Regulatory Information
HSA regulatory responsibility and product classification details
Regulatory Responsibility
Product Classification
Formulation Information
GRANULE, FOR SUSPENSION
**4.2 Posology and method of administration** Posology The dose and frequency of administration are determined based on body weight (see Table 1). 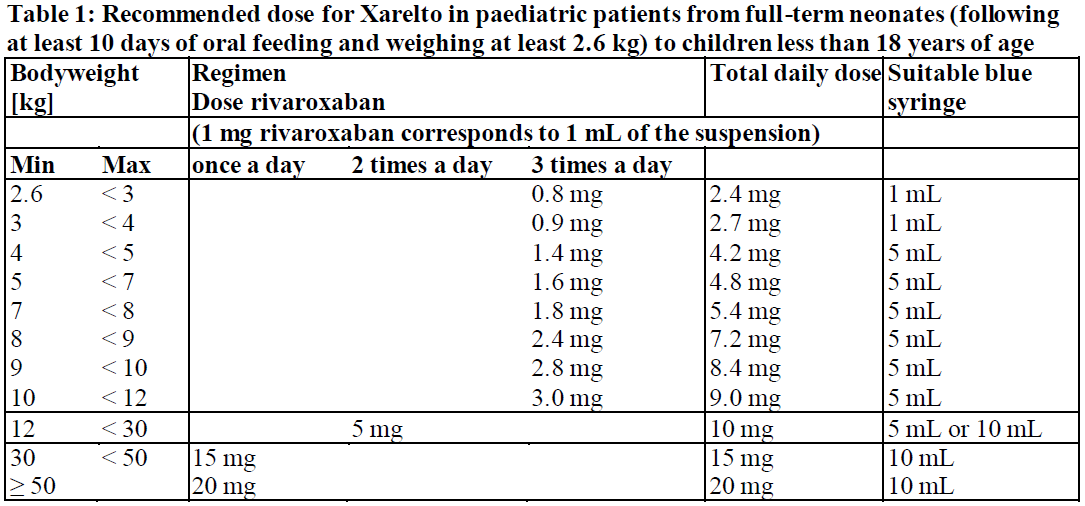 The weight of the child should be monitored and the dose reviewed regularly, especially for children below 12 kg. This is to ensure that a therapeutic dose is maintained. Dose adjustments should be made based on changes in body weight only. _Frequency of dosing:_ - _For a once a day regimen_ The doses should be taken approximately 24 hours apart. - _For a two times a day regimen_ The doses should be taken approximately 12 hours apart. - _For a three times a day regimen_ The doses should be taken approximately 8 hours apart. For patients with body weight of at least 2.6 kg to less than 30 kg only the oral suspension should be used. Do not split Xarelto tablets or use Xarelto tablets of lower strength in an attempt to provide doses for children with body weight below 30 kg. For patients with body weight of at least 30 kg, Xarelto oral suspension or tablets of 15 mg or 20 mg strength can be administered once a day. Xarelto oral suspension is provided with either 1 mL or 5 mL and 10 mL blue syringes (oral dosing syringe) with their adapter. To ensure accurate dosing it is recommended to use the blue syringes as follows (see Table 1): - 1 mL blue syringe (with 0.1 mL graduations) must be used in patients weighing less than 4 kg - 5 mL blue syringe (with 0.2 mL graduations) may be used in patients weighing 4 kg up to less than 30 kg - 10 mL blue syringe (with 0.5 mL graduations) is only recommended for use in patients weighing 12 kg or more For patients weighing 12 kg up to less than 30 kg, either 5 mL or 10 mL blue syringes can be used. It is recommended that the healthcare professional advises the patient or caregiver which blue syringe to use to ensure that the correct volume is administered. Instructions for Use booklet is provided with the medicinal product. _Initiation of treatment_ - _Paediatric patients from term neonates to less than 6 months_ Treatment for paediatric patients from term neonates to less than 6 months of age, who at birth had at least 37 weeks of gestation, weigh at least 2.6 kg, and have had at least 10 days of oral feeding should be initiated following at least 5 days of initial parenteral anticoagulation treatment (see sections 4.4 and 5.1 – _please refer to the Product Insert/Patient Information Leaflet published on HSA for the full drug information_). Xarelto is dosed based on body weight using the oral suspension formulation (see Table 1). - _Paediatric patients from 6 months of age to less than 18 years_ Treatment for paediatric patients from 6 months to less than 18 years of age should be initiated following at least 5 days of initial parenteral anticoagulation treatment (see section 5.1 – _please refer to the Product Insert/Patient Information Leaflet published on HSA for the full drug information_). Xarelto is dosed based on body weight (see Table 1). _Duration of treatment_ - _All children, except those aged less than 2 years with catheter-related thrombosis_ Therapy should be continued for at least 3 months. Treatment can be extended up to 12 months when clinically necessary. There is no data available in children to support a dose reduction after 6 months treatment. The benefit-risk of continued therapy after 3 months should be assessed on an individual basis taking into account the risk for recurrent thrombosis versus the potential bleeding risk. - _Children aged less than 2 years with catheter-related thrombosis_ Therapy should be continued for at least 1 month. Treatment can be extended up to 3 months when clinically necessary. The benefit-risk of continued therapy after 1 month should be assessed on an individual basis taking into account the risk for recurrent thrombosis versus the potential bleeding risk. _Missed doses_ - _Once a day regimen_ If taken once a day, a missed dose should be taken as soon as possible after it is noticed, but only on the same day. If this is not possible, the patient should skip the dose and continue with the next dose as prescribed. The patient