Sufentanil Citrate
These highlights do not include all the information needed to use SUFENTANIL CITRATE INJECTION, safely and effectively. See full prescribing information for SUFENTANIL CITRATE INJECTION. Sufentanil Citrate Injection, for intravenous and epidural use, CIIInitial U.S. Approval: 1984
20293943-46ff-4345-1aa4-929b4e017a25
HUMAN PRESCRIPTION DRUG LABEL
Feb 5, 2024
Hospira, Inc.
DUNS: 141588017
Products 1
Detailed information about drug products covered under this FDA approval, including NDC codes, dosage forms, ingredients, and administration routes.
SUFENTANIL CITRATE
Product Details
FDA regulatory identification and product classification information
FDA Identifiers
Product Classification
Product Specifications
INGREDIENTS (4)
Drug Labeling Information
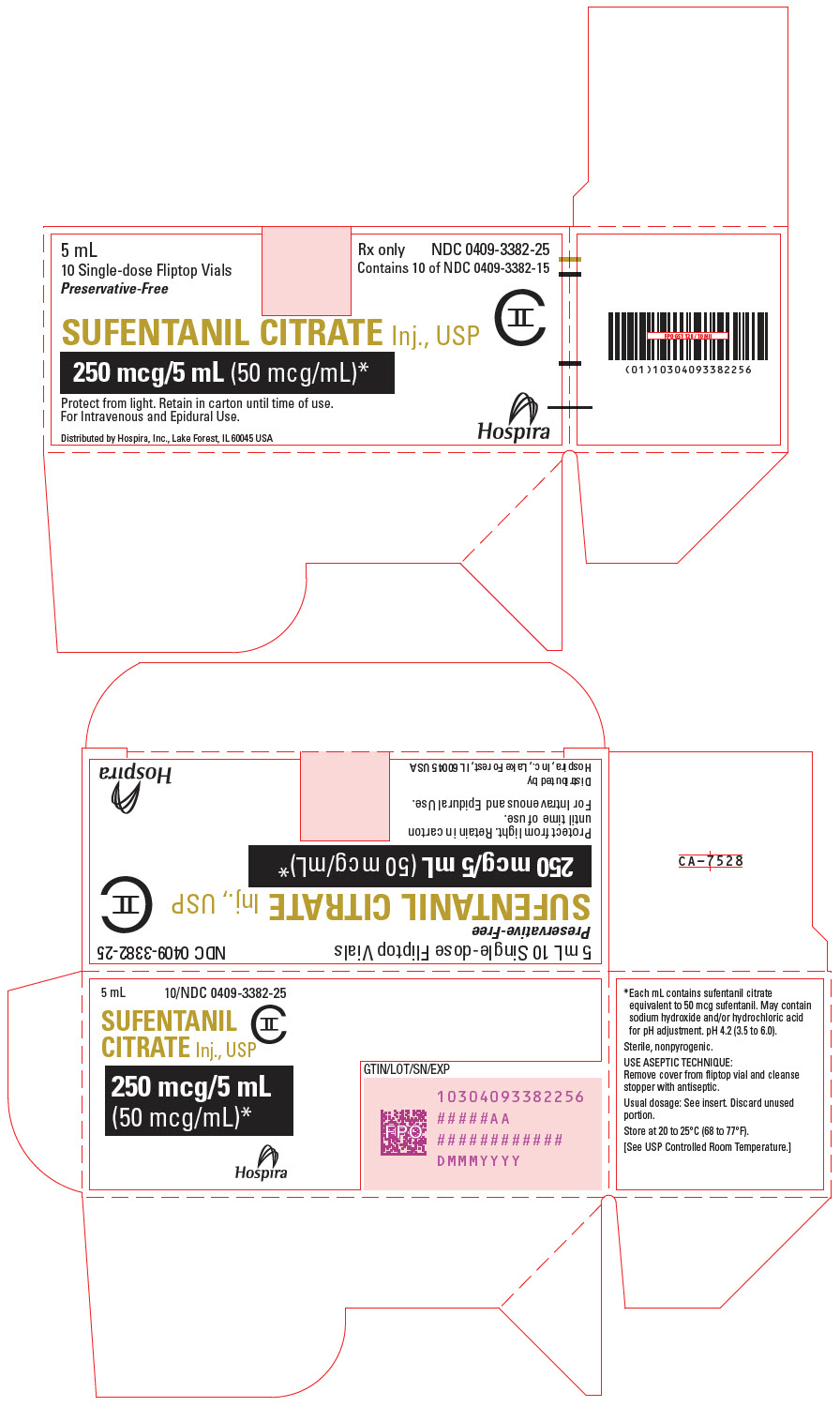
PACKAGE LABEL.PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL
PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL - 5 mL Vial Carton
5 mL
10 Single-dose Fliptop Vials
Preservative-Free
Rx only
NDC 0409-3382-25
Contains 10 of NDC 0409-3382-15
SUFENTANIL CITRATE Inj., USP
CII
250 mcg/5 mL (50 mcg/mL)*
Protect from light. Retain in carton until time of use.
For Intravenous and Epidural Use.
Distributed by Hospira, Inc., Lake Forest, IL 60045 USA
Hospira
Boxed Warning section
WARNING: SERIOUS AND LIFE-THREATENING RISKS FROM USE OF SUFENTANIL CITRATE
INJECTION
INDICATIONS & USAGE SECTION
1 INDICATIONS AND USAGE
Sufentanil Citrate Injection is indicated for intravenous administration in adults and pediatric patients:
•
as an analgesic adjunct in the maintenance of balanced general anesthesia in patients who are intubated and ventilated.
•
as a primary anesthetic agent for the induction and maintenance of anesthesia with 100% oxygen in patients undergoing major surgical procedures, in patients who are intubated and ventilated, such as cardiovascular surgery or neurosurgical procedures in the sitting position, to provide favorable myocardial and cerebral oxygen balance or when extended postoperative ventilation is anticipated.
Sufentanil Citrate Injection is indicated for epidural administration:
•
as an analgesic combined with low dose (usually 12.5 mg per administration) bupivacaine usually during labor and vaginal delivery.
Sufentanil Citrate Injection is an opioid agonist indicated (1):
•
as an analgesic adjunct in the maintenance of balanced general anesthesia in patients who are intubated and ventilated.
