-label randomization to POLIVY in combination with BR versus BR alone (n = 39 treated per arm).
Following premedication with an antihistamine and antipyretic, POLIVY 1.8 mg/kg was administered by intravenous infusion on Day 2 of Cycle 1 and on Day 1 of Cycles 2–6, with a cycle length of 21 days. Bendamustine 90 mg/m2 daily was administered intravenously on Days 2 and 3 of Cycle 1 and on Days 1 and 2 of Cycles 2–6. A rituximab product dosed at 375 mg/m2 was administered intravenously on Day 1 of each cycle. Granulocyte colony-stimulating factor primary prophylaxis was optional and administered to 42% of recipients of POLIVY plus BR.
In POLIVY-treated patients (n = 45), the median age was 67 years (range 33 – 86) with 58% being ≥age 65, 69% were male, 69% were White, and 87% had an Eastern Cooperative Oncology Group (ECOG) performance status of 0 or 1. The trial required an absolute neutrophil count ≥1500/µL, platelet count ≥75/µL, creatinine clearance (CLcr) ≥40 mL/min, hepatic transaminases ≤2.5 times ULN, and bilirubin <1.5 times ULN, unless abnormalities were from the underlying disease. Patients with Grade 2 or higher peripheral neuropathy or prior allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation (HSCT) were excluded.
Patients treated with POLIVY plus BR received a median of 5 cycles, with 49% receiving 6 cycles. Patients treated with BR alone received a median of 3 cycles, with 23% receiving 6 cycles.
Fatal adverse reactions occurred in 7% of recipients of POLIVY plus BR within 90 days of last treatment. Serious adverse reactions occurred in 64%, most often from infection. Serious adverse reactions in ≥5% of recipients of POLIVY plus BR included pneumonia (16%), febrile neutropenia (11%), pyrexia (9%), and sepsis (7%).
In recipients of POLIVY plus BR, adverse reactions led to dose reduction in 18%, dose interruption in 51%, and permanent discontinuation of all treatment in 31%. The most common adverse reactions leading to treatment discontinuation were thrombocytopenia and/or neutropenia.
Table 7 summarizes commonly reported adverse reactions. In recipients of POLIVY plus BR, adverse reactions in ≥20% of patients included neutropenia, thrombocytopenia, anemia, peripheral neuropathy, fatigue, diarrhea, pyrexia, decreased appetite, and pneumonia.
Table 7 Adverse Reactions Occurring in >10% of Patients with Relapsed or Refractory DLBCL and ≥5% More in the POLIVY Plus Bendamustine and Rituximab Product Group in Study GO29365|
Adverse Reactions by Body System |
POLIVY + BR |
BR | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
All Grades, |
Grade 3 or Higher, |
All Grades, |
Grade 3 or Higher, | |
|
The table includes a combination of grouped and ungrouped terms. Events were graded using NCI CTCAE version 4. | ||||
| ||||
|
Blood and Lymphatic System Disorders | ||||
|
Neutropenia |
49 |
42 |
44 |
36 |
|
Thrombocytopenia |
49 |
40 |
33 |
26 |
|
Anemia |
47 |
24 |
28 |
18 |
|
Lymphopenia |
13 |
13 |
8 |
8 |
|
Nervous System Disorders | ||||
|
Peripheral neuropathy |
40 |
0 |
8 |
0 |
|
Dizziness |
13 |
0 |
8 |
0 |
|
Gastrointestinal Disorders | ||||
|
Diarrhea |
38 |
4.4 |
28 |
5 |
|
Vomiting |
18 |
2.2 |
13 |
0 |
|
General Disorders | ||||
|
Infusion-related reaction |
18 |
2.2 |
8 |
0 |
|
Pyrexia |
33 |
2.2 |
23 |
0 |
|
Decreased appetite |
27 |
2.2 |
21 |
0 |
|
Infections | ||||
|
Pneumonia |
22 |
16* |
15 |
2.6† |
|
Upper respiratory tract infection |
13 |
0 |
8 |
0 |
|
Investigations | ||||
|
Weight decreased |
16 |
2.2 |
8 |
2.6 |
|
Metabolism and Nutrition Disorders | ||||
|
Hypokalemia |
16 |
9 |
10 |
2.6 |
|
Hypoalbuminemia |
13 |
2.2 |
8 |
0 |
|
Hypocalcemia |
11 |
2.2 |
5 |
0 |
Other clinically relevant adverse reactions (<10% or with a <5% difference) in recipients of POLIVY plus BR included:
*Blood and lymphatic system disorders: pancytopenia (7%) *Musculoskeletal disorders: arthralgia (7%) *Investigations: hypophosphatemia (9%), transaminase elevation (7%), lipase increased (7%) *Respiratory disorders: pneumonitis (4.4%)
Selected treatment-emergent laboratory abnormalities are summarized in Table 8. In recipients of POLIVY plus BR, >20% of patients developed Grade 3 or 4 neutropenia, leukopenia, or thrombocytopenia, and >10% developed Grade 4 neutropenia (13%) or Grade 4 thrombocytopenia (11%).
Table 8 Select Laboratory Abnormalities Worsening from Baseline in Patients with Relapsed or Refractory DLBCL and ≥5% More in the POLIVY Plus Bendamustine and Rituximab Product Group|
Laboratory Parameter* |
POLIVY + BR |
BR | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
All Grades, |
Grade 3–4, |
All Grades, |
Grade 3–4, | |
| ||||
|
Hematologic | ||||
|
Lymphocyte count decreased |
87 |
87 |
90 |
82 |
|
Neutrophil count decreased |
78 |
61 |
56 |
33 |
|
Hemoglobin decreased |
78 |
18 |
62 |
10 |
|
Platelet count decreased |
76 |
31 |
64 |
26 |
|
Chemistry | ||||
|
Creatinine increased |
87 |
4.4 |
77 |
5 |
|
Calcium decreased |
44 |
9 |
26 |
0 |
|
SGPT/ALT increased |
38 |
0 |
8 |
2.6 |
|
SGOT/AST increased |
36 |
0 |
26 |
2.6 |
|
Lipase increased |
36 |
9 |
13 |
5 |
|
Phosphorus decreased |
33 |
7 |
28 |
8 |
|
Amylase increased |
24 |
0 |
18 |
2.6 |
|
Potassium decreased |
24 |
11 |
28 |
5 |
Safety was also evaluated in 173 adult patients with relapsed or refractory lymphoma who received POLIVY, bendamustine, and either a rituximab product or obinutuzumab in Study GO29365, including the 45 patients with DLBCL described above. In the expanded safety population, the median age was 66 years (range 27 – 86), 57% were male, 91% had an ECOG performance status of 0-1, and 32% had a history of peripheral neuropathy at baseline.
