Bupropion Hydrochloride
These highlights do not include all the information needed to use HYDROCHLORIDE TABLETS safely and effectively. See full prescribing information for HYDROCHLORIDE TABLETS. BUPROPION HYDROCHLORIDE tablets, for oral use Initial U.S. Approval: 1985
fa5fa0d8-d27f-44e1-8868-dfa7206524e2
HUMAN PRESCRIPTION DRUG LABEL
Aug 26, 2025
Bryant Ranch Prepack
DUNS: 171714327
Products 1
Detailed information about drug products covered under this FDA approval, including NDC codes, dosage forms, ingredients, and administration routes.
Bupropion Hydrochloride
Product Details
FDA regulatory identification and product classification information
FDA Identifiers
Product Classification
Product Specifications
INGREDIENTS (11)
Drug Labeling Information
PACKAGE LABEL.PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL
Bupropion Hydrochloride Tablets 100 mg

BOXED WARNING SECTION
WARNING: SUICIDAL THOUGHTS AND BEHAVIORS
****See full prescribing information for complete boxed warning.
CONTRAINDICATIONS SECTION
4 CONTRAINDICATIONS
- Bupropion hydrochloride tablets are contraindicated in patients with a seizure disorder.
- Bupropion hydrochloride tablets are contraindicated in patients with a current or prior diagnosis of bulimia or anorexia nervosa as a higher incidence of seizures was observed in such patients treated with bupropion hydrochloride tablets [see Warnings and Precautions (5.3)].
- Bupropion hydrochloride tablets are contraindicated in patients undergoing abrupt discontinuation of alcohol, benzodiazepines, barbiturates, and antiepileptic drugs [see Warnings and Precautions (5.3), Drug Interactions (7.3)].
- The use of MAOIs (intended to treat psychiatric disorders) concomitantly with bupropion hydrochloride tablets or within 14 days of discontinuing treatment with bupropion hydrochloride tablets are contraindicated. There is an increased risk of hypertensive reactions when bupropion hydrochloride tablets are used concomitantly with MAOIs. The use of bupropion hydrochloride tablets within 14 days of discontinuing treatment with an MAOI is also contraindicated. Starting bupropion hydrochloride tablets in a patient treated with reversible MAOIs such as linezolid or intravenous methylene blue is contraindicated [see Dosage and Administration (2.4, 2.5), Warnings and Precautions (5.4), Drug Interactions (7.6)].
- Bupropion hydrochloride tablets are contraindicated in patients with known hypersensitivity to bupropion or other ingredients of bupropion hydrochloride tablets. Anaphylactoid/anaphylactic reactions and Stevens-Johnson syndrome have been reported [see Warnings and Precautions (5.8)].
- Seizure disorder. (4, 5.3)
- Current or prior diagnosis of bulimia or anorexia nervosa. (4, 5.3)
- Abrupt discontinuation of alcohol, benzodiazepines, barbiturates, antiepileptic drugs. (4, 5.3)
- Monoamine Oxidase Inhibitors (MAOIs): Do not use MAOIs intended to treat psychiatric disorders with bupropion hydrochloride tablets or within 14 days of stopping treatment with bupropion hydrochloride tablets. Do not use bupropion hydrochloride tablets within 14 days of stopping an MAOI intended to treat psychiatric disorders. In addition, do not start bupropion hydrochloride tablets in a patient who is being treated with linezolid or intravenous methylene blue. (4, 7.6)
- Known hypersensitivity to bupropion or other ingredients of bupropion hydrochloride tablets. (4, 5.8)
ADVERSE REACTIONS SECTION
6 ADVERSE REACTIONS
The following adverse reactions are discussed in greater detail in other sections of the labeling:
- Suicidal thoughts and behaviors in adolescents and young adults [see Boxed Warning, Warnings and Precautions (5.1)]
- Neuropsychiatric symptoms and suicide risk in smoking cessation treatment [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2)]
- Seizure [see Warnings and Precautions (5.3)]
- Hypertension [see Warnings and Precautions (5.4)]
- Activation of mania or hypomania [see Warnings and Precautions (5.5)]
- Psychosis and other neuropsychiatric reactions [see Warnings and Precautions (5.6)]
- Angle-closure glaucoma [see Warnings and Precautions (5.7)]
- Hypersensitivity reactions [see Warnings and Precautions (5.8)]
6.1 Clinical Trials Experience
Because clinical trials are conducted under widely varying conditions, adverse reaction rates observed in the clinical trials of a drug cannot be directly compared with rates in the clinical trials of another drug and may not reflect the rates observed in clinical practice.
Adverse Reactions Leading to Discontinuation of Treatment
Adverse reactions were sufficiently troublesome to cause discontinuation of
treatment with bupropion hydrochloride tablets in approximately 10% of the
2,400 subjects and healthy volunteers who participated in clinical trials
during the product’s initial development. The more common events causing
discontinuation include neuropsychiatric disturbances (3%), primarily
agitation and abnormalities in mental status; gastrointestinal disturbances
(2.1%), primarily nausea and vomiting; neurological disturbances (1.7%),
primarily seizures, headaches, and sleep disturbances; and dermatologic
problems (1.4%), primarily rashes. It is important to note, however, that many
of these events occurred at doses that exceed the recommended daily dose.
Commonly Observed Adverse Reactions
Adverse reactions commonly encountered in subjects treated with bupropion
hydrochloride tablets are agitation, dry mouth, insomnia, headache/migraine,
nausea/vomiting, constipation, tremor, dizziness, excessive sweating, blurred
vision, tachycardia, confusion, rash, hostility, cardiac arrhythmia, and
auditory disturbance.
Table 2 summarizes the adverse reactions that occurred in placebo-controlled trials at an incidence of at least 1% of subjects receiving bupropion hydrochloride tablets and more frequently in these subjects than in the placebo group.
