Levothyroxine Sodium
These highlights do not include all the information needed to use LEVOTHYROXINE SODIUM TABLETS safely and effectively. See full prescribing information for LEVOTHYROXINE SODIUM TABLETS. LEVOTHYROXINE SODIUM tablets, for oral use Initial U.S. Approval: 2002
489ffba8-983e-478f-8f62-fe08bf3d0e0b
HUMAN PRESCRIPTION DRUG LABEL
Aug 4, 2023
Bryant Ranch Prepack
DUNS: 171714327
Products 1
Detailed information about drug products covered under this FDA approval, including NDC codes, dosage forms, ingredients, and administration routes.
Levothyroxine Sodium
Product Details
FDA regulatory identification and product classification information
FDA Identifiers
Product Classification
Product Specifications
INGREDIENTS (8)
Drug Labeling Information
WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS SECTION
5 WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS
**5.1 Cardiac Adverse Reactions in the Elderly and in Patients with
Underlying Cardiovascular Disease**
Over-treatment with levothyroxine may cause an increase in heart rate, cardiac wall thickness, and cardiac contractility and may precipitate angina or arrhythmias, particularly in patients with cardiovascular disease and in elderly patients. Initiate levothyroxine sodium tablets therapy in this population at lower doses than those recommended in younger individuals or in patients without cardiac disease [see Dosage and Administration (2.3), Use in Specific Populations (8.5). Monitor for cardiac arrhythmias during surgical procedures in patients with coronary artery disease receiving suppressive levothyroxine sodium tablets therapy. Monitor patients receiving concomitant levothyroxine sodium tablets and sympathomimetic agents for signs and symptoms of coronary insufficiency. If cardiac symptoms develop or worsen, reduce the levothyroxine sodium tablets dose or withhold for one week and restart at a lower dose. ## 5.2 Myxedema Coma Myxedema coma is a life-threatening emergency characterized by poor circulation and hypometabolism, and may result in unpredictable absorption of levothyroxine sodium from the gastrointestinal tract. Use of oral thyroid hormone drug products is not recommended to treat myxedema coma. Administer thyroid hormone products formulated for intravenous administration to treat myxedema coma. ## 5.3 Acute Adrenal Crisis in Patients with Concomitant Adrenal Insufficiency Thyroid hormone increases metabolic clearance of glucocorticoids. Initiation of thyroid hormone therapy prior to initiating glucocorticoid therapy may precipitate an acute adrenal crisis in patients with adrenal insufficiency. Treat patients with adrenal insufficiency with replacement glucocorticoids prior to initiating treatment with levothyroxine sodium tablets [see Contraindications (4)].
**5.4 Prevention of Hyperthyroidism or Incomplete Treatment of
Hypothyroidism**
Levothyroxine sodium tablets has a narrow therapeutic index. Over- or undertreatment with levothyroxine sodium tablets may have negative effects on growth and development, cardiovascular function, bone metabolism, reproductive function, cognitive function, emotional state, gastrointestinal function, and glucose and lipid metabolism. Titrate the dose of levothyroxine sodium tablets carefully and monitor response to titration to avoid these effects [see Dosage and Administration (2.4). Monitor for the presence of drug or food interactions when using levothyroxine sodium tablets and adjust the dose as necessary [see Drug Interactions (7.9) and Clinical Pharmacology (12.3). ## 5.5 Worsening of Diabetic Control Addition of levothyroxine therapy in patients with diabetes mellitus may worsen glycemic control and result in increased antidiabetic agent or insulin requirements. Carefully monitor glycemic control after starting, changing, or discontinuing levothyroxine sodium tablets [see Drug Interactions (7.2)].
**5.6 Decreased Bone Mineral Density Associated with Thyroid Hormone Over-
Replacement**
Increased bone resorption and decreased bone mineral density may occur as a result of levothyroxine over-replacement, particularly in post-menopausal women. The increased bone resorption may be associated with increased serum levels and urinary excretion of calcium and phosphorous, elevations in bone alkaline phosphatase, and suppressed serum parathyroid hormone levels. Administer the minimum dose of levothyroxine sodium tablets that achieves the desired clinical and biochemical response to mitigate this risk.
