Regulatory Information
HSA regulatory responsibility and product classification details
Regulatory Responsibility
Product Classification
Formulation Information
INJECTION, SOLUTION
**DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION** **ADULTS** **Rheumatoid Arthritis, Psoriatic Arthritis and Ankylosing Spondylitis** The recommended dose of Humira for adult patients with rheumatoid arthritis, psoriatic arthritis, or ankylosing spondylitis is 40 mg administered every other week as a single dose via subcutaneous injection. Methotrexate, glucocorticoids, salicylates, nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, analgesics or other DMARDs may be continued during treatment with Humira. In rheumatoid arthritis, some patients not taking concomitant MTX may derive additional benefit from increasing the dosage of Humira to 40 mg every week or 80 mg every other week. **Crohn’s Disease** 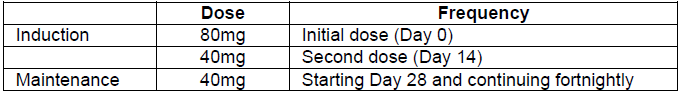 In case there is a need for a more rapid response to therapy, the regimen 160 mg at week 0 (given as 160 mg in one day or as 80 mg per day for two consecutive days), 80 mg at week 2, can be used with the awareness that the risk for adverse events is higher during induction. Some patients who experience a decrease in their response may benefit from an increase in dosage to 40 mg Humira every week or 80mg every other week. Aminosalicylates, corticosteroids, and/or immunomodulatory agents (e.g., 6-mercaptopurine and azathioprine) may be continued during treatment with Humira. Patients usually respond within the induction phase. However, if a patient does not show any response, available data do not sufficiently support further Humira treatment. **Ulcerative Colitis** The recommended Humira induction dose regimen for adult patients with moderate to severe ulcerative colitis is 160 mg at Week 0 (given as 160 mg in one day or as 80 mg per day for two consecutive days) and 80 mg at Week 2. After induction treatment, the recommended dose is 40 mg every other week via subcutaneous injection. Aminosalicylates, corticosteroids, and/or immunomodulatory agents (e.g., 6-mercaptopurine and azathioprine) may be continued during treatment with Humira. During maintenance treatment, corticosteroids may be tapered in accordance with clinical practice guidelines. Some patients who experience decrease in their response may benefit from an increase in dosage to 40 mg Humira every week or 80 mg every other week. Available data suggest that clinical response is usually achieved within 2–8 weeks of treatment. Adalimumab should only be continued in patients who have responded during the first 8 weeks of therapy. **Plaque Psoriasis** The recommended dose of Humira for adult patients with plaque psoriasis is an initial dose of 80 mg, followed by 40 mg given every other week starting one week after the initial dose. Continued therapy beyond 16 weeks should be carefully reconsidered in a patient not responding within this time period. Beyond 16 weeks, patients with inadequate response may benefit from an increase in dosage to 40 mg every week or 80 mg every other week. Response should be periodically evaluated (for example, every 12 weeks). Patients with continued inadequate response should discontinue treatment. If an adequate response is achieved with an increased dosage, the dose may subsequently be reduced to 40mg fortnightly. **Hidradenitis Suppurativa** The recommended Humira dose regimen for adult patients with hidradenitis suppurativa (HS) is 160 mg initially at Day 1 (given as 160 mg in one day or as 80 mg per day for two consecutive days), followed by 80 mg two weeks