Regulatory Information
HSA regulatory responsibility and product classification details
Regulatory Responsibility
Product Classification
Formulation Information
INJECTION, POWDER, LYOPHILIZED, FOR SOLUTION
**4.2 Posology and method of administration** Initiate treatment of IDELVION under the supervision of a physician experienced in the treatment of haemophilia B. The decision for an individual patient on the use of home treatment of bleeding and prophylaxis of bleeding in patients with haemophilia B should be made by the treating physician who should ensure that appropriate training is provided and the use is reviewed at intervals. Posology The dose and duration of the substitution therapy depend on the severity of the factor IX deficiency, the location and extent of the bleeding and the patient’s clinical condition and response. The number of units of factor IX administered is expressed in International Units (IU), which are related to the current WHO standard for factor IX products. One International Unit (IU) of factor IX activity is equivalent to that quantity of factor IX in one ml of normal human plasma. Factor IX activity in plasma is expressed either as a percentage (relative to normal human plasma) or in International Units (relative to an International Standard for factor IX in plasma). On demand treatment The calculation of the required dose of factor IX is based on the empirical finding that 1 International Unit (IU) factor IX per kg body weight is expected to increase the circulating level of factor IX by an average of 1.3 international units/dl (1.3 % of normal) in patients ≥ 12 years of age and by 1.0 international unit/dl (1.0 % of normal) in patients < 12 years of age. The required dose is determined using the following formulae: Required dose (IU) = body weight (kg) x desired factor IX rise (% of normal or IU/dl) x {reciprocal of observed recovery (IU/kg per IU/dl)} Expected factor IX rise (IU/dl or % of normal) = Dose (IU) x Recovery (IU/dl per IU/kg)/body weight (kg) The amount to be administered and the frequency of administration should always be oriented to the clinical effectiveness in the individual case. For determination of adequate maintenance dose take into consideration the extended half-life of the product. Patients < 12 years of Age For an incremental recovery of 1 international unit/dl per 1 international unit/kg, the dose is calculated as follows: Dose (IU) = body weight (kg) x desired factor IX increase (IU/dl) x 1 dl/kg Example 1. A peak level of 50 % of normal is required in a 20 kg patient with severe haemophilia B. The appropriate dose would be 20 kg x 50 international units/dl x 1 dl/kg = 1000 international units. 2. A dose of 1000 international units of IDELVION, administered to a 25 kg patient, should be expected to result in a peak post-injection factor IX increase of 1000 international units/25 kg x 1.0 (international units/dl per international units/kg) = 40 international units/dl (40 % of normal). Patients ≥ 12 years of Age For an incremental recovery of 1.3 international units/dl per 1 international unit/kg, the dose is calculated as follows: Dose (IU) = body weight (kg) x desired factor IX increase (IU/dl) x 0.77 dl/kg Example 1. A peak level of 50 % of normal is required in a 80 kg patient with severe haemophilia B. The appropriate dose would be 80 kg x 50 international units/dl x 0.77 dl/kg = 3080 international units. 