Regulatory Information
HSA regulatory responsibility and product classification details
Regulatory Responsibility
Product Classification
Formulation Information
INJECTION
**DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION** The rapid injection of a large volume of local anesthetic solution should be avoided and fractional (incremental) doses should always be used. The smallest dose and concentration required to produce the desired result should be administered. The dose of any local anesthetic differs with the anesthetic procedure, the area to be anesthetized, the vascularity of the tissues, the number of neuronal segments to be blocked, the intensity of the block, the degree of muscle relaxation required, the duration of the anesthesia desired, individual tolerance, and the physical condition of the patient. Patients in poor general condition due to aging or other compromising factors, such as impaired cardiovascular function, advanced liver disease, or severe renal dysfunction, require special attention. To reduce the risk of potentially serious adverse reactions, attempts should be made to optimize the patient’s condition before major blocks are performed, and the dosage should be adjusted accordingly. Use an adequate test dose (3 to 5 mL) of a short-acting local anesthetic solution containing epinephrine prior to induction of complete nerve block. This test dose should be repeated if the patient is moved in such a fashion as to have displaced the epidural catheter. It is recommended that adequate time be allowed for the onset of anesthesia following administration of each test dose. The use of levobupivacaine is not recommended for more than 24 hours (see **WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS** – _please refer to the Product Insert/Patient Information Leaflet published on HSA for the full drug information_). Disinfecting agents containing heavy metals, which cause release of ions (mercury, zinc, copper, etc.) should not be used for skin or mucous membrane disinfection since they have been related to incidents of swelling and edema. When chemical disinfection of the container surface is desired, either isopropyl alcohol (91%) or ethyl alcohol (70%) is recommended. It is recommended that chemical disinfection be accomplished by wiping the ampule thoroughly with cotton or gauze that has been moistened with the recommended alcohol prior to use. These products are intended for single use and do not contain preservatives; any solution remaining from an open container should be discarded. For specific techniques and procedures, refer to standard contemporary textbooks. **Levobupivacaine Compatibility and Admixtures** Levobupivacaine may not be compatible with alkaline solutions having a pH greater than 8.5. Studies have shown that levobupivacaine is compatible with 0.9% Sodium Chloride Injection USP and with saline solutions containing morphine, fentanyl, and clonidine. Compatibility studies with other parenteral products have not been studied. **Dilution Stability** Levobupivacaine diluted to 0.625 – 2.5 mg levobupivacaine per mL in 0.9% Sodium Chloride Injection is physically and chemically stable when stored in PVC (polyvinyl chloride) bags at ambient room temperature for up to 24 hours. Aseptic technique should be used to prepare the diluted products. Admixtures of levobupivacaine should be prepared for single patient use only and used within 24 hours of preparation. The unused portion of diluted levobupivacaine should be discarded after each use. Note: Parenteral products should be inspected visually for particulate matter and discoloration prior to administration whenever solution and container permit. Solutions that are not clear and colorless should not be used. **Shelf Life** Shelf life after first opening: The product should be used immediately. Shelf life after dilution: Chemical and physical in-use stability has been demonstrated for seven days at 20 – 22°C. Chemical and physical in-use stability with clonidine, morphine or fentanyl has been demonstrated for 40 hours at 20 – 22°C. From a microbiological point of view, the product should be used immediately. If not used immediately, in-use storage times and conditions prior to use are the responsibility of the user and would normally not be longer than 24 hours at 2 to 8°C, unless reconstitution/dilution has taken place in controlled and validated aseptic conditions. 