Table 2. Adverse Reactions Reported by at Least 1% of Subjects and at a Greater Frequency than Placebo in Controlled Clinical Trials
|
Adverse Reaction |
Bupropion Hydrochloride |
Placebo**** |
|
Cardiovascular | ||
|
Cardiac arrhythmias |
5.3 |
4.3 |
|
Dizziness |
22.3 |
16.2 |
|
Hypertension |
4.3 |
1.6 |
|
Hypotension |
2.5 |
2.2 |
|
Palpitations |
3.7 |
2.2 |
|
Syncope |
1.2 |
0.5 |
|
Tachycardia |
10.8 |
8.6 |
|
Dermatologic | ||
|
Pruritus |
2.2 |
0.0 |
|
Rash |
8.0 |
6.5 |
|
Gastrointestinal | ||
|
Appetite increase |
3.7 |
2.2 |
|
Constipation |
26.0 |
17.3 |
|
Dyspepsia |
3.1 |
2.2 |
|
Nausea/vomiting |
22.9 |
18.9 |
|
Genitourinary | ||
|
Impotence |
3.4 |
3.1 |
|
Menstrual complaints |
4.7 |
1.1 |
|
Urinary frequency |
2.5 |
2.2 |
|
Musculoskeletal | ||
|
Arthritis |
3.1 |
2.7 |
|
Neurological | ||
|
Akathisia |
1.5 |
1.1 |
|
Cutaneous temperature disturbance |
1.9 |
1.6 |
|
Dry mouth |
27.6 |
18.4 |
|
Excessive sweating |
22.3 |
14.6 |
|
Headache/migraine |
25.7 |
22.2 |
|
Impaired sleep quality |
4.0 |
1.6 |
|
Insomnia |
18.6 |
15.7 |
|
Sedation |
19.8 |
19.5 |
|
Sensory disturbance |
4.0 |
3.2 |
|
Tremor |
21.1 |
7.6 |
|
Neuropsychiatric | ||
|
Agitation |
31.9 |
22.2 |
|
Anxiety |
3.1 |
1.1 |
|
Confusion |
8.4 |
4.9 |
|
Decreased libido |
3.1 |
1.6 |
|
Delusions |
1.2 |
1.1 |
|
Euphoria |
1.2 |
0.5 |
|
Hostility |
5.6 |
3.8 |
|
Nonspecific | ||
|
Fever/chills |
1.2 |
0.5 |
|
Special senses | ||
|
Auditory disturbance |
5.3 |
3.2 |
|
Blurred vision |
14.6 |
10.3 |
|
Gustatory disturbance |
3.1 |
1.1 |
Other Adverse Reactions Observed during the Clinical Development of Bupropion
Hydrochloride Tablets
The conditions and duration of exposure to bupropion hydrochloride tablets
varied greatly, and a substantial proportion of the experience was gained in
open and uncontrolled clinical settings. During this experience, numerous
adverse events were reported; however, without appropriate controls, it is
impossible to determine with certainty which events were or were not caused by
bupropion hydrochloride tablets.
The following enumeration is organized by organ system and describes events in terms of their relative frequency of reporting in the database. The following definitions of frequency are used: Frequent adverse reactions are defined as those occurring in at least 1/100 subjects. Infrequent adverse reactions are those occurring in 1/100 to 1/1,000 subjects, while rare events are those occurring in less than 1/1,000 subjects.
Cardiovascular: Frequent was edema; infrequent were chest pain, electrocardiogram (ECG) abnormalities (premature beats and nonspecific ST-T changes), and shortness of breath/dyspnea; rare were flushing, and myocardial infarction.
Dermatologic: Infrequent was alopecia.
Endocrine: Infrequent was gynecomastia; rare was glycosuria.
Gastrointestinal: Infrequent were dysphagia, thirst disturbance, and liver damage/jaundice; rare was intestinal perforation.
Genitourinary: Frequent was nocturia; infrequent were vaginal irritation, testicular swelling, urinary tract infection, painful erection, and retarded ejaculation; rare were enuresis, and urinary incontinence.
Neurological: Frequent were ataxia/incoordination, seizure, myoclonus, dyskinesia, and dystonia; infrequent were mydriasis, vertigo, and dysarthria; rare were electroencephalogram (EEG) abnormality, and impaired attention.
Neuropsychiatric: Frequent were mania/hypomania, increased libido, hallucinations, decrease in sexual function, and depression; infrequent were memory impairment, depersonalization, psychosis, dysphoria, mood instability, paranoia, and formal thought disorder; rare was suicidal ideation.
Oral Complaints: Frequent was stomatitis; infrequent were toothache, bruxism, gum irritation, and oral edema.
Respiratory: Infrequent were bronchitis and shortness of breath/dyspnea; rare was pulmonary embolism.
Special Senses: Infrequent was visual disturbance; rare was diplopia.
Nonspecific: Frequent were flu-like symptoms; infrequent was nonspecific pain; rare was overdose.
Altered Appetite and Weight****
****A weight loss of greater than 5 lbs. occurred in 28% of subjects
receiving bupropion hydrochloride tablets. This incidence is approximately
double that seen in comparable subjects treated with tricyclics or placebo.
Furthermore, while 35% of subjects receiving tricyclic antidepressants gained
weight, only 9.4% of subjects treated with bupropion hydrochloride tablets
did. Consequently, if weight loss is a major presenting sign of a patient’s
depressive illness, the anorectic and/or weight-reducing potential of
bupropion hydrochloride tablets should be considered.
6.2 Postmarketing Experience
The following adverse reactions have been identified during postapproval use of bupropion hydrochloride tablets and are not described elsewhere in the label. Because these reactions are reported voluntarily from a population of uncertain size, it is not always possible to reliably estimate their frequency or establish a causal relationship to drug exposure.
Body (General)
Arthralgia, myalgia, and fever with rash and other symptoms suggestive of
delayed hypersensitivity. These symptoms may resemble serum sickness [see Warnings and Precautions (5.8)].
Cardiovascular
Hypertension (in some cases severe), orthostatic hypotension, third degree
heart block, and Brugada pattern/syndrome.
Endocrine
Hyponatremia, syndrome of inappropriate antidiuretic hormone secretion,
hyperglycemia, hypoglycemia.
