Regulatory Information
HSA regulatory responsibility and product classification details
Regulatory Responsibility
Product Classification
Formulation Information
INJECTION, POWDER, LYOPHILIZED, FOR SOLUTION
**DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION** An infusion rate of 10mg/min or less is associated with fewer infusions-related events. Infusion-related events are related to both concentration and rate of administration of vancomycin. Concentrations of no more than 5 mg/ml and rates of no more than 10mg/min are recommended in adults (see also age-specific recommendations). In selected patients in need of fluid restriction, a concentration up to 10 mg/ml may be used; use of such higher concentrations may increase the risk of infusion-related events. Infusion-related events may occur, however, at any rate or concentration. **Patients with normal renal function** **Adults** The usual daily intravenous dose is 2g divided either as 500mg every 6 hours or 1g every 12 hours. Each dose should be administered at no more than 10mg/min, or over a period of at least 60 minutes, whichever is longer. Other patient factors, such as age or obesity, may call for modification of the usual intravenous daily dose. **Pediatric patients** The usual intravenous dosage of vancomycin is 10 mg/kg per dose given every 6 hours. Each dose should be administered over a period of at least 60 minutes. Close monitoring of serum concentrations may be warranted in these patients. **Neonates** In pediatric patients up to the age of 1 month, the total daily intravenous dosage may be lower. In neonates, an initial dose of 15 mg/kg is suggested, followed by 10 mg/kg every 12 hours for neonates in the first week of life and every 8 hours thereafter up to the age of one month. Each dose should be administered over 60 minutes. In premature infants, vancomycin clearance decreases as postconceptional age decreases. Therefore, longer dosing intervals may be necessary in premature infants. Close monitoring of serum concentrations of vancomycin is recommended in these patients. **Patients with impaired renal function and elderly patients** Dosage adjustment must be made in patients with impaired renal function. In premature infants and in the elderly, greater dosage reductions than expected may be necessary because of decreased renal function. Measurement of vancomycin serum concentrations can be helpful in optimizing therapy, especially in seriously ill patients with changing renal function. Vancomycin serum concentrations can be determined by use of microbiologic assay, radioimmunoassay, fluorescence polarization immunoassay, fluorescence immunoassay, or high-pressure liquid chromatography. If creatinine clearance can be measured or estimated accurately, the dosage for most patients with renal impairment can be calculated using the following table. The dosage of vancomycin per day in mg is about 15 times the glomerular filtration rate in ml/min. 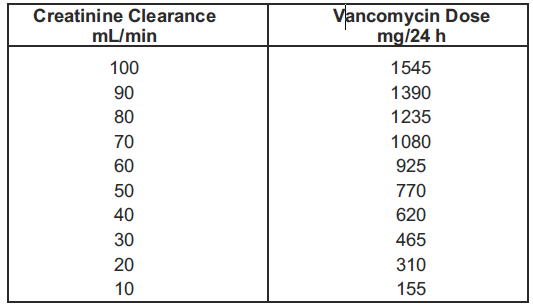 The initial dose should be no less than 15 mg/kg, even in patients with mild to moderate renal insufficiency. The table is not valid for functionally anephric patients. For such patients, an initial dose of 15mg/kg of body weight should be given to achieve prompt therapeutic serum concentrations. The dose required to maintain stable concentrations is 1.9 mg/kg/24h. In patients with marked renal impairment, it may be more convenient to be given maintenance doses of 250 to 1000mg once every several days rather than administering the drug on a daily basis. In anuria, a dose of 1000 mg every 7 to 10 days has been recommended. When only the serum creatinine concentration is known, the following formula (based on sex, weight, and age of the patient) may be used to calculate creatinine clearance. Calculated creatinine clearance (ml/min) are only estimates. The creatinine clearance should be measured promptly. 