(5)
- Cardiac adverse reactions in the elderly and in patients with underlying cardiovascular disease: Initiate levothyroxine sodium tablets at less than the full replacement dose because of the increased risk of cardiac adverse reactions, including atrial fibrillation. (2.3, 5.1, 8.5)
- Myxedema coma: Do not use oral thyroid hormone drug products to treat myxedema coma. (5.2)
- Acute adrenal crisis in patients with concomitant adrenal insufficiency: Treat with replacement glucocorticoids prior to initiation of levothyroxine sodium tablets treatment. (5.3)
- Prevention of hyperthyroidism or incomplete treatment of hypothyroidism: Proper dose titration and careful monitoring is critical to prevent the persistence of hypothyroidism or the development of hyperthyroidism. (5.4)
- Worsening of diabetic control: Therapy in patients with diabetes mellitus may worsen glycemic control and result in increased antidiabetic agent or insulin requirements. Carefully monitor glycemic control after starting, changing, or discontinuing thyroid hormone therapy. (5.5)
- Decreased bone mineral density associated with thyroid hormone over-replacement: Over-replacement can increase bone resorption and decrease bone mineral density. Give the lowest effective dose. (5.6)
(5)
ADVERSE REACTIONS SECTION
6 ADVERSE REACTIONS
Adverse reactions associated with levothyroxine sodium tablets therapy are primarily those of hyperthyroidism due to therapeutic overdosage [see Warnings and Precautions (5), Overdosage (10)]. They include the following:
- General: fatigue, increased appetite, weight loss, heat intolerance, fever, excessive sweating
- Central nervous system: headache, hyperactivity, nervousness, anxiety, irritability, emotional lability, insomnia
- Musculoskeletal: tremors, muscle weakness, muscle spasm
- Cardiovascular: palpitations, tachycardia, arrhythmias, increased pulse and blood pressure, heart failure, angina, myocardial infarction, cardiac arrest
- Respiratory: dyspnea
- Gastrointestinal: diarrhea, vomiting, abdominal cramps, elevations in liver function tests
- Dermatologic: hair loss, flushing, rash
- Endocrine: decreased bone mineral density
- Reproductive: menstrual irregularities, impaired fertility
Seizures have been reported rarely with the institution of levothyroxine therapy.
Adverse Reactions in Children
Pseudotumor cerebri and slipped capital femoral epiphysis have been reported in children receiving levothyroxine therapy. Overtreatment may result in craniosynostosis in infants and premature closure of the epiphyses in children with resultant compromised adult height.
Hypersensitivity Reactions
Hypersensitivity reactions to inactive ingredients have occurred in patients treated with thyroid hormone products. These include urticaria, pruritus, skin rash, flushing, angioedema, various gastrointestinal symptoms (abdominal pain, nausea, vomiting and diarrhea), fever, arthralgia, serum sickness, and wheezing. Hypersensitivity to levothyroxine itself is not known to occur.
Adverse reactions associated with levothyroxine sodium tablets therapy are primarily those of hyperthyroidism due to therapeutic overdosage: arrhythmias, myocardial infarction, dyspnea, muscle spasm, headache, nervousness, irritability, insomnia, tremors, muscle weakness, increased appetite, weight loss, diarrhea, heat intolerance, menstrual irregularities, and skin rash. (6) (6)
To report SUSPECTED ADVERSE REACTIONS, contact Lannett Company, Inc. at 1-844-834-0530 or FDA at 1-800-FDA-1088 or www.fda.gov/medwatch**.** (6)
DRUG INTERACTIONS SECTION
7 DRUG INTERACTIONS
7.1 Drugs Known to Affect Thyroid Hormone Pharmacokinetics
Many drugs can exert effects on thyroid hormone pharmacokinetics and metabolism (e.g., absorption, synthesis, secretion, catabolism, protein binding, and target tissue response) and may alter the therapeutic response to levothyroxine sodium tablets (seeTables 2-5 below).