later at Day 15. Two weeks later (Day 29) continue with a dose of 40 mg every week or 80 mg every other week. Antibiotics may be continued during treatment with Humira if necessary. It is recommended that the patient should use a topical antiseptic wash on their HS lesions on a daily basis during treatment with Humira. Should treatment need to be interrupted, Humira 40 mg every week may be re-introduced. In patients without any benefit after 12 weeks of treatment, continued therapy should be reconsidered. **Uveitis** Ophthalmologists are advised to consult with an appropriate specialist before initiation of treatment with Humira. The recommended dose of Humira for adult patients with uveitis is an initial dose of 80 mg, followed by 40 mg given every other week starting one week after the initial dose. There is limited experience in the initiation of treatment with Humira alone. Treatment with Humira can be initiated in combination with corticosteroids and/or with other non-biologic immunomodulatory agents. Concomitant corticosteroids may be tapered in accordance with clinical practice starting two weeks after initiating treatment with Humira. It is recommended that the benefit and risk of continued long-term treatment should be evaluated on a yearly basis. **PEDIATRICS** **Juvenile Idiopathic Arthritis** **Polyarticular Juvenile Idiopathic Arthritis** The recommended dose of Humira for patients from 2 years of age with polyarticular juvenile idiopathic arthritis (JIA) is based on body weight (Table 31). MTX, glucocorticoids, NSAIDs, and/or analgesics may be continued during treatment with Humira. Humira may be available in different strengths and/or presentations. 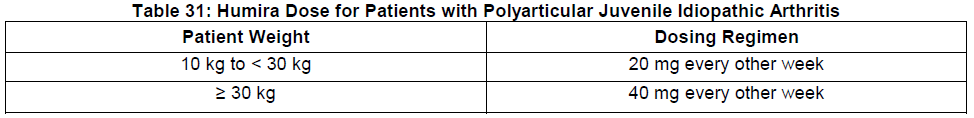 Humira has not been studied in patients with polyarticular juvenile idiopathic arthritis less than 2 years of age or in patients with a weight below 10kg. Available data suggest that clinical response is usually achieved within 12 weeks of treatment. Continued therapy should be carefully reconsidered in a patient not responding within this time period. There is no relevant use of Humira in children aged less than 2 years in this indication. **Enthesitis-Related Arthritis** The recommended dose of Humira for patients from 6 years of age with enthesitis-related arthritis is based on body weight (Table 32). Humira may be available in different strengths and/or presentations. 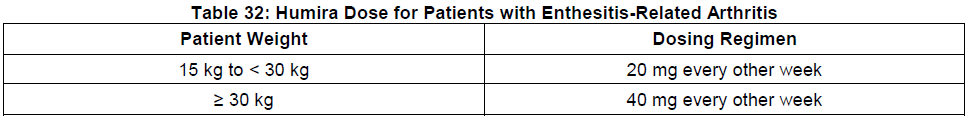 Humira has not been studied in patients with enthesitis-related arthritis aged less than 6 years. **Pediatric Crohn’s Disease** The recommended dose of Humira for patients from 6 to 17 years of age with Crohn’s disease is based on body weight (Table 33). Humira is administered via subcutaneous injection. Humira may be available in different strengths and/or presentations. 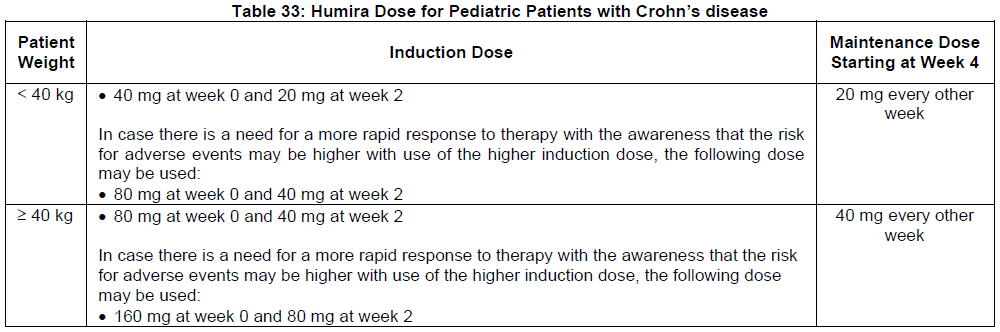 Patients who experience insufficient response may benefit from an increase in dosage: - < 40 kg: 20 mg every week - ≥ 40 kg: 40 mg every week or 80mg every other week Humira has not been studied in children with Crohn’s disease aged less than 6 years. **Pediatric Plaque Psoriasis** The recommended Humira dose for patients from 4 to 17 years of age with plaque psoriasis is based on body weight (Table 34). Humira is administered via subcutaneous injection. Humira may be available in different strengths and/or presentations. 