Adenosine
These highlights do not include all the information needed to use ADENOSINE INJECTION safely and effectively. See full prescribing information for ADENOSINE INJECTION. ADENOSINE injection, for intravenous use Initial U.S. Approval: 1995
61d9b8f6-f93f-46ee-bec2-db8d46999792
HUMAN PRESCRIPTION DRUG LABEL
Sep 5, 2023
Eugia US LLC
DUNS: 968961354
Products 2
Detailed information about drug products covered under this FDA approval, including NDC codes, dosage forms, ingredients, and administration routes.
Adenosine
Product Details
FDA regulatory identification and product classification information
FDA Identifiers
Product Classification
Product Specifications
INGREDIENTS (3)
Adenosine
Product Details
FDA regulatory identification and product classification information
FDA Identifiers
Product Classification
Product Specifications
INGREDIENTS (3)
Drug Labeling Information
DRUG INTERACTIONS SECTION
7 DRUG INTERACTIONS
7.1 Effects of Other Drugs on Adenosine Injection
- The vasoactive effects of adenosine are inhibited by adenosine receptor antagonists, (such as methylxanthines (e.g., caffeine, aminophylline, and theophylline). The safety and efficacy of adenosine injection in the presence of these agents has not been systematically evaluated [see Overdosage (10)].
- The vasoactive effects of adenosine injection are potentiated by nucleoside transport inhibitors such as dipyridamole. The safety and efficacy of adenosine in the presence of dipyridamole has not been systematically evaluated.
- Whenever possible, drugs that might inhibit or augment the effects of adenosine should be withheld for at least five half-lives prior to the use of adenosine injection.
7.2 Effects of Adenosine Injection on Other Drugs
Adenosine injection has been given with other cardioactive drugs (such as beta adrenergic blocking agents, cardiac glycosides, and calcium channel blockers) without apparent adverse interactions, but its effectiveness with these agents has not been systematically evaluated. Because of the potential for additive or synergistic depressant effects on the SA and AV nodes, however, adenosine injection should be used with caution in the presence of these agents [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2)].
- Methylxanthines interfere with the activity of adenosine injection (7.1, 10)
- Nucleoside transport inhibitors such as dipyridamole can increase the activity of adenosine injection (7.1)
DOSAGE & ADMINISTRATION SECTION
2 DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
The recommended adenosine injection, USP dose is 0.14 mg/kg/min infused over six minutes (total dose of 0.84 mg/kg) (Table 1).
- Administer adenosine injection, USP only as a continuous peripheral intravenous infusion
- Inject Thallium-201 at the midpoint of the adenosine infusion (i.e., after the first three minutes of adenosine injection, USP)
- Thallium-201 is physically compatible with adenosine injection, USP and may be injected directly into the adenosine infusion set
- Inject Thallium-201 as close to the venous access as possible to prevent an inadvertent increase in the dose of adenosine injection, USP (the contents of the intravenous tubing) being administered
Visually inspect adenosine injection, USP for particulate matter and discoloration prior to administration. Do not administer adenosine injection, USP if it contains particulate matter or is discolored.
There are no data on the safety or efficacy of alternative adenosine infusion protocols. The safety and efficacy of adenosine injection, USP administered by the intracoronary route have not been established.
Table 1 Dosage Chart for Adenosine Injection, USP|
Patient Weight |
Infusion Rate |
|
45 |
2.1 |
|
50 |
2.3 |
|
55 |
2.6 |
|
60 |
2.8 |
|
65 |
3 |
|
70 |
3.3 |
|
75 |
3.5 |
|
80 |
3.8 |
|
85 |
4 |
|
90 |
4.2 |
The nomogram displayed in Table 1 was derived from the following general formula:
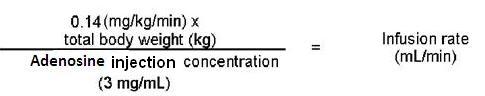
Recommended dose is 0.14 mg/kg/min infused over six minutes as a continuous peripheral intravenous infusion (total dose of 0.84 mg/kg) (2)
USE IN SPECIFIC POPULATIONS SECTION
8 USE IN SPECIFIC POPULATIONS
8.1 Pregnancy
Pregnancy Category C. Animal reproduction studies have not been conducted with adenosine; nor have studies been performed in pregnant women. Because it is not known whether adenosine injection can cause fetal harm when administered to pregnant women, adenosine injection should be used during pregnancy only if clearly needed.
8.3 Nursing Mothers
It is not known whether adenosine injection is excreted in human milk. Because many drugs are excreted in human milk and because of the potential for serious adverse reactions from adenosine injection in nursing infants, the decision to interrupt nursing after administration of adenosine injection or not to administer adenosine injection, should take into account the importance of the drug to the mother.
8.4 Pediatric Use
The safety and effectiveness of adenosine injection in patients less than 18 years of age have not been established.
8.5 Geriatric Use
Clinical studies with adenosine injection did not include sufficient numbers of subjects aged younger than 65 years to determine whether they respond differently. Other reported experience has not revealed clinically relevant differences of the response of elderly in comparison to younger patients.
HOW SUPPLIED SECTION
16 HOW SUPPLIED/STORAGE AND HANDLING
How Supplied
Adenosine injection, USP is supplied as 20 mL and 30 mL vials of sterile, nonpyrogenic, preservative-free, clear colorless solution in normal saline:
60 mg per 20 mL (3 mg/mL):
20 mL Single-Dose Vials in a Carton of 1 NDC 55150-192-01
20 mL Single-Dose Vials in a Carton of 10 NDC 55150-192-20
** 90 mg per 30 mL (3 mg/mL):**
30 mL Single-Dose Vials in a Carton of 1 NDC 55150-193-01
30 mL Single-Dose Vials in a Carton of 10 NDC 55150-193-30
Storage and Handling
- Store at 20° to 25°C (68° to 77°F) [see USP Controlled Room Temperature].
- Do not refrigerate as crystallization may occur. If crystallization has occurred, dissolve crystals by warming to room temperature. The solution must be clear at the time of use
- Discard unused portion
The vial stopper is not made with natural rubber latex.
