VEMLIDY
These highlights do not include all the information needed to use VEMLIDY safely and effectively. See full prescribing information for VEMLIDY. VEMLIDY (tenofovir alafenamide) tablets, for oral use Initial U.S. Approval: 2015
72e6b33c-0351-4070-9172-eeaa186c01d2
HUMAN PRESCRIPTION DRUG LABEL
Mar 6, 2024
Gilead Sciences, Inc.
DUNS: 185049848
Products 1
Detailed information about drug products covered under this FDA approval, including NDC codes, dosage forms, ingredients, and administration routes.
tenofovir alafenamide
Product Details
FDA regulatory identification and product classification information
FDA Identifiers
Product Classification
Product Specifications
INGREDIENTS (10)
Drug Labeling Information
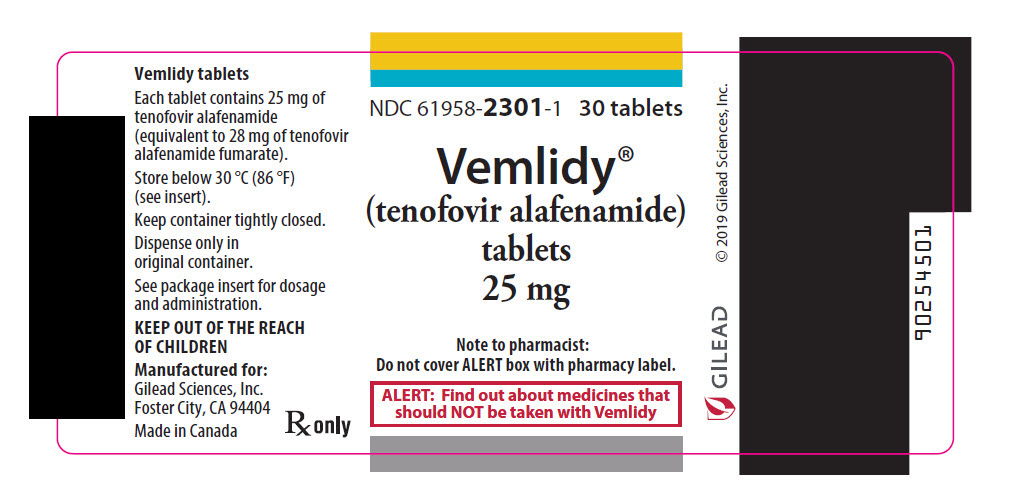
PACKAGE LABEL.PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL
PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL - 25 mg Tablet Bottle Label
NDC 61958-2301-1
30 tablets
Vemlidy®
(tenofovir alafenamide)
tablets, 25 mg
Note to pharmacist:
Do not cover ALERT box with pharmacy label.
ALERT: Find out about medicines that
should NOT be taken with Vemlidy
BOXED WARNING SECTION
WARNING: POSTTREATMENT SEVERE ACUTE EXACERBATION OF HEPATITIS B
INDICATIONS & USAGE SECTION
1 INDICATIONS AND USAGE
VEMLIDY is indicated for the treatment of chronic hepatitis B virus (HBV) infection in adults and pediatric patients 6 years of age and older and weighing at least 25 kg with compensated liver disease [see Clinical Studies (14)].
VEMLIDY is a hepatitis B virus (HBV) nucleoside analog reverse transcriptase inhibitor and is indicated for the treatment of chronic hepatitis B virus infection in adults and pediatric patients 6 years of age and older and weighing at least 25 kg with compensated liver disease. (1)
CONTRAINDICATIONS SECTION
4 CONTRAINDICATIONS
None.
None. (4)
WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS SECTION
5 WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS
5.1 Severe Acute Exacerbation of Hepatitis B after Discontinuation of
Treatment
Discontinuation of anti-hepatitis B therapy, including VEMLIDY, may result in severe acute exacerbations of hepatitis B. Patients who discontinue VEMLIDY should be closely monitored with both clinical and laboratory follow-up for at least several months after stopping treatment. If appropriate, resumption of anti-hepatitis B therapy may be warranted.
5.2 Risk of Development of HIV-1 Resistance in Patients Coinfected with HBV
and HIV-1
Due to the risk of development of HIV-1 resistance, VEMLIDY alone is not recommended for the treatment of HIV-1 infection. The safety and efficacy of VEMLIDY have not been established in patients coinfected with HBV and HIV-1. HIV antibody testing should be offered to all HBV-infected patients before initiating therapy with VEMLIDY, and, if positive, an appropriate antiretroviral combination regimen that is recommended for patients coinfected with HIV-1 should be used.
5.3 New Onset or Worsening Renal Impairment
Postmarketing cases of renal impairment, including acute renal failure, proximal renal tubulopathy (PRT), and Fanconi syndrome have been reported with TAF-containing products; while most of these cases were characterized by potential confounders that may have contributed to the reported renal events, it is also possible these factors may have predisposed patients to tenofovir- related adverse events [see Adverse Reactions (6.2)].
Patients taking tenofovir prodrugs who have impaired renal function and those taking nephrotoxic agents, including non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, are at increased risk of developing renal-related adverse reactions [see Drug Interactions (7.2)].
Prior to or when initiating VEMLIDY, and during treatment with VEMLIDY on a clinically appropriate schedule, assess serum creatinine, estimated creatinine clearance, urine glucose, and urine protein in all patients. In patients with chronic kidney disease, also assess serum phosphorus. Discontinue VEMLIDY in patients who develop clinically significant decreases in renal function or evidence of Fanconi syndrome [see Adverse Reactions (6.1) and Use in Specific Populations (8.6)].
5.4 Lactic Acidosis/Severe Hepatomegaly with Steatosis
Lactic acidosis and severe hepatomegaly with steatosis, including fatal cases, have been reported with the use of nucleoside analogs, including tenofovir disoproxil fumarate (TDF), another prodrug of tenofovir, alone or in combination with other antiretrovirals. Treatment with VEMLIDY should be suspended in any patient who develops clinical or laboratory findings suggestive of lactic acidosis or pronounced hepatotoxicity (which may include hepatomegaly and steatosis even in the absence of marked transaminase elevations).
- HBV and HIV-1 coinfection: VEMLIDY alone is not recommended for the treatment of HIV-1 infection. HIV-1 resistance may develop in these patients. (5.2)
- New onset or worsening renal impairment: Prior to or when initiating VEMLIDY, and during treatment on a clinically appropriate schedule, assess serum creatinine, estimated creatinine clearance, urine glucose, and urine protein in all patients. Also assess serum phosphorus in patients with chronic kidney disease. (5.3)
- Lactic acidosis/severe hepatomegaly with steatosis: Discontinue treatment in patients who develop symptoms or laboratory findings suggestive of lactic acidosis or pronounced hepatotoxicity. (5.4)
ADVERSE REACTIONS SECTION
6 ADVERSE REACTIONS
The following adverse reactions are discussed in other sections of the labeling:
- Severe Acute Exacerbation of Hepatitis B [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)]
- New Onset or Worsening of Renal Impairment [see Warnings and Precautions (5.3)]
- Lactic Acidosis/Severe Hepatomegaly with Steatosis [see Warnings and Precautions (5.4)]
6.1 Clinical Trials Experience
Because clinical trials are conducted under widely varying conditions, adverse reaction rates observed in the clinical trials of a drug cannot be directly compared to rates in the clinical trials of another drug and may not reflect the rates observed in practice.
Adverse Reactions in Adult Subjects with Chronic Hepatitis B and Compensated Liver Disease
The safety assessment of VEMLIDY was based on pooled data through the Week 96 data analysis from 1298 subjects in two randomized, double-blind, active- controlled trials, Trial 108 and Trial 110, in adult subjects with chronic hepatitis B and compensated liver disease. A total of 866 subjects received VEMLIDY 25 mg once daily [see Clinical Studies (14.2)]. Further safety assessment was based on pooled data from Trials 108 and 110 from subjects who continued to receive their original blinded treatment through Week 120 and additionally from subjects who received open-label VEMLIDY from Week 96 through Week 120 (n = 361 remained on VEMLIDY; n = 180 switched from TDF to VEMLIDY at Week 96).
Based on the Week 96 analysis, the most common adverse reaction (all Grades) reported in at least 10% of subjects in the VEMLIDY group was headache. The proportion of subjects who discontinued treatment with VEMLIDY or TDF due to adverse reactions of any severity was 1.5% and 0.9%, respectively. Table 1 displays the frequency of the adverse reactions (all Grades) greater than or equal to 5% in the VEMLIDY group.
Table 1 Adverse Reactions* (All Grades) Reported in ≥5% of Subjects with Chronic HBV Infection and Compensated Liver Disease in Trials 108 and 110 (Week 96 analysis†)|
VEMLIDY |
TDF | |
|---|---|---|
| ||
|
Headache |
12% |
10% |
|
Abdominal pain‡ |
9% |
6% |
|
Cough |
8% |
8% |
|
Back pain |
6% |
6% |
|
Fatigue |
6% |
5% |
|
Nausea |
6% |
6% |
|
Arthralgia |
5% |
6% |
|
Diarrhea |
5% |
5% |
|
Dyspepsia |
5% |
5% |
Additional adverse reactions occurring in less than 5% of subjects in Trials 108 and 110 included vomiting, rash, and flatulence.