Gastrointestinal
Esophagitis, hepatitis.
Hemic and Lymphatic
Ecchymosis, leukocytosis, leukopenia, thrombocytopenia. Altered PT and/or INR,
infrequently associated with hemorrhagic or thrombotic complications, were
observed when bupropion was coadministered with warfarin.
Musculoskeletal
Muscle rigidity/fever/rhabdomyolysis, muscle weakness.
Nervous System
Aggression, coma, completed suicide, delirium, dream abnormalities, paranoid
ideation, paresthesia, parkinsonism, restlessness, suicide attempt, unmasking
of tardive dyskinesia.
Skin and Sybcutaneous Tissue Disorders
Stevens-Johnson syndrome, angioedema, exfoliative dermatitis, urticaria, acute
generalized exanthematous pustulosis, and drug reaction with eosinophilia and
systemic symptoms (DRESS).
Special Senses
Tinnitus, increased intraocular pressure.
Most common adverse reactions (incidence ≥5% and ≥1% more than placebo rate) are: agitation, dry mouth, constipation, headache/migraine, nausea/vomiting, dizziness, excessive sweating, tremor, insomnia, blurred vision, tachycardia, confusion, rash, hostility, cardiac arrhythmias, and auditory disturbance. (6.1)
To report SUSPECTED ADVERSE REACTIONS, contact Apotex Corp. at 1-800-706-5575 or FDA at 1-800-FDA-1088 orwww.fda.gov/medwatch
SPL MEDGUIDE SECTION
MEDICATION GUIDE
Bupropion Hydrochloride(bue proe' pee on hye'' droe klor' ide)
** Tablets.**
Medication Guide available at https://www.apotex.com/products/us/mg.asp
IMPORTANT: Be sure to read the three sections of this Medication Guide. The first section is about the risk of suicidal thoughts and actions with antidepressant medicines; the second section is about the risk of changes in thinking and behavior, depression and suicidal thoughts or actions with medicines used to quit smoking; and the third section is entitled "What Other Important Information Should I Know About Bupropion Hydrochloride Tablets?"
Antidepressant Medicines, Depression and Other Serious Mental Illnesses, and Suicidal Thoughts or Actions
This section of the Medication Guide is only about the risk of suicidal thoughts and actions with antidepressant medicines.
What is the most important information I should know about antidepressant medicines, depression and other serious mental illnesses, and suicidal thoughts or actions?
1.Antidepressant medicines may increase the risk of suicidal thoughts
or actions in some children, teenagers, or young adults within the first few
months of treatment.
2.** Depression or other serious mental illnesses are the most important
causes of suicidal thoughts and actions. Some people may have a particularly
high risk of having suicidal thoughts or actions.**These includepeople who
have (or have a family history of) bipolar illness (also called manic-
depressive illness) or suicidal thoughts or actions.
**3.**How can I watch for and try to prevent suicidal thoughts and actions
in myself or a family member?
- Pay close attention to any changes, especially sudden changes, in mood, behaviors, thoughts, or feelings. This is very important when an antidepressant medicine is started or when the dose is changed.
- Call your healthcare provider right away to report new or sudden changes in mood, behavior, thoughts, or feelings.
- Keep all follow-up visits with your healthcare provider as scheduled. Call the healthcare provider between visits as needed, especially if you have concerns about symptoms.
Call your healthcare provider right away if you or your family member has any of the following symptoms, especially if they are new, worse, or worry you:
- thoughts about suicide or dying
- attempts to commit suicide
- new or worse depression
- new or worse anxiety
- feeling very agitated or restless
- panic attacks
- trouble sleeping (insomnia)
- new or worse irritability
- acting aggressive, being angry, or violent
- acting on dangerous impulses
- an extreme increase in activity and talking (mania)
- other unusual changes in behavior or mood
What else do I need to know about antidepressant medicines?
***Never stop an antidepressant medicine without first talking to a healthcare provider.**Stopping an antidepressant medicine suddenly can causeother symptoms. ***Antidepressants are medicines used to treat depression and other illnesses.**It is important to discuss all the risks of treating depression and alsothe risks of not treating it. Patients and their families or other caregivers should discuss all treatment choices with the healthcare provider, not just the use of antidepressants. ***Antidepressant medicines have other side effects.**Talk to the healthcareprovider about the side effects of the medicine prescribed for you or your family member. ***Antidepressant medicines can interact with other medicines.**Know all ofthe medicines that you or your family member takes. Keep a list of all medicines to show the healthcare provider. Do not start new medicines without first checking with your healthcare provider.
It is not known if bupropion hydrochloride tablets are safe and effective in children under the age of 18.
Quitting Smoking, Quit-Smoking Medications, Changes in Thinking and Behavior, Depression, and Suicidal Thoughts or Actions
This section of the Medication Guide is only about the risk of changes in thinking and behavior, depression and suicidal thoughts or actions with drugs used to quit smoking. Although bupropion hydrochloride tablets are not a treatment for quitting smoking, it contains the same active ingredient (bupropion hydrochloride) as ZYBAN® which is used to help patients quit smoking.
Talk to your healthcare provider or your family member’s healthcare provider about:
- all risks and benefits of quit-smoking medicines.
- all treatment choices for quitting smoking.
When you try to quit smoking, with or without bupropion, you may have symptoms that may be due to nicotine withdrawal, including
- urge to smoke
- depressed mood
- trouble sleeping
- irritability
- frustration
- anger
- feeling anxious
- difficulty concentrating
- restlessness
- decreased heart rate
- increased appetite
- weight gain
Some people have even experienced suicidal thoughts when trying to quit smoking without medication. Sometimes quitting smoking can lead to worsening of mental health problems that you already have, such as depression.
Some people have had serious side effects while taking bupropion to help them quit smoking, including:
**New or worse mental health problems, such as changes in behavior or thinking, aggression, hostility, agitation, depression, or suicidal thoughts or actions.**Some people had these symptoms when they began taking bupropion, and others developed them after several weeks of treatment, or after stopping bupropion.
