Osmitrol
These highlights do not include all the information needed to use OSMITROL safely and effectively. See full prescribing information for OSMITROL. OSMITROL (mannitol injection), for intravenous useInitial U.S. Approval: 1964
0d914965-7001-45cb-ba51-d7c5964b05bc
HUMAN PRESCRIPTION DRUG LABEL
Nov 15, 2018
Baxter Healthcare Corporation
DUNS: 005083209
Products 4
Detailed information about drug products covered under this FDA approval, including NDC codes, dosage forms, ingredients, and administration routes.
Mannitol
Product Details
FDA regulatory identification and product classification information
FDA Identifiers
Product Classification
Product Specifications
INGREDIENTS (4)
Mannitol
Product Details
FDA regulatory identification and product classification information
FDA Identifiers
Product Classification
Product Specifications
INGREDIENTS (4)
Mannitol
Product Details
FDA regulatory identification and product classification information
FDA Identifiers
Product Classification
Product Specifications
INGREDIENTS (4)
Mannitol
Product Details
FDA regulatory identification and product classification information
FDA Identifiers
Product Classification
Product Specifications
INGREDIENTS (4)
Drug Labeling Information
WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS SECTION
5 WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS
5.1 Hypersensitivity Reactions
Serious hypersensitivity reactions, including anaphylaxis, hypotension and dyspnea resulting in cardiac arrest and death have been reported with OSMITROL [see Adverse Reactions (6)].
Stop the infusion immediately if signs or symptoms of a suspected hypersensitivity reaction develop. Initiate appropriate therapeutic countermeasures as clinically indicated.
5.2 Renal Complications Including Renal Failure
Renal complications, including irreversible renal failure have been reported in patients receiving mannitol. Reversible, oliguric acute kidney injury (AKI) has occurred in patients with normal pretreatment renal function who received large intravenous doses of mannitol. Although the osmotic nephrosis associated with mannitol administration is in principle reversible, osmotic nephrosis in general is known to potentially proceed chronic or even end-stage renal failure. Monitor renal function closely, including signs of urine output reduction, during OSMITROL infusion. Patients with pre-existing renal disease, patients with conditions that put them at high risk for renal failure, or those receiving potentially nephrotoxic drugs or other diuretics, are at increased risk of renal failure following administration of OSMITROL. Avoid concomitant administration of nephrotoxic drugs (e.g., aminoglycosides) or, other diuretics with OSMITROL, if possible [see Drug Interactions (7.1, 7.2)].
Patients with oliguric AKI who subsequently develop anuria while receiving mannitol are at risk of congestive heart failure, pulmonary edema, hypertensive crisis, coma and death.
During and following OSMITROL infusion for the reduction in intracranial pressure, monitor the patient clinically and laboratory tests for changes in fluid and electrolyte status. Discontinue OSMITROL if renal function worsens. [see Warnings and Precautions (5.5)].
5.3 Central Nervous System (CNS) Toxicity
CNS toxicity manifested by, e.g., confusion, lethargy, coma has been reported in patients treated with mannitol, some resulting in death, in particular in the presence of impaired renal function CNS toxicity may result from high serum mannitol concentrations, serum hyperosmolarity resulting in intracellular dehydration within CNS, hyponatremia or other disturbances of electrolyte and acid/base balance secondary to mannitol administration [see Warnings and Precautions (5.4)].
At high concentrations, mannitol may cross the blood brain barrier and interfere with the ability of the brain to maintain the pH of the cerebrospinal fluid especially in the presence of acidosis.
In patients with preexisting compromise of the blood brain barrier, the risk of increasing cerebral edema (general and focal) associated with repeated or continued use of OSMITROL must be individually weighed against the expected benefits.
A rebound increase of intracranial pressure may occur several hours after the infusion. Patients with a compromised blood brain barrier are at increased risk.
Concomitant administration of neurotoxic drugs (e.g., aminoglycosides) with OSMITROL may potentiate neurotoxicity. Avoid concomitant use of neurotoxic drugs, if possible [see Drug Interactions (7.3)].
During and following OSMITROL infusion for the reduction in intracranial pressure, monitor the patient clinically and laboratory tests for changes in fluid and electrolyte status. Discontinue OSMITROL if CNS toxicity develops [see Warnings and Precautions (5.5)].
5.4 Fluid and Electrolyte Imbalances, Hyperosmolarity
Depending on dosage and duration, administration of OSMITROL may result in hypervolemia leading to or exacerbating existing congestive heart failure. Accumulation of mannitol due to insufficient renal excretion increases the risk of hypervolemia. Mannitol-induced osmotic diuresis may cause or worsen dehydration/hypovolemia and hemoconcentration. Administration of OSMITROL may also cause hyperosmolarity [see Description (11)].
