Regulatory Information
HSA regulatory responsibility and product classification details
Regulatory Responsibility
Product Classification
Formulation Information
TABLET, FILM COATED
**4.2 Posology and method of administration** General Before instituting therapy with atorvastatin, an attempt should be made to control hypercholesterolemia with appropriate diet, exercise and weight reduction in obese patients, and to treat underlying medical problems. The patient should continue on a standard cholesterol-lowering diet during treatment with atorvastatin. The recommended starting dose of atorvastatin is 10 mg or 20 mg once daily. Patients who require a large reduction in LDL-C (more than 45%) may be started at 40 mg once daily. The dosage range is 10 mg to 80 mg once daily. Atorvastatin can be administered as a single dose at any time of the day, with or without food. The doses should be individualized according to baseline LDL-C levels, the goal of therapy, and patient response. After initiation and/or upon titration of atorvastatin, lipid levels should be analyzed within 2 to 4 weeks, and dosage adjusted accordingly. Prevention of Cardiovascular Disease (CVD) For primary prevention, the recommended dose is 10 mg once daily. For secondary prevention, optimal dosing may range from 10 mg to 80 mg atorvastatin once daily, to be given at the discretion of the prescriber, taking into account the expected benefit and safety considerations relevant to the patient to be treated (see section 5.1 – _please refer to the Product Insert/Patient Information Leaflet published on HSA for the full drug information_). Primary Hypercholesterolaemia and Combined (Mixed) Hyperlipidemia The majority of patients are controlled with atorvastatin 10 mg once daily. A therapeutic response is evident within 2 weeks, and the maximum response is usually achieved within 4 weeks. The response is maintained during chronic therapy. Homozygous Familial Hypercholesterolemia In a compassionate-use study of patients with homozygous familial hypercholesterolemia, most patients responded to 80 mg of atorvastatin with a greater than 15% reduction in LDL-C (18%–45%). Use in Patients with Hepatic Insufficiency See section 4.3 (Contraindications) and section 4.4 (Special warnings and precautions for use) – _please refer to the Product Insert/Patient Information Leaflet published on HSA for the full drug information_. Use in Patients with Renal Insufficiency Renal disease has no influence on the plasma concentrations or on LDL-C reduction with atorvastatin. Thus, no adjustment of dose is required (see section 4.4 – _please refer to the Product Insert/Patient Information Leaflet published on HSA for the full drug information_). Pediatric Use, Hypercholesterolemia Pediatric use should only be carried out by physicians experienced in the treatment of pediatric hyperlipidemia and patients should be re-evaluated on a regular basis to assess progress. For patients aged 10 years and above, the recommended starting dose of atorvastatin is 10 mg daily with titration up to 20 mg daily. Titration should be conducted according to the individual response and tolerability in pediatric patients. Safety information for pediatric patients treated with doses above 20 mg, corresponding to about 0.5 mg/kg, is limited. Experience in pediatric patients older than 6 to less than 10 years of age is derived from open-label studies (see section 4.8, section 5.1, and section 5.2 – _please refer to the Product Insert/Patient Information Leaflet published on HSA for the full drug information_). Atorvastatin is not indicated in the treatment of patients below the age of 10 years. Treatment experience in a pediatric population is limited to doses of atorvastatin up to 80 mg/day for one year in 8 patients with homozygous familial hypercholesterolemia. No clinical or biochemical abnormalities were reported in these patients. Use in the Elderly No differences in safety, efficacy or lipid treatment goal attainment were observed between elderly patients and the overall population (see section 5.2 – _please refer to the Product Insert/Patient Information Leaflet published on HSA for the full drug information_). Use in Combination with Other Medicinal Compounds In cases where co-administration of atorvastatin with cyclosporine, telaprevir, or the combination tipranavir/ritonavir is necessary, the dose of atorvastatin should not exceed 10 mg. Dose of atorvastatin should not exceed 20 mg/day with concomitant use with elbasvir/grazoprevir (see section 