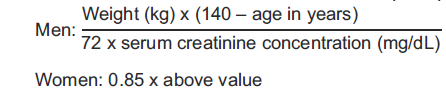 The serum creatinine must represent a steady state of renal function. Otherwise, the estimated value for creatinine clearance is not valid. Such a calculated clearance is an overestimate of actual clearance in patients with conditions: 1. characterized by decreasing renal function, such as shock, severe heart failure or oliguria; 2. in which a normal relationship between muscle mass and total body weight is not present, such as obese patients or those with liver disease, edema or ascites; and 3. accompanied by debilitation, malnutrition or inactivity. The safety and efficacy of vancomycin administration by the intrathecal (intralumbar or intraventricular) routes have not been established. Intermittent infusion is the recommended method of administration. **Compatibility with other Drugs and Intravenous Fluids** The following diluents are physically and chemically compatible (with 4g/L Vancomycin Hydrochloride): - 5% Dextrose Injection, - 5% Dextrose Injection and 0.9% Sodium Chloride Injection, - Lactated Ringer's Injection, - 5% Dextrose, Lactated Ringer's Injection, - 0.9% Sodium Chloride Injection. Good professional practice suggests that compounded admixtures should be administered as soon after preparation as is feasible. Vancomycin solution has a low pH and may cause physical instability of other compounds. Mixtures of solutions of vancomycin and beta-lactam antibiotics have been shown to be physically incompatible. The likelihood of precipitation increases with higher concentrations of vancomycin. It is recommended to adequately flush the intravenous lines between the administrations of these antibiotics. It is also recommended to dilute solutions of vancomycin to mg/mL or less. Although intravitreal injection is not an approved route of administration for vancomycin, precipitation has been reported after intravitreal injection of vancomycin and ceftazidime for endophthalmitis using different syringes and needles. The precipitates dissolved gradually, with complete clearing of the vitreous cavity over two months and with improvement of visual acuity. **Preparation and Stability** At the time of use, reconstitute the vials of Vancomycin Hydrochloride for Injection, USP with Sterile Water for Injection to a concentration of 50 mg of vancomycin/mL (see following table for volume of diluent). 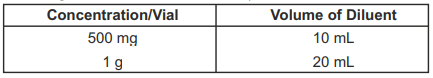 After reconstitution, the vials may be stored in a refrigerator for 96 hours without significant loss of potency. Reconstituted solutions of vancomycin (500 mg/10 mL) must be further diluted with at least 100 mL of a suitable infusion solution. For doses of 1gram (20mL), at least 200 mL of solution must be used. The desired dose, diluted in this manner, should be administered by intermittent IV infusion over a period of at least 60 minutes. Parenteral drug products should be visually inspected for particulate matter and discoloration prior to administration, whenever solution and container permit.
INTRAVENOUS
Medical Information
**INDICATIONS** Vancomycin is indicated for the treatment of serious or severe infections caused by susceptible strains of methicillin-resistant (beta-lactam resistant) staphylococci. It is indicated for penicillin-allergic patients, for patients who cannot receive or who have failed to respond to other drugs, including the penicillins or cephalosporins, and for infections caused by vancomycin-susceptible organisms that are resistant to other antimicrobial drugs. Vancomycin is indicated for initial therapy when methicillin-resistant staphylococci are suspected, but after susceptibility data are available, therapy should be adjusted accordingly. Vancomycin's effectiveness has been documented in other infections due to staphylococci, including septicemia, bone infections, lower respiratory tract infections, skin and skin structure infections. When staphylococcal infections are localized and purulent, antibiotics are used as adjuncts to appropriate surgical measures. Specimens for bacteriologic cultures should be obtained in order to isolate and identify causative organisms and to determine their susceptibilities to vancomycin. To reduce the development of drug-resistant bacteria and maintain the effectiveness of vancomycin and other antibacterial drugs, vancomycin should be used only to treat or prevent infections that are proven or strongly suspected to be caused by susceptible bacteria. When culture and susceptibility information are available, they should be considered in selecting or modifying antibacterial therapy. In the absence of such data, local epidemiology and susceptibility patterns may contribute to the empiric selection of therapy.
**CONTRAINDICATIONS** Vancomycin Hydrochloride for Injection is contraindicated in patients with known hypersensitivity to this antibiotic.
J01XA01
vancomycin
Manufacturer Information
HETERO SINGAPORE PTE. LTD.
Aspiro Pharma Limited
Active Ingredients
Documents
Package Inserts
Vanconex powder for injection PI.pdf
Approved: September 24, 2020