2. A dose of 2000 international units of IDELVION, administered to a 80 kg patient, should be expected to result in a peak post-injection factor IX increase of 2000 international units x 1.3 (international units/dl per international units/kg) /80 kg = 32.5 international units/dl (32.5 % of normal). The following table can be used to guide dosing for control and prevention of bleeding episodes and surgery: 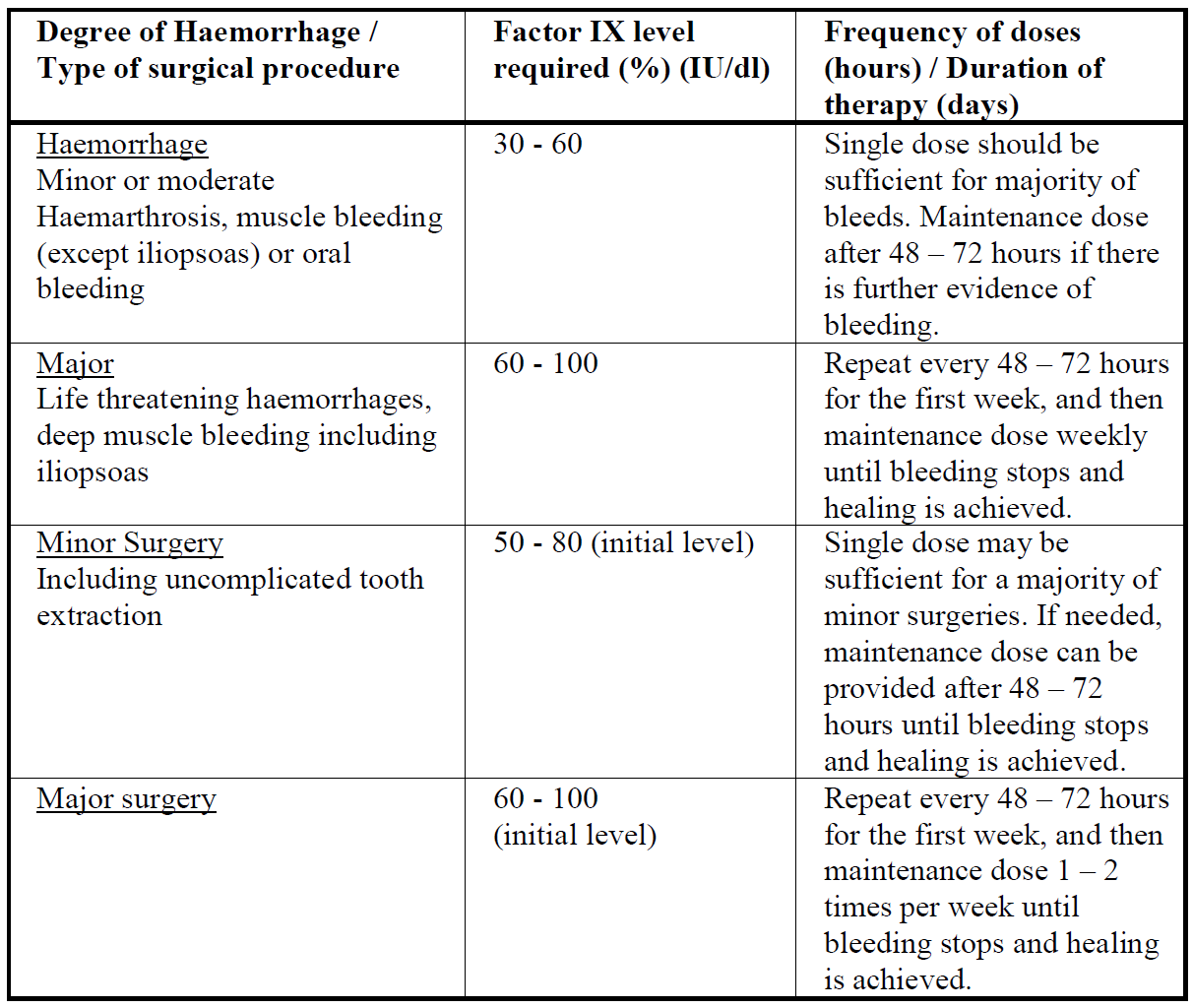 Prophylaxis For routine prophylaxis to prevent bleeding in patients ≥ 12 years with haemophilia B, the recommended regimen is 25 to 40 international units/kg once weekly. Patients who are well-controlled on a once-weekly regimen might be treated with up to 75 international units/kg on an interval of 14 days. Patients ≥18 years who are well-controlled on a 14-day regimen may be switched to 100 international units/kg every 21 days. Adjust dosing regimen based on individual patient’s clinical condition and response. Data for the 21-Day regimen was based on limited number of patients who switched to this regimen after they were well-controlled on the 14-day regimen (see section 5.1 and 5.2 – _please refer to the Product Insert/Patient Information Leaflet published on HSA for the full drug information_). Closer monitoring of the trough concentrations and/or presence of breakthrough bleeds should be undertaken after the switch. Paediatric population Currently available data are described in section 5.2 – _please refer to the Product Insert/Patient Information Leaflet published on HSA for the full drug information_. For routine prophylaxis the recommended dose regimen for patients < 12 years is 35 to 50 international units/kg once weekly (see section 5.2 – _please refer to the Product Insert/Patient Information Leaflet published on HSA for the full drug information_). Dosing regimen should be adjusted based on individual patient’s clinical condition and response. Clinical studies investigating safety and efficacy of longer treatment intervals than once weekly are ongoing. Older people The posology and method of administration in older people (> 65 years) has not been determined in clinical studies. Monitoring for inhibitors Patients should be monitored for the development of factor IX inhibitors. See also section 4.4 – _please refer to the Product Insert/Patient Information Leaflet published on HSA for the full drug information_. Method of administration Intravenous use. For instructions on reconstitution of the medicinal product before administration, see section 6.6 – _please refer to the Product Insert/Patient Information Leaflet published on HSA for the full drug information_. The reconstituted preparation should be injected slowly intravenously at a rate comfortable for the patient. The patient should be observed for any immediate reaction. If any reaction takes place that might be related to the administration of IDELVION, the rate of injection should be decreased or the application should be stopped, as required by the clinical condition of the patient (see also section 4.4 – _please refer to the Product Insert/Patient Information Leaflet published on HSA for the full drug information_).
INTRAVENOUS
Medical Information
**4.1 Therapeutic indications** Prophylaxis and treatment of bleeding in patients with haemophilia B (congenital factor IX deficiency) including control and prevention of bleeding in surgical settings.
**4.3 Contraindications** IDELVION is contraindicated in patients who have a known hypersensitivity to IDELVION, any of its components, excipients or hamster protein (see section 6.1 – _please refer to the Product Insert/Patient Information Leaflet published on HSA for the full drug information_).
B02BD04
coagulation factor IX
Manufacturer Information
CSL BEHRING PTE. LTD.
CSL Behring GmbH (Powder)
CSL Behring GmbH (Solvent)
Active Ingredients
Documents
Package Inserts
Idelvion Injection PI.pdf
Approved: January 10, 2022