The safety profile of VEMLIDY in subjects who continued to receive blinded treatment through Week 120 was similar to that at Week 96. The safety profile of VEMLIDY in subjects who remained on VEMLIDY in the open-label phase through Week 120 was similar to that in subjects who switched from TDF to VEMLIDY at Week 96.
Renal Laboratory Tests
In a pooled analysis of Trials 108 and 110 in adult subjects with chronic hepatitis B and a median baseline estimated creatinine clearance between 106 and 105 mL per minute (for the VEMLIDY and TDF groups, respectively), mean serum creatinine increased by less than 0.1 mg/dL and median serum phosphorus decreased by 0.1 mg/dL in both treatment groups at Week 96. Median change from baseline to Week 96 in estimated creatinine clearance was -1.2 mL per minute in the VEMLIDY group and -4.8 mL per minute in those receiving TDF.
In subjects who remained on blinded treatment beyond Week 96 in Trials 108 and 110, change from baseline in renal laboratory parameter values in each group at Week 120 were similar to those at Week 96. In the open-label phase, median change in estimated creatinine clearance by Cockcroft-Gault method from Week 96 to Week 120 was -0.6 mL per minute in subjects who remained on VEMLIDY and +1.8 mL per minute in those who switched from TDF to VEMLIDY at Week 96. Mean serum creatinine and median serum phosphorus values at Week 120 were similar to those at Week 96 in subjects who remained on VEMLIDY and in subjects who switched from TDF to VEMLIDY.
The long-term clinical significance of these renal laboratory changes on adverse reaction frequencies between VEMLIDY and TDF is not known.
Bone Mineral Density Effects
In a pooled analysis of Trials 108 and 110, the mean percentage change in bone mineral density (BMD) from baseline to Week 96 as assessed by dual-energy X-ray absorptiometry (DXA) was -0.7% with VEMLIDY compared to -2.6% with TDF at the lumbar spine and -0.3% compared to -2.5% at the total hip. BMD declines of 5% or greater at the lumbar spine were experienced by 11% of VEMLIDY subjects and 25% of TDF subjects at Week 96. BMD declines of 7% or greater at the femoral neck were experienced by 5% of VEMLIDY subjects and 13% of TDF subjects at Week 96.
In subjects who remained on blinded treatment beyond Week 96 in Trials 108 and 110, mean percentage change in BMD in each group at Week 120 was similar to that at Week 96. In the open-label phase, mean percentage change in BMD from Week 96 to Week 120 in subjects who remained on VEMLIDY was 0.6% at the lumbar spine and 0% at the total hip, compared to 1.7% at the lumbar spine and 0.6% at the total hip in those who switched from TDF to VEMLIDY.
The long-term clinical significance of these BMD changes is not known.
Laboratory Abnormalities
The frequency of laboratory abnormalities (Grades 3–4) occurring in at least 2% of subjects receiving VEMLIDY in Trials 108 and 110 are presented in Table 2.
Table 2 Laboratory Abnormalities (Grades 3–4) Reported in ≥2% of Subjects with Chronic HBV Infection and Compensated Liver Disease in Trials 108 and 110 (Week 96 analysis*)|
Laboratory Parameter Abnormality† |
VEMLIDY |
TDF |
|---|---|---|
|
ULN=Upper Limit of Normal | ||
| ||
|
ALT (>5 × ULN) |
8% |
10% |
|
LDL-cholesterol (fasted) (>190 mg/dL) |
6% |
1% |
|
Glycosuria (≥3+) |
5% |
2% |
|
AST (>5 × ULN) |
3% |
5% |
|
Creatine Kinase (≥10 × ULN) |
3% |
3% |
|
Serum Amylase (>2.0 × ULN) |
3% |
3% |
The overall incidence of blinded treatment ALT flares (defined as confirmed serum ALT greater than 2 × baseline and greater than 10 × ULN at 2 consecutive postbaseline visits, with or without associated symptoms) was similar between VEMLIDY (0.6%) and TDF (0.9%) through Week 96. ALT flares generally were not associated with coincident elevations in bilirubin, occurred within the first 12 weeks of treatment, and resolved without recurrence.
Based on the Week 120 analysis, the frequencies of lab abnormalities in subjects who remained on VEMLIDY in the open-label phase were similar to those in subjects who switched from TDF to VEMLIDY at Week 96.
Amylase and Lipase Elevations and Pancreatitis
At Week 96, in Trials 108 and 110, eight subjects treated with VEMLIDY with elevated amylase levels had associated symptoms, such as nausea, low back pain; abdominal tenderness, pain, and distension; and biliary pancreatitis and pancreatitis. Of these eight, two subjects discontinued VEMLIDY due to elevated amylase and/or lipase; one subject experienced recurrence of adverse events when VEMLIDY was restarted. No subject treated with TDF had associated symptoms or discontinued treatment.
From Week 96 to Week 120, one additional subject who continued open-label VEMLIDY and none of the subjects who switched from TDF to VEMLIDY had elevated amylase levels and associated symptoms.
Serum Lipids
Changes from baseline in total cholesterol, HDL-cholesterol, LDL-cholesterol, triglycerides, and total cholesterol to HDL ratio among subjects treated with VEMLIDY and TDF in Trials 108 and 110 are presented in Table 3.
Table 3 Lipid Abnormalities: Mean Change from Baseline in Lipid Parameters in Patients with Chronic HBV Infection and Compensated Liver Disease in Trials 108 and 110 (Week 96 analysis)|
VEMLIDY |
TDF | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Baseline |
Week 96 |
Baseline |
Week 96 | |
|
mg/dL |
Change* |
mg/dL |
Change* | |
| ||||
|
Total Cholesterol (fasted) |
188 |
-1 |
193 |
-25 |
|
HDL-Cholesterol (fasted) |
60 |
-5 |
61 |
-12 |
|
LDL-Cholesterol (fasted) |
116 |
+7 |
120 |
-10 |
|
Triglycerides (fasted) |
102 |
+13 |
102 |
-7 |
|
Total Cholesterol to HDL ratio |
3 |
0 |
3 |
0 |
In the open-label phase, lipid parameters at Week 120 in subjects who remained on VEMLIDY were similar to those at Week 96. In subjects who switched from TDF to VEMLIDY, mean change from Week 96 to Week 120 in total cholesterol was 23 mg/dL, HDL-cholesterol was 5 mg/dL, LDL-cholesterol was 16 mg/dL, triglycerides was 30 mg/dL, and total cholesterol to HDL ratio was 0 mg/dL.
Adverse Reactions in Virologically Suppressed Adult Subjects with Chronic Hepatitis B
The safety of VEMLIDY in virologically suppressed adults is based on Week 48 data from a randomized, double-blind, active-controlled trial (Trial 4018) in which subjects taking TDF at baseline were randomized to switch to VEMLIDY (N=243) or to continue their TDF treatment (N=245). Adverse reactions observed with VEMLIDY in Trial 4018 were similar to those in Trials 108 and 110 [see Clinical Studies (14.3)].
Renal Laboratory Tests, Bone Mineral Density Effects, and Serum Lipids
In virologically suppressed adults in Trial 4018, changes from baseline in renal function, BMD, and lipid parameters in the VEMLIDY and TDF groups at Week 48 were similar to those observed in Trials 108 and 110 at Week 96.
Adverse Reactions in Adult Subjects with Chronic Hepatitis B and Renal Impairment
In an open-label trial (Trial 4035) in virologically suppressed adult subjects with chronic hepatitis B switching to VEMLIDY 25 mg, the safety of VEMLIDY was assessed in 78 subjects with moderate to severe renal impairment (estimated creatinine clearance between 15 and 59 mL per minute by Cockcroft-Gault method; Part A, Cohort 1) and 15 subjects with ESRD (estimated creatinine clearance below 15 mL per minute) receiving chronic hemodialysis (Part A, Cohort 2). The safety of VEMLIDY, including changes from baseline in renal function, BMD, and lipid parameters, was similar to that observed in clinical trials of VEMLIDY in subjects with compensated liver disease but without renal impairment [see Use in Specific Populations (8.6) and Clinical Studies (14.4)].
Adverse Reactions in Pediatric Subjects with Chronic Hepatitis B
The safety of VEMLIDY was evaluated in HBV-infected treatment-naïve and treatment-experienced pediatric subjects between the ages of 12 to less than 18 years and weighing at least 35 kg (Cohort 1; N=70) and 6 to less than 12 years and weighing at least 25 kg (Cohort 2, Group 1: N=18) through Week 24 in a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled clinical trial (Trial 1092). Subjects were then eligible to roll over to receive open-label VEMLIDY. Safety data are available through Week 96 [see Clinical Studies (14.5)]. The safety profile of VEMLIDY was similar to that in adults.
