Regulatory Information
HSA regulatory responsibility and product classification details
Regulatory Responsibility
Product Classification
Formulation Information
INJECTION, SOLUTION
**4.2 Posology and method of administration** **Dosage regimen for Allergic Asthma and CRSwNP** Dosing for asthma and CRSwNP follows the same dosing principles. Xolair treatment should be initiated and supervised by specialist physicians experienced in the diagnosis and treatment of severe persistent asthma. The appropriate dose and dosing frequency of Xolair for these conditions is determined by baseline IgE (international units/ml), measured before the start of treatment, and body weight (kg). Prior to initial dosing, patients should have their IgE level determined by any commercial serum total IgE assay for their dose assignment. Based on these measurements 75–600 mg of Xolair in 1 to 4 injections may be needed for each administration. Patients with IgE lower than 76 international units/ml were less likely to experience benefit (see section 5.1 – _please refer to the Product Insert/Patient Information Leaflet published on HSA for the full drug information_). Prescribing physicians should ensure that patients with IgE below 76 international units/ml have unequivocal _in vitro_ reactivity (RAST) to a perennial allergen before starting therapy. See Tables 1 and 2 for a conversion chart and Tables 3 and 4 for dose determination. For doses of 225, 375 or 525 mg Xolair, 150 mg can be used in combination with Xolair 75 mg. Patients whose baseline IgE levels or body weight in kilograms are outside the limits of the dosing table should not be given Xolair. The maximum recommended dose is 600 mg omalizumab every two weeks. Method of administration **Powder and solvent for solution for injection** For subcutaneous administration only. Xolair must not be administered by the intravenous or intramuscular route. Doses of more than 150 mg should be divided across two or more injection sites. The injections are administered subcutaneously in the deltoid region of the arm. Alternatively, the injections can be administered in the thigh if there is any reason precluding administration in the deltoid region. There is limited experience with self-administration of Xolair powder and solvent for solution for injection. Therefore, treatment with this formulation is intended to be administered by a healthcare professional only. Full information for use are provided in section 6.6 – _please refer to the Product Insert/Patient Information Leaflet published on HSA for the full drug information_. **Pre-filled syringe** For subcutaneous administration only. Xolair must not be administered by the intravenous or intramuscular route. Doses of more than 150 mg should be divided across two or more injection sites. 