Fatal adverse reactions occurred in 4.6% of recipients of POLIVY within 90 days of last treatment, with infection as a leading cause. Serious adverse reactions occurred in 60%, most often from infection.
Table 9 summarizes the most common adverse reactions in the expanded safety population. The overall safety profile was similar to that described above. Adverse reactions in ≥20% of patients were diarrhea, neutropenia, peripheral neuropathy, fatigue, thrombocytopenia, pyrexia, decreased appetite, anemia, and vomiting. Infection-related adverse reactions in >10% of patients included upper respiratory tract infection, febrile neutropenia, pneumonia, and herpesvirus infection.
Table 9 Most Common Adverse Reactions (≥20% Any Grade or ≥5% Grade 3 or Higher) in Recipients of POLIVY and Chemoimmunotherapy for Relapsed or Refractory Lymphoma|
Adverse Reaction by Body System |
POLIVY + Bendamustine + Rituximab Product or Obinutuzumab | |
|---|---|---|
|
All Grades, |
Grade 3 or Higher, | |
|
The table includes a combination of grouped and ungrouped terms. | ||
| ||
|
Blood and Lymphatic System Disorders | ||
|
Neutropenia |
44 |
39 |
|
Thrombocytopenia |
31 |
23 |
|
Anemia |
28 |
14 |
|
Febrile neutropenia* |
13 |
13 |
|
Leukopenia |
13 |
8 |
|
Lymphopenia |
12 |
12 |
|
Nervous System Disorders | ||
|
Peripheral neuropathy |
40 |
2.3 |
|
Gastrointestinal Disorders | ||
|
Diarrhea |
45 |
8 |
|
Vomiting |
27 |
2.9 |
|
General Disorders | ||
|
Fatigue |
40 |
5 |
|
Pyrexia |
30 |
2.9 |
|
Decreased appetite |
29 |
1.7 |
|
Infections | ||
|
Pneumonia |
13 |
10† |
|
Sepsis |
6 |
6‡ |
|
Metabolism and Nutrition Disorders | ||
|
Hypokalemia |
18 |
6 |
Other clinically relevant adverse reactions (<20% any grade) included:
*General disorders: infusion-related reaction (7%) *Infection: upper respiratory tract infection (16%), lower respiratory tract infection (10%), herpesvirus infection (12%), cytomegalovirus infection (1.2%) *Respiratory: dyspnea (19%), pneumonitis (1.7%) *Nervous system disorders: dizziness (10%) *Investigations: weight decrease (10%), transaminase elevation (8%), lipase increase (3.5%) *Musculoskeletal disorders: arthralgia (7%) *Eye disorders: blurred vision (1.2%)
The most common adverse reactions (≥20%) in patients with large B-cell lymphoma treated with POLIVY in combination with R-CHP, excluding laboratory abnormalities, are peripheral neuropathy, nausea, fatigue, diarrhea, constipation, alopecia, and mucositis. Grade 3 to 4 laboratory abnormalities (≥10%) are lymphopenia, neutropenia, hyperuricemia, and anemia. (6.1)
The most common adverse reaction (≥20%) in patients with relapsed or refractory DLBCL treated with POLIVY in combination with BR are neutropenia, thrombocytopenia, anemia, peripheral neuropathy, fatigue, diarrhea, pyrexia, decreased appetite, and pneumonia. (6.1)
To report SUSPECTED ADVERSE REACTIONS, contact Genentech at 1-888-835-2555 or FDA at 1-800-FDA-1088 or www.fda.gov/medwatch.
DRUG INTERACTIONS SECTION
7 DRUG INTERACTIONS
7.1 Effects of Other Drugs on POLIVY
Strong CYP3A Inhibitors
Concomitant use with a strong CYP3A4 inhibitor may increase unconjugated MMAE AUC [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)], which may increase POLIVY toxicities. Monitor patients for signs of toxicity.
Strong CYP3A Inducers
Concomitant use with a strong CYP3A4 inducer may decrease unconjugated MMAE AUC [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)].
Concomitant use of strong CYP3A inhibitors or inducers has the potential to affect the exposure to unconjugated monomethyl auristatin E (MMAE). (7.1)
RECENT MAJOR CHANGES SECTION
RECENT MAJOR CHANGES
|
Indications and Usage (1.1, 1.2) |
4/2023 |
|
Dosage and Administration (2.1. 2.2, 2.3, 2.4) |
4/2023 |
|
Warnings and Precautions (5.1, 5.2. 5.3, 5.4, 5.7) |
4/2023 |
DOSAGE & ADMINISTRATION SECTION
2 DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
2.1 Recommended Dosage
Patients with Previously Untreated DLBCL, NOS or HGBL
The recommended dosage of POLIVY is 1.8 mg/kg administered as an intravenous infusion every 21 days for 6 cycles in combination with a rituximab product, cyclophosphamide, doxorubicin, and prednisone [see Clinical Studies (14.1)]. Administer POLIVY, cyclophosphamide, doxorubicin, and a rituximab product in any order on Day 1 after the administration of prednisone. Prednisone is administered on Days 1–5 of each cycle.
Patients with Relapsed or Refractory DLBCL, NOS
The recommended dosage of POLIVY is 1.8 mg/kg administered as an intravenous infusion every 21 days for 6 cycles in combination with bendamustine and a rituximab product. Administer POLIVY, bendamustine, and a rituximab product in any order on Day 1 of each cycle. The recommended dose of bendamustine is 90 mg/m2/day on Days 1 and 2 when administered with POLIVY and a rituximab product. The recommended dose of rituximab product is 375 mg/m2 intravenously on Day 1 of each cycle.
For All Indicated Patients
If not already premedicated, administer an antihistamine and antipyretic at least 30 minutes prior to POLIVY.
If a planned dose of POLIVY is missed, administer as soon as possible. Adjust the schedule of administration to maintain a 21-day interval between doses.
2.2 Management of Adverse Reactions
Previously Untreated DLBCL, NOS or HGBL
Table 1 provides management guidelines for peripheral neuropathy in patients receiving POLIVY plus R-CHP [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)].