Bone Mineral Density Effects
Among the Cohort 1 and Cohort 2, Group 1 subjects treated with VEMLIDY and placebo, the mean percent change in BMD from baseline to Week 24 was 1.6% (N=48) and 1.9% (N=23) for lumbar spine, and 1.9% (N=50) and 2.0% (N=23) for whole body, respectively. At Week 24, mean changes from baseline BMD Z-scores were 0.01 and -0.07 for lumbar spine, and -0.04 and -0.04 for whole body, for the VEMLIDY and placebo groups, respectively. At Week 24, BMD declines of 4% or greater at lumbar spine and whole body were experienced by 6% and 2% of VEMLIDY subjects, respectively.
In the open-label phase, mean percentage change in lumbar spine and whole body BMD and BMD Z-scores from baseline to Week 96 was similar in subjects who remained on VEMLIDY compared to those who switched from placebo to VEMLIDY.
6.2 Postmarketing Experience
The following adverse reactions have been identified during post approval use of VEMLIDY or other products containing tenofovir alafenamide. Because these reactions are reported voluntarily from a population of uncertain size, it is not always possible to reliably estimate their frequency or establish a causal relationship to drug exposure.
Skin and Subcutaneous Tissue Disorders
Angioedema, urticaria
Renal and Urinary Disorders
Acute renal failure, acute tubular necrosis, proximal renal tubulopathy, and Fanconi syndrome
Most common adverse reaction (incidence greater than or equal to 10%, all grades) is headache. (6.1)
To report SUSPECTED ADVERSE REACTIONS, contact Gilead Sciences, Inc. at 1-800-GILEAD-5 or FDA at 1-800-FDA-1088 or www.fda.gov/medwatch.
DRUG INTERACTIONS SECTION
7 DRUG INTERACTIONS
7.1 Potential for Other Drugs to Affect VEMLIDY
VEMLIDY is a substrate of P-glycoprotein (P-gp) and BCRP. Drugs that strongly affect P-gp and BCRP activity may lead to changes in tenofovir alafenamide absorption (see Table 4). Drugs that induce P-gp activity are expected to decrease the absorption of tenofovir alafenamide, resulting in decreased plasma concentrations of tenofovir alafenamide, which may lead to loss of therapeutic effect of VEMLIDY. Coadministration of VEMLIDY with other drugs that inhibit P-gp and BCRP may increase the absorption and plasma concentration of tenofovir alafenamide.
7.2 Drugs Affecting Renal Function
Because tenofovir is primarily excreted by the kidneys by a combination of glomerular filtration and active tubular secretion, coadministration of VEMLIDY with drugs that reduce renal function or compete for active tubular secretion may increase concentrations of tenofovir and other renally eliminated drugs and this may increase the risk of adverse reactions. Some examples of drugs that are eliminated by active tubular secretion include, but are not limited to, acyclovir, cidofovir, ganciclovir, valacyclovir, valganciclovir, aminoglycosides (e.g., gentamicin), and high-dose or multiple NSAIDs [see Warnings and Precautions (5.3)].
7.3 Established and Other Potentially Significant Interactions
Table 4 provides a listing of established or potentially clinically significant drug interactions. The drug interactions described are based on studies conducted with tenofovir alafenamide or are predicted drug interactions that may occur with VEMLIDY [For magnitude of interaction, see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)]. Information regarding potential drug-drug interactions with HIV antiretrovirals is not provided (see the prescribing information for emtricitabine/tenofovir alafenamide for interactions with HIV antiretrovirals). The table includes potentially significant interactions but is not all inclusive.
Table 4 Established and Other Potentially Significant Drug Interactions*|
Concomitant Drug Class: |
Effect on Concentration† |
Clinical Comment |
|---|---|---|
| ||
|
Anticonvulsants: |
↓ tenofovir alafenamide |
When coadministered with carbamazepine, the tenofovir alafenamide dose should
be increased to two tablets once daily. |
|
Carbamazepineठ| ||
|
Oxcarbazepine§ | ||
|
Phenobarbital§ | ||
|
Phenytoin§ | ||
|
Antimycobacterials: |
↓ tenofovir alafenamide |
Coadministration of VEMLIDY with rifabutin, rifampin or rifapentine is not recommended. |
|
Rifabutin§ | ||
|
Rifampin§ | ||
|
Rifapentine§ | ||
|
Herbal Products: |
↓ tenofovir alafenamide |
Coadministration of VEMLIDY with St. John's wort is not recommended. |
|
St. John's wort§ (Hypericum perforatum) |
7.4 Drugs without Clinically Significant Interactions with VEMLIDY
Based on drug interaction studies conducted with VEMLIDY, no clinically significant drug interactions have been observed with: ethinyl estradiol, ledipasvir/sofosbuvir, midazolam, norgestimate, sertraline, sofosbuvir, sofosbuvir/velpatasvir, and sofosbuvir/velpatasvir/voxilaprevir.
VEMLIDY is a substrate of P-glycoprotein (P-gp) and BCRP. Drugs that strongly affect P-gp and BCRP activity may lead to changes in VEMLIDY absorption. Consult the full prescribing information prior to and during treatment for potential drug-drug interactions. (7)
SPL UNCLASSIFIED SECTION
Manufactured and distributed by: Gilead Sciences, Inc. Foster City, CA 94404
© 2024 Gilead Sciences, Inc. All rights reserved.
DOSAGE FORMS & STRENGTHS SECTION
3 DOSAGE FORMS AND STRENGTHS
Tablets: 25 mg of tenofovir alafenamide (equivalent to 28 mg of tenofovir alafenamide fumarate) — yellow, round, film-coated tablets, debossed with "GSI" on one side of the tablet and "25" on the other side.
Tablets: 25 mg of tenofovir alafenamide. (3)
RECENT MAJOR CHANGES SECTION
RECENT MAJOR CHANGES
|
Indications and Usage (1) |
03/2024 |
|
Dosage and Administration: Recommended Dosage in Adults and Pediatric Patients 6 Years of Age and Older and Weighing at Least 25 kg (2.2) |
03/2024 |
OVERDOSAGE SECTION
10 OVERDOSAGE
If overdose occurs, monitor patient for evidence of toxicity. Treatment of overdosage with VEMLIDY consists of general supportive measures including monitoring of vital signs as well as observation of the clinical status of the patient. Tenofovir is efficiently removed by hemodialysis with an extraction coefficient of approximately 54%.
DESCRIPTION SECTION
11 DESCRIPTION
VEMLIDY is a tablet containing tenofovir alafenamide for oral administration. Tenofovir alafenamide, a hepatitis B virus (HBV) nucleoside analog reverse transcriptase inhibitor, is converted in vivo to tenofovir, an acyclic nucleoside phosphonate (nucleotide) analog of adenosine 5′-monophosphate.
Each tablet contains 25 mg of tenofovir alafenamide (equivalent to 28 mg of tenofovir alafenamide fumarate). The tablets include the following inactive ingredients: croscarmellose sodium, lactose monohydrate, magnesium stearate, and microcrystalline cellulose. The tablets are film coated with a coating material containing: iron oxide yellow, polyethylene glycol, polyvinyl alcohol, talc, and titanium dioxide.
The chemical name of tenofovir alafenamide fumarate drug substance is L-alanine, N-[(S)-[[(1R)-2-(6-amino-9H-purin-9-yl)-1-methylethoxy]methyl]phenoxyphosphinyl]-, 1-methylethyl ester, (2E)-2-butenedioate (2:1).
It has an empirical formula of C21H29O5N6P∙½(C4H4O4) and a formula weight of 534.50. It has the following structural formula:
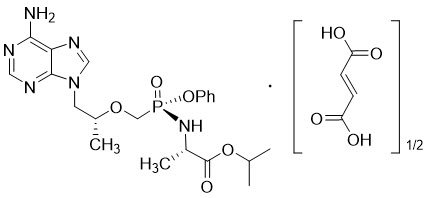
Tenofovir alafenamide fumarate is a white to off-white or tan powder with a solubility of 4.7 mg per mL in water at 20 °C.
CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY SECTION
12 CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY
12.1 Mechanism of Action
Tenofovir alafenamide is an antiviral drug against the hepatitis B virus [see Microbiology (12.4)].
12.2 Pharmacodynamics
Cardiac Electrophysiology
In a thorough QT/QTc study in 48 healthy subjects, tenofovir alafenamide at the recommended dose or at a dose 5 times the recommended dose did not affect the QT/QTc interval and did not prolong the PR interval.
12.3 Pharmacokinetics
The pharmacokinetic properties of VEMLIDY are provided in Table 5. The multiple dose PK parameters of tenofovir alafenamide and its metabolite tenofovir are provided in Table 6.