•
as a primary anesthetic agent for the induction and maintenance of anesthesia with 100% oxygen in patients undergoing major surgical procedures, in patients who are intubated and ventilated, such as cardiovascular surgery or neurosurgical procedures in the sitting position, to provide favorable myocardial and cerebral oxygen balance or when extended postoperative ventilation is anticipated.
•
for epidural administration as an analgesic combined with low dose (usually 12.5 mg per administration) bupivacaine usually during labor and vaginal delivery.
CONTRAINDICATIONS SECTION
4 CONTRAINDICATIONS
Sufentanil Citrate Injection is contraindicated in patients with:
•
Hypersensitivity to sufentanil (e.g., anaphylaxis) [see Adverse Reactions (6.2)]
•
Hypersensitivity to sufentanil. (4)
ADVERSE REACTIONS SECTION
6 ADVERSE REACTIONS
The following serious adverse reactions are described, or described in greater detail, in other sections:
•
Addiction, Abuse, and Misuse [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)]
•
Life-Threatening Respiratory Depression [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2)]
•
Skeletal Muscle Rigidity and Skeletal Muscle Movement [see Warnings and Precautions (5.5)]
•
Interactions with Benzodiazepines or Other CNS Depressants [see Warnings and Precautions (5.3)]
•
Severe Cardiovascular Depression [see Warnings and Precautions (5.6)]
•
Opioid-Induced Hyperalgesia and Allodynia [see Warnings and Precautions (5.7)]
•
Serotonin Syndrome [see Warnings and Precautions (5.8)]
•
Gastrointestinal Adverse Reactions [see Warnings and Precautions (5.11)]
•
Seizures [see Warnings and Precautions (5.12)]
6.1 Clinical Trials Experience
Because clinical trials are conducted under widely varying conditions, adverse reaction rates observed in the clinical trials of a drug cannot be directly compared to rates in the clinical trials of another drug and may not reflect the rates observed in practice.
Epidural Use in Labor and Delivery
Epidural sufentanil was tested in 340 patients in two (one single-center and one multicenter) double-blind, parallel studies. Doses ranged from 10 to 15 mcg sufentanil and were delivered in a 10 mL volume of 0.125% bupivacaine with and without epinephrine 1:200,000. In all cases sufentanil was administered following a dose of local anesthetic to test proper catheter placement. Since epidural opioids and local anesthetics potentiate each other, these results may not reflect the dose or efficacy of epidural sufentanil by itself.
Individual doses of 10 to 15 mcg sufentanil plus bupivacaine 0.125% with epinephrine provided analgesia during the first stage of labor with a duration of 1 to 2 hours. Onset was rapid (within 10 minutes). Subsequent doses (equal dose) tended to have shorter duration. Analgesia was profound (complete pain relief) in 80% to 100% of patients and a 25% incidence of pruritus was observed. The duration of initial doses of sufentanil plus bupivacaine with epinephrine is approximately 95 minutes, and of subsequent doses, 70 minutes.
There are insufficient data to critically evaluate neonatal neuromuscular and adaptive capacity following recommended doses of maternally administered epidural sufentanil with bupivacaine. However, if larger than recommended doses are used for combined local and systemic analgesia, e.g., after administration of a single dose of 50 mcg epidural sufentanil during delivery, then impaired neonatal adaption to sound and light can be detected for 1 to 4 hours and if a dose of 80 mcg is used impaired neuromuscular coordination can be detected for more than 4 hours.
6.2 Postmarketing Experience
The following adverse reactions have been identified during post approval use of sufentanil. Because these reactions are reported voluntarily from a population of uncertain size, it is not always possible to reliably estimate their frequency or establish a causal relationship to drug exposure.
Serotonin syndrome: Cases of serotonin syndrome, a potentially life- threatening condition, have been reported during concomitant use of opioids with serotonergic drugs.
Adrenal insufficiency: Cases of adrenal insufficiency have been reported with opioid use, more often following greater than one month of use.
Anaphylaxis: Anaphylaxis has been reported with ingredients contained in Sufentanil Citrate Injection.
Androgen deficiency: Cases of androgen deficiency have occurred with use of opioids for an extended period of time [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.2)].
Hyperalgesia and Allodynia: Cases of hyperalgesia and allodynia have been reported with opioid therapy of any duration [see Warnings and Precautions (5.7)].
Hypoglycemia: Cases of hypoglycemia have been reported in patients taking opioids. Most reports were in patients with at least one predisposing risk factor (e.g., diabetes).
Most common adverse reactions were apnea, rigidity, and bradycardia. (6)
To report SUSPECTED ADVERSE REACTIONS, contact Hospira, Inc. at 1-800-441-4100 or FDA at 1-800-FDA-1088 or www.fda.gov/medwatch.
DRUG INTERACTIONS SECTION
7 DRUG INTERACTIONS
Table 3 includes clinically significant drug interactions with Sufentanil Citrate Injection.