Table 1 Management of Peripheral Neuropathy in Patients Receiving POLIVY Plus R-CHP|
Adverse reaction |
Grade |
Dose modification* |
|---|---|---|
|
R-CHP should be continued if POLIVY is withheld. | ||
| ||
|
Peripheral sensory neuropathy |
Grade 1 |
None |
|
Grade 2 |
If resolves to Grade 1 or lower before the next scheduled dose, resume at the
same dose level. | |
|
Grade 3 |
Withhold until Grade 2 or lower and reduce one dose level. | |
|
Grade 4 |
Permanently discontinue. | |
|
Peripheral motor neuropathy |
Grade 1 |
None |
|
Grade 2 or 3 |
Withhold until Grade 1 or lower and reduce one dose level. | |
|
Grade 4 |
Permanently discontinue. |
Table 2 provides management guidelines for infusion-related reaction and myelosuppression [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2 and 5.3)].
Table 2 Management of Infusion-Related Reaction and Myelosuppression in Patients Receiving POLIVY Plus R-CHP|
Adverse Reaction |
Dosage Modification* |
|---|---|
|
Toxicity graded per National Cancer Institute (NCI) Common Terminology for Adverse Events (CTCAE) version 4.0. | |
| |
|
Infusion-Related Reaction |
Interrupt POLIVY infusion and give supportive treatment. |
|
Infusion-Related Reaction |
Stop POLIVY infusion immediately. |
|
Neutropenia**†,‡****** |
Hold all treatment until ANC recovers to greater than or equal to
1,000/microliter.
|
|
Thrombocytopenia**†,‡****** |
Hold all treatment until platelets recover to greater than or equal to
75,000/microliter.
|
Relapsed or Refractory DLBCL, NOS
Table 3 provides management guidelines for peripheral neuropathy, infusion- related reaction, and myelosuppression in patients receiving POLIVY in combination with bendamustine and a rituximab product [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1, 5.2, 5.3)].
Table 3 Management of Peripheral Neuropathy, Infusion-Related Reaction, and Myelosuppression in Patients Receiving POLIVY Plus Bendamustine and a Rituximab Product|
Adverse Reaction |
Dosage Modification* |
|---|---|
|
Toxicity graded per NCI CTCAE version 4.0. | |
| |
|
Peripheral Neuropathy |
Hold POLIVY dosing until improvement to Grade 1 or lower. |
|
Peripheral Neuropathy |
Discontinue POLIVY. |
|
Infusion-Related Reaction |
Interrupt POLIVY infusion and give supportive treatment. |
|
Infusion-Related Reaction |
Stop POLIVY infusion immediately. |
|
Neutropenia**†,‡****** |
Hold all treatment until ANC recovers to greater than 1,000/microliter.
|
|
Thrombocytopenia**†,‡****** |
Hold all treatment until platelets recover to greater than 75,000/microliter.
|
2.3 Recommended Prophylactic Medications
If not already premedicated for a rituximab product, administer an antihistamine and antipyretic at least 30 to 60 minutes prior to POLIVY for potential infusion-related reactions [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2)].
Administer prophylaxis for Pneumocystis jiroveci pneumonia and herpesvirus throughout treatment with POLIVY.
Administer prophylactic granulocyte colony-stimulating factor (G-CSF) for neutropenia in patients receiving POLIVY plus R-CHP. Consider prophylactic G-CSF administration for neutropenia in patients receiving POLIVY plus bendamustine and a rituximab product [see Warnings and Precautions (5.3)].
Administer tumor lysis syndrome prophylaxis for patients at increased risk of tumor lysis syndrome [see Warnings and Precautions (5.6)].
2.4 Instructions for Preparation and Administration
Reconstitute and further dilute POLIVY prior to intravenous infusion.
POLIVY is a hazardous drug. Follow applicable special handling and disposal procedures.1
Parenteral drug products should be inspected visually for particulate matter and discoloration prior to administration, whenever solution and container permit.
Reconstitution
- Reconstitute immediately before dilution.
- More than one vial may be needed for a full dose. Calculate the dose, the total volume of reconstituted POLIVY solution required, and the number of POLIVY vials needed.
- Using a sterile syringe, slowly inject Sterile Water for Injection, USP, using the volume provided in Table 4, into the POLIVY vial, with the stream directed toward the inside wall of the vial to obtain a concentration of 20 mg/mL of polatuzumab vedotin-piiq.
|
Strength |
Volume of Sterile Water for Injection, USP required for reconstitution |
|---|---|
|
30 mg vial |
1.8 mL |
|
140 mg vial |
7.2 mL |
- Swirl the vial gently until completely dissolved. Do not shake.
- Inspect the reconstituted solution for discoloration and particulate matter. The reconstituted solution should appear colorless to slightly brown, clear to slightly opalescent, and free of visible particulates. Do not use if the reconstituted solution is discolored, is cloudy, or contains visible particulates. Do not freeze or expose to direct sunlight.
- If needed, store unused reconstituted POLIVY solution refrigerated at 2°C to 8°C (36°F to 46°F) for up to 48 hours or at room temperature (9°C to 25°C, 47°F to 77°F) up to a maximum of 8 hours prior to dilution. Discard vial when cumulative storage time prior to dilution exceeds 48 hours.
Dilution
- Dilute polatuzumab vedotin-piiq to a final concentration of 0.72–2.7 mg/mL in an intravenous infusion bag with a minimum volume of 50 mL containing 0.9% Sodium Chloride Injection, USP, 0.45% Sodium Chloride Injection, USP, or 5% Dextrose Injection, USP.
- Determine the volume of 20 mg/mL reconstituted solution needed based on the required dose.
- Withdraw the required volume of reconstituted solution from the POLIVY vial using a sterile syringe and dilute into the intravenous infusion bag. Discard any unused portion left in the vial.
- Gently mix the intravenous bag by slowly inverting the bag. Do not shake.
- Inspect the intravenous bag for particulates and discard if present.