Table 5 Pharmacokinetic Properties of VEMLIDY|
Tenofovir Alafenamide | |
|---|---|
|
CES1 = carboxylesterase 1; PBMCs = peripheral blood mononuclear cells. | |
| |
|
Absorption | |
|
Tmax (h) |
0.48 |
|
Effect of high fat meal (relative to fasting): AUClast Ratio* |
1.65 (1.51, 1.81) |
|
Distribution | |
|
% Bound to human plasma proteins |
80% |
|
Source of protein binding data |
Ex vivo |
|
Blood-to-plasma ratio |
1.0 |
|
Metabolism | |
|
Metabolism† |
CES1 (hepatocytes) |
|
Elimination | |
|
Major route of elimination |
Metabolism (>80% of oral dose) |
|
t1/2 (h)‡ |
0.51 |
|
% Of dose excreted in urine§ |
<1 |
|
% Of dose excreted in feces§ |
31.7 |
|
Parameter |
Tenofovir Alafenamide* |
Tenofovir* |
|---|---|---|
|
CV = coefficient of variation; NA = not applicable | ||
| ||
|
Cmax |
0.27 (63.3) |
0.03 (24.6) |
|
AUCtau |
0.27 (47.8) |
0.40 (35.2) |
|
Ctrough (mcg per mL) |
NA |
0.01 (39.6) |
Specific Populations
Geriatric Patients, Race, and Gender
Limited data in subjects aged 65 years and over suggest a lack of clinically relevant differences in tenofovir alafenamide or tenofovir pharmacokinetics. No clinically relevant differences in tenofovir alafenamide or tenofovir pharmacokinetics due to race or gender have been identified [see Use in Specific Populations (8.5)].
Pediatric Patients
Steady-state pharmacokinetics of tenofovir alafenamide and its metabolite tenofovir were evaluated in HBV-infected pediatric subjects aged 6 to less than 18 years (Table 7).
Table 7 Multiple Dose PK Parameters of Tenofovir Alafenamide and Tenofovir Following Oral Administration of VEMLIDY 25 mg in HBV-Infected Pediatric Subjects Aged 6 to less than 18 Years|
Age Group |
Parameter |
Tenofovir Alafenamide* |
Tenofovir† |
|---|---|---|---|
|
CV = coefficient of variation; NA = not applicable | |||
| |||
|
12 to <18 Years weighing ≥35 kg |
Cmax (mcg per mL) |
0.188 (45.0) |
0.015 (23.5) |
|
AUCtau (mcg∙hour per mL) |
0.254 (36.4) |
0.244 (28.3) | |
|
Ctrough (mcg per mL) |
NA |
0.0079 (35.0) | |
|
6 to <12 Years weighing ≥25 kg |
Cmax (mcg per mL) |
0.388 (96.9) |
0.017 (19.6) |
|
AUCtau (mcg∙hour per mL) |
0.313 (64.8) |
0.272 (17.5) | |
|
Ctrough (mcg per mL) |
NA |
0.0089 (10.2) |
Patients with Renal Impairment
In a Phase 1, open-label study, tenofovir alafenamide and tenofovir systemic exposures (AUCinf) were evaluated in subjects with severe renal impairment and in subjects with normal renal function (Table 8). In an open-label trial of elvitegravir/cobicistat/emtricitabine/tenofovir alafenamide 150/150/200/10 mg, tenofovir alafenamide and tenofovir AUC were evaluated in a subset of virologically suppressed HIV-1 infected subjects with ESRD receiving chronic hemodialysis (Table 8). In a Phase 2, open-label trial, tenofovir alafenamide and tenofovir AUC were evaluated in a subset of virologically suppressed HBV- infected subjects with ESRD receiving chronic hemodialysis (Table 8) [see Use in Specific Populations (8.6)]. The pharmacokinetics of tenofovir alafenamide were similar among subjects with normal renal function, subjects with severe renal impairment, and subjects with ESRD receiving chronic hemodialysis. Relative to those with normal renal function, increased tenofovir exposures were observed in subjects with severe renal impairment and subjects with ESRD receiving chronic hemodialysis. Within the chronic hemodialysis population, increased tenofovir exposures were observed in subjects with HBV relative to those with HIV.
Table 8 Pharmacokinetics of Tenofovir Alafenamide and its Metabolite Tenofovir in Subjects with Renal Impairment as Compared to Subjects with Normal Renal Function|
Estimated Creatinine Clearance* |
≥90 mL per minute |
15–29 mL per minute |
<15 mL per minute |
<15 mL per minute |
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
CV = coefficient of variation | ||||
Þ ß | ||||
|
Tenofovir alafenamide | ||||
|
AUC (mcg∙hour per mL) |
0.27 (49.2)¶ |
0.51 (47.3)¶ |
0.30 (26.7)# |
0.23 (53.2)# |
|
Cmax (mcg per mL) |
0.20 (62.1) |
0.36 (65.7) |
0.23 (48.4) |
0.25 (75.4) |
|
Tenofovir | ||||
|
AUC (mcg∙hour per mL) |
0.34 (27.2)¶ |
2.07 (47.1)¶ |
18.8 (30.4)Þ |
8.72 (39.4)Þ,ß |
|
Cmax (mcg per mL) |
0.01 (36.5) |
0.03 (32.4) |
0.89 (26.4) |
0.44 (40.9) |
|
C24h (mcg per mL) |
0.004 (25.6) |
0.02 (41.9) |
0.89 (26.4) |
0.26 (73.2)ß |
Patients with Hepatic Impairment
Tenofovir alafenamide and tenofovir pharmacokinetics are similar in subjects with mild (Child-Pugh Class A) hepatic impairment and in subjects with normal hepatic function.
HIV and/or Hepatitis C Virus Coinfection
The pharmacokinetics of tenofovir alafenamide have not been fully evaluated in subjects coinfected with HIV and/or hepatitis C virus.
Drug Interaction Studies
[see Drug Interactions (7)]
The effects of coadministered drugs on the exposure of tenofovir alafenamide are shown in Table 9. The effects of tenofovir alafenamide on the exposure of coadministered drugs are shown in Table 10 [For information regarding clinical recommendations, see Drug Interactions (7)]. Information regarding potential drug-drug interactions with HIV antiretrovirals is not provided (see the prescribing information for emtricitabine/tenofovir alafenamide for interactions with HIV antiretrovirals).
Table 9 Drug Interactions: Changes in Pharmacokinetic Parameters for Tenofovir Alafenamide in the Presence of the Coadministered Drug*|
Coadministered Drug |
Dose of Coadministered Drug (mg) |
Tenofovir Alafenamide (mg) |
N |
Geometric Mean Ratio of TAF Pharmacokinetic Parameters (90% CI)†; | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Cmax |
AUC |
Cmin | ||||
|
NC = not calculated | ||||||
Þ | ||||||
|
Carbamazepine |
300 twice daily |
25 once daily‡ |
26 |
0.43 |
0.45 |
NC |
|
Cobicistat§ |
150 once daily |
8 once daily |
12 |
2.83 |
2.65 |
NC |
|
Ledipasvir/ Sofosbuvir |
90/400 once daily |
25 once daily¶ |
42 |
1.03 |
1.32 |
NC |
|
Sertraline |
50 single dose |
10 once daily# |
19 |
1.00 |
0.96 |
NC |
|
Sofosbuvir/ Velpatasvir/ Voxilaprevir |
400/100/100+100 voxilaprevirÞ once daily |
25 once daily¶ |
30 |
1.32 |
1.52 |
NC |
|
Coadministered Drug |
Dose of Coadministered Drug (mg) |
Tenofovir Alafenamide (mg) |
N |
Geometric Mean Ratio of Coadministered Drug Pharmacokinetic Parameters (90%
CI)†; | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Cmax |
AUC |
Cmin | ||||
|
NC = not calculated | ||||||
Þ ß à | ||||||
|
Ledipasvir |
90 ledipasvir / 400 sofosbuvir once daily |
25 once daily‡ |
41 |
1.01 |
1.02 |
1.02 |
|
Sofosbuvir |
0.96 |
1.05 |
NC | |||
|
GS-331007§ |
1.08 |
1.08 |
1.10 | |||
|
Midazolam¶ |
2.5 single dose orally |
25 once daily |
18 |
1.02 |
1.13 |
NC |
|
1 single dose IV |
0.99 |
1.08 |
NC | |||
|
Norelgestromin |
norgestimate 0.180/0.215/0.250 once daily / ethinyl estradiol 0.025 once daily |
25 once daily# |
29 |
1.17 |
1.12 |
1.16 |
|
Norgestrel |
1.10 |
1.09 |
1.11 | |||
|
Ethinyl estradiol |
1.22 |
1.11 |
1.02 | |||
|
Sertraline |
50 single dose |
10 once dailyÞ |
19 |
1.14 |
0.93 |
NC |
|
Sofosbuvir |
400 once daily |
25 once dailyß |
30 |
0.95 |
1.01 |
NC |
|
GS-331007§ |
1.02 |
1.04 |
NC | |||
|
Velpatasvir |
100 once daily |
1.05 |
1.01 |
1.01 | ||
|
Voxilaprevir |
100+100à once daily |
0.96 |
0.94 |
1.02 |
12.4 Microbiology
Mechanism of Action
Tenofovir alafenamide is a phosphonamidate prodrug of tenofovir (2'-deoxyadenosine monophosphate analog). Tenofovir alafenamide as a lipophilic cell-permeant compound enters primary hepatocytes by passive diffusion and by the hepatic uptake transporters OATP1B1 and OATP1B3. Tenofovir alafenamide is then converted to tenofovir through hydrolysis primarily by carboxylesterase 1 (CES1) in primary hepatocytes. Intracellular tenofovir is subsequently phosphorylated by cellular kinases to the pharmacologically active metabolite tenofovir diphosphate. Tenofovir diphosphate inhibits HBV replication through incorporation into viral DNA by the HBV reverse transcriptase, which results in DNA chain-termination.
