Regulatory Information
HSA regulatory responsibility and product classification details
Regulatory Responsibility
Product Classification
Formulation Information
INJECTION, POWDER, FOR SOLUTION
**4.2 Posology and method of administration** Posology Treatment should be initiated under the supervision of a physician experienced in the treatment of haemophilia. The dosage and duration of the substitution therapy depend on the severity of factor VIII deficiency, on the location and extent of the bleeding and on the patient’s clinical condition. The number of units of factor VIII administered is expressed in International Units (IU), which are related to the current WHO standard for factor VIII products. Factor VIII activity in plasma is expressed either as a percentage (relative to normal human plasma) or in International Units (relative to an International Standard for factor VIII in plasma). One International Unit (IU) of factor VIII activity is equivalent to that quantity of factor VIII in 1 ml of normal human plasma. The calculation of the required dosage of factor VIII is based on the empirical finding that one International Unit (IU) factor VIII per kg of body weight raises the plasma factor VIII activity by 1.5% to 2%. The required dosage is determined using the following formula: Required units = body weight (kg) x desired factor VIII rise (%) (IU/dl) x 0.5 IU/kg The amount to be administered and the frequency of administrations should always be oriented to the clinical effectiveness in the individual case. In the case of the following haemorrhagic events, the factor VIII activity should not fall below the given factor VIII level in the corresponding period of treatment. The following table can be used to guide dosing in bleeding episodes and surgery: 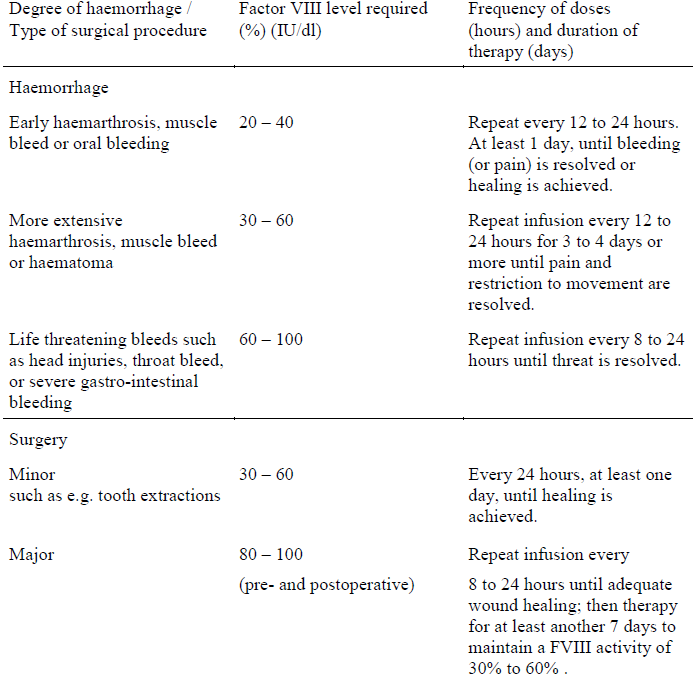 Under certain circumstances larger amounts than those calculated may be required, especially in the case of the initial dose. During the course of treatment, appropriate determination of factor VIII level is advised to guide the dose to be administered and the frequency of repeated infusions. In the case of major surgical interventions in particular, precise monitoring of the substitution therapy by means of coagulation analysis (plasma factor VIII activity) is indispensable. Individual patients may vary in their response to factor VIII, achieving different levels of in vivo recovery and demonstrating different half-lives. For long term prophylaxis against bleeds in patients with severe haemophilia A, dose of 20 to 60 International Units of factor VIII per kg body weight should be given at intervals of 2 to 3 days. In some cases, especially in younger patients, shorter dosage intervals or higher doses may be necessary. Patients should be monitored for the development of factor VIII inhibitors. If the expected factor VIII activity plasma levels are note attained, or if bleeding is not controlled with an appropriate dose, an assay should be performed to determine if a factor VIII inhibitor is present. If inhibitors are present at levels less than 10 Bethesda Units per ml, administration of additional human factor VIII may neutralise the inhibitors. In patients with inhibitor titres above 10 Bethesda Units per ml, the use of (activated) prothrombin complex concentrate or recombinant activated factor VII (rFVIIa) preparations has to be considered. These therapies should be directed by physicians with experience in the care of patients with haemophilia. There is insufficient data available relating to the administration of OCTANATE® in children younger than 6 years of age. See also 4.4 – _please refer to the Product Insert/Patient Information Leaflet published on HSA for the full drug information_. Method of administration Dissolve the preparation as described at 6.6 – _please refer to the Product Insert/Patient Information Leaflet published on HSA for the full drug information_. OCTANATE® should be administered via the intravenous route at a rate of 2 to 3 ml / min.
INTRAVENOUS
Medical Information
**4.1 Therapeutic indications** Treatment and prophylaxis of bleeding in patients with haemophilia A (congenital factor VIII deficiency).
**4.3 Contra-indications** Absolute contra-indication: - known allergic reactions to constituents in the preparation.
B02BD02
coagulation factor VIII
Manufacturer Information
WELLCHEM PHARMACEUTICALS PTE LTD
OCTAPHARMA PHARMAZEUTIKA PRODUKTIONSGES MBH
Octapharma Produktionsgesellschaft Deutschland mbH (Intermediate)
OCTAPHARMA S.A.S
OCTAPHARMA AB
Solupharm Pharmazeutische Erzeugnisse GmbH (Solvent)
Active Ingredients
Documents
Package Inserts
Octanate PI.pdf
Approved: March 20, 2017