- If not used immediately, store the diluted POLIVY solution as specified in Table 5. Discard if storage time exceeds these limits. Do not freeze or expose to direct sunlight.
|
Diluent Used to Prepare Solution for Infusion |
Diluted POLIVY Solution Storage Conditions* |
|---|---|
| |
|
0.9% Sodium Chloride Injection, USP |
Up to 36 hours at 2°C to 8°C (36°F to 46°F) or up to 4 hours at room temperature (9 to 25°C, 47 to 77°F) |
|
0.45% Sodium Chloride Injection, USP |
Up to 18 hours at 2°C to 8°C (36°F to 46°F) or up to 4 hours at room temperature (9 to 25°C, 47 to 77°F) |
|
5% Dextrose Injection, USP |
Up to 36 hours at 2°C to 8°C (36°F to 46°F) or up to 6 hours at room temperature (9 to 25°C, 47 to 77°F) |
- Limit transportation to 30 minutes at 9°C to 25°C or 24 hours at 2°C to 8°C (refer to instructions below). The total storage plus transportation times of the diluted product should not exceed the storage duration specified in Table 5.
- Agitation stress can result in aggregation. Limit agitation of diluted product during preparation and transportation to administration site. Do not transport diluted product through an automated system (e.g., pneumatic tube or automated cart). If the prepared solution will be transported to a separate facility, remove air from the infusion bag to prevent aggregation. If air is removed, an infusion set with a vented spike is required to ensure accurate dosing during the infusion.
- No incompatibilities have been observed between POLIVY and intravenous infusion bags with product-contacting materials of polyvinyl chloride (PVC) or polyolefins (PO) such as polyethylene (PE) and polypropylene (PP). No incompatibilities have been observed with infusion sets or infusion aids with product-contacting materials of PVC, PE, polyurethane (PU), polybutadiene (PBD), acrylonitrile butadiene styrene (ABS), polycarbonate (PC), polyetherurethane (PEU), fluorinated ethylene propylene (FEP), or polytetrafluorethylene (PTFE), or with filter membranes composed of polyether sulfone (PES) or polysulfone (PSU).
Administration
- Administer POLIVY as an intravenous infusion only.
- Administer the initial dose of POLIVY over 90 minutes. Monitor patients for infusion-related reactions during the infusion and for a minimum of 90 minutes following completion of the initial dose. If the previous infusion was well tolerated, the subsequent dose of POLIVY may be administered as a 30-minute infusion and patients should be monitored during the infusion and for at least 30 minutes after completion of the infusion.
- POLIVY must be administered using a dedicated infusion line equipped with a sterile, non-pyrogenic, low-protein-binding in-line or add-on filter (0.2- or 0.22-micron pore size) and a catheter.
- Do not mix POLIVY with or administer as an infusion with other drugs.
- The recommended dose of POLIVY is 1.8 mg/kg as an intravenous infusion every 21 days for 6 cycles. (2)
- Administer the initial POLIVY dose over 90 minutes. Subsequent infusions may be administered over 30 minutes if the previous infusion is tolerated. (2)
- Premedicate with an antihistamine and antipyretic before POLIVY. (2)
- See Full Prescribing Information for instructions on preparation and administration. (2.4)
DOSAGE FORMS & STRENGTHS SECTION
3 DOSAGE FORMS AND STRENGTHS
For injection: 30 mg/vial or 140 mg/vial of polatuzumab vedotin-piiq as a white to grayish-white lyophilized powder in a single-dose vial for reconstitution and further dilution.
For injection: 30 mg or 140 mg of polatuzumab vedotin-piiq as a lyophilized powder in a single-dose vial. (3)
DESCRIPTION SECTION
11 DESCRIPTION
Polatuzumab vedotin-piiq is a CD79b-directed antibody and microtubule inhibitor conjugate. It consists of three components: 1) the humanized immunoglobulin G1 (IgG1) monoclonal antibody specific for human CD79b; 2) the small molecule anti-mitotic agent MMAE; and 3) a protease-cleavable linker maleimidocaproyl-valine-citrulline-p-aminobenzyloxycarbonyl (mc-vc-PAB) that covalently attaches MMAE to the polatuzumab antibody.
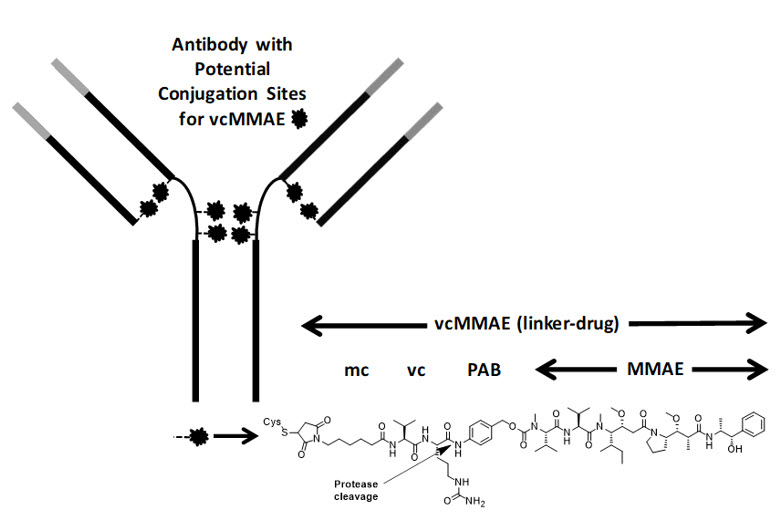
Polatuzumab vedotin-piiq has an approximate molecular weight of 150 kDa. An average of 3.5 molecules of MMAE are attached to each antibody molecule. Polatuzumab vedotin-piiq is produced by chemical conjugation of the antibody and small molecule components. The antibody is produced by mammalian (Chinese hamster ovary) cells, and the small molecule components are produced by chemical synthesis.
POLIVY (polatuzumab vedotin-piiq) for injection is supplied as a sterile, white to grayish-white, preservative-free, lyophilized powder, which has a cake-like appearance, for intravenous infusion after reconstitution and dilution.
Each single-dose 30 mg POLIVY vial delivers 30 mg of polatuzumab vedotin-piiq, polysorbate-20 (1.8 mg), sodium hydroxide (0.82 mg), succinic acid (1.77 mg), and sucrose (62 mg). After reconstitution with 1.8 mL of Sterile Water for Injection, USP, the final concentration is 20 mg/mL with a pH of approximately 5.3.
Each single-dose 140 mg POLIVY vial delivers 140 mg of polatuzumab vedotin- piiq, polysorbate-20 (8.4 mg), sodium hydroxide (3.80 mg), succinic acid (8.27 mg), and sucrose (288 mg). After reconstitution with 7.2 mL of Sterile Water for Injection, USP, the final concentration is 20 mg/mL with a pH of approximately 5.3.
