Glimepiride
These highlights do not include all the information needed to use GLIMEPIRIDE TABLETS safely and effectively. See full prescribing information for GLIMEPIRIDE TABLETS. GLIMEPIRIDE tablets for oral use Initial U.S. Approval: 1995
fc359d31-ef3d-4d6f-bd5a-8636f8211aea
HUMAN PRESCRIPTION DRUG LABEL
Jul 11, 2023
Preferred Pharmaceuticals Inc.
DUNS: 791119022
Products 1
Detailed information about drug products covered under this FDA approval, including NDC codes, dosage forms, ingredients, and administration routes.
Glimepiride
Product Details
FDA regulatory identification and product classification information
FDA Identifiers
Product Classification
Product Specifications
INGREDIENTS (6)
Drug Labeling Information
PACKAGE LABEL.PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL
PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL
4 mg :

WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS SECTION
5 WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS
5.1 Hypoglycemia
All sulfonylureas, including glimepiride, can cause severe hypoglycemia [see Adverse Reactions ( 6.1)]. The patient's ability to concentrate and react may be impaired as a result of hypoglycemia. These impairments may present a risk in situations where these abilities are especially important, such as driving or operating other machinery. Severe hypoglycemia can lead to unconsciousness or convulsions and may result in temporary or permanent impairment of brain function or death.
Patients must be educated to recognize and manage hypoglycemia. Use caution when initiating and increasing glimepiride doses in patients who may be predisposed to hypoglycemia (e.g., the elderly, patients with renal impairment, patients on other anti- diabetic medications). Debilitated or malnourished patients, and those with adrenal, pituitary, or hepatic impairment are particularly susceptible to the hypoglycemic action of glucose- lowering medications. Hypoglycemia is also more likely to occur when caloric intake is deficient, after severe or prolonged exercise, or when alcohol is ingested.
Early warning symptoms of hypoglycemia may be different or less pronounced in patients with autonomic neuropathy, the elderly, and in patients who are taking beta-adrenergic blocking medications or other sympatholytic agents. These situations may result in severe hypoglycemia before the patient is aware of the hypoglycemia.
5.2 Hypersensitivity Reactions
There have been postmarketing reports of hypersensitivity reactions in patients treated with glimepiride, including serious reactions such as anaphylaxis, angioedema, and Stevens- Johnson Syndrome [ see Adverse Reactions ( 6.2)]. If a hypersensitivity reaction is suspected, promptly discontinue glimepiride, assess for other potential causes for the reaction, and institute alternative treatment for diabetes.
5.3 Hemolytic Anemia
Sulfonylureas can cause hemolytic anemia in patients with glucose 6-phosphate dehydrogenase (G6PD) deficiency. Because glimepiride is a sulfonylurea, use caution in patients with G6PD deficiency and consider the use of a non- sulfonylurea alternative. There are also postmarketing reports of hemolytic anemia in patients receiving glimepiride who did not have known G6PD deficiency [see Adverse Reactions ( 6.2)].
5.4 Increased Risk of Cardiovascular Mortality with Sulfonylureas
The administration of oral hypoglycemic drugs has been reported to be associated with increased cardiovascular mortality as compared to treatment with diet alone or diet plus insulin. This warning is based on the study conducted by the University Group Diabetes Program (UGDP), a long-term, prospective clinical trial designed to evaluate the effectiveness of glucose-lowering drugs in preventing or delaying vascular complications in patients with non-insulin-dependent diabetes. The study involved 823 patients who were randomly assigned to one of four treatment groups.
UGDP reported that patients treated for 5 to 8 years with diet plus a fixed dose of tolbutamide (1.5 grams per day) had a rate of cardiovascular mortality approximately 2 and a half times that of patients treated with diet alone. A significant increase in total mortality was not observed, but the use of tolbutamide was discontinued based on the increase in cardiovascular mortality, thus limiting the opportunity for the study to show an increase in overall mortality. Despite controversy regarding the interpretation of these results, the findings of the UGDP study provide an adequate basis for this warning. The patient should be informed of the potential risks and advantages of glimepiride and of alternative modes of therapy.
Although only one drug in the sulfonylurea class (tolbutamide) was included in this study, it is prudent from a safety standpoint to consider that this warning may also apply to other oral hypoglycemic drugs in this class, in view of their close similarities in mode of action and chemical structure.
5.5 Macrovascular Outcomes
There have been no clinical studies establishing conclusive evidence of macrovascular risk reduction with glimepiride or any other anti-diabetic drug.
•
Hypoglycemia: May be severe. Ensure proper patient selection, dosing, and instructions, particularly in at-risk populations (e.g., elderly, renally impaired) and when used with other anti-diabetic medications ( 5.1).
•
Hypersensitivity Reactions: Postmarketing reports include anaphylaxis, angioedema and Stevens-Johnson Syndrome. If a reaction is suspected, promptly discontinue glimepiride, assess for other potential causes for the reaction, and institute alternative treatment for diabetes. ( 5.2).
•
Hemolytic Anemia: Can occur if glucose 6-phosphate dehydrogenase (G6PD) deficient. Consider a non-sulfonylurea alternative. ( 5.3).
•
Potential Increased Risk of Cardiovascular Mortality with Sulfonylureas: Inform patient of risks, benefits and treatment alternatives. ( 5.4).
•
Macrovascular Outcomes: No clinical studies establishing conclusive evidence of macrovascular risk reduction with glimepiride or any other anti-diabetic drug ( 5.5).