Tenofovir diphosphate is a weak inhibitor of mammalian DNA polymerases that include mitochondrial DNA polymerase γ and there is no evidence of toxicity to mitochondria in cell culture.
Antiviral Activity in Cell Culture
The antiviral activity of tenofovir alafenamide was assessed in a transient transfection assay using HepG2 cells against a panel of HBV clinical isolates representing genotypes A-H. The EC50 (50% effective concentration) values for tenofovir alafenamide ranged from 34.7 to 134.4 nM, with an overall mean EC50 value of 86.6 nM. The CC50 (50% cytotoxicity concentration) values in HepG2 cells were greater than 44,400 nM. In cell culture combination antiviral activity studies of tenofovir with the HBV nucleoside reverse transcriptase inhibitors entecavir, lamivudine, and telbivudine, no antagonistic activity was observed.
Resistance in Clinical Trials
Genotypic resistance analysis was performed on paired baseline and on- treatment HBV isolates for subjects who either experienced virologic breakthrough (2 consecutive visits with HBV DNA greater than or equal to 69 IU/mL [400 copies/mL] after having been less than 69 IU/mL, or 1.0-log10 or greater increase in HBV DNA from nadir) through Week 48, or had HBV DNA greater than or equal to 69 IU/mL at early discontinuation at or after Week 24.
In a pooled analysis of treatment-naïve and treatment-experienced subjects receiving VEMLIDY in Trials 108 and 110 [see Clinical Studies (14.2)], treatment-emergent amino acid substitutions in the HBV reverse transcriptase domain, all occurring at polymorphic positions, were observed in some HBV isolates evaluated (5/20); however, no specific substitutions occurred at a sufficient frequency to be associated with resistance to VEMLIDY.
In virologically suppressed subjects receiving VEMLIDY in Trial 4018 [see Clinical Studies (14.3)], no subjects qualified for resistance analysis through 48 weeks of VEMLIDY treatment.
In pediatric Trial 1092, 17/70 subjects in Cohort 1 (aged 12 to less than 18 years) and 7/18 subjects in Cohort 2, Group 1 (aged 6 to less than 12 years) receiving VEMLIDY qualified for resistance analysis at Week 96. Results were obtained from 19/24 qualified subjects. No HBV amino acid substitutions known to be associated with resistance to tenofovir alafenamide were detected through 96 weeks of treatment [see Clinical Studies (14.5)].
Cross-Resistance
The antiviral activity of tenofovir alafenamide was evaluated against a panel of isolates containing substitutions associated with HBV nucleoside reverse transcriptase inhibitor resistance in a transient transfection assay using HepG2 cells. HBV isolates expressing the lamivudine resistance-associated substitutions rtM204V/I (±rtL180M±rtV173L) and expressing the entecavir resistance-associated substitutions rtT184G, rtS202G, or rtM250V in the presence of rtL180M and rtM204V showed less than 2-fold reduced susceptibility (within the inter-assay variability) to tenofovir alafenamide. HBV isolates expressing the rtA181T, rtA181V, or rtN236T single substitutions associated with resistance to adefovir also had less than 2-fold changes in EC50 values; however, the HBV isolate expressing the rtA181V plus rtN236T double substitutions exhibited reduced susceptibility (3.7-fold) to tenofovir alafenamide. The clinical relevance of these substitutions is not known.
HOW SUPPLIED SECTION
16 HOW SUPPLIED/STORAGE AND HANDLING
VEMLIDY tablets containing 25 mg of tenofovir alafenamide are yellow, round, film-coated, debossed with "GSI" on one side and "25" on the other side. Each bottle contains 30 tablets (NDC 61958-2301-1), a silica gel desiccant, polyester coil, and is closed with a child-resistant closure.
Store below 30 °C (86 °F).
- Keep container tightly closed.
- Dispense only in original container.
SPL PATIENT PACKAGE INSERT SECTION
|
This Patient Information has been approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration. |
Revised: 03/2024 |
|
Patient Information | |
|
What is the most important information I should know about VEMLIDY? *Worsening of hepatitis B virus (HBV) infection. Your HBV infection may get worse (flare-up) if you take VEMLIDY and then stop taking it. A "flare-up" is when your HBV infection suddenly returns in a worse way than before. *Do not run out of VEMLIDY. Refill your prescription or talk to your healthcare provider before your VEMLIDY is all gone. *Do not stop taking VEMLIDY without first talking to your healthcare provider. * If you stop taking VEMLIDY, your healthcare provider will need to check your health often and do blood tests regularly for several months to check your liver. Tell your healthcare provider about any new or unusual symptoms you may have after you stop taking VEMLIDY. For more information about side effects, see the section "What are the possible side effects of VEMLIDY?" | |
|
What is VEMLIDY?
It is not known if VEMLIDY is safe and effective in children with chronic HBV infection who are under 6 years of age or weigh less than 55 pounds (25 kg). | |
|
What should I tell my healthcare provider before taking VEMLIDY?
Tell your healthcare provider about all the medicines you take, including
prescription and over-the-counter medicines, vitamins, and herbal supplements.
| |
|
How should I take VEMLIDY?
| |
|
What are the possible side effects of VEMLIDY? *See "What is the most important information I should know about VEMLIDY?" *New or worse kidney problems, including kidney failure. Your healthcare provider should do blood and urine tests to check your kidneys when starting and during treatment with VEMLIDY. Your healthcare provider may tell you to stop taking VEMLIDY if you develop new or worse kidney problems. *Too much lactic acid in your blood (lactic acidosis). Too much lactic acid is a serious but rare medical emergency that can lead to death. Tell your healthcare provider right away if you get these symptoms: weakness or being more tired than usual, unusual muscle pain, being short of breath or fast breathing, stomach pain with nausea and vomiting, cold or blue hands and feet, feel dizzy or lightheaded, or a fast or abnormal heartbeat. *Severe liver problems. In rare cases, severe liver problems can happen that can lead to death. Tell your healthcare provider right away if you get these symptoms: skin or the white part of your eyes turns yellow, dark "tea-colored" urine, light-colored stools, loss of appetite for several days or longer, nausea, or stomach-area pain. The most common side effect of VEMLIDY is headache. Tell your healthcare
provider if you have any side effect that bothers you or that does not go
away. | |
|
How should I store VEMLIDY?
Keep VEMLIDY and all medicines out of reach of children. | |
|
General information about the safe and effective use of VEMLIDY. | |
|
What are the ingredients in VEMLIDY? |
DOSAGE & ADMINISTRATION SECTION
2 DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
2.1 Testing Prior to Initiation of VEMLIDY
Prior to initiation of VEMLIDY, patients should be tested for HIV-1 infection. VEMLIDY alone should not be used in patients with HIV-1 infection [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2)].
Prior to or when initiating VEMLIDY, and during treatment with VEMLIDY on a clinically appropriate schedule, assess serum creatinine, estimated creatinine clearance, urine glucose, and urine protein in all patients. In patients with chronic kidney disease, also assess serum phosphorus [see Warnings and Precautions (5.3)].
2.2 Recommended Dosage in Adults and Pediatric Patients 6 Years of Age and
Older and Weighing at Least 25 kg
The recommended dosage of VEMLIDY in adults and pediatric patients 6 years of age and older and weighing at least 25 kg is one 25 mg tablet taken orally once daily with food [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)].
2.3 Dosage in Patients with Renal Impairment
No dosage adjustment of VEMLIDY is required in patients with estimated creatinine clearance greater than or equal to 15 mL per minute, or in patients with end stage renal disease (ESRD; estimated creatinine clearance below 15 mL per minute) who are receiving chronic hemodialysis. On days of hemodialysis, administer VEMLIDY after completion of hemodialysis treatment.
VEMLIDY is not recommended in patients with ESRD who are not receiving chronic hemodialysis [see Use in Specific Populations (8.6) and Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)].
No data are available to make dose recommendations in pediatric patients with renal impairment.
2.4 Dosage in Patients with Hepatic Impairment
No dosage adjustment of VEMLIDY is required in patients with mild hepatic impairment (Child-Pugh A). VEMLIDY is not recommended in patients with decompensated (Child-Pugh B or C) hepatic impairment [see Use in Specific Populations (8.7) and Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)].