The POLIVY vial stoppers are not made with natural rubber latex.
CLINICAL STUDIES SECTION
14 CLINICAL STUDIES
14.1 Previously Untreated DLBCL, NOS or HGBL
GO39942 (POLARIX)
The efficacy of POLIVY was evaluated in POLARIX (NCT03274492), a randomized double-blind, placebo-controlled, multicenter trial in patients with previously untreated large B-cell lymphoma. Eligible patients were aged 18–80 and had an International Prognostic Index (IPI) score of 2–5 and ECOG performance status of 0–2. The study excluded patients with transformed lymphoma, primary mediastinal large B-cell lymphoma, known CNS lymphoma, or Grade 2 or higher peripheral neuropathy.
Patients were randomized in a 1:1 ratio to receive POLIVY plus R-CHP or to receive R-CHOP for six 21-day cycles followed by two additional cycles of rituximab alone in both arms. Randomization was stratified by IPI score (2 vs 3–5), presence or absence of bulky disease (lesion ≥7.5 cm), and geographical region. Dosing in each treatment arm was as follows:
- POLIVY + R-CHP arm: POLIVY 1.8 mg/kg intravenously, rituximab 375 mg/m2 intravenously, cyclophosphamide 750 mg/m2 intravenously, and doxorubicin 50 mg/m2 intravenously on Day 1 and prednisone 100 mg orally once daily on Days 1–5 for 6 cycles. Rituximab 375 mg/m2 was administered intravenously on Day 1 of cycles 7 and 8.
- R-CHOP arm: rituximab 375 mg/m2 intravenously, cyclophosphamide 750 mg/m2 intravenously, doxorubicin 50 mg/m2 intravenously, and vincristine 1.4 mg/m2 intravenously on Day 1 and prednisone 100 mg orally once daily on Days 1–5 for 6 cycles. Rituximab 375 mg/m2 was administered intravenously on Day 1 of cycles 7 and 8.
Prophylaxis with granulocyte-colony stimulating factor (G-CSF) was mandated for both arms. Dosing in both treatment arms was preceded by premedication.
Of the 879 patients randomized (440 to POLIVY plus R-CHP, 439 to R-CHOP), the median age was 65 years (range 19 to 80 years), 54% were male, 54% were White, 19% were Asian, 1.8% were Black or African American, and 6% were Hispanic or Latino. In total, 38% had an IPI score of 2, 62% had an IPI score of 3–5, 89% had Stage 3 or 4 disease, and 44% had bulky disease. The majority of patients had DLBCL, NOS (84%; n = 740), 11% (n = 93) had HGBL with MYC and BCL2 and/or BCL6 rearrangements or HGBL, NOS, and 5% had other large B-cell lymphomas.
Efficacy was based on investigator-assessed progression-free survival (PFS). Other efficacy measures included modified event-free survival. Efficacy results are summarized in Table 11 and in Figure 1.
Table 11 Summary of Efficacy in POLARIX by Intention-to-Treat Analysis|
Outcomes |
POLIVY + R-CHP |
R-CHOP |
|---|---|---|
|
CI=confidence interval; CR=complete response; EFS=event-free survival; HR=hazard ratio; PFS=progression-free survival. | ||
| ||
|
Progression-Free Survival per Investigator***** | ||
|
Number (%) of patients with event |
107 (24) |
134 (31) |
|
Progression |
88 |
114 |
|
Death |
19 |
20 |
|
HR (95% CI) |
0.73 (0.57, 0.95) | |
|
p-value† |
0.0177 | |
|
Modified Event-Free Survival per Investigator**‡** | ||
|
Number (%) of patients with event |
112 (26) |
138 (31) |
|
HR (95% CI) |
0.75 (0.58, 0.96) | |
|
p-value† |
0.0244 | |
|
Objective Response at End of Treatment**§** | ||
|
Objective response rate, % (95% CI) |
86 (82, 89) |
84 (80, 87) |
|
CR rate, % |
78 (74, 82) |
74 (70, 78) |
|
Difference in CR rate, % (95% CI) |
3.9 (–1.9, 9.7) | |
|
p-value¶ |
0.1557 |
Figure 1 Kaplan-Meier Curve of Investigator-Assessed Progression-Free Survival in POLARIX by Intention-to-Treat Analysis
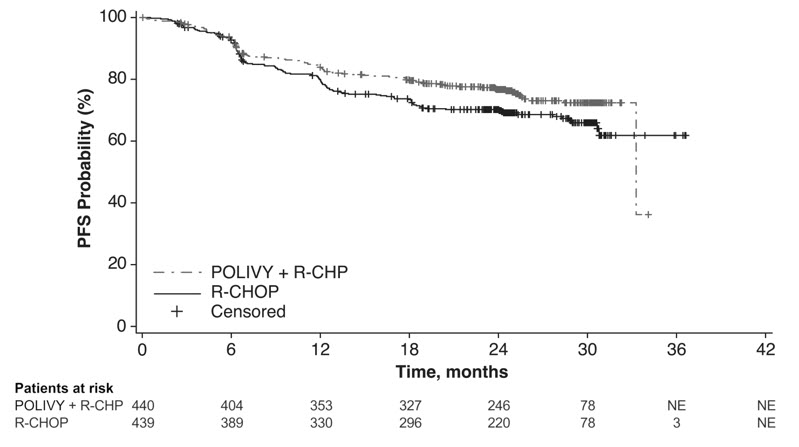
In a prespecified descriptive analysis of the largest lymphoma subgroup, DLBCL, NOS, the PFS HR was 0.75 (95% CI: 0.57, 0.99). In patients with HGBL, the PFS HR was 0.48 (95% CI: 0.21, 1.08). There were insufficient data to evaluate efficacy in other large B-cell lymphomas.
With an estimated median follow-up of 3.3 years, the prespecified final analysis of overall survival (OS) showed no statistically significant difference, with a HR of 0.94 (95% CI: 0.67, 1.33). In a descriptive analysis, the OS HR in patients with DLBCL, NOS was 1.02 (95% CI: 0.70, 1.49). The OS HR in patients with HGBL was 0.42 (95% CI: 0.15, 1.19).