Table 3: Clinically Significant Drug Interactions with Sufentanil Citrate Injection|
Inhibitors of CYP3A4 | |
|
Clinical Impact: |
The concomitant use of Sufentanil Citrate Injection and CYP3A4 inhibitors can increase the plasma concentration of sufentanil, resulting in increased or prolonged opioid effects, particularly when an inhibitor is added after a stable dose of Sufentanil Citrate Injection is achieved [see Warnings and Precautions (5.4)]. After stopping a CYP3A4 inhibitor, as the effects of the inhibitor decline, the sufentanil plasma concentration will decrease [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)], resulting in decreased opioid efficacy or a withdrawal syndrome in patients who had developed physical dependence to sufentanil. |
|
Intervention: |
If concomitant use is necessary, consider dosage reduction of Sufentanil Citrate Injection until stable drug effects are achieved. Monitor patients at frequent intervals for respiratory depression and sedation. If a CYP3A4 inhibitor is discontinued, consider increasing the Sufentanil Citrate Injection dosage until stable drug effects are achieved. Monitor for signs of opioid withdrawal. |
|
Examples: |
Macrolide antibiotics (e.g., erythromycin), azole-antifungal agents (e.g., ketoconazole), protease inhibitors (e.g., ritonavir), grapefruit juice. |
|
CYP3A4 Inducers | |
|
Clinical Impact: |
The concomitant use of Sufentanil Citrate Injection and CYP3A4 inducers can decrease the plasma concentration of sufentanil [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)], resulting in decreased efficacy or onset of a withdrawal syndrome in patients who have developed physical dependence to sufentanil [see Warnings and Precautions (5.4)]. After stopping a CYP3A4 inducer, as the effects of the inducer decline, the sufentanil plasma concentration will increase [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)], which could increase or prolong both the therapeutic effects and adverse reactions and may cause serious respiratory depression. |
|
Intervention: |
If concomitant use is necessary, consider increasing the Sufentanil Citrate Injection dosage until stable drug effects are achieved. Monitor for signs of opioid withdrawal. If a CYP3A4 inducer is discontinued, consider Sufentanil Citrate Injection dosage reduction and monitor for signs of respiratory depression. |
|
Examples: |
Rifampin, carbamazepine, phenytoin |
|
Benzodiazepines and Other Central Nervous System (CNS) Depressants | |
|
Clinical Impact: |
The concomitant use of Sufentanil Citrate Injection with CNS depressants my result in decreased pulmonary artery pressure and may cause hypotension. Even small dosages of diazepam may cause cardiovascular depression when added to high dose or anesthetic dosages of Sufentanil Citrate Injection. As postoperative analgesia, concomitant use of Sufentanil Citrate Injection can increase the risk of hypotension, respiratory depression, profound sedation, coma, and death [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2, 5.3)]. |
|
Intervention: |
As postoperative analgesia, start with a lower dose of Sufentanil Citrate Injection and monitor patients for signs of respiratory depression, sedation, and hypotension. Fluids or other measures to counter hypotension should be available [see Warnings and Precautions (5.3)]. |
|
Examples: |
Benzodiazepines and other sedatives/hypnotics, anxiolytics, tranquilizers, muscle relaxants, general anesthetics, antipsychotics, other opioids, alcohol. |
|
Serotonergic Drugs | |
|
Clinical Impact: |
The concomitant use of opioids with other drugs that affect the serotonergic neurotransmitter system has resulted in serotonin syndrome [see Warnings and Precautions (5.8)]. |
|
Intervention: |
If concomitant use is warranted, carefully observe the patient, particularly during treatment initiation and dose adjustment. Discontinue Sufentanil Citrate Injection if serotonin syndrome is suspected. |
|
Examples: |
Selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs), serotonin and norepinephrine reuptake inhibitors (SNRIs), tricyclic antidepressants (TCAs), triptans, 5-HT3 receptor antagonists, drugs that effect the serotonin neurotransmitter system (e.g., mirtazapine, trazodone, tramadol), certain muscle relaxants (i.e., cyclobenzaprine, metaxalone), monoamine oxidase inhibitors (those intended to treat psychiatric disorders and also others, such as linezolid and intravenous methylene blue). |
|
Monoamine Oxidase Inhibitors (MAOIs) | |
|
Clinical Impact: |
MAOI interactions with opioids may manifest as serotonin syndrome or opioid toxicity (e.g., respiratory depression, coma) [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2)]. |
|
Intervention: |
The use of Sufentanil Citrate Injection is not recommended for patients taking MAOIs or within 14 days of stopping such treatment. |
|
Examples: |
phenelzine, tranylcypromine, linezolid |
|
Mixed Agonist/Antagonist and Partial Agonist Opioid Analgesics | |
|
Clinical Impact: |
May reduce the analgesic effect of Sufentanil Citrate Injection and/or precipitate withdrawal symptoms. |
|
Intervention: |
Avoid concomitant use. |
|
Examples: |
butorphanol, nalbuphine, pentazocine, buprenorphine |
|
Muscle Relaxants | |
|
Clinical Impact: |
Sufentanil may enhance the neuromuscular blocking action of skeletal muscle relaxants and produce an increased degree of respiratory depression. |
|
Intervention: |
Monitor patients for signs of respiratory depression that may be greater than otherwise expected and decrease the dosage of Sufentanil Citrate Injection and/or the muscle relaxant as necessary. |
|
Diuretics | |
|
Clinical Impact: |
Opioids can reduce the efficacy of diuretics by inducing the release of antidiuretic hormone. |
|
Intervention: |
Monitor patients for signs of diminished diuresis and/or effects on blood pressure and increase the dosage of the diuretic as needed. |
|
Anticholinergic Drugs | |
|
Clinical Impact: |
The concomitant use of anticholinergic drugs may increase risk of urinary retention and/or severe constipation, which may lead to paralytic ileus. |
|
Intervention: |
Monitor patients for signs of urinary retention or reduced gastric motility when Sufentanil Citrate Injection is used concomitantly with anticholinergic drugs. |
|
Nitrous oxide | |
|
Clinical Impact: |
Nitrous oxide has been reported to produce cardiovascular depression when given with higher doses of Sufentanil Citrate Injection. |
|
Intervention: |
Monitor patients for signs of cardiovascular depression that may be greater than otherwise expected. |
•
Concomitant Use of CNS Depressants: May decrease pulmonary arterial pressure and may cause hypotension. See FPI for management instructions. For post-operative pain, start with the lowest effective dosage and monitor for potentiation of CNS depressant effects. (5.3, 7)
•
Mixed Agonist/Antagonist and Partial Agonist Opioid Analgesics: Avoid use with Sufentanil Citrate Injection because they may reduce analgesic effect of Sufentanil Citrate Injection or precipitate withdrawal symptoms. (7)
RECENT MAJOR CHANGES SECTION
RECENT MAJOR CHANGES
|
Boxed Warning |
7/2023 |
|
Warnings and Precautions (5.7) |
7/2023 |
DOSAGE & ADMINISTRATION SECTION
2 DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
2.1 Important Dosage and Administration Instructions
Sufentanil Citrate Injection should be administered only by persons specifically trained in the use of intravenous or epidural anesthetics and management of the respiratory effects of potent opioids.
In patients administered high doses of Sufentanil Citrate Injection, it is essential that qualified personnel and adequate facilities are available for the management of postoperative respiratory depression.
For purposes of administering small volumes of Sufentanil Citrate Injection accurately, the use of a tuberculin syringe or equivalent is recommended.
•
Ensure that an opioid antagonist, resuscitative and intubation equipment, and oxygen are readily available.
•
Individualize dosage based on factors such as age, body weight, physical status, underlying pathological condition, use of other drugs, type of anesthesia to be used, and the surgical procedure involved.
•
Monitor vital signs regularly.
•
The selection of preanesthetic medications should be based upon the needs of the individual patient.
