Regulatory Information
HSA regulatory responsibility and product classification details
Regulatory Responsibility
Product Classification
Formulation Information
INJECTION, POWDER, FOR SOLUTION
**DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATIONS** **Dosage** _Vancomycin powder for solution for infusion must be administered intravenously. Each dose should be administered at a rate not exceeding 10 mg/min or over a period of time of at least 60 minutes (whichever is longer)._ The dose should be individually adapted according to weight, age and renal function. The following dosage regimens are recommended: Patients with normal renal function _Adults and adolescents above 12 years of age:_ _The recommended daily intravenous dose is 2000 mg, divided into doses of 500 mg every 6 hours or 1000 mg every 12 hours._ For bacterial endocarditis, the generally accepted regimen is 1000 mg vancomycin intravenously every 12 hours for 4 weeks either alone or in combination with other antibiotics (gentamicin plus rifampin, gentamicin, streptomycin). Enterococcal endocarditis is treated for 6 weeks with vancomycin in combination with an aminoglycoside – according to national recommendations. Perioperative prophylaxis against bacterial endocarditis: Adults receive 1000 mg vancomycin intravenously prior to surgery (prior to induction of anaesthesia) and depending on time and type of surgery, the dose of 1000 mg of vancomycin i.v. 12 hours postoperatively can be given. _Children one month to 12 years of age:_ The recommended intravenous dose is 10 mg/kg, every 6 hours or 20 mg/kg every 12 hours. _Infants and newborns:_ The recommended initial dose is 15 mg/kg, followed by 10 mg/kg every 12 hours during the first week of life and every 8 hours after that age and up to 1 month of age. Careful monitoring of serum concentration of vancomycin is recommended (see below). _Elderly patients:_ Lower maintenance doses may be required due to the age-related reduction in renal function. _Obese patients:_ Modification of the usual daily doses may be required. _Patients with hepatic insufficiency_ There is no evidence that the dose has to be reduced in patients with hepatic insufficiency. _Patients with impaired renal function_ The dose must be adjusted in patients with impaired renal function and the following monogram can serve as guidance. Careful monitoring of serum concentration of vancomycin is recommended (see below). 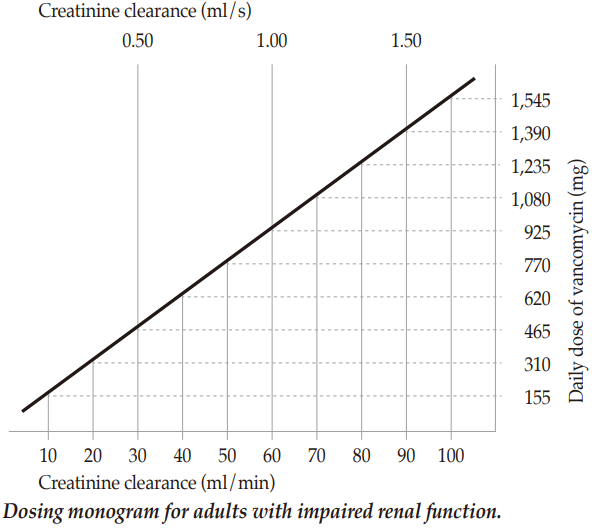 In patients with mild or moderate renal failure, the starting dose must not be less than 15 mg/kg. In patients with severe renal failure, it is preferable to administer a maintenance dose between 250 mg and 1000 mg at a spacing of several days rather than administer lower daily doses. Patients with _anuria_ (with practically no renal function) should receive a dose of 15 mg/kg body weight until the therapeutic serum concentration is reached. The maintenance doses are 1.9 mg/kg body weight per 24 hours. In order to facilitate the procedure, adult patients with strongly impaired renal function may obtain a maintenance dose of 250 – 1000 mg at intervals of several days instead of a daily dose. Dosage in case of haemodialysis For patients without any renal function, even under regular hemodialysis, the following dosage is also possible: Saturating dose 1000 mg, maintenance dose 1000 mg every 7 – 10 days. If polysulfone membranes are used in haemodialysis (high flux dialysis), the half-life of vancomycin is reduced. An additional maintenance dose may be necessary in patients on regular haemodialysis. Monitoring of vancomycin serum concentrations: The serum concentration of vancomycin should be monitored at the second day of treatment immediately prior to the next dose, and one hour post infusion. Therapeutic vancomycin blood levels should be between 30 and 40 mg/l (maximum 50 mg/l) one hour after the end of the infusion, the minimum level (short prior to the next administration) between 5 and 10 mg/l. The concentrations should normally be monitored twice or three times per week. **Administration** Method of administration: Parenterally vancomycin shall only be administered as slow intravenous infusion (not more than 10 mg/min – over at least 60 min) which is sufficiently diluted (at least 100 ml per 500 mg or at least 200 ml per 1000 mg). Patients requiring fluid restriction can receive a solution of 500 mg / 50 ml or 1000 mg / 100 ml. With these higher concentrations the risk for infusion related side effects can be increased. For information about the preparation of the solution, please refer to the section "Preparation of the solution for infusion" below. Duration of treatment The duration of the treatment depends on the severity of the infection as well as on the clinical and bacteriological progress. The product must be reconstituted and the resulting concentrate must then be diluted prior to use. Preparation of the solution for infusion Step 1: Reconstitution Dissolve Vancomycin 1000 mg in 20 ml of sterile Water for injection or dissolve Vancomycin 500 mg in 10 ml of sterile Water for injection to form reconstituted solution contains 50 mg of vancomycin in each ml. After reconstitution the solution is clear and colorless to slightly yellowish brown without visible particles. For storage conditions of the reconstituted medicinal product, see section STORAGE CONDITIONS – _please refer to the Product Insert/Patient Information Leaflet published on HSA for the full drug information_. Step 2: Reconstituted solutions containing 50 mg/ml of vancomycin should be further diluted. Suitable diluents are: 5% Glucose Injection or 0.9% Sodium Chloride Injection or 5% Glucose Injection with 0.9% Sodium Chloride Injection. **_Intermittent infusion:_** Reconstituted solution containing 500 mg or 1000 mg vancomycin (50 mg/ml) must be diluted further with at least 100 ml or 200 ml diluent (respectively) (to 5mg/ml). The concentration of vancomycin in Solution for infusion should not exceed 5 mg/ml. The desired dose should be administered slowly by intravenous use at a rate of no more than 10 mg/minute, for at least 60 minutes or even longer. **_Continuous infusion:_** This should be used only if treatment with an intermittent infusion is not possible. Dilute 1000 mg to 2000 mg of dissolved vancomycin in a sufficient amount of the above suitable diluent and administer it in the form of a drip infusion, so that the patient will receive the prescribed daily dose in 24 hours. For storage conditions of the diluted medicinal product, see section STORAGE CONDITIONS – _please refer to the Product Insert/Patient Information Leaflet published on HSA for the full drug information_ _Before administration, the reconstituted and diluted solutions should be inspected visually for particulate matter and discoloration. Only clear, and colorless solution free from particles should be used_.
INTRAVENOUS
Medical Information
**INDICATIONS** Vancomycin, used intravenously is indicated in the therapy of severe, potentially life-threatening infections due to susceptible gram-positive microorganisms which cannot be treated with or failed to respond to other effective, less toxic antimicrobial medicinal products, such as penicillins and cephalosporins. Vancomycin should be reserved for those cases where there is a specific indication, to minimize the chance of resistance emerging. Vancomycin is useful in the treatment of the following severe infections caused by susceptible microorganisms (see section PHARMACODYNAMIC – _please refer to the Product Insert/Patient Information Leaflet published on HSA for the full drug information_): - endocarditis, - infections of bones (osteomyelitis), - pneumonia, - soft-tissue infections. Endocarditis caused by enterococci, _Streptococcus viridans_ or _S. bovis_ should be treated with a combination of vancomycin and an aminoglycoside. Vancomycin may be used for the perioperative prophylaxis against bacterial endocarditis, in patients at high risk of developing bacterial endocarditis when they undergo major surgical procedures (e.g., cardiac and vascular procedures, etc) and are unable to receive a suitable beta-lactam antibacterial agent. **_Consideration should be given to official guidance on the appropriate use of antibacterial agents._**
**CONTRAINDICATION** Hypersensitivity to vancomycin
J01XA01
vancomycin
Manufacturer Information
ZYFAS PHARMA PTE. LTD.
BCWorld Pharm. Co., Ltd
Active Ingredients
Documents
Package Inserts
Vancomycin HCl Injection PI.pdf
Approved: February 20, 2023