14.2 Relapsed or Refractory DLBCL, NOS
GO29365
The efficacy of POLIVY was evaluated in Study GO29365 (NCT02257567), an open- label, multicenter clinical trial that included a cohort of 80 patients with relapsed or refractory DLBCL after at least one prior regimen. Patients were randomized 1:1 to receive either POLIVY in combination with bendamustine and a rituximab product (BR) or BR alone for six 21-day cycles. Randomization was stratified by duration of response (DOR) to last therapy. Eligible patients were not candidates for autologous HSCT at study entry. The study excluded patients with Grade 2 or higher peripheral neuropathy, prior allogeneic HSCT, active central nervous system lymphoma, or transformed lymphoma.
Following premedication with an antihistamine and antipyretic, POLIVY was given by intravenous infusion at 1.8 mg/kg on Day 2 of Cycle 1 and on Day 1 of Cycles 2–6. Bendamustine was administered at 90 mg/m2 intravenously daily on Days 2 and 3 of Cycle 1 and on Days 1 and 2 of Cycles 2–6. A rituximab product was administered at a dose of 375 mg/m2 intravenously on Day 1 of Cycles 1–6. The cycle length was 21 days.
Of the 80 patients randomized to receive POLIVY plus BR (n = 40) or BR alone (n = 40), the median age was 69 years (range: 30–86 years), 66% were male, and 71% were White. Most patients (98%) had DLBCL not otherwise specified. The primary reasons patients were not candidates for HSCT included age (40%), insufficient response to salvage therapy (26%), and prior transplant failure (20%). The median number of prior therapies was 2 (range: 1–7), with 29% receiving one prior therapy, 25% receiving 2 prior therapies, and 46% receiving 3 or more prior therapies. Eighty percent of patients had refractory disease to last therapy.
In the POLIVY plus BR arm, patients received a median of 5 cycles, with 49% receiving 6 cycles. In the BR arm, patients received a median of 3 cycles, with 23% receiving 6 cycles.
Efficacy was based on complete response (CR) rate at the end of treatment and DOR, as determined by an independent review committee (IRC). Other efficacy measures included IRC-assessed best overall response.
Response rates are summarized in Table 12.
Table 12 Response Rates in Patients with Relapsed or Refractory DLBCL|
Response per IRC, n (%)* |
POLIVY + BR |
BR |
|---|---|---|
|
CR=complete response; PR=partial remission. | ||
| ||
|
Objective Response at End of Treatment**†** |
18 (45) |
7 (18) |
|
CR |
16 (40) |
7 (18) |
|
Difference in CR rates, % (95% CI)‡ |
22 (3, 41) | |
|
Best Overall Response of CR or PR**§** |
25 (63) |
10 (25) |
|
Best Response of CR |
20 (50) |
9 (23) |
In the POLIVY plus BR arm, of the 25 patients who achieved a partial or complete response, 16 (64%) had a DOR of at least 6 months, and 12 (48%) had a DOR of at least 12 months. In the BR arm, of the 10 patients who achieved a partial or complete response, 3 (30%) had a DOR lasting at least 6 months, and 2 (20%) had a DOR lasting at least 12 months.
REFERENCES SECTION
15 REFERENCES
- "OSHA Hazardous Drugs." OSHA. http://www.osha.gov/SLTC/hazardousdrugs/index.html
SPL UNCLASSIFIED SECTION
Representative sample of labeling (see the HOW SUPPLIED section for complete listing):
USE IN SPECIFIC POPULATIONS SECTION
8 USE IN SPECIFIC POPULATIONS
8.1 Pregnancy
Risk Summary
Based on findings from animal studies and its mechanism of action [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.1)], POLIVY can cause fetal harm. There are no available data in pregnant women to inform the drug-associated risk. In animal reproduction studies, administration of the small molecule component of POLIVY, MMAE, to pregnant rats during organogenesis at exposures below the clinical exposure at the recommended dose of 1.8 mg/kg POLIVY every 21 days resulted in embryo-fetal mortality and structural abnormalities (see Data). Advise a pregnant woman of the potential risks to a fetus.
The estimated background risk of major birth defects and miscarriage for the indicated population is unknown. All pregnancies have a background risk of birth defect, loss, or other adverse outcomes. In the U.S. general population, the estimated background risk of major birth defects and miscarriage in clinically recognized pregnancies is 2–4% and 15–20%, respectively.
Data
Animal Data
No embryo-fetal development studies in animals have been performed with polatuzumab vedotin-piiq. In an embryo-fetal developmental study in pregnant rats, administration of two intravenous doses of MMAE, the small molecule component of POLIVY, on gestational days 6 and 13 caused embryo-fetal mortality and structural abnormalities, including protruding tongue, malrotated limbs, gastroschisis, and agnathia compared to controls at a dose of 0.2 mg/kg (approximately 0.5-fold the human area under the curve [AUC] at the recommended dose).
8.2 Lactation
Risk Summary
There is no information regarding the presence of polatuzumab vedotin-piiq in human milk, the effects on the breastfed child, or milk production. Because of the potential for serious adverse reactions in breastfed children, advise women not to breastfeed during treatment with POLIVY and for 2 months after the last dose.
8.3 Females and Males of Reproductive Potential
POLIVY can cause embryo-fetal harm when administered to pregnant women [see Use in Specific Populations (8.1)].
Pregnancy Testing
Verify pregnancy status in females of reproductive potential prior to initiating POLIVY [see Use in Specific Populations (8.1)].
Contraception
Females
Advise females of reproductive potential to use effective contraception during treatment with POLIVY and for 3 months after the last dose [see Nonclinical Toxicology (13.1)].
Males
Based on genotoxicity findings, advise males with female partners of reproductive potential to use effective contraception during treatment with POLIVY and for 5 months after the final dose [see Nonclinical Toxicity (13.1)].
Infertility
Females
Based on findings in animal studies with MMAE-containing antibody-drug conjugates (ADCs), POLIVY may impair female fertility. The effect on fertility is reversible [see Nonclinical Toxicology (13.1)].
Males
Based on findings from animal studies, POLIVY may impair male fertility. The reversibility of this effect is unknown [see Nonclinical Toxicology (13.1)].
8.4 Pediatric Use
Safety and effectiveness of POLIVY have not been established in pediatric patients.
8.5 Geriatric Use
Among 435 patients treated with POLIVY plus R-CHP in POLARIX, 227 (52%) were ≥65 years of age. No overall differences in safety or efficacy were observed between patients aged ≥65 years and younger patients.