4.4. and section 4.5 – _please refer to the Product Insert/Patient Information Leaflet published on HSA for the full drug information_). Use of atorvastatin is not recommended in patients taking letermovir co-administered with cyclosporine. Pharmacokinetic drug interactions that result in increased systemic concentration of atorvastatin have also been noted with other human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) protease inhibitors (lopinavir/ritonavir, saquinavir/ritonavir, darunavir/ritonavir, fosamprenavir, fosamprenavir/ritonavir and nelfinavir), hepatitis C (HCV) protease inhibitors (boceprevir, elbasvir/grazoprevir, simeprevir), clarithromycin, itraconazole and letermovir. Caution should be used when co-prescribing atorvastatin, and appropriate clinical assessment is recommended to ensure that the lowest dose of atorvastatin necessary is employed (see section 4.4 and section 4.5 – _please refer to the Product Insert/Patient Information Leaflet published on HSA for the full drug information_). **THE FOLLOWING TREATMENT GUIDELINES MAY BE USED TO ESTABLISH TREATMENT GOALS** 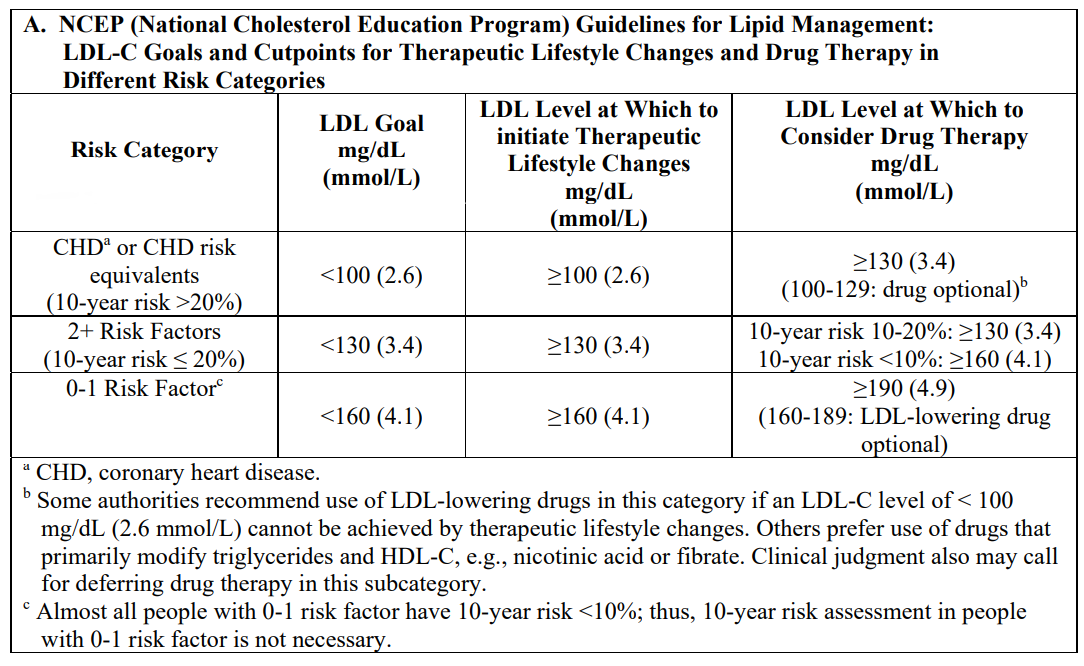 After the LDL-C goal has been achieved, if the TG is still ≥200 mg/dL (2.2mmol/L), non-HDL-C (total-C minus HDL-C) becomes a secondary target of therapy. Non-HDL-C goals are set 30 mg/dL (0.8 mmol/L) higher than LDL-C goals for each risk category. Method of administration For oral administration.
ORAL
Medical Information
**4.1 Therapeutic indications** _Hypercholesterolaemia_ Atorvastatin is indicated as an adjunct to diet for reduction of elevated total-cholesterol (total-C), low density lipoprotein cholesterol (LDL-C), apolipoprotein B (apo B) and triglycerides (TG) in adults, adolescents and children aged 10 years or older with primary hypercholesterolemia, heterozygous familial hypercholesterolemia or combined (mixed) hyperlipidaemia (Fredrickson Types IIa and IIb), elevated serum triglyceride (TG) levels (Fredrickson Type IV), and for patients with dysbetalipoproteinemia (Fredrickson Type III) when response to diet and other non-pharmacological measures is inadequate. Atorvastatin also raises high density lipoprotein cholesterol (HDL-C) and lowers the LDL/HDL and total cholesterol/HDL ratios. Atorvastatin is also indicated to reduce total-C and LDL-C in adults with homozygous familial hypercholesterolemia as an adjunct to other lipid-lowering treatments (e.g. LDL apheresis) or if such treatments are unavailable. _Prevention of cardiovascular disease_ Atorvastatin is indicated to reduce the risk of myocardial infarction (MI) in adult hypertensive patients without clinically evident coronary heart disease, but with at least three additional risk factors for coronary heart disease (CHD) such as age ≥ 55 years, male sex, smoking, left ventricular hypertrophy, other specified abnormalities on electrocardiogram (ECG), microalbuminuria or proteinuria, ratio of plasma total cholesterol (total-C) to HDL-cholesterol ≥ 6, or premature family history of coronary heart disease (CHD). In adults with type 2 diabetes and without clinically evident coronary heart disease (CHD), but with multiple risk factors for coronary heart disease (CHD) such as retinopathy, albuminuria, smoking or hypertension, Atorvastatin is indicated to: - Reduce the risk of myocardial infarction (MI) - Reduce the risk of stroke In adults with clinically evident coronary heart disease (CHD), atorvastatin is indicated to: - Reduce the risk of non-fatal myocardial infarction - Reduce the risk of fatal and non-fatal stroke - Reduce the risk for revascularization procedures - Reduce the risk of hospitalization for congestive heart failure (CHF) - Reduce the risk of angina
**4.3 Contraindications** Atorvastatin is contraindicated in patients who have: - Hypersensitivity to the active substance or to any of the excipients. - Active liver disease or unexplained persistent elevations of serum transaminases exceeding three times the upper limit of normal (ULN). - Pregnant, breast-feeding, or of child-bearing potential who are not using adequate contraceptive measures. Atorvastatin should be administered to women of child-bearing age only when such patients are highly unlikely to conceive and have been informed of the potential hazards to the fetus. - Concomitantly treated with glecaprevir/pibrentasvir.
C10AA05
atorvastatin
Manufacturer Information
SANDOZ SINGAPORE PTE. LTD.
Lek S.A.
Active Ingredients
Documents
Package Inserts
Atorvastatin Sandoz Tablet PI.pdf
Approved: June 28, 2022