Table 2. Drugs That May Decrease T4 Absorption (Hypothyroidism)|
Potential impact: Concurrent use may reduce the efficacy of levothyroxine sodium tablets by binding and delaying or preventing absorption, potentially resulting in hypothyroidism. | |
|
Drug or Drug Class |
Effect |
|
Calcium Carbonate |
Calcium carbonate may form an insoluble chelate with levothyroxine, and ferrous sulfate likely forms a ferric-thyroxine complex. Administer levothyroxine sodium tablets at least 4 hours apart from these agents. |
|
Orlistat |
Monitor patients treated concomitantly with orlistat and levothyroxine sodium tablets for changes in thyroid function. |
|
Bile Acid Sequestrants |
Bile acid sequestrants and ion exchange resins are known to decrease levothyroxine absorption. Administer levothyroxine sodium tablets at least 4 hours prior to these drugs or monitor TSH levels. |
|
Other drugs: Sucralfate |
Gastric acidity is an essential requirement for adequate absorption of levothyroxine. Sucralfate, antacids and proton pump inhibitors may cause hypochlorhydria, affect intragastric pH, and reduce levothyroxine absorption. Monitor patients appropriately. |
|
Drug or Drug Class |
Effect |
|---|---|
|
Clofibrate |
These drugs may increase serum thyroxine-binding globulin (TBG) concentration. |
|
Androgens / Anabolic Steroids |
These drugs may decrease serum TBG concentration. |
|
Potential impact (below): Administration of these agents with levothyroxine sodium tablets results in an initial transient increase in FT4. Continued administration results in a decrease in serum T4 and normal FT4 and TSH concentrations. | |
|
Salicylates (> 2 g/day) |
Salicylates inhibit binding of T4 and T3 to TBG and transthyretin. An initial increase in serum FT4 is followed by return of FT4 to normal levels with sustained therapeutic serum salicylate concentrations, although total T4 levels may decrease by as much as 30%. |
|
Other drugs: |
These drugs may cause protein-binding site displacement. Furosemide has been shown to inhibit the protein binding of T4 to TBG and albumin, causing an increase free T4 fraction in serum. Furosemide competes for T4-binding sites on TBG, prealbumin, and albumin, so that a single high dose can acutely lower the total T4 level. Phenytoin and carbamazepine reduce serum protein binding of levothyroxine, and total and free T4 may be reduced by 20% to 40%, but most patients have normal serum TSH levels and are clinically euthyroid. Closely monitor thyroid hormone parameters. |
|
Potential impact: Stimulation of hepatic microsomal drug-metabolizing enzyme activity may cause increased hepatic degradation of levothyroxine, resulting in increased levothyroxine sodium tablets requirements. | |
|
Drug or Drug Class |
Effect |
|
Phenobarbital Rifampin |
Phenobarbital has been shown to reduce the response to thyroxine. Phenobarbital increases L-thyroxine metabolism by inducing uridine 5'-diphospho-glucuronosyltransferase (UGT) and leads to a lower T4 serum levels. Changes in thyroid status may occur if barbiturates are added or withdrawn from patients being treated for hypothyroidism. Rifampin has been shown to accelerate the metabolism of levothyroxine. |
|
Potential impact: Administration of these enzyme inhibitors decreases the peripheral conversion of T4 to T3, leading to decreased T3 levels. However, serum T4 levels are usually normal but may occasionally be slightly increased. | |
|
Drug or Drug Class |
Effect |
|
Beta-adrenergic antagonists (e.g., Propranolol > 160 mg/day) |
In patients treated with large doses of propranolol (> 160 mg/day), T3 and T4 levels change, TSH levels remain normal, and patients are clinically euthyroid. Actions of particular beta-adrenergic antagonists may be impaired when a hypothyroid patient is converted to the euthyroid state. |
|
Glucocorticoids (e.g., Dexamethasone ≥ 4 mg/day) |
Short-term administration of large doses of glucocorticoids may decrease serum T3 concentrations by 30% with minimal change in serum T4 levels. However, long-term glucocorticoid therapy may result in slightly decreased T3 and T4 levels due to decreased TBG production (See above). |
|
Other drugs: Amiodarone |
Amiodarone inhibits peripheral conversion of levothyroxine (T4) to triiodothyronine (T3) and may cause isolated biochemical changes (increase in serum free-T4, and decreased or normal free-T3) in clinically euthyroid patients. |
7.2 Antidiabetic Therapy
Addition of levothyroxine sodium tablets therapy in patients with diabetes mellitus may worsen glycemic control and result in increased antidiabetic agent or insulin requirements. Carefully monitor glycemic control, especially when thyroid therapy is started, changed, or discontinued [see Warnings and Precautions (5.5)].
7.3 Oral Anticoagulants
Levothyroxine sodium tablets increases the response to oral anticoagulant therapy. Therefore, a decrease in the dose of anticoagulant may be warranted with correction of the hypothyroid state or when the levothyroxine sodium tablets dose is increased. Closely monitor coagulation tests to permit appropriate and timely dosage adjustments.