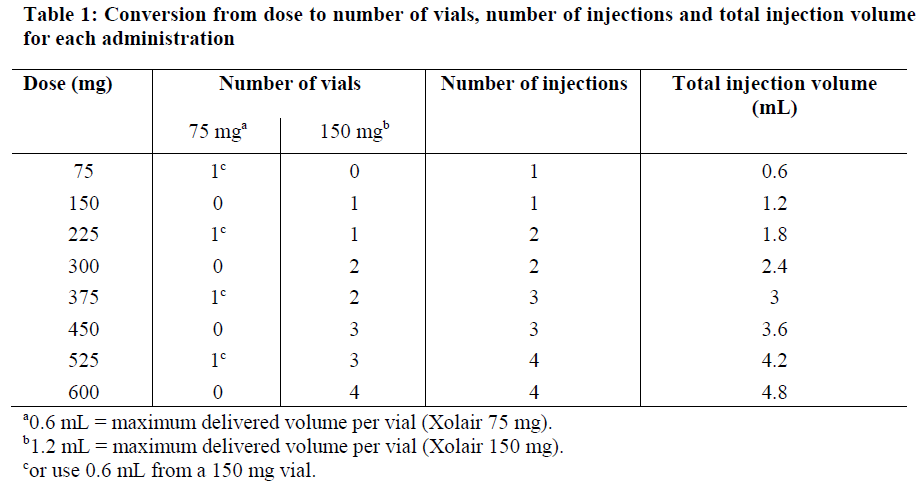 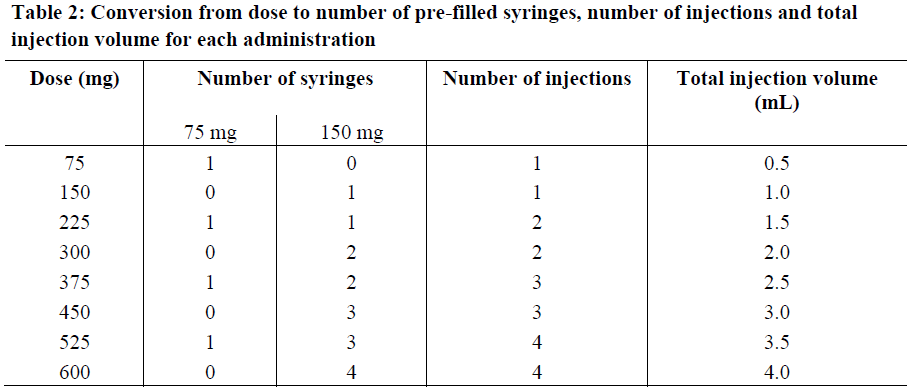 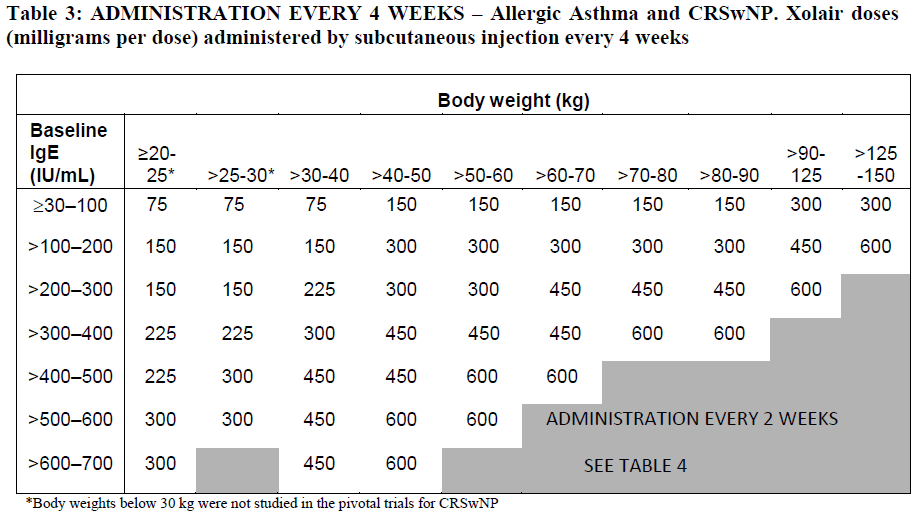 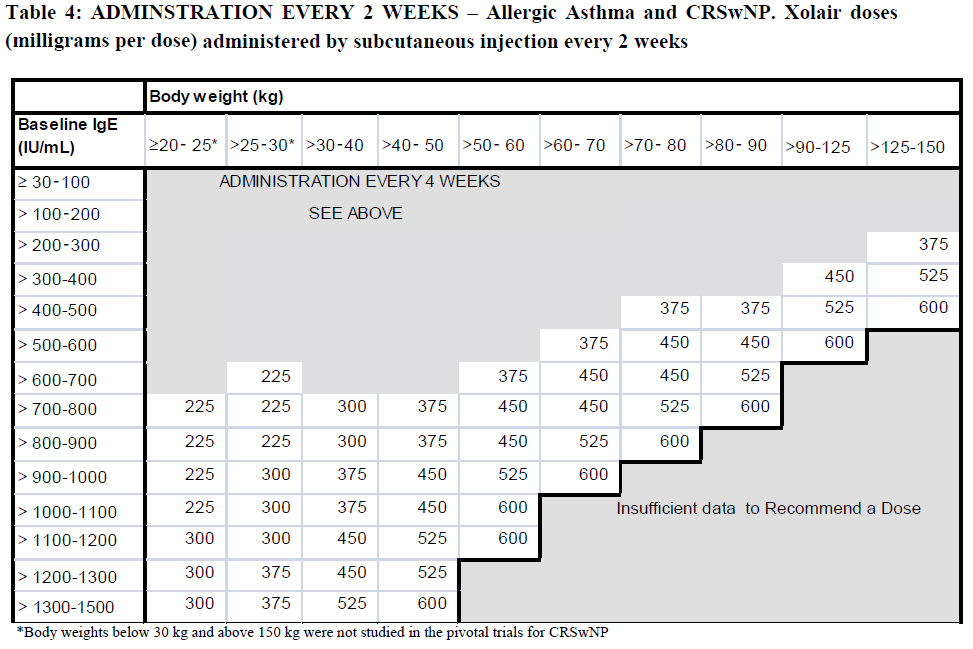 Treatment duration, monitoring and dose adjustments Discontinuation of Xolair treatment generally results in a return to elevated free IgE levels and associated symptoms. At 16 weeks after commencing Xolair therapy patients should be assessed by their physician for treatment effectiveness before further injections are administered. The decision to continue Xolair should be based on whether a marked improvement in overall asthma control is seen (see section 5.1; Physician’s overall assessment of treatment effectiveness – _please refer to the Product Insert/Patient Information Leaflet published on HSA for the full drug information_). In clinical trials for CRSwNP, changes in nasal polyps score (NPS) and nasal congestion score (NCS) were observed as early as the first assessment at 4 weeks. The need for continued therapy should be periodically reassessed based upon the patient’s disease severity and level of symptom control. Total IgE levels are elevated during treatment and remain elevated for up to one year after the discontinuation of treatment. Therefore, re-testing of IgE levels during Xolair treatment cannot be used as a guide for dose determination. Dose determination after treatment interruptions lasting less than one year should be based on serum IgE levels obtained at the initial dose determination. Total serum IgE levels may be re-tested for dose determination if treatment with Xolair has been interrupted for one year or more. Doses should be adjusted for significant changes in body weight (see Tables 3 and 4). **Dosage regimen for Chronic Spontaneous Urticaria (CSU)** The recommended dose is 300 mg by subcutaneous injection every four weeks. Some patients may achieve control of their symptoms with a dose of 150 mg every four weeks. Prescribers are advised to periodically reassess the need for continued therapy. Clinical trial experience of long-term treatment beyond 6 months in this indication is limited. **Special populations** Renal or hepatic impairment There have been no studies on the effect of impaired renal or hepatic function on the pharmacokinetics of omalizumab. Because omalizumab clearance at clinical doses is dominated by IgG clearance process, including degradation in the reticular endothelial system (RES) it is unlikely to be altered by renal or hepatic impairment. While no particular dose adjustment is recommended, Xolair should be administered with caution in these patients (see section 