Regulatory Information
HSA regulatory responsibility and product classification details
Regulatory Responsibility
Product Classification
Formulation Information
INJECTION, POWDER, FOR SOLUTION
**4.2 Posology and method of administration** **4.2.1 Method of administration** Due to unit differences in the potency assay, unit doses recommended for XEOMIN are not interchangeable with those for other preparations of Botulinum toxin. XEOMIN may only be administered by health care professionals with suitable qualifications and proven experience in the application of Botulinum neurotoxin type A. XEOMIN is reconstituted prior to use with sodium chloride 9 mg/ml (0.9%) solution for injection. It is good practice to perform vial reconstitution and syringe preparation over plastic-lined paper towels to catch any spillage. An appropriate amount of solvent is drawn up into a syringe. A 20–27 G short bevel needle is recommended for reconstitution. After vertical insertion of the needle through the rubber stopper the solvent is injected gently into the vial in order to avoid foam formation. The vial must be discarded if the vacuum does not pull the solvent into the vial. Remove the syringe from the vial and mix XEOMIN with the solvent by carefully swirling and inverting/flipping the vial - do not shake vigorously. If needed, the needle used for reconstitution should remain in the vial and the required amount of solution should be drawn up with a new sterile syringe suitable for injection. 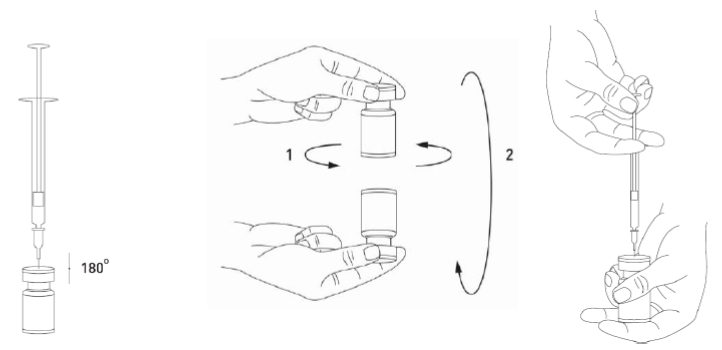 Reconstituted XEOMIN is a clear, colourless solution free of particulate matter. XEOMIN should not be used if the reconstituted solution has a cloudy appearance or contains floccular or particulate matter. Reconstituted XEOMIN is intended for intramuscular injection. **Neurological indications** _**Cervical dystonia (spasmodic torticollis)**_ A suitable sterile needle (e.g. 25–30 gauge / 0.30–0.50 mm diameter / 37mm length) is used for injections into superficial muscles, and an e.g. 22 gauge / 0.70 mm diameter / 75 mm length needle may be used for injections into deeper musculature. In the management of spasmodic torticollis, XEOMIN is injected into the sternocleidomastoid, levator scapulae, scalenus, splenius capitis, and/or the trapezius muscle(s). This list is not exhaustive as any of the muscles responsible for controlling head position may be involved and therefore require treatment. If difficulties arise isolating single muscles, injections should be performed using electromyographic guidance. The muscle mass and the degree of hypertrophy or atrophy are factors to be taken into consideration when selecting the appropriate dose. Multiple injection sites permit XEOMIN more uniform coverage of the innervated areas of the dystonic muscle and are especially useful in larger muscles. The optimum number of injection sites is dependent upon the size of the muscle to be chemically denervated. The sternocleidomastoid should not be injected bilaterally as there is an increased risk of adverse reactions (in particular dysphagia) when bilateral injections or doses in excess of 100 units are administered into this muscle. _**Blepharospasm**_ After reconstitution, the XEOMIN solution is injected using a suitable sterile needle (e.g. 27–30 gauge / 0.30–0.40 mm diameter / 12.5 mm length). Electromyographic guidance is not necessary. XEOMIN is injected into the medial and lateral orbicularis oculi muscle of the upper lid and the lateral orbicularis oculi muscle of the lower lid. Additional sites in the brow area, the lateral orbicularis oculi muscle and in the upper facial area may also be injected if spasms here interfere with vision. _**Spasticity of the upper limb**_ Reconstituted XEOMIN is injected using a suitable sterile needle (e.g. 26 gauge / 0.45 mm diameter / 37 mm length, for superficial muscles and a longer needle, e.g. 22 gauge / 0.7 mm diameter / 75 mm length, for