•
The neuromuscular blocking agent selected should be compatible with the patient's condition, taking into account the hemodynamic effects of a particular muscle relaxant and the degree of skeletal muscle relaxation required.
As with other potent opioids, the respiratory depressant effect of sufentanil may persist longer than the measured analgesic effect. The total dose of all opioid agonists administered should be considered by the practitioner before ordering opioid analgesics during recovery from anesthesia.
If Sufentanil Citrate Injection is administered with a CNS depressant, become familiar with the properties of each drug, particularly each product's duration of action. In addition, when such a combination is used, fluids and other countermeasures to manage hypotension should be available [see Warnings and Precautions (5.3)].
Inspect parenteral drug products visually for particulate matter and discoloration prior to administration, whenever solution and container permit.
2.2 Intravenous use
Sufentanil Citrate may be administered intravenously by slow injection or infusion.
Adjunct to general anesthesia:
•
Doses of up to 8 mcg/kg (see Table 1)
•
Total Dosage Requirements of 1 mcg/kg/hr or less are recommended
•
Dosage should be individualized and adjusted to remaining operative time anticipated.
|
Total dosage |
Maintenance dosage |
|---|---|
|
Duration of anesthesia 1 to 2 hours | |
|
Incremental or Infusion: 1 to 2 mcg/kg Dosages in this range are generally administered with nitrous oxide/oxygen in patients undergoing general surgery in which endotracheal intubation and mechanical ventilation are required. |
**Incremental: 10 to 25 mcg (0.2 to 0.5 mL)**may be administered in increments as needed when movement and/or changes in vital signs indicate surgical stress or lightening of analgesia. Supplemental dosages should be individualized and adjusted to remaining operative time anticipated. **Infusion:**Intermittent or continuous infusion as needed in response to signs of lightening of analgesia. In absence of signs of lightening of analgesia, infusion rates should always be adjusted downward until there is some response to surgical stimulation. Maintenance infusion rates should be adjusted based upon the induction dose of sufentanil so that the total dose does not exceed 1 mcg/kg/hr of expected surgical time. |
|
Duration of anesthesia 2 to 8 hours | |
|
Incremental or Infusion: 2 to 8 mcg/kg Dosages in this range are generally administered with nitrous oxide/oxygen in patients undergoing more complicated major surgical procedures in which endotracheal intubation and mechanical ventilation are required. At dosages in this range, sufentanil has been shown to provide some attenuation of sympathetic reflex activity in response to surgical stimuli, provide hemodynamic stability, and provide relatively rapid recovery. |
**Incremental: 10 to 50 mcg (0.2 to 1 mL)**may be administered in increments as needed when movement and/or changes in vital signs indicate surgical stress or lightening of analgesia. Supplemental dosages should be individualized and adjusted to the remaining operative time anticipated. **Infusion:**Intermittent or continuous infusion as needed in response to signs of lightening of analgesia. In the absence of signs of lightening of analgesia, infusion rates should always be adjusted downward until there is some response to surgical stimulation. Maintenance infusion rates should be adjusted based upon the induction dose of sufentanil so that the total dose does not exceed 1 mcg/kg/hr of expected surgical time. |
Induction And Maintenance Of Anesthesia
•
As the primary anesthetic agent: doses ≥8 mcg/kg (see Dosage Range Chart, Table 2).
•
Dosage should be titrated to individual patient response
•
In children less than 12 years of age undergoing cardiovascular surgery: 10 to 25 mcg/kg administered with 100% oxygen
o
Supplemental dosages of up to 25 to 50 mcg are recommended for maintenance, based on response to initial dose and as determined by changes in vital signs indicating surgical stress or lightening of anesthesia.
|
Incremental or Infusion: 8 to 30 mcg/kg Sufentanil with 100% oxygen and a muscle relaxant has been found to produce sleep at dosages ≥8 mcg/kg and to maintain a deep level of anesthesia without the use of additional anesthetic agents. The addition of N2O to these dosages will reduce systolic blood pressure. At dosages in this range of up to 25 mcg/kg, catecholamine release is attenuated. Dosages of 25 to 30 mcg/kg have been shown to block sympathetic response including catecholamine release. High doses are indicated in patients undergoing major surgical procedures, in which endotracheal intubation and mechanical ventilation are required, such as cardiovascular surgery and neurosurgery in the sitting position with maintenance of favorable myocardial and cerebral oxygen balance. Postoperative observation is essential and postoperative mechanical ventilation may be required at the higher dosage range due to extended postoperative respiratory depression. |
**Incremental:**Depending on the initial dose, maintenance doses of 0.5 to 10 mcg/kg may be administered by slow injection in anticipation of surgical stress such as incision, sternotomy or cardiopulmonary bypass. **Infusion:**Sufentanil citrate may be administered by continuous or intermittent infusion as needed in response to signs of lightening of anesthesia. In the absence of lightening of anesthesia, infusion rates should always be adjusted downward until there is some response to surgical stimulation. The maintenance infusion rate for sufentanil should be based upon the induction dose so that the total dose for the procedure does not exceed 30 mcg/kg. |
2.3 Epidural Use in Labor and Delivery
Proper placement of the needle or catheter in the epidural space should be verified before sufentanil citrate is injected to assure that unintentional intravascular or intrathecal administration does not occur. Unintentional intravascular injection of sufentanil could result in a potentially serious overdose, including acute truncal muscular rigidity and apnea. Unintentional intrathecal injection of the full sufentanil, bupivacaine epidural doses and volume could produce effects of high spinal anesthesia including prolonged paralysis and delayed recovery.
•
Sufentanil should be administered by slow injection. Respiration should be closely monitored following each administration of an epidural injection of sufentanil.
•
If analgesia is inadequate, the placement and integrity of the catheter should be verified prior to the administration of any additional epidural medications.
Dosage for Labor and Delivery
•
10 to 15 mcg administered with 10 mL bupivacaine 0.125% with or without epinephrine.
•
Sufentanil and bupivacaine should be mixed together before administration.
•
Doses can be repeated twice (for a total of three doses) at not less than one-hour intervals until delivery.
•
Sufentanil Citrate Injection should be administered only by persons specifically trained in the use of intravenous anesthetics and management of the respiratory effects of potent opioids.