These symptoms happened more often in people who had a history of mental health problems before taking bupropion than in people without a history of mental health problems.
Stop taking bupropion**hydrochloride tablets**** and call your healthcare provider right away if you, your family, or caregiver notice any of these symptoms.**Work with your healthcare provider to decide whether you should continue to take bupropion. In many people, these symptoms went away after stopping bupropion, but in some people symptoms continued after stopping bupropion. It is important for you to follow-up with your healthcare provider until your symptoms go away.
Before taking bupropion****hydrochloride tablets, tell your healthcare provider if you have ever had depression or other mental health problems. You should also tell your healthcare provider about any symptoms you had during other times you tried to quit smoking, with or without bupropion.
What Other Important Information Should I Know About Bupropion Hydrochloride Tablets?
*Seizures: There is a chance of having a seizure (convulsion, fit) with bupropion hydrochloride tablets, especially in people: * with certain medical problems. * who take certain medicines.
The chance of having seizures increases with higher doses of bupropion hydrochloride tablets. For more information, see the sections "Who should not take bupropion hydrochloride tablets?" and "What should I tell my healthcare provider before taking bupropion hydrochloride tablets?" Tell your healthcare provider about all of your medical conditions and all the medicines you take. Do not take any other medicines while you are taking bupropion hydrochloride tablets****unless your healthcare provider has said it is okay to take them.
**If you have a seizure while taking bupropion hydrochloride tablets, stop taking the tablets and call your healthcare provider right away.**Do not take bupropion hydrochloride tablets againif you have a seizure.
***High blood pressure (hypertension). Some people get high blood pressure that can be severe, while taking bupropion hydrochloride tablets.**The chance ofhigh blood pressure may be higher if you also use nicotine replacement therapy (such as a nicotine patch) to help you stop smoking (see the section of this Medication Guide called "How should I take bupropion hydrochloride tablets?". ***Manic episodes.**Some people may have periods of mania while takingbupropion hydrochloride tablets, including: * Greatly increased energy * Severe trouble sleeping * Racing thoughts * Reckless behavior * Unusually grand ideas * Excessive happiness or irritability * Talking more or faster than usual
If you have any of the above symptoms of mania, call your healthcare provider.
***Unusual thoughts or behaviors.**Some patients have unusual thoughts orbehaviors while taking bupropion hydrochloride tablets, including delusions (believe you are someone else), hallucinations (seeing or hearing things that are not there), paranoia (feeling that people are against you), or feeling confused. If this happens to you, call your healthcare provider. *Visual problems. * eye pain * changes in vision * swelling or redness in or around the eye
Only some people are at risk for these problems. You may want to undergo an eye examination to see if you are at risk and receive preventative treatment if you are.
***Severe allergic reactions. Some people can have severe allergic reactions to bupropion hydrochloride tablets. Stop taking bupropion hydrochloride tablets and call your healthcare provider right away**if you get a rash, itching, hives, fever,swollen lymph glands, painful sores in the mouth or around the eyes, swelling of the lips or tongue, chest pain, or have trouble breathing. These could be signs of a serious allergic reaction.
What are bupropion hydrochloride tablets?
Bupropion hydrochloride tablets are a prescription medicine used to treat adults with a certain type of depression called major depressive disorder.
Who should not take bupropion hydrochloride tablets?
Do not take bupropion hydrochloride tablets if you
- have or had a seizure disorder or epilepsy.
- have or had an eating disorder such as anorexia nervosa or bulimia. are taking any other medicines that contain bupropion, including ZYBAN***®******** (used to help people stop smoking), WELLBUTRIN SR********®, WELLBUTRIN XL®, APLENZIN®, or FORFIVO XL®********.****Bupropion is the same activeingredient that is in bupropion hydrochloride tablets.
- drink a lot of alcohol and abruptly stop drinking, or use medicines called sedatives (these make you sleepy), benzodiazepines, or anti-seizure medicines, and you stop using them all of a sudden.
- take a monoamine oxidase inhibitor (MAOI). Ask your healthcare provider or pharmacist if you are not sure if you take an MAOI, including the antibiotic linezolid.
- do not take an MAOI within 2 weeks of stopping bupropion hydrochloride tablets unless directed to do so by your healthcare provider.
- do not start bupropion hydrochloride tablets if you stopped taking an MAOI in the last 2 weeks unless directed to do so by your healthcare provider.
- are allergic to the active ingredient in bupropion hydrochloride tablets, bupropion, or to any of the inactive ingredients. See the end of this Medication Guide for a complete list of ingredients in bupropion hydrochloride tablets.
What should I tell my healthcare provider before taking bupropion hydrochloride tablets?
Tell your healthcare provider if you have ever had depression, suicidal thoughts or actions, or other mental health problems. See "Antidepressant Medicines, Depression and Other Serious Mental Illnesses, and Suicidal Thoughts or Actions."
- Tell your healthcare provider about your other medical conditions including if you:
- have liver problems, especially cirrhosis of the liver.
- have kidney problems.
- have, or have had, an eating disorder, such as anorexia nervosa or bulimia.
- have had a head injury.
- have had a seizure (convulsion, fit).
- have a tumor in your nervous system (brain or spine).
- have had a heart attack, heart problems, or high blood pressure.
- are a diabetic taking insulin or other medicines to control your blood sugar.
- drink alcohol.
- abuse prescription medicines or street drugs.
- are pregnant or plan to become pregnant. Talk to your healthcare provider about the risk to your unborn baby if you take bupropion hydrochloride tablets during pregnancy.
- Tell your healthcare provider if you become pregnant or think you are pregnant during treatment with bupropion hydrochloride tablets.
- If you become pregnant during treatment with bupropion hydrochloride tablets, talk to your healthcare provider about registering with the National Pregnancy Registry for Antidepressants. You can register by calling 1-844-405-6185.
- are breastfeeding or plan to breastfeed during treatment with bupropion hydrochloride tablets. Bupropion passes into your milk. Talk to your healthcare provider about the best way to feed your baby during treatment with bupropion hydrochloride tablets.
