Regulatory Information
HSA regulatory responsibility and product classification details
Regulatory Responsibility
Product Classification
Formulation Information
TABLET, FILM COATED
**Posology and method of administration** Zestril should be administered orally in a single daily dose. As with all other medication taken once daily, Zestril should be taken at approximately the same time each day. The absorption of Zestril tablets is not affected by food. The dose should be individualised according to patient profile and blood pressure response (see Special warnings and precautions for use – _please refer to the Product Insert/Patient Information Leaflet published on HSA for the full drug information_). **Hypertension** Zestril may be used as monotherapy or in combination with other classes of antihypertensive therapy. _Starting dose_ In patients with hypertension the usual recommended starting dose is 10 mg. Patients with a strongly activated renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system (in particular, renovascular hypertension, salt and/or volume depletion, cardiac decompensation, or severe hypertension) may experience an excessive blood pressure fall following the initial dose. A starting dose of 2.5 – 5 mg is recommended in such patients and the initiation of treatment should take place under medical supervision. A lower starting dose is required in the presence of renal impairment (see Table 1 below). _Maintenance dose_ The usual effective maintenance dosage is 20 mg administered in a single daily dose. In general, if the desired therapeutic effect cannot be achieved in a period of 2 to 4 weeks on a certain dose level, the dose can be further increased. The maximum dose used in long-term, controlled clinical trials was 80 mg/day. _Diuretic-treated patients_ Symptomatic hypotension may occur following initiation of therapy with Zestril. This is more likely in patients who are being treated currently with diuretics. Caution is recommended, therefore, since these patients may be volume and/or salt depleted. If possible, the diuretic should be discontinued 2 to 3 days before beginning therapy with Zestril. In hypertensive patients in whom the diuretic cannot be discontinued, therapy with Zestril should be initiated with a 5 mg dose. Renal function and serum potassium should be monitored. The subsequent dosage of Zestril should be adjusted according to blood pressure response. If required, diuretic therapy may be resumed (see Special warnings and precautions for use & Interactions – _please refer to the Product Insert/Patient Information Leaflet published on HSA for the full drug information_). _Dosage adjustment in renal impairment_ Dosage in patients with renal impairment should be based on creatinine clearance as outlined in Table 1 below. 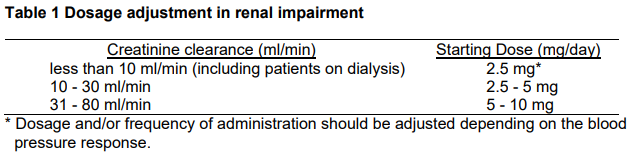 The dosage may be titrated upward until blood pressure is controlled or to a maximum of 40 mg daily. **Use in Hypertensive Paediatric Patients aged 6–16 years** The recommended initial dose is 2.5 mg once daily in patients 20 to <50 kg, and 5 mg once daily in patients ≥50 kg. The dosage should be individually adjusted to a maximum of 20 mg daily in patients weighing 20 to <50 kg, and 40 mg in patients ≥50 kg. Doses above 0.61 mg/kg (or in excess of 40 mg) have not been studied in paediatric patients (see Pharmacodynamics – _please refer to the Product Insert/Patient Information Leaflet published on HSA for the full drug information_). Zestril is not recommended in pediatric patients <6 years or in pediatric patients with glomerular filtration rate <30 ml/min/1.73 m2. **Congestive Heart failure** In patients with symptomatic heart failure, Zestril should be used as adjunctive therapy to diuretics and, where appropriate, digitalis or beta-blockers. Zestril may be initiated at a starting dose of 2.5 mg once a day, which should be administered under medical supervision to determine the initial effect on the blood pressure. The dose of Zestril should be increased: - By increments of no greater than 10 mg - At intervals of no less than 2 weeks The usual effective dosage range is 5 to 20 mg per day administered in a single daily dose. Dose adjustment should be based on the clinical response of individual patients. Patients at high risk of symptomatic hypotension e.g. patients with salt depletion with or without hyponatraemia, patients with hypovolaemia or patients who have been receiving vigorous diuretic therapy should have these conditions corrected, if possible, prior to therapy with Zestril. Renal function and serum potassium should be monitored (see Special warnings and precautions for use – _please refer to the Product Insert/Patient Information Leaflet published on HSA for the full drug information_). **Acute myocardial infarction** Patients should receive, as appropriate, the standard recommended treatments such as thrombolytics, aspirin, and beta-blockers. Intravenous or transdermal glyceryl trinitrate may be used together with Zestril. _Starting