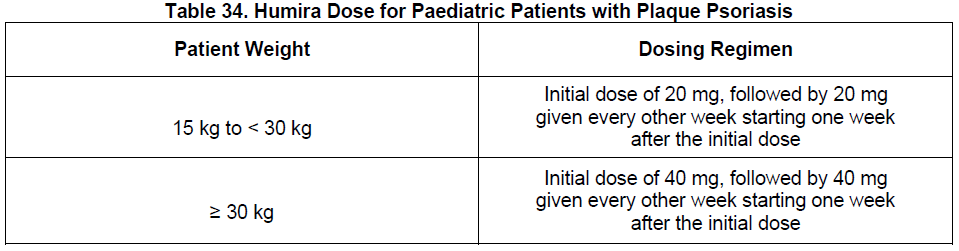 Continued therapy beyond 16 weeks should be carefully considered in a patient not responding within this time period. If retreatment with Humira is indicated, the above guidance on dose and treatment duration should be followed. There is no relevant use of Humira in children aged less than 4 years in this indication. **Adolescent hidradenitis suppurativa** There are no clinical trials with Humira in adolescent patients with hidradenitis suppurativa (HS). The posology of Humira in these patients has been determined from pharmacokinetic modeling and simulation. The recommended Humira dose in adolescent patients from 12 years of age weighing at least 30 kg with hidradenitis suppurativa is 80 mg at Week 0 followed by 40 mg every other week starting at Week 1 via subcutaneous injection. Humira may be available in different strengths and/or presentations. In adolescent patients with inadequate response to Humira 40 mg every other week, an increase in dosage to 40 mg every week or 80 mg every other week may be considered. Antibiotics may be continued during treatment with Humira if necessary. It is recommended that the patient should use a topical antiseptic wash on their HS lesions on a daily basis during treatment with Humira. Continued therapy beyond 12 weeks should be carefully reconsidered in a patient with no improvement within this time period. Should treatment be interrupted, Humira may be re-introduced as appropriate. The benefit and risk of continued long-term treatment should be periodically evaluated. There is no relevant use of Humira in children aged less than 12 years in this indication. **Pediatric Uveitis** The recommended dose of Humira for pediatric patients 2 years of age and older with chronic non-infectious anterior uveitis is based on body weight (Table 35). Humira is administered via subcutaneous injection. Humira may be available in different strengths and/or presentations. In paediatric uveitis, there is no experience in the treatment with Humira without concomitant treatment with methotrexate. 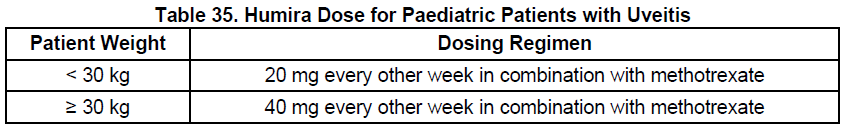 When Humira is initiated, a loading dose of 40 mg for patients <30 kg or 80 mg for patients ≥30 kg may be administered one week prior to the start of maintenance therapy. No clinical data are available on the use of a Humira loading dose in children < 6 years of age (see section Pharmacokinetics – _please refer to the Product Insert/Patient Information Leaflet published on HSA for the full drug information_). There is no relevant use of Humira in children aged less than 2 years in this indication. It is recommended that the benefit and risk of continued long-term treatment should be evaluated on a yearly basis. **Pediatric Ulcerative Colitis** The recommended dose of Humira for patients from 5 to 17 years of age with ulcerative colitis is based on body weight (Table 36). Humira is administered via subcutaneous injection. Humira may be available in different strengths and/or presentations. 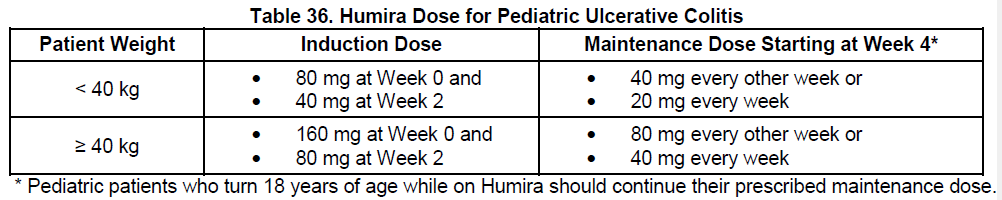 Continued therapy beyond 8 weeks should be carefully considered in patients not showing signs of response within this time period. There is no relevant use of Humira in children aged less than 5 years in this indication. **Pediatric Use** Humira has not been studied in children less than 2 years of age and there are limited data on Humira treatment in children with weight < 10kg. The safety and efficacy of Humira in pediatric patients for indications other than juvenile idiopathic arthritis (polyarticular juvenile idiopathic arthritis and enthesitis-related arthritis), pediatric Crohn’s disease, pediatric plaque psoriasis, adolescent hidradenitis suppurativa, pediatric uveitis and pediatric ulcerative colitis have not been established. **Geriatric Use** Of the total number of subjects in clinical