**Tell your healthcare provider about all the medicines you take, **includingprescription, over-the-counter medicines, vitamins, and herbal supplements. Many medicines increase your chances of having seizures or other serious side effects if you take them while you are taking bupropion hydrochloride tablets.
How should I take bupropion hydrochloride tablets?
- Take bupropion hydrochloride tablets exactly as prescribed by your healthcare provider. Do not change your dose or stop taking bupropion hydrochloride tablets without talking with your healthcare provider first. *Swallow bupropion hydrochloride tablets whole. Do not chew, cut, or crush bupropion hydrochloride tablets.
- Take bupropion hydrochloride tablets at the same time each day.
- Take your doses of bupropion hydrochloride tablets at least 6 hours apart.
- You may take bupropion hydrochloride tablets with or without food.
- If you miss a dose, do not take an extra dose to make up for the dose you missed. Wait and take your next dose at the regular time.**This is very****important.**Too much bupropion hydrochloride tablets can increase your chance of having aseizure.
- If you take too much bupropion hydrochloride tablets, or overdose, call your local emergency room or poison control center right away. *Do not take any other medicines while taking bupropion hydrochloride tablets unless your healthcare provider has told you it is okay.
- If you are taking bupropion hydrochloride tablets for the treatment of major depressive disorder, it may take several weeks for you to feel that bupropion hydrochloride tablets are working. Once you feel better, it is important to keep taking bupropion hydrochloride tablets exactly as directed by your healthcare provider. Call your healthcare provider if you do not feel bupropion hydrochloride tablets are working for you.
What should I avoid while taking bupropion hydrochloride tablets?
- Limit or avoid using alcohol during treatment with bupropion hydrochloride tablets. If you usually drink a lot of alcohol, talk with your healthcare provider before suddenly stopping. If you suddenly stop drinking alcohol, you may increase your risk of having seizures.
- Do not drive a car or use heavy machinery until you know how bupropion hydrochloride tablets affect you. Bupropion hydrochloride tablets can affect your ability to do these things safely.
What are possible side effects of bupropion hydrochloride tablets?
Bupropion hydrochloride tablets can cause serious side effects. See the sections at the beginning of this Medication Guide for information about serious side effects of bupropion hydrochloride tablets.
The most common side effects of bupropion hydrochloride tablets include:
- nervousness
- dry mouth
- constipation
- headache
- nausea or vomiting
- dizziness
- heavy sweating
- shakiness (tremor)
- trouble sleeping
- blurred vision
- fast heartbeat
If you have nausea, take your medicine with food. If you have trouble sleeping, do not take your medicine too close to bedtime.
Tell your healthcare provider right away about any side effects that bother you.
These are not all the possible side effects of bupropion hydrochloride tablets. For more information, ask your healthcare provider or pharmacist.
Call your healthcare provider for medical advice about side effects. You may report side effects to FDA at 1-800-FDA-1088.
You may also report side effects to Apotex Corp. at 1-800-706-5575.
How should I store bupropion hydrochloride tablets?
- Store bupropion hydrochloride tablets at room temperature between 68°F and 77°F (20°C to 25°C).
- Keep bupropion hydrochloride tablets dry and out of the light.
Keep bupropion hydrochloride tablets and all medicines out of the reach of children.
General information about****the safe and effective use of ****bupropion hydrochloride tablets.
Medicines are sometimes prescribed for purposes other than those listed in a Medication Guide. Do not use bupropion hydrochloride tablets for a condition for which it was not prescribed. Do not give bupropion hydrochloride tablets to other people, even if they have the same symptoms you have. It may harm them.
If you take a urine drug screening test, bupropion hydrochloride tablets may make the test result positive for amphetamines. If you tell the person giving you the drug screening test that you are taking bupropion hydrochloride tablets, they can do a more specific drug screening test that should not have this problem.
This Medication Guide summarizes important information about bupropion hydrochloride tablets. If you would like more information, talk with your healthcare provider. You can ask your healthcare provider or pharmacist for information about bupropion hydrochloride tablets that is written for healthcare professionals.
For more information about bupropion hydrochloride tablets, call 1-800-706-5575.
What are the ingredients in bupropion hydrochloride tablets?
Active ingredient: Bupropion hydrochloride.
Inactive ingredients: 75-mg tablet – colloidal silicon dioxide, crospovidone, FD&C Yellow #6 Aluminum Lake, fumaric acid granular, hydroxypropyl cellulose, hypromellose, magnesium stearate, methylcellulose, polyethylene glycol and titanium dioxide.
100-mg tablet – colloidal silicon dioxide, crospovidone, D&C Red #7 Calcium Lake, fumaric acid granular, hydroxypropyl cellulose, hypromellose, magnesium stearate, methylcellulose, polyethylene glycol and titanium dioxide.
This Medication Guide has been approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration.
All registered trademarks in this document are the property of their respective owners.
APOTEX INC.****
BUPROPION HYDROCHLORIDE TABLETS, USP
75 mg and 100 mg
|
Manufactured by |
Manufactured for |
|
Apotex Inc. |
Apotex Corp. |
|
Toronto, Ontario |
Weston, Florida |
|
Canada M9L 1T9 |
USA 33326 |
Revised: May 2024
Revision No. 21
CLINICAL STUDIES SECTION
14 CLINICAL STUDIES
The efficacy of bupropion hydrochloride tablets in the treatment of major depressive disorder was established in two 4-week, placebo-controlled trials in adult inpatients with MDD (Trials 1 and 2 in Table 4) and in one 6-week, placebo-controlled trial in adult outpatients with MDD (Trial 3 in Table 4). In the first trial, the dose range of bupropion hydrochloride tablets was 300 mg to 600 mg/day administered in 3 divided doses; 78% of subjects were treated with doses of 300 mg to 450 mg/day. The trial demonstrated the efficacy of bupropion hydrochloride tablets as measured by the Hamilton Depression Rating Scale (HDRS) total score, the HDRS depressed mood item (Item 1), and the Clinical Global Impressions-severity score (CGI-S). The second trial included 2 doses of bupropion hydrochloride tablets (300 and 450 mg/day) and placebo. This trial demonstrated the effectiveness of bupropion hydrochloride tablets for only the 450-mg/day dose. The efficacy results were statistically significant for the HDRS total score and the CGI-S score, but not for HDRS Item 1. In the third trial, outpatients were treated with 300 mg/day of bupropion hydrochloride tablets. This trial demonstrated the efficacy of bupropion hydrochloride tablets as measured by the HDRS total score, the HDRS Item 1, the Montgomery-Asberg Depression Rating Scale (MADRS), the CGI-S score, and the CGI-Improvement Scale (CGI-I) score. Effectiveness of bupropion hydrochloride tablets in long-term use, that is, for more than 6 weeks, has not been systematically evaluated in controlled trials.