deeper musculature). In case of any difficulty in isolating the individual muscles, injections should be made under electromyographic assistance. Multiple injection sites may allow XEOMIN to have more uniform contact with the innervation areas of the muscle and are especially useful when larger muscles are injected. **Aesthetic indications** Reconstituted XEOMIN is injected using a thin sterile needle (e.g. 30–33 gauge needle / 0.20–0.30 mm diameter / 13 mm length). _**Glabellar frown lines**_ Before and during the injection, the thumb or index finger should be used to apply firm pressure below the edge of the eye socket in order to prevent diffusion of the solution in this region. Superior and medial alignment of the needle should be maintained during the injection. To reduce the risk of blepharoptosis, injections near the levator palpebrae superioris and into the cranial portion of the orbicularis oculi should be avoided. Injections into the corrugator muscle should be done in the medial portion of the muscle, and in the central portion of the muscle belly at least 1 cm above the bony edge of the eye socket. _**Lateral periorbital lines (Crow's Feet lines)**_ Injection should be done intramuscularly into the orbicularis oculi muscle, directly under the dermis to avoid diffusion of Xeomin. Injections too close to the zygomaticus major muscle should be avoided to prevent lip ptosis. _**Horizontal forehead lines**_ Paralyzing of lower muscle fibers by injecting XEOMIN near the orbital rim should be avoided to reduce the risk of brow ptosis. **4.2.2 Posology** **Neurological indications** _**General**_ The optimum dosage, frequency and number of injection sites in the treated muscle(s) should be individualised for each patient and determined by the physician. Possible dilutions for the treatment of neurological indications are indicated in the following table: 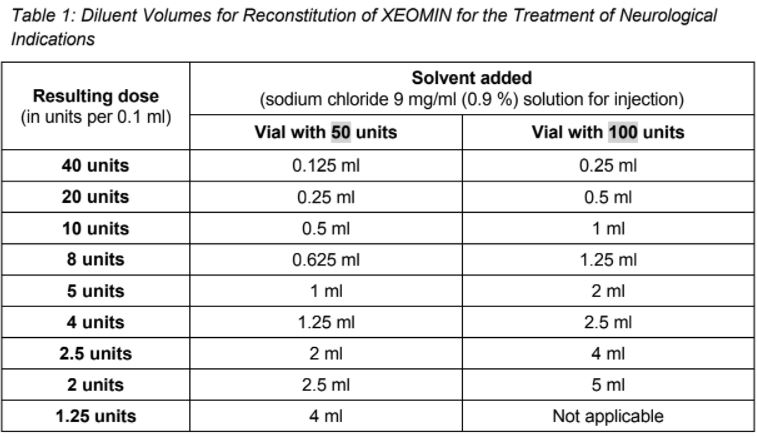 _**Cervical dystonia (spasmodic torticollis)**_ In the management of spasmodic torticollis, XEOMIN dosing must be tailored to the individual patient, based on the patient's head and neck position, location of possible pain, muscle hypertrophy, patient's body weight, and response to the injection. Injection volume per injection site: approximately 0.1 to 0.5 ml. Total dose: should not exceed 200 units in the first treatment session. Dose: up to 300 units may be given in subsequent injection sessions. No more than 50 units should be given at any single injection site. XEOMIN is usually injected into the sternocleidomastoid, levator scapulae, splenius capitis, scalenus, and/or the trapezius muscle(s). This list is not exhaustive as any of the muscles responsible for controlling head position may require treatment. Median time to first onset of effect: usually within seven days after injection. Duration of effect: up to 3–4 months, however, it may last significantly longer or shorter. Treatment intervals should be determined based on the actual clinical need of the individual patient. Improved patient benefit may be achieved by retreating when symptoms return to a clinically significant level of discomfort and severity. Duration of action is dependent on dosing, injection technique, and other variables. Generally, the patient should be treated using the lowest effective dose at the longest clinically indicated intervals between injections. If in individual cases the duration of effect is shorter than 12 weeks, the next injection can be given earlier, upon consideration of the risk-benefit ratio. Injection intervals should not be shorter than 6 weeks, and one single injection given earlier than 12 weeks does not indicate a general need for regular earlier re-injection. If an injection interval reduction is necessary, the following recommendations should be followed: 1. Active request from the patient 2. An objective confirmation of the necessity for an injection 3. Absence of adverse reactions