- Testing: Prior to initiation of VEMLIDY, test patients for HIV infection. VEMLIDY alone should not be used in patients with HIV infection. Prior to or when initiating VEMLIDY, and during treatment on a clinically appropriate schedule, assess serum creatinine, estimated creatinine clearance, urine glucose, and urine protein in all patients. Also assess serum phosphorus in patients with chronic kidney disease. (2.1)
- Recommended dosage: 25 mg (one tablet) taken orally once daily with food. (2.2)
- Renal Impairment: VEMLIDY is not recommended in patients with estimated creatinine clearance below 15 mL per minute who are not receiving chronic hemodialysis. In patients on chronic hemodialysis, on hemodialysis days, administer VEMLIDY after hemodialysis. (2.3)
- Hepatic Impairment: VEMLIDY is not recommended in patients with decompensated (Child-Pugh B or C) hepatic impairment. (2.4)
USE IN SPECIFIC POPULATIONS SECTION
8 USE IN SPECIFIC POPULATIONS
8.1 Pregnancy
Pregnancy Exposure Registry
There is a pregnancy exposure registry that monitors pregnancy outcomes in women exposed to VEMLIDY during pregnancy. Healthcare providers are encouraged to register patients by calling the Antiretroviral Pregnancy Registry (APR) at 1-800-258-4263.
Risk Summary
Available data from the APR show no statistically significant difference in the overall risk of birth defects for tenofovir alafenamide (TAF) compared with the background rate for major birth defects of 2.7% in the U.S. reference population of the Metropolitan Atlanta Congenital Defects Program (MACDP) (see Data). The rate of miscarriage is not reported in the APR. The estimated background rate of miscarriage in clinically recognized pregnancies in the U.S. general population is 15% to 20%.
In animal studies, no adverse developmental effects were observed when tenofovir alafenamide was administered during the period of organogenesis at exposure equal to or 51 times (rats and rabbits, respectively) the tenofovir alafenamide exposure at the recommended daily dose of VEMLIDY (see Data). No adverse effects were observed in the offspring when TDF was administered through lactation at tenofovir exposures of approximately 12 times the exposure at the recommended daily dosage of VEMLIDY.
Data
Human Data
Based on prospective reports to the APR of over 1330 exposures to TAF- containing regimens during pregnancy resulting in live births (including over 1080 exposed in the first trimester and over 240 exposed in the second/third trimester), the prevalence of birth defects in live births was 3.9% (95% CI: 2.8% to 5.2%) and 4.8% (95% CI: 2.5% to 8.3%) following first and second/third trimester exposure, respectively, to TAF-containing regimens. Methodologic limitations of the APR include the use of MACDP as the external comparator group. The MACDP population is not disease-specific, evaluates women and infants from a limited geographic area, and does not include outcomes for births that occurred at less than 20 weeks gestation.
Animal Data
Embryonic fetal development studies performed in rats and rabbits revealed no evidence of impaired fertility or harm to the fetus. The embryo-fetal NOAELs (no observed adverse effect level) in rats and rabbits occurred at tenofovir alafenamide exposures similar to and 51 times higher than, respectively, the exposure in humans at the recommended daily dose. Tenofovir alafenamide is rapidly converted to tenofovir; the observed tenofovir exposure in rats and rabbits were 54 (rats) and 85 (rabbits) times higher than human tenofovir exposures at the recommended daily dose.
Tenofovir alafenamide was administered orally to pregnant rats (25, 100, or 250 mg/kg/day) and rabbits (10, 30, or 100 mg/kg/day) through organogenesis (on gestation days 6 through 17, and 7 through 20, respectively). No adverse embryo-fetal effects were observed in rats and rabbits at tenofovir alafenamide exposures approximately similar to (rats) and 51 (rabbits) times higher than the exposure in humans at the recommended daily dose of VEMLIDY. Tenofovir alafenamide is rapidly converted to tenofovir; the observed tenofovir exposures in rats and rabbits were 54 (rats) and 85 (rabbits) times higher than human tenofovir exposures at the recommended daily dose. Since tenofovir alafenamide is rapidly converted to tenofovir and a lower tenofovir exposure in rats and mice was observed after tenofovir alafenamide administration compared to TDF, another prodrug for tenofovir administration, a pre/postnatal development study in rats was conducted only with TDF. Doses up to 600 mg/kg/day were administered through lactation; no adverse effects were observed in the offspring on gestation day 7 [and lactation day 20] at tenofovir exposures of approximately 12 [18] times higher than the exposures in humans at the recommended daily dose of VEMLIDY.
8.2 Lactation
Risk Summary
Data from the published literature report the presence of TAF and tenofovir in human milk. Data from the published literature have not reported adverse effects of TAF on a breastfed child. There are no data on the effects of TAF on milk production.
The developmental and health benefits of breastfeeding should be considered along with the mother's clinical need for VEMLIDY and any potential adverse effects on the breastfed infant from VEMLIDY or from the underlying maternal condition.
8.4 Pediatric Use
The pharmacokinetics, safety, and effectiveness of VEMLIDY for the treatment of chronic HBV infection have been established in pediatric patients between the ages of 6 to less than 18 years and weighing at least 25 kg (N=59) in Trial 1092 up to 96 weeks. No clinically meaningful differences in pharmacokinetics or safety were observed in comparison to those observed in adults [see Adverse Reactions (6.1), Clinical Pharmacology (12.3), and Clinical Studies (14.5)].
Safety and effectiveness of VEMLIDY has not been established in pediatric patients with chronic HBV infection who are less than 6 years of age or weigh less than 25 kg.
8.5 Geriatric Use
In clinical trials, VEMLIDY was administered to 89 subjects aged 65 and over. No clinically significant differences in safety or efficacy have been observed between elderly subjects and subjects between 18 and less than 65 years of age.
8.6 Renal Impairment
No dosage adjustment of VEMLIDY is required in patients with mild, moderate, or severe renal impairment, or in patients with ESRD (estimated creatinine clearance below 15 mL per minute) who are receiving chronic hemodialysis. On days of hemodialysis, administer VEMLIDY after completion of hemodialysis treatment [see Dosage and Administration (2.3)].
The safety and efficacy of VEMLIDY in HBV-infected adult subjects with moderate to severe renal impairment (estimated creatinine clearance between 15 and 59 mL per minute by Cockcroft-Gault method) and ESRD (estimated creatinine clearance of less than 15 mL per minute by Cockcroft-Gault method) receiving chronic hemodialysis were evaluated in 78 and 15 subjects, respectively, in an open-label trial (Trial 4035, Part A). Overall, 98% of subjects achieved HBV DNA <20 IU/mL at Week 24 (Cohort 1, 97%; Cohort 2, 100%) and the safety of VEMLIDY was similar to that observed in clinical trials of VEMLIDY in subjects with compensated liver disease but without renal impairment [see Adverse Reactions (6.1) and Clinical Studies (14.4)].
The safety and efficacy of elvitegravir/cobicistat/emtricitabine/tenofovir alafenamide 150/150/200/10 mg was previously evaluated in 55 virologically suppressed HIV-1 infected subjects with ESRD receiving chronic hemodialysis in an open-label trial (Trial 1825). Tenofovir alafenamide exposures are similar when comparing tenofovir alafenamide 25 mg and tenofovir alafenamide 10 mg as part of elvitegravir/cobicistat/emtricitabine/tenofovir alafenamide.
Among subjects with ESRD receiving chronic hemodialysis and administered tenofovir alafenamide, higher exposures of tenofovir were observed in HBV- infected subjects (Trial 4035 Part A) compared to HIV-infected subjects (Trial 1825). The clinical significance of these higher exposures is not established [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)].
VEMLIDY is not recommended in patients with ESRD (estimated creatinine clearance below 15 mL per minute by Cockcroft-Gault method) who are not receiving chronic hemodialysis as the safety of VEMLIDY has not been established in this population [see Dosage and Administration (2.3) and Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)].
8.7 Hepatic Impairment
No dosage adjustment of VEMLIDY is required in patients with mild hepatic impairment (Child-Pugh A). The safety and efficacy of VEMLIDY in patients with decompensated cirrhosis (Child-Pugh B or C) have not been established; therefore, VEMLIDY is not recommended in patients with decompensated (Child- Pugh B or C) hepatic impairment [see Dosage and Administration (2.4) and Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)].
NONCLINICAL TOXICOLOGY SECTION
13 NONCLINICAL TOXICOLOGY
13.1 Carcinogenesis, Mutagenesis, Impairment of Fertility
Since tenofovir alafenamide is rapidly converted to tenofovir and a lower tenofovir exposure in rats and mice was observed after tenofovir alafenamide administration compared to TDF administration, carcinogenicity studies were conducted only with TDF. Long-term oral carcinogenicity studies of TDF in mice and rats were carried out at exposures up to approximately 10 times (mice) and 4 times (rats) those observed in humans at the 300 mg therapeutic dose of TDF for chronic hepatitis B. The tenofovir exposure in these studies was approximately 151 times (mice) and 50 times (rat) those observed in humans after administration of VEMLIDY treatment. At the high dose in female mice, liver adenomas were increased at tenofovir exposures approximately 151 times those observed after VEMLIDY administration in humans. In rats, the study was negative for carcinogenic findings.