studies of Humira, 9.4% were 65 years and over, while approximately 2.0% were 75 and over. No overall differences in effectiveness were observed between these subjects and younger subjects. No dose adjustment is needed for this population. **Preparation of Humira** Humira is intended for use under the guidance and supervision of a physician. Patients may self-inject Humira if their physician determines that it is appropriate and with medical follow-up, as necessary, after proper training in injection technique. Sites for self-injection include thigh or abdomen. Injection sites should be rotated. New injections should never be given into areas where the skin is tender, bruised, red or hard. Parenteral drug products should be inspected visually for particulate matter and discoloration prior to administration, whenever solution and container permit. Humira should not be mixed in the same syringe with any other medicine. Any unused product or waste material should be disposed of in accordance with local requirements.
SUBCUTANEOUS
Medical Information
**INDICATIONS** **ADULTS** **Rheumatoid Arthritis** Humira is indicated for reducing signs and symptoms and inhibiting the progression of structural damage and improving physical function in adult patients with moderately to severely active rheumatoid arthritis who have had an inadequate response to one or more DMARDs. Humira can be used alone or in combination with methotrexate or other DMARDs. Humira, in combination with MTX, can also be used in the treatment of patients with recently diagnosed moderate to severely active rheumatoid arthritis who have not received methotrexate. **Psoriatic Arthritis** Humira is indicated for reducing signs and symptoms of active arthritis in adult patients with moderate to severe psoriatic arthritis when the response to previous DMARD therapy has been inadequate. Humira has been shown to reduce the rate of progression of peripheral joint damage as measured by X-ray in patients with polyarticular symmetrical subtypes of the disease and to improve physical function. Humira can be used alone or in combination with DMARDs. **Ankylosing Spondylitis** Humira is indicated for reducing signs and symptoms in adult patients with active ankylosing spondylitis who have had an inadequate response to conventional therapy. **Crohn’s Disease** Humira is indicated for the treatment of moderate to severe active Crohn’s disease in adults to reduce the signs and symptoms of the disease and to induce and maintain clinical remission in patients who have had an inadequate response to conventional therapies, or who have lost response to or are intolerant of infliximab. For induction treatment, Humira should be given in combination with corticosteroids. Humira can be given as monotherapy in case of intolerance to corticosteroids or when continued treatment with corticosteroids is inadequate. **Ulcerative Colitis** Humira is indicated for treatment of moderately to severely active ulcerative colitis in adult patients who have had an inadequate response to conventional therapy including corticosteroids and/or 6-mercaptopurine (6-MP) or azathioprine (AZA), or who are intolerant to or have medical contraindications for such therapies. **Plaque Psoriasis** Humira is indicated for the treatment of adult patients with moderate to severe chronic plaque psoriasis who are candidates for systemic therapy or phototherapy and when other systemic therapies are medically less appropriate. **Hidradenitis Suppurativa** Humira is indicated for the treatment of active moderate to severe hidradenitis suppurativa (acne inversa) in adult patients with