Regulatory Information
HSA regulatory responsibility and product classification details
Regulatory Responsibility
Product Classification
Formulation Information
INFUSION, SOLUTION
**4.2 Posology and method of administration** Replacement therapy should be commenced and monitored under the supervision of a physician experienced in the treatment of immunodeficiency. Posology The dose and dose regimen is dependent on the indication. In replacement therapy the dose may need to be individualised for each patient depending on the clinical response. Dose based on bodyweight may require adjustment in underweight or overweight patients. The following dose regimens are given as a guideline. _Replacement therapy in primary immunodeficiency (PID) syndromes_ The dose regimen should achieve a trough IgG level (measured before the next infusion) of at least 6 g/l or within the normal reference range for the population age. Three to six months are required after the initiation of therapy for equilibration to occur. The recommended starting dose is 0.4 to 0.8 g/kg body weight (bw) given once, followed by at least 0.2 g/kg bw every 3 to 4 weeks. The dose required to achieve a trough level of IgG of6 g/l is of the order of 0.2 to 0.8 g/kg bw/month. The dosage interval when steady state has been reached varies from 3 to 4 weeks. IgG trough levels should be measured and assessed in conjunction with the incidence of infection. To reduce the rate of bacterial infections, it may be necessary to increase the dosage and aim for higher trough levels. _Secondary immunodeficiencies (as defined in 4.1)_ The dose regimen should achieve a trough IgG level (measured before the next infusion) of at least 6 g/l or within the normal reference range for the population age. The recommended dose is 0.2 – 0.4 g/kg every three to four weeks. IgG trough levels should be measured and assessed in conjunction with the incidence of infection. Dose should be adjusted as necessary to achieve optimal protection against infections, an increase may be necessary in patients with persisting infection; a dose decrease can be considered when the patient remains infection free. _Primary immune thrombocytopenia (ITP)_ There are two alternative treatment schedules: - 0.8 to 1g/kg bw given on day 1; this dose may be repeated once within 3 days - 0.4 g/kg bw given daily for 2 to 5 days. The treatment can be repeated if relapse occurs. _Guillain-Barré syndrome_ 0.4 g/kg bw/day over 5 days (possible repeat of dosing in case of relapse). _Kawasaki disease_ 2.0 g/kg bw should be administered as a single dose. Patients should receive concomitant treatment with acetylsalicylic acid. _Chronic inflammatory demyelinating polyneuropathy (CIDP)\*_ The recommended starting dose is 2 g/kg bw divided over 2 to 5 consecutive days followed by maintenance doses of 1 g/kg bw over 1 to 2 consecutive days every 3 weeks. The treatment effect should be evaluated after each cycle; if no treatment effect is seen after 6 months, the treatment should be discontinued. If the treatment is effective long term treatment should be subject to the physicians discretion based upon the patient response and maintenance response. The dosing and intervals may have to be adapted according to the individual course of the disease. _Multifocal Motor Neuropathy (MMN)_ Starting dose: 2 g/kg given over 2–5 consecutive days. Maintenance dose: 1 g/kg every 2 to 4 weeks or 2 g/kg every 4 to 8 weeks. The treatment effect should be evaluated after each cycle. If insufficient treatment effect is seen after 6 months, the treatment should be discontinued. If the treatment is effective, long term treatment should be subject to