Tenofovir alafenamide was not genotoxic in the reverse mutation bacterial test (Ames test), mouse lymphoma or rat micronucleus assays.
There were no effects on fertility, mating performance or early embryonic development when tenofovir alafenamide was administered to male rats at a dose equivalent to 155 times the human dose based on body surface area comparisons for 28 days prior to mating and to female rats for 14 days prior to mating through Day 7 of gestation.
13.2 Animal Toxicology and/or Pharmacology
Minimal to slight infiltration of mononuclear cells in the posterior uvea was observed in dogs with similar severity after three- and nine-month administration of tenofovir alafenamide; reversibility was seen after a three- month recovery period. At the NOAEL for eye toxicity, the systemic exposure in dogs was 5 (tenofovir alafenamide) and 14 (tenofovir) times the exposure seen in humans at the recommended daily VEMLIDY dosage.
CLINICAL STUDIES SECTION
14 CLINICAL STUDIES
14.1 Description of Clinical Trials
The efficacy and safety of VEMLIDY were evaluated in the trials summarized in Table 11.
Table 11 Trials Conducted with VEMLIDY in Subjects with Chronic HBV Infection|
Trial |
Population |
Trial Arms (N) |
Primary Endpoint |
|---|---|---|---|
|
TE = treatment-experienced, TN = treatment-naive | |||
| |||
|
Trial 108* |
HBeAg-negative TN and TE adults with compensated liver disease |
VEMLIDY (285) |
48 |
|
Trial 110* |
HBeAg-positive TN and TE adults with compensated liver disease |
VEMLIDY (581) |
48 |
|
Trial 4018* |
HBeAg-negative and HBeAg-positive virologically suppressed† adults with compensated liver disease |
VEMLIDY (243) |
48 |
|
Trial 4035 (Part A, Cohort 1)‡ |
Virologically suppressed† adults with moderate to severe renal impairment§ |
VEMLIDY (78) |
24 |
|
Trial 4035 (Part A, Cohort 2)‡ |
Virologically suppressed† adults with ESRD¶ receiving chronic hemodialysis |
VEMLIDY (15) |
24 |
|
Trial 1092# |
Pediatric subjects between the ages of 6 to less than 18 years (at least 25 kg) with compensated liver disease |
VEMLIDY (59) |
24 |
14.2 Clinical Trials in Adults with Chronic Hepatitis B Virus Infection and
Compensated Liver Disease
The efficacy and safety of VEMLIDY in the treatment of adults with chronic hepatitis B virus infection with compensated liver disease are based on 48-week data from two randomized, double-blind, active-controlled trials, Trial 108 (N=425) and Trial 110 (N=873). In both trials, besides trial treatment, subjects were not allowed to receive other nucleosides, nucleotides, or interferon.
In Trial 108, HBeAg-negative treatment-naïve and treatment-experienced subjects with compensated liver disease (no evidence of ascites, hepatic encephalopathy, variceal bleeding, INR <1.5× ULN, total bilirubin <2.5× ULN, and albumin >3.0 mg/dL) were randomized in a 2:1 ratio to receive VEMLIDY 25 mg (N=285) once daily or TDF 300 mg (N=140) once daily for 48 weeks. The mean age was 46 years, 61% were male, 72% were Asian, 25% were White, 2% were Black, and 1% were other races. 24%, 38%, and 31% had HBV genotype B, C, and D, respectively. 21% were treatment experienced [previous treatment with oral antivirals, including entecavir (N=41), lamivudine (N=42), TDF (N=21), or other (N=18)]. At baseline, mean plasma HBV DNA was 5.8 log10 IU/mL, mean serum ALT was 94 U/L, and 9% of subjects had a history of cirrhosis.
In Trial 110, HBeAg-positive treatment-naïve and treatment-experienced subjects with compensated liver disease were randomized in a 2:1 ratio to receive VEMLIDY 25 mg (N=581) once daily or TDF 300 mg (N=292) once daily for 48 weeks. The mean age was 38 years, 64% were male, 82% were Asian, 17% were White, and 1% were Black or other races. 17%, 52%, and 23% had HBV genotype B, C, and D, respectively. 26% were treatment experienced [previous treatment with oral antivirals, including adefovir (N=42), entecavir (N=117), lamivudine (N=84), telbivudine (N=25), TDF (N=70), or other (n=17)]. At baseline, mean plasma HBV DNA was 7.6 log10 IU/mL, mean serum ALT was 120 U/L, and 7% of subjects had a history of cirrhosis.
In both trials, randomization was stratified on prior treatment history (nucleoside naïve or experienced) and baseline HBV DNA (<7, ≥7 to <8, and ≥8 log10 IU/mL in Trial 108; and <8 and ≥8 log10 IU/mL in Trial 110). The efficacy endpoint in both trials was the proportion of subjects with plasma HBV DNA levels below 29 IU/mL at Week 48. Additional efficacy endpoints include the proportion of subjects with ALT normalization, HBsAg loss and seroconversion, and HBeAg loss and seroconversion in Trial 110.
Treatment outcomes of Trials 108 and 110 at Week 48 are presented in Table 12 and Table 13.
Table 12 Trials 108 and 110: HBV DNA Virologic Outcome at Week 48* in Subjects with Chronic HBV Infection and Compensated Liver Disease|
Trial 108 (HBeAg-Negative) |
Trial 110 (HBeAg-Positive) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
VEMLIDY |
TDF |
VEMLIDY |
TDF | |
| ||||
|
HBV DNA |
94% |
93% |
64% |
67% |
|
Treatment Difference† |
1.8% (95% CI = -3.6% to 7.2%) |
-3.6% (95% CI = -9.8% to 2.6%) | ||
|
HBV DNA ≥29 IU/mL |
2% |
3% |
31% |
30% |
|
Baseline HBV DNA | ||||
|
<7 log10 IU/mL |
96% (221/230) |
92% (107/116) |
N/A |
N/A |
|
≥7 log10 IU/mL |
85% (47/55) |
96% (23/24) |
N/A |
N/A |
|
Baseline HBV DNA | ||||
|
<8 log10 IU/mL |
N/A |
N/A |
82% (254/309) |
82% (123/150) |
|
≥8 log10 IU/mL |
43% (117/272) |
51% (72/142) | ||
|
Nucleoside Naïve‡ |
94% (212/225) |
93% (102/110) |
68% (302/444) |
70% (156/223) |
|
Nucleoside Experienced |
93% (56/60) |
93% (28/30) |
50% (69/137) |
57% (39/69) |
|
No Virologic Data at Week 48§ |
4% |
4% |
5% |
3% |
In Trial 108, the proportion of subjects with cirrhosis who achieved HBV DNA <29 IU/mL at Week 48 was 92% (22/24) in the VEMLIDY group and 93% (13/14) in the TDF group. The corresponding proportions in Trial 110 were 63% (26/41) and 67% (16/24) in the VEMLIDY and TDF groups, respectively.
Table 13 Additional Efficacy Parameters at Week 48*|
Trial 108 (HBeAg-Negative) |
Trial 110 (HBeAg-Positive) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
VEMLIDY |
TDF |
VEMLIDY |
TDF | |
|
N/A = not applicable | ||||
| ||||
|
ALT |
83% |
75% |
72% |
67% |
|
Normalized ALT (AASLD)‡ |
50% |
32% |
45% |
36% |
|
Serology |
N/A |
N/A |
14% / 10% |
12% / 8% |
|
HBsAg Loss / Seroconversion |
0 / 0 |
0 / 0 |
1% / 1% |
<1% / 0 |
14.3 Clinical Trials in Virologically Suppressed Adults with Chronic
Hepatitis B Virus Infection Who Switched to VEMLIDY
The efficacy and safety of switching from TDF to VEMLIDY in virologically suppressed adults with chronic hepatitis B virus infection is based on 48-week data from a randomized, double-blind, active-controlled trial, Trial 4018 (N=488). Subjects must have been taking TDF 300 mg once daily for at least 12 months, with HBV DNA less than the Lower Limit of Quantitation by local laboratory assessment for at least 12 weeks prior to screening and HBV DNA <20 IU/mL at screening. Subjects were stratified by HBeAg status (HBeAg-positive or HBeAg-negative) and age (≥50 or <50 years) and randomized in a 1:1 ratio to either switch to VEMLIDY 25 mg once daily (N=243) or stay on TDF 300 mg once daily (N=245). The mean age was 51 years (22% were ≥60 years), 71% were male, 82% were Asian, 14% were White, and 68% were HBeAg-negative. At baseline, median duration of prior TDF treatment was 220 and 224 weeks in the VEMLIDY and TDF groups, respectively. At baseline, mean serum ALT was 27 U/L, and 16% of subjects had a history of cirrhosis.
The primary efficacy endpoint was the proportion of subjects with plasma HBV DNA levels ≥20 IU/mL at Week 48. Additional efficacy endpoints in Trial 4018 included the proportion of subjects with HBV DNA <20 IU/mL, ALT normal and normalization, HBsAg loss and seroconversion, and HBeAg loss and seroconversion.