an inadequate response to conventional systemic HS therapy. **Uveitis** Humira is indicated for the treatment of non-infectious intermediate, posterior and panuveitis in adult patients who have had an inadequate response to corticosteroids, in patients in need of corticosteroid-sparing, or in whom corticosteroid treatment is inappropriate. **PEDIATRICS** **Juvenile Idiopathic Arthritis** **_Polyarticular Juvenile Idiopathic Arthritis_** Humira in combination with methotrexate is indicated for the treatment of active polyarticular juvenile idiopathic arthritis (pJIA), in patients 2 years of age and older, who have had an inadequate response to one or more disease-modifying anti-rheumatic drugs (DMARDS). Humira can be given as monotherapy in case of intolerance to methotrexate or when continued treatment with methotrexate is inappropriate (for the efficacy in monotherapy see **CLINICAL STUDIES** – _please refer to the Product Insert/Patient Information Leaflet published on HSA for the full drug information_). Humira has not been studied in patients aged less than 2 years. **_Enthesitis-Related Arthritis_** Humira is indicated for the treatment of active enthesitis-related arthritis in patients, 6 years of age and older, who have had an inadequate response to, or who are intolerant of, conventional therapy. **Pediatric Crohn’s Disease** Humira is indicated for reducing signs and symptoms and inducing and maintaining clinical remission in pediatric patients, 6 years of age and older, with moderately to severely active Crohn’s disease who have had an inadequate response to conventional therapy. **Pediatric Plaque Psoriasis** Humira is indicated for the treatment of severe chronic plaque psoriasis in children and adolescents from 4 years of age who have had an inadequate response to or are inappropriate candidates for topical therapy and phototherapy. **Adolescent Hidradenitis Suppurativa** Humira is indicated for the treatment of active moderate to severe hidradenitis suppurativa (acne inversa) in adolescents from 12 years of age with an inadequate response to conventional systemic hidradenitis suppurativa (HS) therapy. **Pediatric Uveitis** Humira is indicated for the treatment of chronic non-infectious anterior uveitis in pediatric patients 2 years of age and older who have had an inadequate response to or are intolerant to conventional therapy, or in whom conventional therapy is inappropriate. **Pediatric Ulcerative Colitis** Humira is indicated for inducing and maintaining clinical remission in pediatric patients 5 years of age or older with moderately to severely active ulcerative colitis who have had an inadequate response to conventional therapy including corticosteroids and/or 6-mercaptopurine (6-MP) or azathioprine (AZA), or who are intolerant to or have medical contraindications for such therapies.
**CONTRAINDICATIONS** Humira should not be administered to patients with known hypersensitivity to Humira or any of its excipients. Active tuberculosis or other severe infections such as sepsis, abscesses, and opportunistic infections (see **WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS** – _please refer to the Product Insert/Patient Information Leaflet published on HSA for the full drug information_). Moderate to severe heart failure (NYHA class III/IV) (see **WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS** – _please refer to the Product Insert/Patient Information Leaflet published on HSA for the full drug information_).
L04AB04
adalimumab
Manufacturer Information
ABBVIE PTE. LTD.
Vetter Pharma-Fertigung GmbH & Co. KG (Ravensburg)
AbbVie Biotechnology Ltd