the physician’s discretion based upon the patient response. The dosing and intervals may have to be adapted according to the individual course of the disease. The dosage recommendations are summarised in the following table: 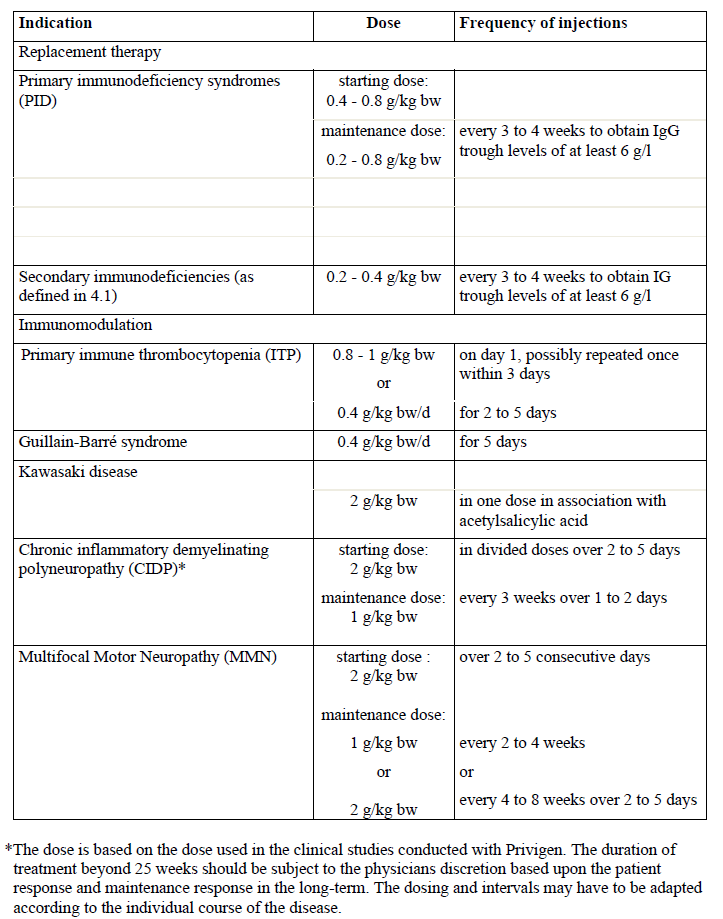 _Paediatric population_ The posology in children and adolescents (0–18 years) is not different from that of adults as the posology for each indication is given by body weight and adjusted to the clinical outcome of the above mentioned conditions. _Hepatic impairment_ No evidence is available to require a dose adjustment. _Renal impairment_ No dose adjustment unless clinically warranted, see section 4.4 – _please refer to the Product Insert/Patient Information Leaflet published on HSA for the full drug information_. _Elderly_ No dose adjustment unless clinically warranted, see section 4.4 – _please refer to the Product Insert/Patient Information Leaflet published on HSA for the full drug information_. Method of administration For intravenous use. Privigen should be infused intravenously at an initial infusion rate of 0.3 ml/kg bw/hr for approximately 30 min. If well tolerated (see section 4.4 – _please refer to the Product Insert/Patient Information Leaflet published on HSA for the full drug information_), the rate of administration may gradually be increased to 4.8 ml/kg bw/hr. In PID patients who have tolerated the infusion rate of 4.8 ml/kg bw/hr well, the rate may be further increased gradually to a maximum of 7.2 ml/kg bw/hr. If dilution prior to infusion is desired, Privigen may be diluted with 5% glucose solution to a final concentration of 50 mg/ml (5%). For instruction, see section 6.6 – _please refer to the Product Insert/Patient Information Leaflet published on HSA for the full drug information_.
INTRAVENOUS
Medical Information
**4.1 Therapeutic indications** Replacement therapy in adults, and children and adolescents (0–18 years) in: - Primary immunodeficiency (PID) syndromes with impaired antibody production (see section 4.4 – _please refer to the Product Insert/Patient Information Leaflet published on HSA for the full drug information_). - Secondary immunodeficiencies (SID) in patients who suffer from severe or recurrent infections, ineffective antimicrobial treatment and either proven specific antibody failure (PSAF)\* or serum IgG level of <4 g/l. \\* PSAF = failure to mount at least a 2-fold rise in IgG antibody titre to pneumococcal polysaccharide and polypeptide antigen vaccines. Immunomodulation in adults, and children and adolescents (0–18 years) in: - Primary immune thrombocytopenia (ITP), in patients at high risk of bleeding or prior to surgery to correct the platelet count. - Guillain-Barré syndrome. - Kawasaki disease. (in conjunction with acetylsalicylic acid; see section 4.2.). - Chronic inflammatory demyelinating polyneuropathy (CIDP). Only limited experience is available of use of intravenous immunoglobulins in children with CIDP. - Multifocal motor neuropathy (MMN)
**4.3 Contraindications** Hypersensitivity to the active substance (human immunoglobulins) or to any of the excipients listed in section 6.1 (see also section 4.4 – _please refer to the Product Insert/Patient Information Leaflet published on HSA for the full drug information_). Patients with selective IgA deficiency who developed antibodies to IgA, as administering an IgA-containing product can result in anaphylaxis.Patients with hyperprolinaemia type I or II.
J06BA02
immunoglobulins, normal human, for intravascular adm.
Manufacturer Information
CSL BEHRING PTE. LTD.
CSL Behring AG
Active Ingredients
Documents
Package Inserts
Privigen PI.pdf
Approved: August 30, 2022