7.4 Digitalis Glycosides
Levothyroxine sodium tablets may reduce the therapeutic effects of digitalis glycosides. Serum digitalis glycoside levels may decrease when a hypothyroid patient becomes euthyroid, necessitating an increase in the dose of digitalis glycosides.
7.5 Antidepressant Therapy
Concurrent use of tricyclic (e.g., amitriptyline) or tetracyclic (e.g., maprotiline) antidepressants and levothyroxine sodium tablets may increase the therapeutic and toxic effects of both drugs, possibly due to increased receptor sensitivity to catecholamines. Toxic effects may include increased risk of cardiac arrhythmias and central nervous system stimulation. Levothyroxine sodium tablets may accelerate the onset of action of tricyclics. Administration of sertraline in patients stabilized on levothyroxine sodium tablets may result in increased levothyroxine sodium tablets requirements.
7.6 Ketamine
Concurrent use of ketamine and levothyroxine sodium tablets may produce marked hypertension and tachycardia. Closely monitor blood pressure and heart rate in these patients.
7.7 Sympathomimetics
Concurrent use of sympathomimetics and levothyroxine sodium tablets may increase the effects of sympathomimetics or thyroid hormone. Thyroid hormones may increase the risk of coronary insufficiency when sympathomimetic agents are administered to patients with coronary artery disease.
7.8 Tyrosine-Kinase Inhibitors
Concurrent use of tyrosine-kinase inhibitors such as imatinib may cause hypothyroidism. Closely monitor TSH levels in such patients.
7.9 Drug-Food Interactions
Consumption of certain foods may affect levothyroxine sodium tablets absorption thereby necessitating adjustments in dosing [see Dosage and Administration (2.1)]. Soybean flour, cottonseed meal, walnuts, and dietary fiber may bind and decrease the absorption of levothyroxine sodium tablets from the gastrointestinal tract. Grapefruit juice may delay the absorption of levothyroxine and reduce its bioavailability.
7.10 Drug-Laboratory Test Interactions
Consider changes in TBG concentration when interpreting T4 and T3 values. Measure and evaluate unbound (free) hormone and/or determine the free-T4 index (FT4I) in this circumstance. Pregnancy, infectious hepatitis, estrogens, estrogen-containing oral contraceptives, and acute intermittent porphyria increase TBG concentration. Nephrosis, severe hypoproteinemia, severe liver disease, acromegaly, androgens, and corticosteroids decrease TBG concentration. Familial hyper- or hypo-thyroxine binding globulinemias have been described, with the incidence of TBG deficiency approximating 1 in 9000.
See full prescribing information for drugs that affect thyroid hormone pharmacokinetics and metabolism (e.g., absorption, synthesis, secretion, catabolism, protein binding, and target tissue response) and may alter the therapeutic response to levothyroxine sodium tablets. (7) (7)
DOSAGE FORMS & STRENGTHS SECTION
3 DOSAGE FORMS AND STRENGTHS
Levothyroxine Sodium Tablets, USP are available as follows:
|
Tablet Strength |
Tablet Color/Shape |
Tablet Markings |
|---|---|---|
|
25 mcg |
Orange/Caplet |
"25" and "GG/331" |
|
50 mcg |
White/ Caplet |
"50" and "GG/332" |
|
75 mcg |
Violet/ Caplet |
"75" and "GG/333" |
|
88 mcg |
Olive Green/ Caplet |
"88" and "GG/334" |
|
100 mcg |
Yellow/ Caplet |
"100" and "GG/335" |
|
112 mcg |
Rose/ Caplet |
"112" and "GG/336" |
|
125 mcg |
Brown/ Caplet |
"125" and "GG/337" |
|
137 mcg |
Turquoise/ Caplet |
"137" and "GG/330" |
|
150 mcg |
Blue/ Caplet |
"150" and "GG/338" |
|
175 mcg |
Lilac/ Caplet |
"175" and "GG/339" |
|
200 mcg |
Pink/ Caplet |
"200" and "GG/340" |
|
300 mcg |
Green/ Caplet |
"300" and "GG/341" |
Tablets: 25, 50, 75, 88, 100, 112, 125, 137, 150, 175, 200, and 300 mcg (3) (3)
OVERDOSAGE SECTION
10 OVERDOSAGE
The signs and symptoms of overdosage are those of hyperthyroidism [see Warnings and Precautions (5) and Adverse Reactions (6)]. In addition, confusion and disorientation may occur. Cerebral embolism, shock, coma, and death have been reported. Seizures occurred in a 3-year-old child ingesting 3.6 mg of levothyroxine. Symptoms may not necessarily be evident or may not appear until several days after ingestion of levothyroxine sodium.