•
Ensure that an opioid antagonist, resuscitative and intubation equipment, and oxygen are readily available. (2.1)
•
Individualize dosing based on factors such as age, body weight, physical status, underlying pathological condition, use of other drugs, type of anesthesia to be used, and the surgical procedure involved. (2.1)
•
Initiate analgesic treatment with 1 to 2 mcg/kg intravenously. (2.2)
•
Initiate epidural injection for labor and delivery at 10 to 15 mcg of sufentanil administered with 10 mL bupivacaine 0.125% with or without epinephrine. (2.3)
DOSAGE FORMS & STRENGTHS SECTION
3 DOSAGE FORMS AND STRENGTHS
Sufentanil Citrate Injection, USP 50 mcg/mL (equivalent to 50 mcg/mL sufentanil base).
Solution for injection (sterile): eq. to 50 mcg/mL sufentanil base; 1 mL, 2 mL and 5 mL vials. (3)
DESCRIPTION SECTION
11 DESCRIPTION
Sufentanil Citrate Injection, USP is a sterile, nonpyrogenic solution of sufentanil citrate in water for injection. Sufentanil Citrate is a potent opioid analgesic which is administered either epidurally or by intravenous injection.
Each mL contains sufentanil citrate equivalent to 50 mcg of sufentanil. May contain sodium hydroxide and/or hydrochloric acid for pH adjustment. pH 4.2 (3.5 to 6.0).
The solution contains no bacteriostat, antimicrobial agent or added buffer and is intended for use only as a single-use injection. When smaller doses are required, the unused portion should be discarded in an appropriate manner.
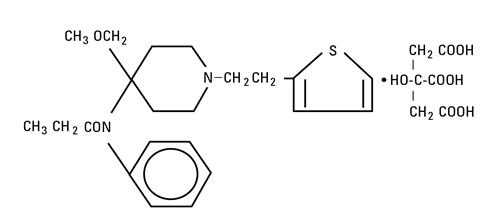
Sufentanil Citrate, USP, occurs as a white crystalline powder and is chemically designated as N-[-4-(methyoxymethyl)-1-[2-(2-thienyl)ethyl]-4-piperidinyl]-N-phenylpropanamide 2-hydroxy-1,2,3-propanetricarboxylate (1:1).
The molecular formula of sufentanil citrate is C22H30N2O2S∙C6H8O7 and the molecular weight is 578.69. Sufentanil Citrate has the following structural formula:
SPL UNCLASSIFIED SECTION

Distributed by Hospira, Inc., Lake Forest, IL 60045 USA
LAB-1124-10.0
USE IN SPECIFIC POPULATIONS SECTION
8 USE IN SPECIFIC POPULATIONS
8.1 Pregnancy
Risk Summary
Use of opioid analgesics for an extended period of time during pregnancy may cause neonatal opioid withdrawal syndrome. Available data with Sufentanil Citrate Injection in pregnant women are insufficient to inform a drug- associated risk for major birth defects and miscarriage.
In animal reproduction studies, embryolethality and maternal toxicity were noted in rabbits when sufentanil was administered intravenously at 0.9 times the human procedural dose of 30 mcg/kg during organogenesis. Decreased live fetuses and pup survival were noted in rats treated with sufentanil late in gestation and throughout lactation at doses below the human procedural dose. No malformations were observed in either rats or rabbits at doses below the human procedural dose [see Data].
The background risk of major birth defects and miscarriage for the indicated population is unknown. All pregnancies have a background risk of birth defect, loss, or other adverse outcomes. In the U.S. general population, the estimated background risk of major birth defects and miscarriage in clinically recognized pregnancies is 2% to 4% and 15% to 20%, respectively.
Clinical Considerations
Fetal/Neonatal Adverse Reactions
Use of opioid analgesics for an extended period of time during pregnancy for medical or nonmedical purposes can result in physical dependence in the neonate and neonatal opioid withdrawal syndrome shortly after birth.
Neonatal opioid withdrawal syndrome presents as irritability, hyperactivity and abnormal sleep pattern, high pitched cry, tremor, vomiting, diarrhea and failure to gain weight. The onset, duration, and severity of neonatal opioid withdrawal syndrome vary based on the specific opioid used, duration of use, timing and amount of last maternal use, and rate of elimination of the drug by the newborn. Observe newborns for symptoms of neonatal opioid withdrawal syndrome and manage accordingly [see Warnings and Precautions (5.4)].
Labor or Delivery
Opioids cross the placenta and may produce respiratory depression and psycho- physiologic effects in neonates. An opioid antagonist, such as naloxone, must be available for reversal of opioid-induced respiratory depression in the neonate. Sufentanil Citrate Injection is not recommended for use in pregnant women during or immediately prior to labor, when other analgesic techniques are more appropriate. Opioid analgesics, including Sufentanil Citrate Injection, can prolong labor through actions which temporarily reduce the strength, duration, and frequency of uterine contractions. However, this effect is not consistent and may be offset by an increased rate of cervical dilation, which tends to shorten labor. Monitor neonates exposed to opioid analgesics during labor for signs of excess sedation and respiratory depression.
The use of epidurally administered sufentanil in combination with bupivacaine 0.125% with or without epinephrine is indicated for labor and delivery. Sufentanil is not recommended for intravenous use or for use of larger epidural doses during labor and delivery because of potential risks to the newborn infant after delivery. In clinical trials, one case of severe fetal bradycardia associated with maternal hypotension was reported within 8 minutes of maternal administration of sufentanil 15 mcg plus bupivacaine 0.125% (10 mL total volume).
Data
Animal Data
Pregnant rats were treated with intravenous sufentanil doses of 0.005, 0.02, or 0.08 mg/kg/day (0.03, 0.1, or 0.4 times the human total procedural dose of 30 mcg/kg based on body surface area, respectively). No malformations or embryotoxic effects were noted despite maternal toxicity (increased mortality in the mid- and high-dose group).
Pregnant rabbits were treated with intravenous sufentanil doses of 0.005, 0.02, or 0.08 mg/kg/day (0.05, 0.2, or 0.9 times the human total procedural dose of 30 mcg/kg based on body surface area, respectively). Decreased live fetuses per litter and decreased litter size in the high dose group were noted in the presence of maternal toxicity (decreased body weight gain and mortality in the high-dose group).