Among 173 patients treated with POLIVY plus BR in Study GO29365, 95 (55%) were ≥65 years of age. Patients aged ≥65 had a numerically higher incidence of serious adverse reactions (64%) than patients aged <65 (53%). This study did not include sufficient numbers of patients to determine whether efficacy differed in patients aged ≥65 and younger patients.
8.6 Hepatic Impairment
Avoid the administration of POLIVY in patients with moderate or severe hepatic impairment (total bilirubin greater than 1.5 × ULN and any AST). Patients with moderate or severe hepatic impairment are likely to have increased exposure to MMAE, which may increase the risk of adverse reactions. POLIVY has not been studied in patients with moderate or severe hepatic impairment [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3) and Warnings and Precautions (5.7)].
No adjustment in the starting dose is required when administering POLIVY to patients with mild hepatic impairment (total bilirubin 1 to 1.5 × ULN or AST greater than ULN).
- Hepatic impairment has the potential to increase exposure to MMAE. Monitor patients for adverse reactions. (8.6)
- Lactation: Advise not to breastfeed. (8.2)
CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY SECTION
12 CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY
12.1 Mechanism of Action
Polatuzumab vedotin-piiq is a CD79b-directed antibody-drug conjugate with activity against dividing B cells. The small molecule, MMAE, is an anti- mitotic agent covalently attached to the antibody via a cleavable linker. The monoclonal antibody binds to CD79b, a B-cell specific surface protein, which is a component of the B-cell receptor. Upon binding CD79b, polatuzumab vedotin-piiq is internalized, and the linker is cleaved by lysosomal proteases to enable intracellular delivery of MMAE. MMAE binds to microtubules and kills dividing cells by inhibiting cell division and inducing apoptosis.
12.2 Pharmacodynamics
Over polatuzumab vedotin-piiq dosages of 0.1 to 2.4 mg/kg (0.06 to 1.33 times the approved recommended dosage), higher exposures (AUC and Cmax) of antibody- conjugated MMAE (acMMAE) and unconjugated MMAE were associated with higher incidence of some adverse reactions (including ≥Grade 3 thrombocytopenia and ≥Grade 3 anemia). Higher exposure (AUC and Cmax) of unconjugated MMAE was associated with higher incidence of ≥Grade 2 peripheral neuropathy. Lower acMMAE exposure (AUC) was associated with lower efficacy in patients with relapsed or refractory DLBCL.
Cardiac Electrophysiology
Polatuzumab vedotin-piiq did not prolong the mean QTc interval to any clinically relevant extent based on ECG data from two open-label studies in patients with previously treated B-cell malignancies at the recommended dosage.
12.3 Pharmacokinetics
The exposure parameters of acMMAE and unconjugated MMAE (the cytotoxic component of polatuzumab vedotin-piiq) are summarized in Table 10. The plasma exposure of acMMAE and unconjugated MMAE increased proportionally over a polatuzumab vedotin-piiq dose range from 0.1 to 2.4 mg/kg (0.06 to 1.33 times the approved recommended dosage). Cycle 3 acMMAE AUC were predicted to increase by approximately 30% over Cycle 1 AUC, and achieved more than 90% of the Cycle 6 AUC. Unconjugated MMAE plasma exposures were <3% of acMMAE exposures, and the AUC and Cmax were predicted to decrease after repeated every-3-week dosing.
Table 10 Cycle 1 Exposure of acMMAE and Unconjugated MMAE*,†|
R/R DLBCL, NOS |
Previously Untreated DLBCL, NOS or HGBL | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
acMMAE |
Unconjugated MMAE |
acMMAE |
Unconjugated MMAE | |
|
Cmax=maximum concentration; AUC=area under the concentration-time curve from time zero to day 21. | ||||
| ||||
|
Cmax (ng/mL) |
688 (15%) |
3.19 (57%) |
587 (15%) |
2.45 (46%) |
|
AUC (day*ng/mL) |
2040 (35%) |
31.0 (56%) |
1690 (22%) |
20.8 (50%) |
Distribution
The acMMAE central volume of distribution is 3.15 L. For humans, MMAE plasma protein binding is 71% to 77% and the blood-to-plasma ratio is 0.79 to 0.98, in vitro.
Elimination
At the end of Cycle 6, the median (min, max) acMMAE terminal half-life was 12.2 days (4.5 to 36.7 days) and the clearance was 0.9 L/day in patients with B-cell malignancies. The median (min, max) unconjugated MMAE terminal half- life was 3.74 days (1.58 to 10.1 days) days after the first polatuzumab vedotin-piiq dose.
Metabolism
Polatuzumab vedotin-piiq catabolism has not been studied in humans; however, it is expected to undergo catabolism to small peptides, amino acids, unconjugated MMAE, and unconjugated MMAE-related catabolites. MMAE is a substrate for CYP3A4.
Specific Populations
No clinically significant differences in the pharmacokinetics of acMMAE or unconjugated MMAE were observed based on age (19 to 89 years), sex (males versus females), race (White 69%, Asian 11%), or mild to moderate renal impairment (CLcr 30 to 89 mL/min).
The effect of severe renal impairment (CLcr 15 to 29 mL/min) or end-stage renal disease with or without dialysis on the pharmacokinetics of acMMAE or unconjugated MMAE is unknown.
Patients with Hepatic Impairment
Compared to patients with normal hepatic function, geometric mean MMAE exposure was 11% higher in patients with previously untreated DLBCL and mild hepatic impairment (total bilirubin 1 to 1.5 × ULN or any AST greater than ULN) and 40% higher in patients with relapsed or refractory DLBCL and mild hepatic impairment. The effect of mild hepatic impairment on MMAE exposure is not expected to have a clinically significant impact.
Mild hepatic impairment was not associated with a significant difference in acMMAE exposure. The effect of moderate to severe hepatic impairment (total bilirubin greater than 1.5 × ULN and any AST) or liver transplantation on the pharmacokinetics of acMMAE or unconjugated MMAE is unknown.
Drug Interaction Studies
No dedicated clinical drug-drug interaction studies with POLIVY in humans have been conducted.
Physiologically-Based Pharmacokinetic (PBPK) Modeling Predictions:
Strong CYP3A Inhibitor: Concomitant use of polatuzumab vedotin-piiq with ketoconazole (strong CYP3A inhibitor) is predicted to increase unconjugated MMAE AUC by 45%.
Strong CYP3A Inducer: Concomitant use of polatuzumab vedotin-piiq with rifampin (strong CYP3A inducer) is predicted to decrease unconjugated MMAE AUC by 63%.