Treatment outcomes of Trial 4018 at Week 48 are presented in Table 14 and Table 15.
Table 14 Trial 4018: HBV DNA Virologic Outcome at Week 48* in Virologically Suppressed Subjects with Chronic HBV Infection|
VEMLIDY |
TDF | |
|---|---|---|
| ||
|
HBV DNA ≥20 IU/mL† |
<1% |
<1% |
|
Treatment Difference‡ |
0.0% (95% CI = -1.9% to 2.0%) | |
|
HBV DNA <20 IU/mL |
96% |
96% |
|
Treatment Difference‡ |
0.0% (95% CI = -3.7% to 3.7%) | |
|
No Virologic Data at Week 48 |
3% |
3% |
|
Discontinued Study Drug Due to AE or Death and Last Available HBV DNA <20 IU/mL |
1% |
0 |
|
Discontinued Study Drug Due to Other Reasons§ and Last Available HBV DNA <20 IU/mL |
2% |
3% |
|
VEMLIDY |
TDF | |
|---|---|---|
| ||
|
ALT | ||
|
Normal ALT (Central Lab) |
89% |
85% |
|
Normal ALT (AASLD) |
79% |
75% |
|
Normalized ALT (Central Lab)†,‡ |
50% |
37% |
|
Normalized ALT (AASLD)§,¶ |
50% |
26% |
|
Serology | ||
|
HBeAg Loss / Seroconversion# |
8% / 3% |
6% / 0 |
|
HBsAg Loss / Seroconversion |
0 / 0 |
2% / 0 |
14.4 Clinical Trial in Adults with Chronic Hepatitis B Virus Infection and
Renal Impairment
In Trial 4035, Part A, the efficacy and safety of switching from TDF and/or other antivirals to VEMLIDY were evaluated in an open-label clinical trial of virologically suppressed chronic hepatitis B infected adults with moderate to severe renal impairment (estimated creatinine clearance between 15 and 59 mL per minute by Cockcroft-Gault method) (Cohort 1, N=78) or ESRD (estimated creatinine clearance below 15 mL per minute by Cockcroft-Gault method) on hemodialysis (Cohort 2, N=15). At baseline, 98% of subjects in Part A had baseline HBV DNA <20 IU/mL. Median age was 65 years, 74% were male, 77% were Asian, 16% were White, and 83% were HBeAg-negative. Previous treatment with oral antivirals included TDF (Cohort 1, N=57; Cohort 2, N=1), lamivudine (N=46), adefovir dipivoxil (N=46), and entecavir (N=43). At baseline, 97% and 95% of subjects had ALT ≤ULN based on central laboratory criteria and 2018 AASLD criteria, respectively; median estimated creatinine clearance by Cockcroft-Gault was 43 mL per minute (45 mL per minute in Cohort 1 and 7 mL per minute in Cohort 2); and 34% of subjects had a history of cirrhosis.
Overall, 98% of subjects achieved HBV DNA <20 IU/mL at Week 24 (Cohort 1, 97%; Cohort 2, 100%). Two subjects in Cohort 1 discontinued treatment early (due to subject decision); last available HBV DNA for both of these subjects was <20 IU/mL. The overall mean (SD) change from baseline in ALT values was +1 (11.3) U/L (Cohort 1, +1 [11.9] U/L; Cohort 2, +3 [7.9] U/L) at Week 24. No subject had HBeAg or HBsAg loss at Week 24. The mean (SD) changes in HBsAg level from baseline were -0.05 (0.122) log10 IU/mL (-0.05 [0.124] log10 IU/mL for Cohort 1 and -0.07 [0.115] log10 IU/mL for Cohort 2) at Week 24.
14.5 Clinical Trial in Pediatric Subjects 6 Years of Age and Older with
Chronic Hepatitis B Virus Infection
In Trial 1092, the efficacy and safety of VEMLIDY in chronic HBV-infected subjects were evaluated in a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled clinical trial of treatment-naïve and treatment-experienced subjects between the ages of 12 to less than 18 years weighing at least 35 kg (Cohort 1; N=70) and 6 to less than 12 years weighing at least 25 kg (Cohort 2, Group 1; N=18). Subjects were randomized to receive VEMLIDY (N=59) or placebo (N=29) once daily. Baseline demographics and HBV disease characteristics were comparable between the VEMLIDY treatment arm and the placebo arm: in the VEMLIDY group, 58% were male, 63% were Asian, and 27% were White; 9%, 24%, 22%, and 44% had HBV genotype A, B, C, and D, respectively; 98% percent were HBeAg positive. At baseline, overall median HBV DNA was 8.1 log10 IU/mL, mean ALT was 107 U/L, median HBsAg was 4.5 log10 IU/mL. Previous treatment included oral antivirals (N=20 [23%]), including entecavir (N=10 [11%]), lamivudine (N=10 [11%]), and TDF (N=2 [2%]), and/or interferons (N=13 [15%]).
The results for each treatment group and cohort for HBV DNA < 20 IU/mL at Weeks 24, 48 and 96 are presented in Table 16 below.
Table 16 Trial 1092: HBV DNA Virologic Outcome in Pediatric Subjects 6 Years of Age and Older with Chronic HBV|
TAF |
PBO-TAF | |
|---|---|---|
| ||
|
HBV DNA <20 IU/mL at Week 24 (total) |
11/59 (19%) |
0/29 |
|
- Cohort 1 (12– <18 and at least 35 kg) |
10/47 (21%) |
0/23 |
|
- Cohort 2 Group 1 (6– <12 and at least 25 kg) |
1/12 (8%) |
0/6 |
|
HBV DNA <20 IU/mL at Week 48 (total) |
22/59 (37%) |
6/29 (21%)* |
|
- Cohort 1 (12– <18 and at least 35 kg) |
19/47 (40%) |
5/23 (22) |
|
- Cohort 2 Group 1 (6– <12 and at least 25 kg) |
3/12 (25%) |
1/6 (17%) |
|
HBV DNA <20 IU/mL at Week 96 (total) |
36/59 (61%) |
14/29 (48%)† |
|
- Cohort 1 (12– <18 and at least 35 kg) |
30/47 (64%) |
12/23 (52%) |
|
- Cohort 2 Group 1 (6– <12 and at least 25 kg) |
6/12 (50%) |
2/6 (33%) |
At Week 96, the overall mean (SD) change from baseline in HBV DNA for VEMLIDY- treated subjects and subjects who switched from placebo to VEMLIDY, respectively, was -6.18 (1.495) log10 IU/mL and -5.92 (1.775) log10 IU/mL. The overall median change from baseline in ALT values for the VEMLIDY and placebo- VEMLIDY treatment groups, respectively, was -39.5 U/L and -46.5 U/L at Week 96. ALT normalization (AASLD criteria) was achieved for 54% of VEMLIDY-treated subjects and 57% of subjects who switched from placebo to VEMLIDY.
At Week 96, 14/58 (24%) VEMLIDY-treated subjects and 5/29 (17%) subjects who switched from placebo to VEMLIDY experienced HBeAg loss with anti-HBe seroconversion. One of 47 (2%) subjects in the Cohort 1 VEMLIDY group achieved HBsAg loss at Week 96.
INFORMATION FOR PATIENTS SECTION
17 PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATION
Advise the patient to read the FDA-approved patient labeling (Patient Information).
Severe Acute Exacerbation of Hepatitis after Discontinuation of Treatment
Inform patients that discontinuation of anti-hepatitis B therapy, including VEMLIDY, may result in severe acute exacerbations of hepatitis B. Advise the patient to not discontinue VEMLIDY without first informing their healthcare provider [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)].
Risk of Development of HIV-1 Resistance in Patients with HIV-1 Coinfection
Inform patients that if they have or develop HIV infection and are not receiving effective HIV treatment, VEMLIDY may increase the risk of development of resistance to HIV medication [see Dosage and Administration (2.1) and Warnings and Precautions (5.2)].
New Onset or Worsening Renal Impairment
Postmarketing cases of renal impairment, including acute renal failure, have been reported [see Warnings and Precautions (5.3)].
Lactic Acidosis and Severe Hepatomegaly
Lactic acidosis and severe hepatomegaly with steatosis, including fatal cases, have been reported with use of drugs similar to VEMLIDY. Advise patients to contact their healthcare provider immediately and stop VEMLIDY if they develop clinical symptoms suggestive of lactic acidosis or pronounced hepatotoxicity [see Warnings and Precautions (5.4)].
Drug Interactions
Advise patients to report to their healthcare provider the use of any other prescription or non-prescription medication or herbal products including St. John's wort, as VEMLIDY may interact with other drugs [see Drug Interactions (7)].
Missed Dosage
Inform patients that it is important to take VEMLIDY on a regular dosing schedule with food and to avoid missing doses, as it can result in development of resistance [see Dosage and Administration (2.2)].
Pregnancy Registry
Inform patients that there is an antiretroviral pregnancy registry to monitor fetal outcomes of pregnant women exposed to VEMLIDY [see Use in Specific Populations (8.1)].