No evidence of malformations or adverse effects on the fetus was reported in a published study in which pregnant rats were administered 10, 50, or 100 mcg/kg/day sufentanil (0.05, 0.27, or 0.54 times the human procedural dose of 30 mcg/kg/day based on body surface area) continuously from Gestation Day 5 through Gestation Day 20 via subcutaneously implanted osmotic minipumps.
Pregnant rats were treated intravenously with sufentanil 0.005, 0.02, or 0.08 mg/kg/day (0.03, 0.1, or 0.4 times the human total procedural dose of 30 mcg/day based on body surface area, respectively) from Gestation Day 16 through Lactation Day 21. Sufentanil reduced birth weights in the mid- and high-dose groups, decreased live fetuses in the high-dose group, and decreased pup survival in all groups in the presence of maternal toxicity (decreased weight gain and increased mortality in all groups).
8.2 Lactation
Risk Summary
The developmental and health benefits of breastfeeding should be considered along with the mother's clinical need for Sufentanil Citrate Injection and any potential adverse effects on the breastfed infant from Sufentanil Citrate Injection or from the underlying maternal condition.
Clinical Considerations
Monitor infants exposed to Sufentanil Citrate Injection through breast milk for excess sedation and respiratory depression. Withdrawal symptoms can occur in breastfed infants when maternal administration of an opioid analgesic is stopped, or when breastfeeding is stopped.
8.3 Females and Males of Reproductive Potential
Infertility
Use of opioids for an extended period of time may cause reduced fertility in females and males of reproductive potential. It is not known whether these effects on fertility are reversible [see Adverse Reactions (6.2)].
8.4 Pediatric Use
The safety and efficacy of intravenous sufentanil in pediatric patients as young as 1 day old undergoing cardiovascular surgery have been documented in a limited number of cases. The clearance of sufentanil in healthy neonates is approximately one-half that in adults and children. The clearance rate of sufentanil can be further reduced by up to a third in neonates with cardiovascular disease, resulting in an increase in the elimination half-life of the drug.
8.5 Geriatric Use
Elderly patients (aged 65 years or older) may have increased sensitivity to sufentanil. In general, use caution when selecting a dosage for an elderly patient, usually starting at the low end of the dosing range, reflecting the greater frequency of decreased hepatic, renal, or cardiac function and of concomitant disease or other drug therapy.
Respiratory depression is the chief risk for elderly patients treated with opioids, and has occurred after large initial doses were administered to patients who were not opioid-tolerant or when opioids were co-administered with other agents that depress respiration. Titrate the dosage of Sufentanil Citrate Injection slowly in geriatric patients and monitor closely for signs of central nervous system and respiratory depression [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2)].
8.6 Hepatic Impairment
Sufentanil Citrate Injection should be administered with caution to patients with liver dysfunction because of the extensive hepatic metabolism. Reduce the dosage as needed and monitor closely for signs of respiratory depression, sedation, and hypotension.
8.7 Renal Impairment
Sufentanil Citrate Injection should be administered with caution to patients with kidney dysfunction because of the renal excretion of sufentanil citrate and its metabolites. Reduce the dosage as needed and monitor for signs of respiratory depression, sedation, and hypotension.
•
Pregnancy: May cause fetal harm. (8.1)
•
Lactation: Infants exposed to Sufentanil Citrate Injection through breast milk should be monitored for excess sedation and respiratory depression. (8.2)
DRUG ABUSE AND DEPENDENCE SECTION
9 DRUG ABUSE AND DEPENDENCE
9.1 Controlled Substance
Sufentanil Citrate Injection contains sufentanil, a Schedule II controlled substance.
9.2 Abuse
Sufentanil Citrate Injection contains sufentanil, a substance with high potential for misuse and abuse, which can lead to the development of substance use disorder, including addiction [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)].
Misuse is the intentional use, for therapeutic purposes, of a drug by an individual in a way other than prescribed by a healthcare provider or for whom it was not prescribed.
Abuse is the intentional, non-therapeutic use of a drug, even once, for its desirable psychological or physiological effects.
Drug addiction is a cluster of behavioral, cognitive, and physiological phenomena that may include a strong desire to take the drug, difficulties in controlling drug use (e.g., continuing drug use despite harmful consequences, giving a higher priority to drug use than other activities and obligations), and possible tolerance or physical dependence.
Misuse and abuse of Sufentanil Citrate Injection increases risk of overdose, which may lead to central nervous system and respiratory depression, hypotension, seizures, and death. The risk is increased with concurrent abuse of Sufentanil Citrate Injection with alcohol and/or other CNS depressants. Abuse of and addiction to opioids in some individuals may not be accompanied by concurrent tolerance and symptoms of physical dependence. In addition, abuse of opioids can occur in the absence of addiction.
All patients treated with opioids require careful and frequent reevaluation for signs of misuse, abuse, and addiction, because use of opioid analgesic products carries the risk of addiction even under appropriate medical use. Patients at high risk of Sufentanil Citrate Injection abuse include those with a history of prolonged use of any opioid, including products containing sufentanil, those with a history of drug or alcohol abuse, or those who use Sufentanil Citrate Injection in combination with other abused drugs.
“Drug-seeking” behavior is very common in persons with substance use disorders. Drug-seeking tactics include emergency calls or visits near the end of office hours, refusal to undergo appropriate examination, testing, or referral, repeated “loss” of prescriptions, tampering with prescriptions, and reluctance to provide prior medical records or contact information for other treating healthcare provider(s). “Doctor shopping” (visiting multiple prescribers to obtain additional prescriptions) is common among people who abuse drugs and people with substance use disorder. Preoccupation with achieving adequate pain relief can be appropriate behavior in a patient with inadequate pain control.
Sufentanil Citrate Injection, like other opioids, can be diverted for nonmedical use into illicit channels of distribution. Careful record-keeping of prescribing information, including quantity, frequency, and renewal requests, as required by state and federal law, is strongly advised.
Proper assessment of the patient, proper prescribing practices, periodic reevaluation of therapy, and proper dispensing and storage are appropriate measures that help to limit abuse of opioid drugs.
Risks Specific to Abuse of Sufentanil Citrate Injection
Abuse of Sufentanil Citrate Injection poses a risk of overdose and death. The risk is increased with concurrent use of Sufentanil Citrate Injection with alcohol and/or other CNS depressants. Parenteral drug abuse is commonly associated with transmission of infectious diseases such as hepatitis and HIV.
9.3 Dependence
Both tolerance and physical dependence can develop during use of opioid therapy.