Sensitive CYP3A Substrate: Concomitant use of polatuzumab vedotin-piiq is predicted not to affect exposure to midazolam (sensitive CYP3A substrate).
Population Pharmacokinetic (popPK) Modeling Predictions:
Bendamustine or Rituximab: No clinically significant differences in the pharmacokinetics of acMMAE or unconjugated MMAE are predicted when polatuzumab vedotin-piiq is used concomitantly with bendamustine or rituximab.
Rituximab, Cyclophosphamide, Doxorubicin, or Prednisone (R-CHP): No clinically significant differences in the pharmacokinetics of acMMAE or unconjugated MMAE are predicted when polatuzumab vedotin-piiq is used concomitantly with R-CHP.
In Vitro Studies Where Drug Interaction Potential Was Not Further Evaluated Clinically:
Cytochrome P450 (CYP) Enzymes: MMAE does not inhibit CYP1A2, CYP2B6, CYP2C8, CYP2C9, CYP2C19, or CYP2D6. MMAE does not induce major CYP enzymes.
Transporter Systems: MMAE does not inhibit P-gp. MMAE is a P-gp substrate.
12.6 Immunogenicity
The observed incidence of anti-drug antibodies is highly dependent on the sensitivity and specificity of the assay. Differences in assay methods preclude meaningful comparisons of the incidence of anti-drug antibodies in the studies described below with the incidence of anti-drug antibodies in other studies, including those of POLIVY or of other polatuzumab products.
In studies POLARIX and GO29365, 1.4% (6/427) and 6% (8/134) of patients tested positive for antibodies against polatuzumab vedotin-piiq, respectively, of which none were positive for neutralizing antibodies. Because of the low occurrence of anti-drug antibodies, the effect of these antibodies on the pharmacokinetics, pharmacodynamics, safety, and/or effectiveness of polatuzumab products is unknown.
NONCLINICAL TOXICOLOGY SECTION
13 NONCLINICAL TOXICOLOGY
13.1 Carcinogenesis, Mutagenesis, Impairment of Fertility
Carcinogenicity studies in animals have not been performed with polatuzumab vedotin-piiq or MMAE.
MMAE was positive for genotoxicity in the in vivo rat bone marrow micronucleus study through an aneugenic mechanism. MMAE was not mutagenic in the bacterial reverse mutation (Ames) assay or the L5178Y mouse lymphoma forward mutation assay.
Fertility studies in animals have not been performed with polatuzumab vedotin- piiq or MMAE. However, results of repeat-dose toxicity indicate the potential for polatuzumab vedotin-piiq to impair female and male fertility. In the 4-week repeat-dose toxicity study in rats with weekly dosing of 2, 6, and 10 mg/kg, dose-dependent testicular seminiferous tubule degeneration with abnormal lumen contents in the epididymis was observed. Findings in the testes and epididymis did not reverse and correlated with decreased testes weight and gross findings of small and/or soft testes at recovery necropsy in males given doses ≥2 mg/kg (below the exposure at the recommended dose based on unconjugated MMAE AUC).
MMAE-containing ADCs have been associated with adverse ovarian effects when administered to sexually immature animals. Adverse effects included decrease in, or absence of, secondary and tertiary ovarian follicles after weekly administration to cynomolgus monkeys in studies of 4-week duration. These effects showed a trend towards recovery 6 weeks after the end of dosing; no changes were observed in primordial follicles.
HOW SUPPLIED SECTION
16 HOW SUPPLIED/STORAGE AND HANDLING
How Supplied
POLIVY (polatuzumab vedotin-piiq) for injection is a preservative-free, white to grayish-white lyophilized powder, which has a cake-like appearance. POLIVY is supplied as:
|
Carton Contents |
NDC |
|---|---|
|
One 30 mg single-dose vial |
NDC 50242-103-01 |
|
One 140 mg single-dose vial |
NDC 50242-105-01 |
Storage and Handling
Store refrigerated at 2°C to 8°C (36°F to 46°F) in original carton to protect from light. Do not use beyond the expiration date shown on the carton. Do not freeze. Do not shake.
POLIVY is a hazardous drug. Follow applicable special handling and disposal procedures.1
INFORMATION FOR PATIENTS SECTION
17 PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATION
Peripheral Neuropathy
Advise patients that POLIVY can cause peripheral neuropathy. Advise patients to report to their healthcare provider any numbness or tingling of the hands or feet or any muscle weakness [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)].
Infusion-Related Reactions
Advise patients to contact their healthcare provider if they experience signs and symptoms of infusion reactions, including fever, chills, rash, or breathing problems, within 24 hours of infusion [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2)].
Myelosuppression
Advise patients to report signs or symptoms of bleeding or infection immediately. Advise patients of the need for periodic monitoring of blood counts [see Warnings and Precautions (5.3)].
Infections
Advise patients to contact their healthcare provider if a fever of 38°C (100.4°F) or greater or other evidence of potential infection such as chills, cough, or pain on urination develops. Advise patients of the need for periodic monitoring of blood counts [see Warnings and Precautions (5.4)].
Progressive Multifocal Leukoencephalopathy
Advise patients to seek immediate medical attention for new or changes in neurological symptoms such as confusion, dizziness, or loss of balance; difficulty talking or walking; or changes in vision [see Warnings and Precautions (5.5)].
Tumor Lysis Syndrome
Advise patients to seek immediate medical attention for symptoms of tumor lysis syndrome such as nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, and lethargy [see Warnings and Precautions (5.6)].
Hepatotoxicity
Advise patients to report symptoms that may indicate liver injury, including fatigue, anorexia, right upper abdominal discomfort, dark urine, or jaundice [see Warnings and Precautions (5.7)].
Embryo-Fetal Toxicity
Advise females of reproductive potential of the potential risk to a fetus. Advise females to contact their healthcare provider if they become pregnant, or if pregnancy is suspected, during treatment with POLIVY [see Warnings and Precautions (5.8) and Use in Specific Populations (8.1)].
Females and Males of Reproductive Potential
Advise females of reproductive potential, and males with female partners of reproductive potential, to use effective contraception during treatment with POLIVY and for 3 months and 5 months after the last dose, respectively [see Use in Specific Populations (8.3)].
Lactation
Advise women not to breastfeed while receiving POLIVY and for 2 months after the last dose [see Use in Specific Populations (8.2)].