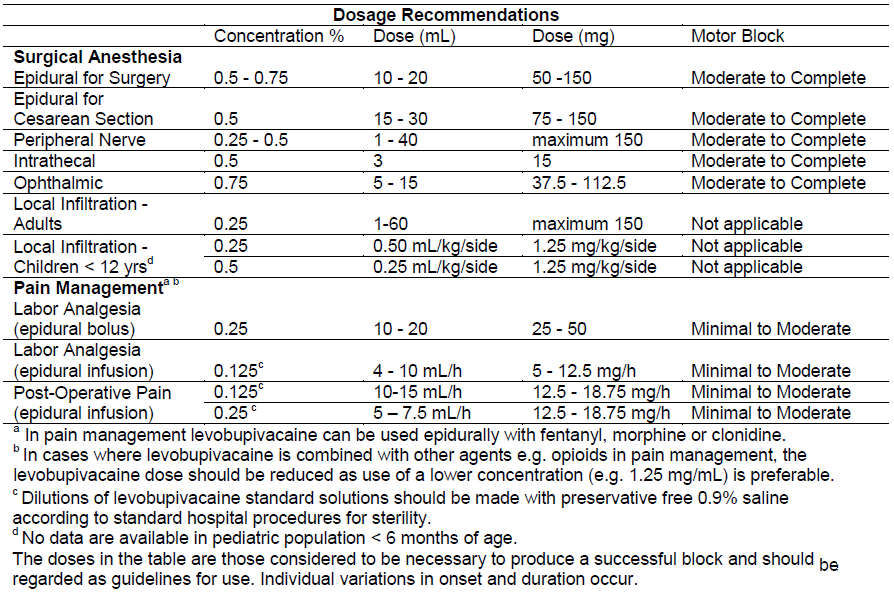 Epidural doses of up to 375 mg have been administered incrementally to patients during a surgical procedure. The maximum dose in 24 hours for intraoperative block and post-operative pain management was 695 mg. The maximum dose administered as a post-operative epidural infusion over 24 hours was 570 mg. The maximum dose administered to patients as a single fractionated injection was 300 mg for brachial plexus block. For cesarean section, the maximum recommended dose is 150 mg. In children, the maximum recommended dose for infiltration analgesia (ilioinguinal-iliohypogastric block) is 1.25 mg/kg/side.
EPIDURAL
Medical Information
**INDICATIONS** **Adults** Levobupivacaine is indicated in adults for: **Surgical Anesthesia** Major: Epidural (including for cesarean section), intrathecal, peripheral nerve block. Minor: Local infiltration, peribulbar block in ophthalmic surgery. For cesarean section, the 7.5 mg/mL concentration is not recommended (see **CONTRAINDICATIONS, WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS** – _please refer to the Product Insert/Patient Information Leaflet published on HSA for the full drug information_). **Pain Management** Continuous epidural infusion, single or multiple bolus administration for post-operative, labor or chronic pain. For continuous epidural analgesia, levobupivacaine may be administered in combination with epidural fentanyl, morphine or clonidine. For labor analgesia, the 7.5 mg/mL concentration is not recommended (see **CONTRAINDICATIONS, WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS, PREGNANCY AND LACTATION – Labor and Delivery** – _please refer to the Product Insert/Patient Information Leaflet published on HSA for the full drug information_) **Children** Levobupivacaine is indicated in children for infiltration analgesia (ilioinguinal/iliohypogastric blocks) (see **DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION**).
**CONTRAINDICATIONS** General contraindications related to regional anesthesia should be taken into account with the use of any regional anesthetic agent, including levobupivacaine. Levobupivacaine solutions are contraindicated in those with a known sensitivity to local anesthetic amide agents. Levobupivacaine is contraindicated in patients with severe hypotension such as cardiogenic or hypovolemic shock (see **WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS** – _please refer to the Product Insert/Patient Information Leaflet published on HSA for the full drug information_). Levobupivacaine solutions 2.5 mg/mL, 5 mg/mL, and 7.5 mg/mL, are contraindicated for use in paracervical block in obstetrics, and for intravenous regional anesthesia (e.g. Bier block). Additionally, levobupivacaine 7.5 mg/mL solution should not be employed for any obstetric procedures. Contraindications for use in paracervical block, Bier block, and levobupivacaine 7.5 mg/mL use in obstetric procedures are based upon documented experiences with bupivacaine. Levobupivacaine has not been tested in such instances.
N01BB10
levobupivacaine
Manufacturer Information
ABBVIE PTE. LTD.
Curida AS
Active Ingredients
Documents
Package Inserts
1.4.3 Proposed Chirocaine Injection PI_CCDS03020916_pristine.pdf
Approved: March 21, 2017
