Regulatory Information
HSA regulatory responsibility and product classification details
Regulatory Responsibility
Product Classification
Formulation Information
CAPSULE
**DOSE AND METHOD OF ADMINISTRATION** The dose range is 150 to 600 mg per day given in either two or three divided doses. Pregabalin may be taken with or without food. **Neuropathic pain** Pregabalin treatment can be started at a dose of 150 mg per day. Based on individual patient response and tolerability, the dosage may be increased to 300 mg per day after an interval of 3 to 7 days, and if needed, to a maximum dose of 600 mg per day after an additional 7-day interval. **Epilepsy** Pregabalin treatment can be started with a dose of 150 mg per day. Based on individual patient response and tolerability, the dosage may be increased to 300 mg per day after 1 week. The maximum dosage of 600 mg per day may be achieved after an additional week. **Generalised anxiety disorder** The dose range is 150 to 600 mg per day given as two or three divided doses. The need for treatment should be reassessed regularly. Pregabalin treatment can be started with a dose of 150 mg per day. Based on individual patient response and tolerability, the dosage may be increased to 300 mg per day after 1 week. Following an additional week, the dosage may be increased to 450 mg per day. The maximum dosage of 600 mg per day may be achieved after an additional week. **Fibromyalgia** The recommended dose of pregabalin is 300 to 450 mg per day. Dosing should begin at 75 mg two times a day (150 mg per day) and may be increased to 150 mg two times a day (300 mg per day) within 1 week based on efficacy and tolerability. Patients who do not experience sufficient benefit with 300 mg per day may be further increased to 225 mg two times a day (450 mg per day). Although pregabalin was also reportedly studied at 600 mg per day, there is no evidence that this dose confers additional benefit and that this dose was less tolerated. In view of the dose-dependent adverse reactions, treatment with doses above 450 mg per day is not recommended. **Discontinuation of pregabalin** If pregabalin has to be discontinued, it is recommended this should be done gradually over a minimum of 1 week independent of the indication. **Patients with renal impairment** Dosage reduction in patients with compromised renal function must be individualised according to creatinine clearance (CLcr) (see **PHARMACODYNAMIC AND PHARMACOKINETIC PROPERTIES, Pharmacokinetics** – _please refer to the Product Insert/Patient Information Leaflet published on HSA for the full drug information_), as indicated in Table 1 determined using the following formula: 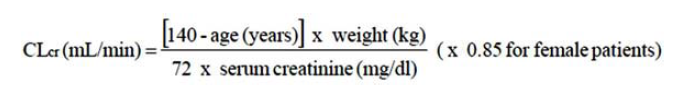 For patients receiving haemodialysis, the pregabalin daily dose should be adjusted based on renal function. In addition to the daily dose, a supplementary dose should be given immediately following every 4-hour haemodialysis treatment (see Table 1). 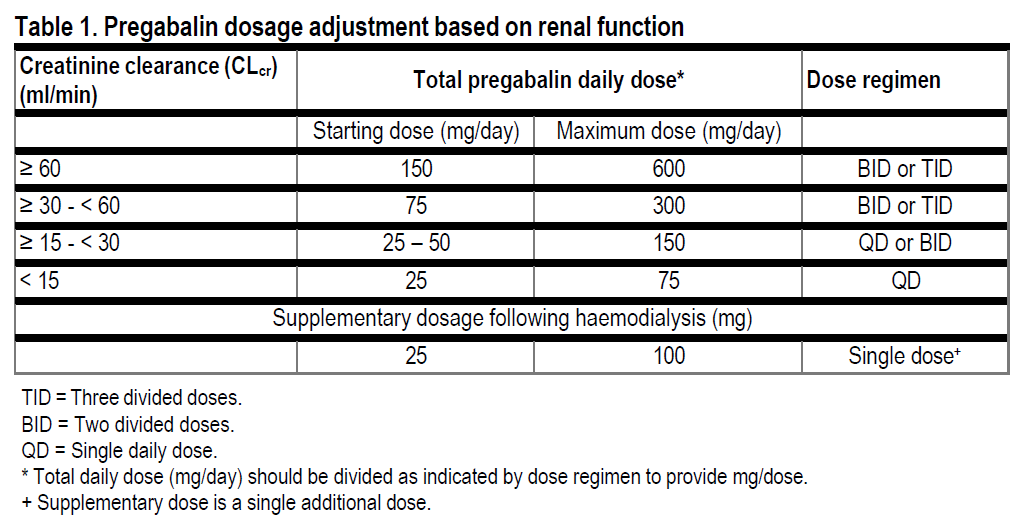 **Use in patients with hepatic impairment** No dosage adjustment is required for patients with hepatic impairment (see **PHARMACODYNAMIC AND PHARMACOKINETIC PROPERTIES, Pharmacokinetics**, _Pharmacokinetics in special patient groups, Hepatic impairment_ – _please refer to the Product Insert/Patient Information Leaflet published on HSA for the full drug information_). **Use in children and adolescents (12 to 17 years of age)** The safety and effectiveness of pregabalin in paediatric patients below the age of 12 years and adolescents have not been established. The use in children and adolescents is not recommended (see **PRECLINICAL SAFETY** – _please refer to the Product Insert/Patient Information Leaflet published on HSA for the full drug information_). **Use in the elderly (over 65 years of age)** Elderly patients may require a dose reduction of pregabalin due to decreased renal function (see **PHARMACODYNAMIC AND PHARMACOKINETIC PROPERTIES, Pharmacokinetics**, _Pharmacokinetics in special patient groups, Elderly (over 65 years of age)_ – _please refer to the Product Insert/Patient Information Leaflet published on HSA for the full drug information_).
ORAL
Medical Information
**INDICATIONS** **Neuropathic pain** Pregabalin is indicated for the treatment of neuropathic pain, which includes diabetic peripheral neuropathy and post-herpetic neuralgia, in adults. **Epilepsy** Pregabalin is indicated as adjunctive therapy of partial seizures, with or without secondary generalisation, in adults. **Generalised anxiety disorder** Pregabalin is indicated for the treatment of Generalised Anxiety Disorder (GAD) in adults. **Fibromyalgia** Pregabalin is indicated for the management of fibromyalgia.
**CONTRAINDICATIONS** Hypersensitivity to pregabalin or to any of the excipients of the formulation.
N02BF02
pregabalin
Manufacturer Information
RANBAXY (MALAYSIA) SDN. BHD.
SUN PHARMACEUTICAL INDUSTRIES LIMITED
Active Ingredients
Documents
Package Inserts
Maxgalin Capsule PI.pdf
Approved: September 15, 2023