to the previous injection The dose should not be increased when the interval is reduced. In case of intervals reduction below 12 weeks, a close monitoring of adverse reaction should be performed. In a controlled clinical trial XEOMIN has been efficacious and well-tolerated when injected in intervals between 6 and 20 weeks (median: 12 weeks). _**Blepharospasm**_ Initial dose and injection volume per injection site: 1.25 to 2.5 units (0.05–0.1 ml). Dosing: - The initial dose should not exceed 25 units per eye. - Normally, the total dose should not exceed 100 units per treatment session. XEOMIN is injected into the medial and lateral orbicularis oculi of the upper lid and the lateral orbicularis oculi muscle of the lower lid. Additional sites in the brow area, the lateral orbicularis and in the upper facial area may also be injected if spasms here interfere with vision. Injections near the levator palpebrae superioris should be avoided to reduce the occurrence of ptosis. Diplopia may develop as a result of Botulinum neurotoxin type A diffusion into the inferior oblique. Avoiding medial injections into the lower lid may reduce this adverse reaction. Median time to first onset of effect: usually within four days after injection. Duration of effect: up to 3–4 months, however, it may last significantly longer or shorter in individual patients. Treatment intervals should be determined based on the actual clinical need of the individual patient. Improved patient benefit may be achieved by retreating when symptoms return to a clinically significant level of discomfort and severity. Duration of action is dependent on dosing, injection technique, and other variables. Generally, the patient should be treated using the lowest effective dose at the longest clinically indicated intervals between injections. If in individual cases the duration of effect is shorter than 12 weeks, the next injection can be given earlier, upon consideration of the risk-benefit ratio. Injection intervals should not be shorter than 6 weeks, and one single injection given earlier than 12 weeks does not indicate a general need for regular earlier re-injection. If an injection interval reduction is necessary, the following recommendations should be followed: 1. Active request from the patient 2. An objective confirmation of the necessity for an injection 3. Absence of adverse reactions to the previous injection The dose should not be increased when the interval is reduced. In case of intervals reduction below 12 weeks, a close monitoring of adverse reaction should be performed. In a controlled clinical trial XEOMIN has been efficacious and well-tolerated when injected in intervals between 6 and 20 weeks (median: 12 weeks). _**Spasticity of the upper limb**_ Injection volume per injection site: approximately 0.2 to 1 ml (can be exceeded to 1.5 ml in selected cases). The exact dosage and number of injection sites should be tailored to the individual patient based on the size, number and location of involved muscles, the severity of spasticity, and the presence of local muscle weakness. 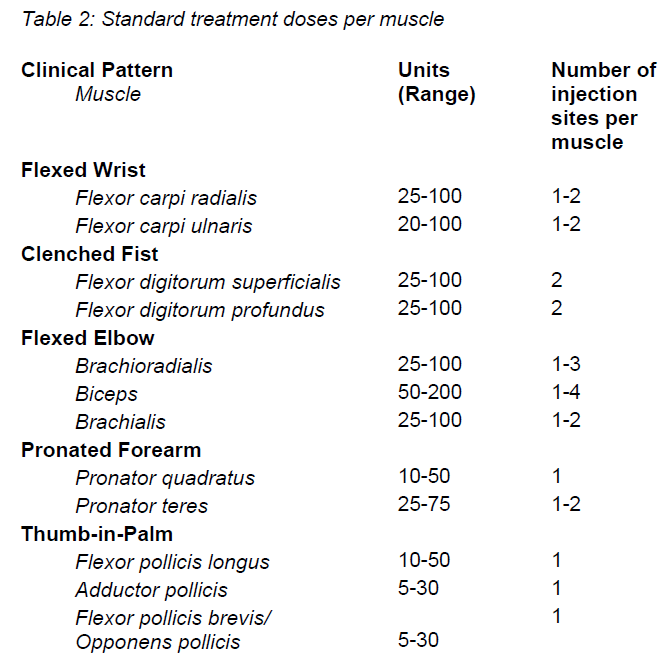 This list is not exhaustive as any of the muscles of the upper limb may require treatment, e.g. shoulder. The total recommended dose is up to 400 units per treatment session. Median time to first onset of effect: usually within 4 days after injection. Maximum effect: usually within 4 weeks. Duration of effect: usually up to 12 weeks, however, it may last longer or shorter in individual patients. Repeat treatment should generally be no more frequent than every 12 weeks. Treatment intervals should be determined based on the actual clinical need of the individual patient. **Aesthetic indications** Possible dilutions of XEOMIN for the treatment of aesthetic indications are indicated in the following table: 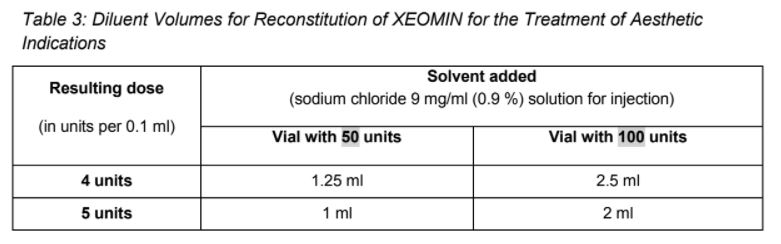 The intervals between aesthetic indications treatments should not be shorter than 3 months. _**Glabellar frown lines**_ Dose per injection site: 4 units into each of the 5 injection sites: two injections in each corrugator muscle and one injection in the procerus muscle, which corresponds to a standard dose of 20 units. The dose may be increased by the physician to up to 30 units if required by the individual needs of the patients, with at least 3-months' interval between treatments. 