Depending on dosage and duration of administration, electrolyte and acid/base imbalances may also result from transcellular shifts in water and electrolytes, osmotic diuresis and/or other mechanisms. Such imbalances may be severe and potentially fatal.
Imbalances that may result from OSMITROL administration include:
•
Hypernatremia, dehydration and hemoconcentration
•
Hyponatremia, which can lead to headache, nausea, seizures, lethargy, coma, cerebral edema, and death. Acute symptomatic hyponatremic encephalopathy is considered a medical emergency.
•
Hypo/hyperkalemia. The development of electrolyte imbalances (e.g., hyperkalemia, hypokalemia) associated with mannitol administration may result in cardiac adverse reactions in patients receiving drugs that are sensitive to such imbalances (e.g., digoxin, agents that may cause QT prolongation, neuromuscular blocking agents) [see Drug Interactions (7.4)].
•
Other electrolyte disturbances
•
Metabolic acidosis/alkalosis
Pediatric patients less than two years of age, particularly preterm and term neonates, may be at higher risk for fluid and electrolyte abnormalities following OSMITROL administration due to decreased glomerular filtration rate and limited ability to concentrate urine [see Use in Specific Populations (8.4)].
During and following OSMITROL infusion for the reduction in intracranial pressure, monitor fluid and electrolyte status and discontinue OSMITROL if imbalances occur [see Warnings and Precautions (5.5)].
5.5 Monitoring/Laboratory Tests
During and following OSMITROL infusion for the reduction in intracranial pressure, monitor:
•
serum osmolarity, serum electrolytes (including sodium, potassium, calcium and phosphate) and acid base balance,
•
the osmol gap
•
signs of hypo- or hypervolemia, including urine output
•
renal, cardiac and pulmonary function
•
intracranial pressure
Discontinue OSMITROL if renal, cardiac, or pulmonary status worsens or CNS toxicity develops [see Contraindications (4)].
5.6 Infusion Site Reactions
The infusion of hypertonic solutions through a peripheral vein, including OSMITROL at a concentration of 10% w/v or greater, may result in peripheral venous irritation, including phlebitis. Other severe infusion site reactions, such as compartment syndrome and swelling associated with extravasation, can occur with administration of OSMITROL [see Adverse Reactions (6)]. OSMITROL is preferably for administration into a large central vein [see Dosage and Administration (2.1)].
5.7 Interference with Laboratory Tests
High concentrations of mannitol can cause false low results for inorganic phosphorus blood concentrations [see Drug Interactions (7.6)].
Mannitol may produce false positive results in tests for blood ethylene glycol concentrations [see Drug Interactions (7.6)].
•
Hypersensitivity Reactions, including anaphylaxis: Stop infusion immediately if hypersensitivity reactions develop. (5.1)
•
Renal Complications Including Renal Failure: Risk factors include pre-existing renal failure, concomitant use of nephrotoxic drugs or other diuretics. Avoid use of nephrotoxic drugs. Discontinue OSMITROL if renal function worsens. (5.2, 8.6)
•
Central Nervous System (CNS) Toxicity: Confusion, lethargy and coma may occur during or after infusion. Concomitant neurotoxic drugs may potentiate toxicity. Avoid use of neurotoxic drugs. Discontinue OSMITROL if CNS toxicity develops. (5.3)
•
Fluid and Electrolyte Imbalances, Hyperosmolarity: Hypervolemia may exacerbate congestive heart failure, hyponatremia can lead to encephalopathy; hypo/hyperkalemia can result in cardiac adverse reactions in sensitive patients. Discontinue OSMITROL if fluid and/or electrolyte imbalances occur. (5.4)
•
Monitoring/Laboratory Tests: Monitor fluid and electrolytes, serum osmolarity and renal, cardiac and pulmonary function. Discontinue if toxicity develops. (5.5)
•
Infusion Site Reactions: May include irritation and inflammation, as well as severe reactions (compartment syndrome) when associated with extravasation. (5.6)
•
Interference with Laboratory Tests: High concentrations of mannitol may cause false low results of inorganic phosphorus blood concentrations. Mannitol may produce false positive results for blood ethylene glycol. (5.7, 7.6)
OVERDOSAGE SECTION
10 OVERDOSAGE
Signs and symptoms of overdose with OSMITROL include renal failure and AKI, hypo/hypervolemia, hyperosmolarity and electrolyte imbalances, CNS toxicity (e.g., coma, seizures), some of which can be fatal [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2, 5.3, 5.4)].