DOSAGE & ADMINISTRATION SECTION
2 DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
2.1 Recommended Dosing
Glimepiride tablets should be administered with breakfast or the first main meal of the day.
The recommended starting dose of glimepiride tablet is 1 mg or 2 mg once daily. Patients at increased risk for hypoglycemia (e.g., the elderly or patients with renal impairment) should be started on 1 mg once daily [see Warnings and Precautions ( 5.1) and Use in Specific Populations ( 8.5, 8.6)].
After reaching a daily dose of 2 mg, further dose increases can be made in increments of 1 mg or 2 mg based upon the patient’s glycemic response. Uptitration should not occur more frequently than every 1 to 2 weeks. A conservative titration scheme is recommended for patients at increased risk for hypoglycemia [see Warnings and Precautions ( 5.1) and Use in Specific Populations ( 8.5, 8.6)].
The maximum recommended dose is 8 mg once daily.
Patients being transferred to glimepiride from longer half-life sulfonylureas (e.g., chlorpropamide) may have overlapping drug effect for 1 to 2 weeks and should be appropriately monitored for hypoglycemia.
When colesevelam is coadministered with glimepiride, maximum plasma concentration and total exposure to glimepiride is reduced. Therefore, glimepiride should be administered at least 4 hours prior to colesevelam.
•
Recommended starting dose is 1 or 2 mg once daily. Increase in 1 or 2 mg increments no more frequently than every 1 to 2 weeks based on glycemic response. Maximum recommended dose is 8 mg once daily. ( 2.1)
•
Administer with breakfast or first meal of the day. ( 2.1)
•
Use 1 mg starting dose and titrate slowly in patients at increased risk for hypoglycemia (e.g., elderly, patients with renal impairment). ( 2.1 )
DESCRIPTION SECTION
11 DESCRIPTION
Glimepiride is an oral sulfonylurea that contains the active ingredient glimepiride. Chemically, glimepiride is identified as 1-[[p-[2-(3-ethyl-4-methyl-2-oxo-3-pyrroline-1‑carboxamido) ethyl]phenyl]sulfonyl]-3-(trans-4-methylcyclohexyl)urea (C 24H 34N 4O 5S) with a molecular weight of 490.62. Glimepiride is a white to yellowish-white, crystalline, odorless to practically odorless powder and is practically insoluble in water.
The structural formula is:
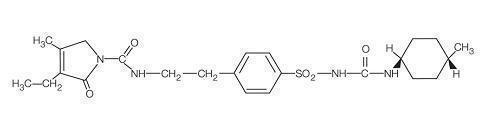
Glimepiride tablets, USP contain the active ingredient glimepiride and the following inactive ingredients: lactose monohydrate, sodium starch glycolate, povidone, and magnesium stearate. In addition, glimepiride tablets, USP 1 mg contain ferric oxide red, glimepiride tablets, USP 2 mg contain ferric oxide yellow and FD &C blue #2 aluminum lake, and glimepiride tablets, USP 4 mg contain FD&C blue #2 aluminum lake.
NONCLINICAL TOXICOLOGY SECTION
13NONCLINICAL TOXICOLOGY
13.1 Carcinogenesis, Mutagenesis, and Impairment of Fertility
Studies in rats at doses of up to 5000 parts per million (ppm) in complete feed (approximately 340 times the maximum recommended human dose, based on surface area) for 30 months showed no evidence of carcinogenesis. In mice, administration of glimepiride for 24 months resulted in an increase in benign pancreatic adenoma formation that was dose-related and was thought to be the result of chronic pancreatic stimulation.
No adenoma formation in mice was observed at a dose of 320 ppm in complete feed, or 46 to 54 mg/kg body weight/day. This is at least 28 times the maximum human recommended dose of 8 mg once daily based on surface area.
Glimepiride was non-mutagenic in a battery ofin vitro and in vivo mutagenicity studies (Ames test, somatic cell mutation, chromosomal aberration, unscheduled DNA synthesis, and mouse micronucleus test).
There was no effect of glimepiride on male mouse fertility in animals exposed up to 2500 mg/kg body weight (>1,500 times the maximum recommended human dose based on surface area). Glimepiride had no effect on the fertility of male and female rats administered up to 4000 mg/kg body weight (approximately 4,000 times the maximum recommended human dose based on surface area).
INFORMATION FOR PATIENTS SECTION
17 PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATION
Hypoglycemia
Explain the symptoms and treatment of hypoglycemia as well as conditions that predispose to hypoglycemia. Inform patients that their ability to concentrate and react may be impaired as a result of hypoglycemia and that this may present a risk in situations where these abilities are especially important, such as driving or operating other machinery [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)].
Hypersensitivity Reactions
Inform patients that hypersensitivity reactions may occur with glimepiride and that if a reaction occurs to seek medical treatment and discontinue glimepiride [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2)].
Pregnancy
Advise females of reproductive potential to inform their prescriber of a known or suspected pregnancy [see Use in Specific Populations (8.1)].
Lactation
Advise breastfeeding women taking glimepiride to monitor breastfed infants for signs of hypoglycemia (e.g., jitters, cyanosis, apnea, hypothermia, excessive sleepiness, poor feeding, seizures) [see Use in Specific Populations (8.2)].
**Manufactured For:**
Accord Healthcare, Inc.,
1009 Slater Road,
Suite 210-B,
Durham, NC 27703,
USA.
10 1677 2 693003
Issued February 2019
Repackaged By: Preferred Pharmaceuticals Inc.