should not take two doses to make up for a missed dose. - _Two times a day regimen_ If taken twice a day, a missed morning dose should be taken immediately when it is noticed, and it may be taken together with the evening dose. A missed evening dose can only be taken during the same evening, the patient should not take two doses the next morning. - _Three times a day regimen_ If taken three times a day, the three times daily administration schedule with approximately 8-hour intervals should simply be resumed at the next scheduled dose without compensating for the missed dose. On the following day, the child should continue with the regular once, twice or three times daily regimen. _Converting from parenteral anticoagulants to Xarelto_ For patients currently receiving a parenteral anticoagulant, start Xarelto 0 to 2 hours before the time of the next scheduled administration of the parenteral medicinal product (e.g. LMWH) or at the time of discontinuation of a continuously administered parenteral medicinal product (e.g. intravenous unfractionated heparin). _Converting from Xarelto to parenteral anticoagulants_ Discontinue Xarelto and give the first dose of parenteral anticoagulant at the time that the next Xarelto dose would be taken. _Converting from Vitamin K antagonists (VKA) to Xarelto_ VKA treatment should be stopped and Xarelto therapy should be initiated once the International Normalised Ratio (INR) is ≤ 2.5. When converting patients from VKAs to Xarelto, INR values will be falsely elevated after the intake of Xarelto. The INR is not valid to measure the anticoagulant activity of Xarelto, and therefore should not be used (see section 4.5 – _please refer to the Product Insert/Patient Information Leaflet published on HSA for the full drug information_). _Converting from Xarelto to Vitamin K antagonists (VKA)_ There is a potential for inadequate anticoagulation during the transition from Xarelto to VKA. Continuous adequate anticoagulation should be ensured during any transition to an alternate anticoagulant. It should be noted that Xarelto can contribute to an elevated INR. Children who convert from Xarelto to VKA need to continue Xarelto for 48 hours after the first dose of VKA. After 2 days of co-administration an INR should be obtained prior to the next scheduled dose of Xarelto. Co-administration of Xarelto and VKA is advised to continue until the INR is ≥ 2.0. Once Xarelto is discontinued INR testing may be done reliably 24 hours after the last dose (see above and section 4.5 – _please refer to the Product Insert/Patient Information Leaflet published on HSA for the full drug information_). _Special populations_ _Renal impairment_ - Children 1 year or older with mild renal impairment (glomerular filtration rate 50 – 80 mL/min/1.73 m2): no dose adjustment is required, based on data in adults and limited data in paediatric patients (see section 5.2 – _please refer to the Product Insert/Patient Information Leaflet published on HSA for the full drug information_). - Children 1 year or older with moderate or severe renal impairment (glomerular filtration rate < 50 mL/min/1.73 m2): Xarelto is not recommended as no clinical data is available (see section 4.4 – _please refer to the Product Insert/Patient Information Leaflet published on HSA for the full drug information_). - Children below 1 year: the renal function should only be determined using serum creatinine. Xarelto is not recommended in children younger than 1 year with serum creatinine results above 97.5th percentile (see Table 2 – _please refer to the Product Insert/Patient Information Leaflet published on HSA for the full drug information_), as no data are available (see section 4.4 – _please refer to the Product Insert/Patient Information Leaflet published on HSA for the full drug information_). 