Table 4. Efficacy of Bupropion Hydrochloride Tablets for the Treatment of Major Depressive Disorder
|
Trial |
Treatment Group |
Primary Efficacy Measure: HDRS | |||
|
Mean Baseline****Score (SD) |
LS Mean Score at** Endpoint Visit****(SE)** |
Placebo**-subtracted** | |||
|
Trial 1 |
Bupropion Hydrochloride Tablets |
28.5 (5.1) |
14.9 (1.3) |
-4.7 (-8.8, -0.6) | |
|
Placebo (n = 27) |
29.3 (7.0) |
19.6 (1.6) |
- | ||
|
Mean Baseline****Score (SD) |
LS Mean Change |
Placebo-subtracted | |||
|
Trial 2 |
Bupropion Hydrochloride Tablets |
32.4 (5.9) |
-15.5 (1.7) |
-4.1 | |
|
Bupropion Hydrochloride Tablets |
34.8 (4.6) |
-17.4 (1.7) |
-5.9 (-10.5, -1.4) | ||
|
Placebo (n=39) |
32.9 (5.4) |
-11.5 (1.6) |
- | ||
|
Trial 3 |
Bupropion Hydrochloride Tablets |
26.5 (4.3) |
-12.0 (NA) |
-3.9 (-5.7, -1.0) | |
|
Placebo (n = 106) |
27.0 (3.5) |
-8.7 (NA) |
- |
n: sample size; SD: standard deviation; SE: standard error; LS Mean: least- squares mean; CI: unadjusted confidence interval included for doses that were demonstrated to be effective; NA: not available.
a Difference (drug minus placebo) in least-squares estimates with respect to the primary efficacy parameter. For Trial 1, it refers to the mean score at the endpoint visit; for Trials 2 and 3, it refers to the mean change from baseline to the endpoint visit.
b Doses that are demonstrated to be statistically significantly superior to placebo.
USE IN SPECIFIC POPULATIONS SECTION
8 USE IN SPECIFIC POPULATIONS
8.1 Pregnancy
Pregnancy Exposure Registry
There is an independent pregnancy exposure registry that monitors pregnancy outcomes in women exposed to any antidepressants during pregnancy. Healthcare providers are encouraged to register patients by calling the National Pregnancy Registry for Antidepressants at 1-844-405-6185 or visiting online at
https://womensmentalhealth.org/research/pregnancyregistry/antidepressants/.
Risk Summary
Data from epidemiological studies of pregnant women exposed to bupropion in the first trimester have not identified an increased risk of congenital malformations overall (see Data). There are risks to the mother associated with untreated depression in pregnancy (see Clinical Considerations). When bupropion was administered to pregnant rats during organogenesis, there was no evidence of fetal malformations at doses up to approximately 10 times the maximum recommended human dose (MRHD) of 450 mg/day. When given to pregnant rabbits during organogenesis, non-dose–related increases in incidence of fetal malformations and skeletal variations were observed at doses approximately equal to the MRHD and greater. Decreased fetal weights were seen at doses twice the MRHD and greater (see Animal Data).
The estimated background risk for major birth defects and miscarriage is unknown for the indicated population. All pregnancies have a background risk of birth defect, loss, or other adverse outcomes. In the U.S. general population, the estimated background risk of major birth defects and of miscarriage in clinically recognized pregnancies is 2% to 4% and 15% to 20%, respectively.
Clinical Considerations
Disease-Associated Maternal and/or Embryo/Fetal Risk: A prospective, longitudinal study followed 201 pregnant women with a history of major depressive disorder who were euthymic and taking antidepressants during pregnancy at the beginning of pregnancy. The women who discontinued antidepressants during pregnancy were more likely to experience a relapse of major depression than women who continued antidepressants. Consider the risks to the mother of untreated depression and potential effects on the fetus when discontinuing or changing treatment with antidepressant medications during pregnancy and postpartum.
Data
Human Data: Data from the international bupropion Pregnancy Registry (675 first trimester exposures) and a retrospective cohort study using the United Healthcare database (1,213 first trimester exposures) did not show an increased risk for malformations overall. The Registry was not designed or powered to evaluate specific defects but suggested a possible increase in cardiac malformations.
No increased risk for cardiovascular malformations overall has been observed after bupropion exposure during the first trimester. The prospectively observed rate of cardiovascular malformations in pregnancies with exposure to bupropion in the first trimester from the international Pregnancy Registry was 1.3% (9 cardiovascular malformations/675 first trimester maternal bupropion exposures), which is similar to the background rate of cardiovascular malformations (approximately 1%). Data from the United Healthcare database, which had a limited number of exposed cases with cardiovascular malformations, and a case-control study (6,853 infants with cardiovascular malformations and 5,763 with non-cardiovascular malformations) of self-reported bupropion use from the National Birth Defects Prevention Study (NBDPS) did not show an increased risk for cardiovascular malformations overall after bupropion exposure during the first trimester.
Study findings on bupropion exposure during the first trimester and risk for left ventricular outflow tract obstruction (LVOTO) are inconsistent and do not allow conclusions regarding a possible association. The United Healthcare database lacked sufficient power to evaluate this association; the NBDPS found increased risk for LVOTO (n = 10; adjusted OR = 2.6; 95% CI: 1.2, 5.7), and the Slone Epidemiology case control study did not find increased risk for LVOTO.