Management of overdosage with OSMITROL is symptomatic and supportive. Discontinue the infusion and institute appropriate corrective measures with particular attention to renal, cardiac and pulmonary systems. Correct fluid and electrolyte imbalances.
OSMITROL is dialyzable (hemodialysis and peritoneal dialysis), hemodialysis may increase OSMITROL elimination.
DESCRIPTION SECTION
11 DESCRIPTION
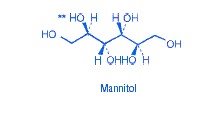
OSMITROL is a sterile, nonpyrogenic solution of Mannitol, USP in a single-dose flexible container for intravenous administration as an osmotic diuretic. It contains no antimicrobial agents. Mannitol is a six carbon sugar alcohol prepared commercially by the reduction of dextrose. The pH is adjusted with sodium hydroxide or hydrochloric acid. Composition, osmolarity, and pH are shown in Table 1.
| ||||
|
Table 11 |
Size |
Composition |
*Osmolarity |
pH |
|
(mL) |
Mannitol, USP |
(mOsmol/L) | ||
|
5% |
1000 |
50 |
274 |
5.0 |
|
10% |
500 |
100 |
549 |
5.0 |
|
15% |
500 |
150 |
823 |
5.0 |
|
20% |
250 |
200 |
1098 |
5.0 |
|
500 |
The plastic container is fabricated from a specially formulated polyvinyl chloride (PL 146 Plastic). The amount of water that can permeate from inside the container into the overwrap is insufficient to affect the solution significantly. Solutions in contact with the plastic container can leach out certain of its chemical components in very small amounts within the expiration period, e.g., di-2-ethylhexyl phthalate (DEHP), up to 5 parts per million. However, the safety of the plastic has been confirmed in tests in animals according to USP biological tests for plastic containers as well as by tissue culture toxicity studies.
CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY SECTION
12 CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY
12.1 Mechanism of Action
Mannitol, when administered intravenously, exerts its osmotic diuretic effect as a solute of relatively small molecular size being largely confined to the extracellular space. Mannitol hinders tubular reabsorption of water and enhances excretion of sodium and chloride by elevating the osmolarity of the glomerular filtrate.
This increase in extracellular osmolarity affected by the intravenous administration of mannitol will induce the movement of intracellular water to the extracellular and vascular spaces. This action underlies the role of mannitol in reducing intracranial pressure, intracranial edema, and intraocular pressure.
12.3 Pharmacokinetics
Distribution
Mannitol distributes largely in the extracellular space in 20 to 40 minutes after intravenous administration. The volume of distribution of mannitol is approximately 17 L in adults.
Elimination
In subjects with normal renal function, the total clearance is 87 to 109 mL/min. The elimination half-life of mannitol is 0.5 to 2.5 hours.
Metabolism
Only relatively small amount of the dose administered is metabolized after intravenous administration of mannitol to healthy subjects.
Excretion
Mannitol is eliminated primarily via the kidneys in unchanged form. Mannitol is filtered by the glomeruli, exhibits less than 10% of tubular reabsorption, and is not secreted by tubular cells. Following intravenous administration, approximately 80% of an administered dose of mannitol is estimated to be excreted in the urine in three hours with lesser amounts thereafter.
Specific Populations
Patients with Renal Impairment
In patients with renal impairment, the elimination half-life of mannitol is prolonged. In a published study, in patients with renal impairment including acute renal failure and end stage renal failure, the elimination half-life of mannitol was estimated at about 36 hours, based on serum osmolarity. In patients with renal impairment on dialysis, the elimination half-life of mannitol was reduced to 6 and 21 hours during hemodialysis and peritoneal dialysis, respectively. [see Use in Specific Populations (8.6), Overdosage (10)].
HOW SUPPLIED SECTION
16 HOW SUPPLIED/STORAGE AND HANDLING
OSMITROL injection is supplied in single-dose, flexible VIAFLEX plastic containers and is available as follows:
|
Code |
Size (mL) |
NDC |
Product Name |
|
2D5604 |
1000 |
0338-0351-04 |
5% (0.05 g/mL mannitol, USP) |
|
2D5613 |
500 |
0338-0353-03 |
10% (0.1 g/mL mannitol, USP) |
|
2D5623 |
500 |
0338-0355-03 |
15% (0.15 g/mL mannitol, USP) |
|
2D5632 |
250 |
0338-0357-02 |
20% (0.2 g/mL mannitol, USP) |
|
2D5633 |
500 |
0338-0357-03 |
20% (0.2 g/mL mannitol, USP) |
Do not remove container from overwrap until intended for use.
Exposure of pharmaceutical products to heat should be minimized. Avoid excessive heat. Store at room temperature (25°C); brief exposure up to 40°C does not adversely affect the product.