dose (first 3 days after infarction)_ Treatment with Zestril may be started within 24 hours of the onset of symptoms. Treatment should not be started if systolic blood pressure is lower than 100 mmHg. The first dose of Zestril is 5 mg given orally, followed by 5 mg after 24 hours, 10 mg after 48 hours and then 10 mg once daily. Patients with a low systolic blood pressure (120 mmHg or less) when treatment is started or during the first 3 days after the infarction should be given a lower dose – 2.5 mg orally (see Special warnings and precautions for use – _please refer to the Product Insert/Patient Information Leaflet published on HSA for the full drug information_). In cases of renal impairment (creatinine clearance <80 ml/min), the initial Zestril dosage should be adjusted according to the patient’s creatinine clearance (see Table 1). _Maintenance dose_ The maintenance dose is 10 mg once daily. If hypotension occurs (systolic blood pressure less than or equal to 100 mmHg) a daily maintenance dose of 5 mg may be given with temporary reductions to 2.5 mg if needed. If prolonged hypotension occurs (systolic blood pressure less than 90 mmHg for more than 1 hour) Zestril should be withdrawn. Treatment should continue for 6 weeks and then the patient should be re-evaluated. Patients who develop symptoms of heart failure should continue with Zestril (see Posology and method of administration). **Renal complications of diabetes mellitus** In normotensive insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus patients, the daily dose is 10 mg Zestril once daily which can be increased to 20 mg once daily, if necessary, to achieve a sitting diastolic blood pressure below 75 mmHg. In hypertensive non-insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus patients, the dose schedule is as above to achieve a sitting diastolic blood pressure below 90 mmHg. In cases of renal impairment (creatinine clearance <80 ml/min), the initial Zestril dosage should be adjusted according to the patient’s creatinine clearance (see Table 1). **Pediatric Use** There is limited efficacy and safety experience in hypertensive children >6 years old, but no experience in other indications. Zestril is not recommended in children in other indications than hypertension. **Use in the elderly** In clinical studies, there was no age-related change in the efficacy or safety profile of the drug. When advanced age is associated with decrease in renal function, however, the guidelines set out in Table 1 should be used to determine the starting dose of Zestril. Thereafter, the dosage should be adjusted according to the blood pressure response. **Use in kidney transplant patients** There is no experience regarding the administration of Zestril in patients with recent kidney transplantation. Treatment with Zestril is therefore not recommended.
ORAL
Medical Information
**Therapeutic indications** **Hypertension** Zestril is indicated in the treatment of hypertension and in renovascular hypertension. It may be used alone or concomitantly with other classes of antihypertensive agents. **Congestive Heart Failure** Zestril is indicated in the management of congestive heart failure as an adjunctive treatment with diuretics and, where appropriate, digitalis (see Posology and method of administration). **Acute myocardial infarction** Zestril is indicated for the treatment of haemodynamically stable patients within 24 hours of an acute myocardial infarction, to prevent the subsequent development of left ventricular dysfunction or heart failure and to improve survival. Patients should receive, as appropriate, the standard recommended treatments such as thrombolytics, aspirin and beta-blocker. **Renal complications of diabetes mellitus** In normotensive insulin-dependent and hypertensive non-insulin dependent diabetes mellitus patients who have incipient nephropathy characterised by microalbuminuria, Zestril reduces urinary albumin excretion rate.
**Contraindications** - Hypersensitivity to Zestril, to any of the excipients or any other angiotensin-converting enzyme (ACE) inhibitor. - History of anaphylactic/anaphylactoid reactions or angioedema associated with previous ACE inhibitor therapy. - Hereditary or idiopathic angioedema. - Second or third trimesters of pregnancy (see Pregnancy and lactation – _please refer to the Product Insert/Patient Information Leaflet published on HSA for the full drug information_). - The concomitant use of Zestril with aliskiren-containing products is contraindicated in patients with diabetes mellitus or renal impairment (GFR <60 ml/min/1.73m2) (see Interaction with other medicinal products and other forms of interaction – _please refer to the Product Insert/Patient Information Leaflet published on HSA for the full drug information_).
C09AA03
lisinopril
Manufacturer Information
DKSH SINGAPORE PTE. LTD.
AstraZeneca Pharmaceutical Co. Ltd
ROVI Pharma Industrial Services S.A.
Active Ingredients
Documents
Package Inserts
Zestril Tablet PI.pdf
Approved: October 12, 2021