Study findings on bupropion exposure during the first trimester and risk for ventricular septal defect (VSD) are inconsistent and do not allow conclusions regarding a possible association. The Slone Epidemiology Study found an increased risk for VSD following first trimester maternal bupropion exposure (n = 17; adjusted OR = 2.5; 95% CI: 1.3, 5) but did not find increased risk for any other cardiovascular malformations studied (including LVOTO as above). The NBDPS and United Healthcare database study did not find an association between first trimester maternal bupropion exposure and VSD.
For the findings of LVOTO and VSD, the studies were limited by the small number of exposed cases, inconsistent findings among studies, and the potential for chance findings from multiple comparisons in case control studies.
Animal Data: In studies conducted in pregnant rats and rabbits, bupropion was administered orally during the period of organogenesis at doses of up to 450 and 150 mg/kg/day, respectively (approximately 10 and 6 times the MRHD, respectively, on a mg/m2 basis). There was no evidence of fetal malformations in rats. When given to pregnant rabbits during organogenesis, non-dose–related increases in incidence of fetal malformations and skeletal variations were observed at the lowest dose tested (25 mg/kg/day, approximately equal to the MRHD on a mg/m2 basis) and greater. Decreased fetal weights were observed at doses of 50 mg/kg/day (approximately 2 times the MRHD on a mg/m2 basis) and greater. No maternal toxicity was evident at doses of 50 mg/kg/day or less.
In a pre-and postnatal development study, bupropion administered orally to pregnant rats at doses of up to 150 mg/kg/day (approximately 3 times the MRHD on a mg/m2 basis) from embryonic implantation through lactation had no effect on pup growth or development.
8.2 Lactation
Risk Summary
Data from published literature report the presence of bupropion and its metabolites in human milk (see Data). There are no data on the effects of bupropion or its metabolites on milk production. Limited data from postmarketing reports have not identified a clear association of adverse reactions in the breastfed infant. The developmental and health benefits of breastfeeding should be considered along with the mother’s clinical need for bupropion hydrochloride tablets and any potential adverse effects on the breastfed child from bupropion hydrochloride tablets or from the underlying maternal condition.
Data
In a lactation study of 10 women, levels of orally dosed bupropion and its active metabolites were measured in expressed milk. The average daily infant exposure (assuming 150 mL/kg daily consumption) to bupropion and its active metabolites was 2% of the maternal weight-adjusted dose. Postmarketing reports have described seizures in breastfed infants. The relationship of bupropion exposure and these seizures is unclear.
8.4 Pediatric Use
Safety and effectiveness in the pediatric population have not been established [see Boxed Warning, Warnings and Precautions (5.1)].
8.5 Geriatric Use
Of the approximately 6,000 subjects who participated in clinical trials with bupropion sustained-release tablets (depression and smoking cessation trials), 275 were aged ≥65 years and 47 were aged ≥75 years. In addition, several hundred subjects aged ≥65 years participated in clinical trials using the immediate-release formulation of bupropion (depression trials). No overall differences in safety or effectiveness were observed between these subjects and younger subjects. Reported clinical experience has not identified differences in responses between the elderly and younger patients, but greater sensitivity of some older individuals cannot be ruled out.
Bupropion is extensively metabolized in the liver to active metabolites, which are further metabolized and excreted by the kidneys. The risk of adverse reactions may be greater in patients with impaired renal function. Because elderly patients are more likely to have decreased renal function, it may be necessary to consider this factor in dose selection; it may be useful to monitor renal function [see Dosage and Administration (2.3), Use in Specific Populations (8.6), Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)].
8.6 Renal Impairment
Consider a reduced dose and/or dosing frequency of bupropion hydrochloride tablets in patients with renal impairment (GFR: less than 90 mL/min). Bupropion and its metabolites are cleared renally and may accumulate in such patients to a greater extent than usual. Monitor closely for adverse reactions that could indicate high bupropion or metabolite exposures [see Dosage and Administration (2.3), Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)].
8.7 Hepatic Impairment
In patients with moderate to severe hepatic impairment (Child-Pugh score: 7 to 15), the maximum dose of bupropion hydrochloride tablets is 75 mg daily. In patients with mild hepatic impairment (Child-Pugh score: 5 to 6), consider reducing the dose and/or frequency of dosing [see Dosage and Administration (2.2), Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)].
DESCRIPTION SECTION
11 DESCRIPTION
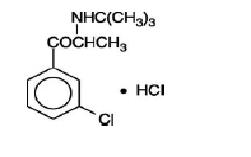
Bupropion hydrochloride, an antidepressant of the aminoketone class, is chemically unrelated to tricyclic, tetracyclic, selective serotonin re-uptake inhibitor, or other known antidepressant agents. Its structure closely resembles that of diethylpropion; it is related to phenylethylamines. It is designated as (±)-1-(3-chlorophenyl)-2-[(1,1-dimethylethyl)amino]-1-propanone hydrochloride. The molecular weight is 276.21 g/mol. The molecular formula is C13H18ClNO•HCl. Bupropion hydrochloride powder is white to off-white crystalline, and highly soluble in water. It has a bitter taste and produces the sensation of local anesthesia on the oral mucosa. The structural formula is:
Bupropion hydrochloride is supplied for oral administration as 75-mg (orange) and 100-mg (purple) film-coated tablets. Each tablet contains the labeled amount of bupropion hydrochloride and the following inactive ingredients:
75-mg tablet –colloidal silicon dioxide, crospovidone, FD&C Yellow #6 Aluminum Lake, fumaric acid granular, hydroxypropyl cellulose, hypromellose, magnesium stearate, methylcellulose, polyethylene glycol and titanium dioxide.
100-mg tablet –colloidal silicon dioxide, crospovidone, D&C Red #7 Calcium Lake, fumaric acid granular, hydroxypropyl cellulose, hypromellose, magnesium stearate, methylcellulose, polyethylene glycol and titanium dioxide.