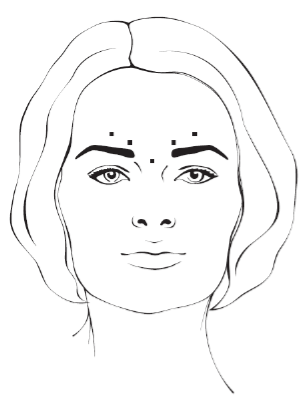 Duration of effect: up to 4 months after the injection, however, it may last longer or shorter in individual patients. _**Lateral periorbital lines (Crow's Feet lines)**_ Dose per injection site: 4 units bilaterally into each of the 3 injection sites - one injection approximately 1 cm lateral from the bony orbital rim - two injections approximately 1 cm above and below the area of the first injection 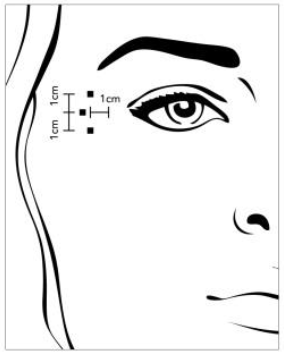 Total dose: 24 units (12 units per side) may be given. Duration of effect: up to 4 months after the injection, however, it may last longer or shorter in individual patients. No efficacy and safety data are currently available for more than two injections in lateral periorbital lines seen at maximum smile separated by a 4-month interval. _**Horizontal forehead lines**_ Total dose: 10 to 20 units may be given according to the individual needs of the patients. Dose per injection sites: - 10 to 20 units into the frontalis muscle in five horizontally aligned injection sites at least 2 cm above the orbital rim - 2 units, 3 units, or 4 units per injection point, respectively. 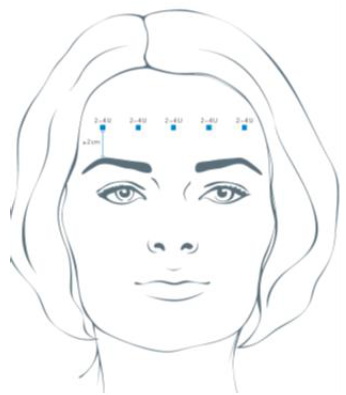 Duration of effect: up to 4 months after injection, however, it may last longer or shorter in individual patients. Currently available efficacy and safety data in horizontal forehead lines seen at maximum contraction are limited to two injection cycles separated by a 4 to 5-month interval. **General Information** If no treatment effect occurs within one month after the initial injection, the following measures should be taken: - For Blepharospasm, Spasmodic torticollis, spasticity of the upper limb only: clinical verification of the neurotoxin effect on the injected muscle: e.g. an electromyographic investigation in a specialised facility. - Analysis of the reason for non-response, e.g. poor isolation of the muscles intended to be injected, too low dose, poor injection technique, fixed contracture, too weak antagonist, possible development of antibodies. - Review of Botulinum neurotoxin type A treatment as an adequate therapy. - If no adverse reactions have occurred during the initial treatment, an additional course of treatment can be performed under the following conditions: 1. dose adjustment with regard to analysis of the most recent therapy failure, 2. EMG guidance, 3. the recommended minimum interval between the initial and repeat treatment is followed.
INTRAMUSCULAR
Medical Information
**4.1 Therapeutic indications** XEOMIN is indicated in adults for the treatment of: - Cervical dystonia (spasmodic torticollis) - Blepharospasm - Spasticity of the upper limb XEOMIN is indicated for the temporary improvement in the appearance of moderate to severe - Upper facial lines - Glabellar frown lines - Lateral periorbital lines (crow's feet lines) - Horizontal forehead lines in adults below 65 years of age.
**4.3 Contraindications** - Hypersensitivity to the active substance or to any of the excipients. - Generalised disorders of muscle activity (e.g. myasthenia gravis, Lambert-Eaton syndrome). - Presence of infection or inflammation at the proposed injection sites.
M03AX01
botulinum toxin
Manufacturer Information
MERZ ASIA PACIFIC PTE. LTD.
Merz Pharma GmbH & Co. KGaA
IDT Biologika GmbH
Active Ingredients
Clostridium Botulinum neurotoxin type A (150 kDa), free from complexing proteins
50 LD50 units
Documents
Package Inserts
Xeomin 50U PI (clean).pdf
Approved: October 26, 2018