4.4 – _please refer to the Product Insert/Patient Information Leaflet published on HSA for the full drug information_). Pediatric patients In allergic asthma, safety and efficacy in patients below the age of 6 years have not been established and use of Xolair in such patients is therefore not recommended. In CRSwNP, safety and efficacy in patients below the age of 18 years have not been established. In chronic spontaneous urticaria, safety and efficacy in patients below the age of 12 years have not been established. Geriatric patients (65 years or above) There are limited data available on the use of Xolair in patients 65 years and older but there is no evidence that elderly patients require a different dosage from younger adult patients.
SUBCUTANEOUS
Medical Information
**4.1 Therapeutic indications** **Allergic Asthma** Xolair treatment should only be considered for patients with convincing IgE mediated asthma (see section 4.2). **Adults and adolescents (12 years of age and above)** Xolair is indicated as add-on therapy to improve asthma control in adult and adolescent (12 years of age and above) with severe persistent allergic asthma who have a positive skin test or _in vitro_ reactivity to a perennial aeroallergen and who have reduced lung function (FEV1 <80%) as well as frequent daytime symptoms or night-time awakenings and who have had multiple documented severe asthma exacerbations despite daily high-dose inhaled corticosteroids, plus a long-acting inhaled beta2-agonist. **Children (6 to < 12 years of age)** Xolair is indicated as add-on therapy to improve asthma control with severe persistent allergic asthma who have a positive skin test or in vitro reactivity to a perennial aeroallergen and frequent daytime symptoms or night-time awakenings and who have had multiple documented severe asthma exacerbations despite daily high-dose inhaled corticosteroids, plus a long-acting inhaled beta2-agonist. **Chronic rhinosinusitis with nasal polyps (CRSwNP)** Xolair is indicated as an add-on therapy to intranasal corticosteroids for the treatment of CRSwNP in adults (18 years of age and above) with inadequate response to intranasal corticosteroids. **Chronic Spontaneous Urticaria (CSU)** Xolair is indicated as add-on therapy for the treatment of chronic spontaneous urticaria in adult and adolescent (12 years and above) patients with inadequate response to H1 antihistamine treatment.
**4.3 Contraindications** Hypersensitivity to the active substance or to any of the excipients.
R03DX05
omalizumab
Manufacturer Information
NOVARTIS (SINGAPORE) PTE LTD
Vetter Pharma-Fertigung GmbH & Co. KG
Active Ingredients
Documents
Package Inserts
Xolair PI.pdf
Approved: January 27, 2023