HOW SUPPLIED SECTION
16 HOW SUPPLIED/STORAGE AND HANDLING
Bupropion hydrochloride tablets, USP 100 mg are available for oral administration as purple, round, unscored, film coated tablets, imprinted "APO" on one side and "BUP" over "100" on the other side.
- NDC 72162-2097-1: 100 Tablets in a BOTTLE.
Store at 20ºC to 25ºC (68ºF to 77ºF); excursions permitted from 15ºC to 30ºC (59ºF to 86ºF) [see USP Controlled Room Temperature]. Protect from moisture.
Store in a tight, light resistant container [see USP].
Repackaged/Relabeled by:
Bryant Ranch Prepack, Inc.
Burbank, CA 91504
INFORMATION FOR PATIENTS SECTION
17 PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATION
Advise the patient to read the FDA-approved patient labeling (Medication Guide).
Suicidal Thoughts and Behaviors
Instruct patients, their families, and/or their caregivers to be alert to the emergence of anxiety, agitation, panic attacks, insomnia, irritability, hostility, aggressiveness, impulsivity, akathisia (psychomotor restlessness), hypomania, mania, other unusual changes in behavior, worsening of depression, and suicidal ideation, especially early during antidepressant treatment and when the dose is adjusted up or down. Advise families and caregivers of patients to observe for the emergence of such symptoms on a day-to-day basis, since changes may be abrupt. Such symptoms should be reported to the patient’s prescriber or healthcare professional, especially if they are severe, abrupt in onset, or were not part of the patient’s presenting symptoms. Symptoms such as these may be associated with an increased risk for suicidal thinking and behavior and indicate a need for very close monitoring and possibly changes in the medication.
Neuropsychiatric Adverse Events and Suicide Risk in Smoking Cessation Treatment
Although bupropion hydrochloride tablets are not indicated for smoking cessation treatment, it contains the same active ingredient as ZYBAN® which is approved for this use. Inform patients that some patients have experienced changes in mood (including depression and mania), psychosis, hallucinations, paranoia, delusions, homicidal ideation, aggression, hostility, agitation, anxiety, and panic, as well as suicidal ideation and suicide when attempting to quit smoking while taking bupropion. Instruct patients to discontinue bupropion and contact a healthcare professional if they experience such symptoms [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2), Adverse Reactions (6.2)].
Severe Allergic Reactions
Educate patients on the symptoms of hypersensitivity and to discontinue bupropion hydrochloride tablets if they have a severe allergic reaction.
Seizure
Instruct patients to discontinue and not restart bupropion hydrochloride tablets if they experience a seizure while on treatment. Advise patients that the excessive use or abrupt discontinuation of alcohol, benzodiazepines, antiepileptic drugs, or sedatives/hypnotics can increase the risk of seizure. Advise patients to minimize or avoid use of alcohol.
Angle-Closure Glaucoma
Patients should be advised that taking bupropion hydrochloride tablets can cause mild pupillary dilation, which in susceptible individuals, can lead to an episode of angle- closure glaucoma. Pre-existing glaucoma is almost always open-angle glaucoma because angle-closure glaucoma, when diagnosed, can be treated definitively with iridectomy. Open-angle glaucoma is not a risk factor for angle-closure glaucoma. Patients may wish to be examined to determine whether they are susceptible to angle closure, and have a prophylactic procedure (e.g., iridectomy), if they are susceptible [see Warnings and Precautions (5.7)].
Bupropion-Containing Products
Educate patients that bupropion hydrochloride tablets contains the same active ingredient (bupropion hydrochloride) found in ZYBAN®, which is used as an aid to smoking cessation treatment, and that bupropion hydrochloride tablets should not be used in combination with ZYBAN® or any other medications that contain bupropion (such as WELLBUTRIN SR®, the sustained-release formulation and WELLBUTRIN XL® or FORFIVO XL®, the extended-release formulations, and APLENZIN®, the extended-release formulation of bupropion hydrobromide). In addition, there are a number of generic bupropion HCl products for the immediate-, sustained-, and extended-release formulations.
Potential for Cognitive and Motor Impairment
Advise patients that any CNS-active drug like bupropion hydrochloride tablets may impair their ability to perform tasks requiring judgment or motor and cognitive skills. Advise patients that until they are reasonably certain that bupropion hydrochloride tablets do not adversely affect their performance, they should refrain from driving an automobile or operating complex, hazardous machinery. Bupropion hydrochloride tablets may lead to decreased alcohol tolerance.
Concomitant Medications
Counsel patients to notify their healthcare provider if they are taking or plan to take any prescription or over-the-counter drugs because bupropion hydrochloride tablets and other drugs may affect each others’ metabolisms.
Pregnancy
Advise patients to notify their healthcare provider if they become pregnant or intend to become pregnant during therapy with bupropion hydrochloride tablets. Advise patients that there is a pregnancy exposure registry that monitors pregnancy outcomes in women exposed to bupropion hydrochloride tablets during pregnancy [see Use in Specific Populations (8.1)].
Storage Information
Instruct patients to store bupropion hydrochloride tablets at room temperature, between 68°F and 77°F (20°C to 25°C) and keep the tablets dry and out of the light.
Administration Information
Instruct patients to take bupropion hydrochloride tablets in equally divided doses 3 or 4 times a day, with doses separated by at least 6 hours to minimize the risk of seizure. Instruct patients if they miss a dose, not to take an extra tablet to make up for the missed dose and to take the next tablet at the regular time because of the dose-related risk of seizure. Instruct patients that bupropion hydrochloride tablets should be swallowed whole and not crushed, divided, or chewed. Bupropion hydrochloride tablets can be taken with or without food.
All registered trademarks in this document are the property of their respective owners.
Dispense with Medication Guide available at https://www.apotex.com/products/us/mg.asp****
APOTEX INC.
BUPROPION HYDROCHLORIDE TABLETS, USP
75 mg and 100 mg
|
Manufactured by |
Manufactured for |
|
Apotex Inc. |
Apotex Corp. |
|
Toronto, Ontario |
Weston, Florida |
|
Canada M9L 1T9 |
USA 33326 |
Rev. 21
