Regulatory Information
HSA regulatory responsibility and product classification details
Regulatory Responsibility
Product Classification
Formulation Information
INJECTION
**4.2 Dose and method of administration** **Each ampoule is for use in a single patient on one occasion only** Gentamicin is normally given by intramuscular injection. Intravenous administration may be used for particular indications when the intramuscular route is not appropriate. The dosage is the same for either route of administration. It is desirable to measure both peak and trough serum levels during treatment. Prior to administration, the patient’s bodyweight should be measured for the correct calculation of dosage. In obese patients, the appropriate dose can be calculated by assuming the bodyweight is the patient’s estimated lean bodyweight plus 40% of the excess. Blood specimens for the determination of peak gentamicin concentrations should be obtained approximately one hour following IM administration and 30 minutes after completion of a 30 minute infusion. Blood specimens for the trough gentamicin concentration should be obtained immediately prior to the next IM or IV dose. **Intravenous administration** For IV administration, the prescribed dose of gentamicin may be diluted in 100–200 mL of sterile normal saline or 5% glucose in water. The concentration of gentamicin in the solution should not exceed 1 mg/mL. Infusion periods of 30 minutes to 2 hours have been advocated. Administration of the dose by bolus injection produces serum levels which are initially in excess of what is regarded as being safe from toxic side effects. The high serum level does however rapidly fall and the potential danger or safety of this method is yet to be established. Gentamicin Injection must not be mixed with other drugs, but should be administered by separate infusion (see **Section 4.5 Interactions with other medicines and other forms of interactions** – _please refer to the Product Insert/Patient Information Leaflet published on HSA for the full drug information_). **Adults (Dosage in patients with normal renal function**) For serious infections (Systemic and urinary tract infections): 3 mg/kg/day in three doses given every eight hours. Life threatening infections: Up to 5 mg/kg/day in 3 or 4 equal doses with reduction to 3 mg/kg/day as soon as clinically indicated. Doses should never exceed 5 mg/kg/day unless serum levels are monitored. The following table should be used as a guide: 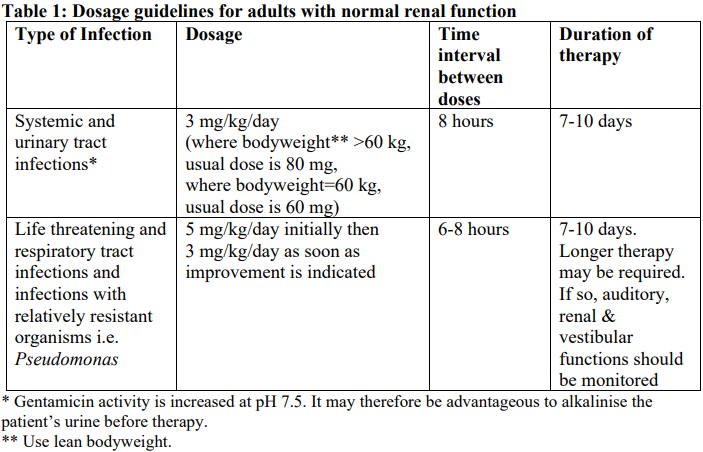 **Paediatrics** The following table should be used as a guide: 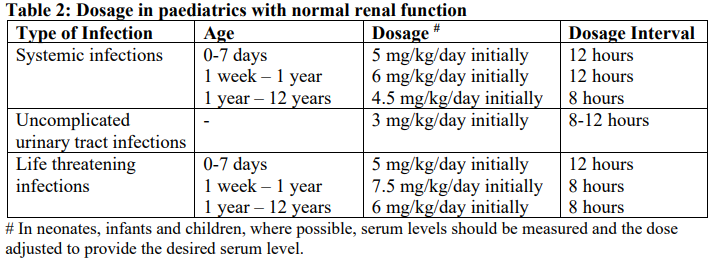 **Dosage in patients with impaired renal function** Dosage should be adjusted to minimise the risk of toxicity. The first dose should be as normal e.g. 80 mg (bodyweight >60 kg) and subsequent doses should be given less frequently, depending on the degree of renal impairment. The following table should be used as a guide: 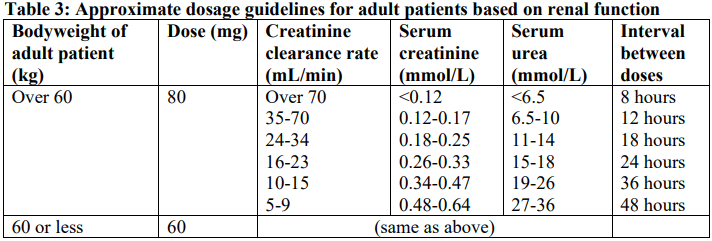 When only a serum urea concentration is available, this value may be utilised initially, however, it should be supplemented with a serum creatinine level or creatinine clearance rate whenever possible. N.B. The standard dose of 80 mg three times a day may be inappropriate and a more appropriate dose can be calculated using a nomogram which takes into account the patient’s serum creatinine levels, bodyweight and age. This dose can be adjusted if necessary following determination of serum creatinine levels. Desirable serum levels of gentamicin are 5–8 micrograms/mL as a peak and 1–2 micrograms/mL as a trough. Note: In children with impaired renal function serum levels should be monitored and frequency of dosage reduced if indicated. In adults with renal failure undergoing haemodialysis, the amount of gentamicin removed from the blood may vary depending upon several factors including the dialysis method used. An eight hour haemodialysis may reduce serum concentrations of gentamicin by approximately 50%. The recommended dosage at the end of each dialysis period is 1 to 1.7 mg/kg depending upon the severity of infection.
INTRAVENOUS, INTRAMUSCULAR
Medical Information
**4.1 Therapeutic indications** For the treatment of infections due to one or more susceptible strains of bacteria, including _Pseudomonas aeruginosa_, _Proteus_ species (indole positive and indole negative), _Escherichia coli_, _Klebsiella_, _Enterobacter_ and _Serratia_ species and _Staphylococcus_ (including strains resistant to other antibiotics). Gentamicin may also be used for the treatment of the following conditions when caused by susceptible organisms: bacteraemia, respiratory tract infections, urinary tract infections, skin and skin structure infections, bone infections, peritonitis, septic abortion and burns complicated by sepsis. Aminoglycosides, including gentamicin are generally not indicated in uncomplicated initial episodes of urinary tract infection unless the causative organisms are not susceptible to less toxic antibiotics. In suspected or documented Gram-negative sepsis, gentamicin should be considered for initial antimicrobial therapy. Therapy may be instituted before obtaining results of susceptibility tests. The decision to continue therapy is based on results of the susceptibility tests, the severity of the infection and risk of toxicity. If anaerobic organisms are suspected, antimicrobial therapy in addition to the gentamicin regimen should be considered.
**4.3 Contraindications** Known hypersensitivity to gentamicin, any of the excipients, or patients who have experienced previous toxic reactions (ototoxicity, nephrotoxicity) resulting from aminoglycoside therapy.
J01GB03
gentamicin
Manufacturer Information
PFIZER PRIVATE LIMITED
PFIZER (PERTH) PTY LTD
Active Ingredients
Documents
Package Inserts
Gentamicin Injection BP PI.pdf
Approved: April 6, 2023