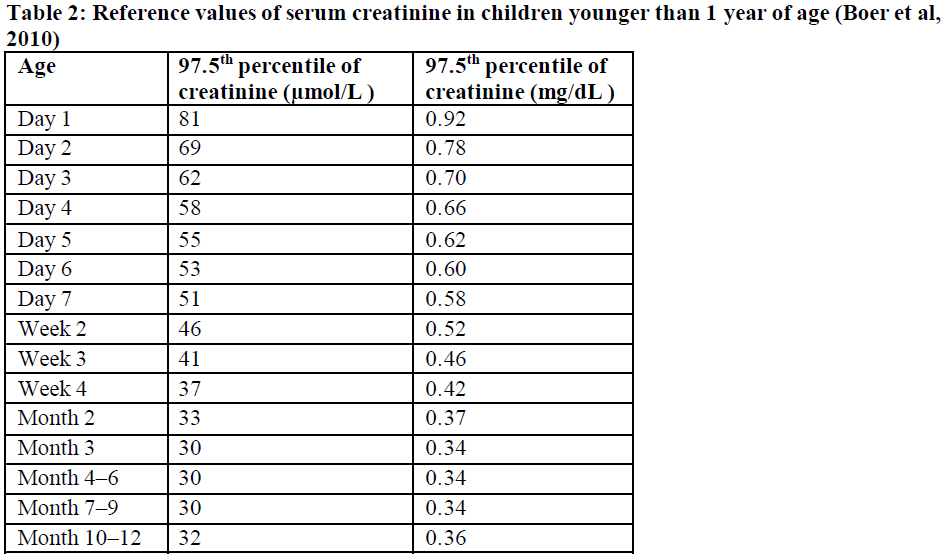 _Hepatic impairment_ No clinical data is available in children with hepatic impairment. Xarelto is contraindicated in patients with hepatic disease associated with coagulopathy and clinically relevant bleeding risk including cirrhotic patients with Child Pugh B and C (see section 4.3 and 5.2 – _please refer to the Product Insert/Patient Information Leaflet published on HSA for the full drug information_). _Body weight_ For children the dose is determined based on body weight (see Posology above). _Gender_ No dose adjustment (see section 5.2 – _please refer to the Product Insert/Patient Information Leaflet published on HSA for the full drug information_). _Paediatric population_ The safety and efficacy of Xarelto in children aged 0 to < 18 years have not been established in indications other than treatment of venous thromboembolism (VTE) and prevention of VTE recurrence. No data are available for other indications. Therefore, Xarelto is not recommended for use in children below 18 years of age in indications other than the treatment of VTE and prevention of VTE recurrence. Method of administration Xarelto is for oral use. The oral suspension should be taken with feeding or with food (see section 5.2 – _please refer to the Product Insert/Patient Information Leaflet published on HSA for the full drug information_). For details on preparation and administration of the oral suspension see section 6.6 – _please refer to the Product Insert/Patient Information Leaflet published on HSA for the full drug information_. The oral suspension may be given through a nasogastric or gastric feeding tube (see sections 5.2 and 6.6 – _please refer to the Product Insert/Patient Information Leaflet published on HSA for the full drug information_). Each dose should be immediately followed by the intake of one typical serving of liquid. This typical serving may include liquid volume used for feeding. In case the patient immediately spits up the dose or vomits within 30 minutes after receiving the dose, a new dose should be given. However, if the patient vomits more than 30 minutes after the dose, the dose should not be re-administered and the next dose should be taken as scheduled. If the oral suspension is not immediately available, when doses of 15 mg or 20 mg rivaroxaban are prescribed, these could be provided by crushing the 15 mg or 20 mg tablet and mixing it with water or apple puree immediately prior to use and administering it orally (see sections 5.2 and 6.6 – _please refer to the Product Insert/Patient Information Leaflet published on HSA for the full drug information_).
ORAL
Medical Information
**4.1 Therapeutic indications** Treatment of venous thromboembolism (VTE) and prevention of VTE recurrence in term neonates, infants and toddlers, children, and adolescents aged less than 18 years after at least 5 days of initial parenteral anticoagulation treatment.
**4.3 Contraindications** Hypersensitivity to the active substance or to any of the excipients listed in section 6.1 – _please refer to the Product Insert/Patient Information Leaflet published on HSA for the full drug information_. Active clinically significant bleeding. Lesion or condition, if considered to be a significant risk for major bleeding. This may include current or recent gastrointestinal ulceration, presence of malignant neoplasms at high risk of bleeding, recent brain or spinal injury, recent brain, spinal or ophthalmic surgery, recent intracranial haemorrhage, known or suspected oesophageal varices, arteriovenous malformations, vascular aneurysms or major intraspinal or intracerebral vascular abnormalities. Concomitant treatment with any other anticoagulants, e.g. unfractionated heparin (UFH), low molecular weight heparins (enoxaparin, dalteparin, etc.), heparin derivatives (fondaparinux, etc.), oral anticoagulants (warfarin, dabigatran etexilate, apixaban, etc.) except under specific circumstances of switching anticoagulant therapy (see section 4.2) or when UFH is given at doses necessary to maintain an open central venous or arterial catheter (see section 4.5 – _please refer to the Product Insert/Patient Information Leaflet published on HSA for the full drug information_). Hepatic disease associated with coagulopathy and clinically relevant bleeding risk including cirrhotic patients with Child Pugh B and C (see section 5.2 – _please refer to the Product Insert/Patient Information Leaflet published on HSA for the full drug information_). Pregnancy and breast-feeding (see section 4.6 – _please refer to the Product Insert/Patient Information Leaflet published on HSA for the full drug information_).
B01AF01
rivaroxaban
Manufacturer Information
BAYER (SOUTH EAST ASIA) PTE LTD
Bayer AG, Leverkusen
Active Ingredients
Documents
Package Inserts
Xarelto Oral Suspension PI.pdf
Approved: February 16, 2023