Reduce the levothyroxine sodium tablets dose or discontinue temporarily if signs or symptoms of overdosage occur. Initiate appropriate supportive treatment as dictated by the patient's medical status.
For current information on the management of poisoning or overdosage, contact the National Poison Control Center at 1-800-222-1222 or www.poison.org.
DESCRIPTION SECTION
11 DESCRIPTION
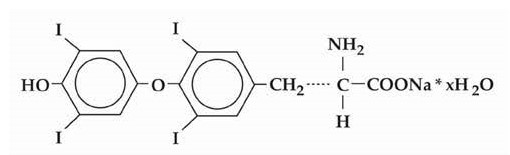
Levothyroxine sodium tablets, USP contain synthetic crystalline L-3,3',5,5'- tetraiodothyronine sodium salt [levothyroxine (T4) sodium]. Synthetic T4 is chemically identical to that produced in the human thyroid gland. Levothyroxine (T4) sodium has an empirical formula of C15H10I4NNaO4**•**xH2O (where x = 5), molecular weight of 798.86 g/mol (anhydrous) and structural formula as shown:
Levothyroxine sodium tablets for oral administration are supplied in the following strengths: 25 mcg, 50 mcg, 75 mcg, 88 mcg, 100 mcg, 112 mcg, 125 mcg, 137 mcg, 150 mcg, 175 mcg, 200 mcg and 300 mcg. Each levothyroxine sodium tablet contains the inactive ingredients Magnesium Stearate, NF; Microcrystalline Cellulose, NF; Colloidal Silicone Dioxide, NF; and Sodium Starch Glycolate, NF. Each tablet strength meets USP Dissolution Test 2. Table 6 provides a listing of the color additives by tablet strength:
Table 6. Levothyroxine Sodium Tablets Color Additives
|
Strength (mcg) |
Color additive(s) |
|
25 |
FD&C Yellow No. 6 Aluminum Lake |
|
50 |
None |
|
75 |
FD&C Blue No. 2 Aluminum Lake, D&C Red No. 27 Aluminum Lake |
|
88 |
FD&C Blue No. 1 Aluminum Lake, D&C Yellow No. 10 Aluminum Lake, D&C RedNo. 30 Aluminum Lake |
|
100 |
D&C Yellow No. 10 Aluminum Lake, D&C Red Lake Blend (D&C Red No. 27 Lake and D&C Red No. 30 Lake) |
|
112 |
D&C Red No. 27 Aluminum Lake, D&C Red No. 30 Aluminum Lake |
|
125 |
FD&C Yellow No. 6 Aluminum Lake, FD&C Red No. 40 Aluminum Lake, FD&C Blue No. 1 Aluminum Lake |
|
137 |
FD&C Blue No. 1 Aluminum Lake |
|
150 |
FD&C Blue No. 2 Aluminum Lake |
|
175 |
D&C Red No. 27 Aluminum Lake, D&C Red No. 30 Aluminum Lake, FD&C Blue No. 1 Aluminum Lake |
|
200 |
D&C Yellow No. 10 Aluminum Lake, D&C Red No. 27 Aluminum Lake |
|
300 |
D&C Yellow No. 10 Aluminum Lake, FD&C Yellow No. 6 Aluminum Lake, FD&C Blue No. 1 Aluminum Lake |
NONCLINICAL TOXICOLOGY SECTION
13 NONCLINICAL TOXICOLOGY
13.1 Carcinogenesis, Mutagenesis, Impairment of Fertility
Standard animal studies have not been performed to evaluate the carcinogenic potential, mutagenic potential or effects on fertility of levothyroxine.
INFORMATION FOR PATIENTS SECTION
17 PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATION
Inform the patient of the following information to aid in the safe and effective use oflevothyroxine sodium tablets:
Dosing and Administration
- Instruct patients that levothyroxine sodium tablets should be taken with a full glass of water since the tablet may rapidly disintegrate.
- Instruct patients to take levothyroxine sodium tablets only as directed by their healthcare provider.