Tolerance is a physiological state characterized by a reduced response to a drug after repeated administration (i.e., a higher dose of a drug is required to produce the same effect that was once obtained at a lower dose).
Physical dependence is a state that develops as a result of a physiological adaptation in response to repeated drug use, manifested by withdrawal signs and symptoms after abrupt discontinuation or a significant dose reduction of a drug.
Withdrawal may be precipitated through the administration of drugs with opioid antagonist activity (e.g., naloxone), mixed agonist/antagonist analgesics (e.g., pentazocine, butorphanol, nalbuphine), or partial agonists (e.g., buprenorphine). Physical dependence may not occur to a clinically significant degree until after several days to weeks of continued use.
Sufentanil Citrate Injection should not be abruptly discontinued in a physically-dependent patient. If Sufentanil Citrate Injection is abruptly discontinued in a physically-dependent patient, a withdrawal syndrome may occur, typically characterized by restlessness, lacrimation, rhinorrhea, perspiration, chills, myalgia, and mydriasis. Other signs and symptoms also may develop, including irritability, anxiety, backache, joint pain, weakness, abdominal cramps, insomnia, nausea, anorexia, vomiting, diarrhea, or increased blood pressure, respiratory rate, or heart rate.
Infants born to mothers physically-dependent on opioids will also be physically-dependent and may exhibit respiratory difficulties and withdrawal signs [see Use in Specific Populations (8.1)].
OVERDOSAGE SECTION
10 OVERDOSAGE
Clinical Presentation
Acute overdose with sufentanil can be manifested by respiratory depression, somnolence progressing to stupor or coma, skeletal muscle flaccidity, cold and clammy skin, constricted pupils, and, in some cases, pulmonary edema, bradycardia, hypotension, hypoglycemia, partial or complete airway obstruction, atypical snoring, and death. Marked mydriasis rather than miosis may be seen with hypoxia in overdose situations [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.2)].
Treatment of Overdose
In case of overdose, priorities are the reestablishment of a patent and protected airway and institution of assisted or controlled ventilation, if needed. Employ other supportive measures (including oxygen and vasopressors) in the management of circulatory shock and pulmonary edema as indicated. Cardiac arrest or arrhythmias will require advanced life-support measures.
Opioid antagonists, such as naloxone, are specific antidotes to respiratory depression resulting from opioid overdose. For clinically significant respiratory or circulatory depression secondary to sufentanil overdose, administer an opioid antagonist.
Because the duration of opioid reversal is expected to be less than the duration of action of sufentanil in Sufentanil Citrate Injection, carefully monitor the patient until spontaneous respiration is reliably reestablished. If the response to an opioid antagonist is suboptimal or only brief in nature, administer additional antagonist as directed by the product's prescribing information.
In an individual physically-dependent on opioids, administration of the recommended usual dosage of the antagonist will precipitate an acute withdrawal syndrome. The severity of the withdrawal symptoms experienced will depend on the degree of physical dependence and the dose of the antagonist administered. If a decision is made to treat serious respiratory depression in the physically-dependent patient, administration of the antagonist should be initiated with care and by titration with smaller than usual doses of the antagonist.
CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY SECTION
12 CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY
12.1 Mechanism of Action
Sufentanil is an opioid agonist. When used in balanced general anesthesia, sufentanil has been reported to be as much as 10 times as potent as fentanyl. When administered intravenously as a primary anesthetic agent with 100% oxygen, sufentanil is approximately 5 to 7 times as potent as fentanyl.
12.2 Pharmacodynamics
Effects on the Central Nervous System
Sufentanil produces respiratory depression by direct action on brain stem respiratory centers. The respiratory depression involves both a reduction in the responsiveness of the brain stem respiratory centers to increases in carbon dioxide tension and to electrical stimulation.
Sufentanil causes miosis, even in total darkness. Pinpoint pupils are a sign of opioid overdose but are not pathognomonic (e.g., pontine lesions of hemorrhagic or ischemic origins may produce similar findings). Marked mydriasis rather than miosis may be seen due to hypoxia in overdose situations.
Effects on the Gastrointestinal Tract and Other Smooth Muscle
Sufentanil causes a reduction in motility associated with an increase in smooth muscle tone in the antrum of the stomach and duodenum. Digestion of food in the small intestine is delayed and propulsive contractions are decreased. Propulsive peristaltic waves in the colon are decreased, while tone may be increased to the point of spasm resulting in constipation. Other opioid-induced effects may include a reduction in biliary and pancreatic secretions, spasm of sphincter of Oddi, and transient elevations in serum amylase.
Effects on the Cardiovascular System
Sufentanil produces peripheral vasodilation which may result in orthostatic hypotension or syncope. Manifestations of histamine release and/or peripheral vasodilation may include pruritus, flushing, red eyes and sweating and/or orthostatic hypotension.
Effects on the Endocrine System
Opioids inhibit the secretion of adrenocorticotropic hormone (ACTH), cortisol, and luteinizing hormone (LH) in humans. They also stimulate prolactin, growth hormone (GH) secretion, and pancreatic secretion of insulin and glucagon [see Adverse Reactions (6.2)].
Use of opioids for an extended period of time may influence the hypothalamic- pituitary-gonadal axis, leading to androgen deficiency that may manifest as low libido, impotence, erectile dysfunction, amenorrhea, or infertility. The causal role of opioids in the clinical syndrome of hypogonadism is unknown because the various medical, physical, lifestyle, and psychological stressors that may influence gonadal hormone levels have not been adequately controlled for in studies conducted to date [see Adverse Reactions (6.2)].
Effects on the Immune System
Opioids have been shown to have a variety of effects on components of the immune system in in vitro and animal models. The clinical significance of these findings is unknown. Overall, the effects of opioids appear to be modestly immunosuppressive.
Concentration–Efficacy Relationships
The minimum effective analgesic concentration will vary widely among patients, especially among patients who have been previously treated with opioid agonists [see Dosage and Administration (2.1, 2.2)]. The minimum effective analgesic concentration of sufentanil for any individual patient may increase over time due to an increase in pain, the development of a new pain syndrome and/or the development of analgesic tolerance.
Concentration–Adverse Reaction Relationships
There is a relationship between increasing sufentanil plasma concentration and increasing frequency of dose-related opioid adverse reactions such as nausea, vomiting, CNS effects, and respiratory depression. In opioid-tolerant patients, the situation may be altered by the development of tolerance to opioid-related adverse reactions [see Dosage and Administration (2.1, 2.2, 2.3)].