- Instruct patients to take levothyroxine sodium tablets as a single dose, preferably on an empty stomach, one-half to one hour before breakfast.
- Inform patients that agents such as iron and calcium supplements and antacids can decrease the absorption of levothyroxine. Instruct patients not to take levothyroxine sodium tablets within 4 hours of these agents.
- Instruct patients to notify their healthcare provider if they are pregnant or breastfeeding or are thinking of becoming pregnant while taking levothyroxine sodium tablets.
Important Information
- Inform patients that it may take several weeks before they notice an improvement in symptoms.
- Inform patients that the levothyroxine in levothyroxine sodium tablets is intended to replace a hormone that is normally produced by the thyroid gland. Generally, replacement therapy is to be taken for life.
- Inform patients that levothyroxine sodium tablets should not be used as a primary or adjunctive therapy in a weight control program.
- Instruct patients to notify their healthcare provider if they are taking any other medications, including prescription and over-the-counter preparations.
- Instruct patients to notify their physician of any other medical conditions they may have, particularly heart disease, diabetes, clotting disorders, and adrenal or pituitary gland problems, as the dose of medications used to control these other conditions may need to be adjusted while they are taking levothyroxine sodium tablets. If they have diabetes, instruct patients to monitor their blood and/or urinary glucose levels as directed by their physician and immediately report any changes to their physician. If patients are taking anticoagulants, their clotting status should be checked frequently.
- Instruct patients to notify their physician or dentist that they are taking levothyroxine sodium tablets prior to any surgery.
Adverse Reactions
- Instruct patients to notify their healthcare provider if they experience any of the following symptoms: rapid or irregular heartbeat, chest pain, shortness of breath, leg cramps, headache, nervousness, irritability, sleeplessness, tremors, change in appetite, weight gain or loss, vomiting, diarrhea, excessive sweating, heat intolerance, fever, changes in menstrual periods, hives or skin rash, or any other unusual medical event.
- Inform patients that partial hair loss may occur rarely during the first few months of levothyroxine sodium tablets therapy, but this is usually temporary.
Dosing and Administration
- Instruct patients that levothyroxine sodium tablets should be taken with a full glass of water since the tablet may rapidly disintegrate.
- Instruct patients to take levothyroxine sodium tablets only as directed by their healthcare provider.
- Instruct patients to take levothyroxine sodium tablets as a single dose, preferably on an empty stomach, one-half to one hour before breakfast.
- Inform patients that agents such as iron and calcium supplements and antacids can decrease the absorption of levothyroxine. Instruct patients not to take levothyroxine sodium tablets tablets within 4 hours of these agents.
- Instruct patients to notify their healthcare provider if they are pregnant or breastfeeding or are thinking of becoming pregnant while taking levothyroxine sodium tablets.
Important Information
- Inform patients that it may take several weeks before they notice an improvement in symptoms.
- Inform patients that the levothyroxine in levotyhroxine sodium tablets is intended to replace a hormone that is normally produced by the thyroid gland. Generally, replacement therapy is to be taken for life.
- Inform patients that levotyhroxine sodium tablets should not be used as a primary or adjunctive therapy in a weight control program.
- Instruct patients to notify their healthcare provider if they are taking any other medications, including prescription and over-the-counter preparations.
- Instruct patients to notify their physician of any other medical conditions they may have, particularly heart disease, diabetes, clotting disorders, and adrenal or pituitary gland problems, as the dose of medications used to control these other conditions may need to be adjusted while they are taking levotyhroxine sodium tablets. If they have diabetes, instruct patients to monitor their blood and/or urinary glucose levels as directed by their physician and immediately report any changes to their physician. If patients are taking anticoagulants, their clotting status should be checked frequently.
- Instruct patients to notify their physician or dentist that they are taking levotyhroxine sodium tablets prior to any surgery.
Adverse Reactions
- Instruct patients to notify their healthcare provider if they experience any of the following symptoms: rapid or irregular heartbeat, chest pain, shortness of breath, leg cramps, headache, nervousness, irritability, sleeplessness, tremors, change in appetite, weight gain or loss, vomiting, diarrhea, excessive sweating, heat intolerance, fever, changes in menstrual periods, hives or skin rash, or any other unusual medical event.
- Inform patients that partial hair loss may occur rarely during the first few months of levothyroxine sodium tablets therapy, but this is usually temporary.