12.3 Pharmacokinetics
Sufentanil Citrate Injection is administered by the intravenous or epidural route. The pharmacokinetics of intravenous sufentanil can be described as a three-compartment model.
Absorption
After epidural administration of incremental doses totaling 5 to 40 mcg sufentanil during labor and delivery, maternal and neonatal sufentanil plasma concentrations were at or near the 0.05 to 0.1 ng/mL limit of detection, and were slightly higher in mothers than in their infants.
Distribution
Plasma protein binding of sufentanil, related to the alpha acid glycoprotein concentration, was approximately 93% in healthy males, 91% in mothers and 79% in neonates. Sufentanil has a distribution time of 1.4 minutes and redistribution time of 17.1 minutes.
Elimination
The elimination half-life is 164 minutes in adults. The elimination half-life of sufentanil is shorter (e.g., 97 +/- 42 minutes) in infants and children, and longer in neonates (e.g., 434 +/- 160 minutes) compared to that of adolescents and adults.
Metabolism
The liver and small intestine are the major sites of biotransformation.
Excretion
Approximately 80% of the administered dose is excreted within 24 hours and only 2% of the dose is eliminated as unchanged drug.
NONCLINICAL TOXICOLOGY SECTION
13 NONCLINICAL TOXICOLOGY
13.1 Carcinogenesis, Mutagenesis, Impairment of Fertility
Carcinogenesis
Long-term studies in animals to evaluate the carcinogenic potential of sufentanil have not been conducted.
Mutagenesis
Sufentanil was not genotoxic in the in vitro bacterial reverse mutation assay (Ames assay) or in the in vivo rat bone marrow micronucleous assay.
Impairment of Fertility
Fertility and early embryonic development studies were conducted in male and female rats treated with 0.005, 0.02 or 0.08 mg/kg sufentanil IV for 56 days and 14 days prior to mating through gestation respectively. Increased mortality was noted in all treatment groups. Lower pregnancy rated were noted following treatment of males at doses of 0.02 and 0.08 mg/kg (0.1 and 0.4 times the maximum human total procedural dose of 30 mcg/kg IV, based on a body surface area comparison), suggesting the potential for an adverse effect on fertility in males. Increased resorption of fetuses and reduced litter size was noted in the high dose females (0.4 times the maximum human total procedural dose of 30 mcg/kg IV, based on a body surface area comparison) suggesting the potential for fetotoxicity, likely due to maternal toxicity.
CLINICAL STUDIES SECTION
14 CLINICAL STUDIES
Epidural Use in Labor and Delivery
Epidural sufentanil was tested in 340 patients in two (one single-center and one multicenter) double-blind, parallel studies. Doses ranged from 10 to 15 mcg sufentanil and were delivered in a 10 mL volume of 0.125% bupivacaine with and without epinephrine 1:200,000. In all cases sufentanil was administered following a dose of local anesthetic to test proper catheter placement. Since epidural opioids and local anesthetics potentiate each other, these results may not reflect the dose or efficacy of epidural sufentanil by itself.
Individual doses of 10 to 15 mcg sufentanil plus bupivacaine 0.125% with epinephrine provided analgesia during the first stage of labor with a duration of 1 to 2 hours. Onset was rapid (within 10 minutes). Subsequent doses (equal dose) tended to have shorter duration. Analgesia was profound (complete pain relief) in 80% to 100% of patients and a 25% incidence of pruritus was observed. The duration of initial doses of sufentanil plus bupivacaine with epinephrine is approximately 95 minutes, and of subsequent doses, 70 minutes.
There are insufficient data to critically evaluate neonatal neuromuscular and adaptive capacity following recommended doses of maternally administered epidural sufentanil with bupivacaine. However, if larger than recommended doses are used for combined local and systemic analgesia, e.g., after administration of a single dose of 50 mcg epidural sufentanil during delivery, then impaired neonatal adaption to sound and light can be detected for 1 to 4 hours and if a dose of 80 mcg is used impaired neuromuscular coordination can be detected for more than 4 hours.
HOW SUPPLIED SECTION
16 HOW SUPPLIED/STORAGE AND HANDLING
Sufentanil Citrate Injection, USP equivalent to 50 mcg/mL sufentanil is supplied in the following single-dose containers:
|
Unit of Sale |
Concentration |
|---|---|
|
NDC 0409-3382-21 |
50 mcg/mL |
|
Carton of 10 Single-dose Fliptop Vials | |
|
NDC 0409-3382-22 |
100 mcg/2 mL |
|
Carton of 10 Single-dose Fliptop Vials |
(50 mcg/mL) |
|
NDC 0409-3382-25 |
250 mcg/5 mL |
|
Carton of 10 Single-dose Fliptop Vials |
(50 mcg/mL) |
Protect from light. Retain in carton until time of use.
Store at 20°C to 25°C (68°F to 77°F). [See USP Controlled Room Temperature.]
INFORMATION FOR PATIENTS SECTION
17 PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATION
Addiction, Abuse, and Misuse
Inform patients that the use of Sufentanil Citrate Injection, even when taken as recommended, can result in addiction, abuse, and misuse, which can lead to overdose and death [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)].
Life-Threatening Respiratory Depression
Inform patients of the risk of life-threatening respiratory depression, including information that the risk is greatest when starting Sufentanil Citrate Injection or when the dosage is increased, and that it can occur even at recommended dosages.
Hyperalgesia and Allodynia
Advise patients to inform their healthcare provider if they experience symptoms of hyperalgesia, including worsening pain, increased sensitivity to pain, or new pain [see Warnings and Precautions (5.7), Adverse Reactions (6)].
Serotonin Syndrome
Inform patients that opioids could cause a rare but potentially life- threatening condition called serotonin syndrome resulting from concomitant administration of serotonergic drugs. Warn patients of the symptoms of serotonin syndrome and to seek medical attention right away if symptoms develop after discharge from the hospital. Instruct patients to inform their healthcare provider if they are taking, or plan to take serotonergic medications [see Warnings and Precautions (5.8), Drug Interactions (7)].
Constipation
Advise patients of the potential for severe constipation, including management instructions and when to seek medical attention [see Adverse Reactions (6), Clinical Pharmacology (12.2)].
