Regulatory Information
HSA regulatory responsibility and product classification details
Regulatory Responsibility
Product Classification
Formulation Information
INJECTION, POWDER, FOR SOLUTION
**3\. DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION** **General:** The use of one vial for more than one patient is not recommended because the product and diluent do not contain a preservative. Once opened and reconstituted, store in a refrigerator and use within twenty four hours. Discard any remaining solution. Do not freeze reconstituted BOTOX®. Reconstituted BOTOX® is injected with the purpose of reaching the motor endplate region of the muscle to be treated. **Route of Administration:** Intramuscular injection. May be subcutaneous injection for blepharospasm. Intradermal for primary hyperhidrosis of axillae. Intradetrusor for neurogenic detrusor overactivity. **Reconstitution of vial: _Dilution Technique:_** Prior to injection, reconstitute vacuum-dried BOTOX® with sterile normal saline **without** a preservative; 0.9% Sodium Chloride is the recommended diluent. It is good practice to perform vial reconstitution and syringe preparation over plastic-lined paper towels to catch any spillage. Remove the flip-off plastic seal from the BOTOX® vial. An appropriate amount of diluent (see dilution table below, or for specific instructions for intradetrusor injections for neurogenic detrusor activity, refer to DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION, Neurogenic Detrusor Overactivity) is drawn up into a syringe. The exposed portion of the rubber septum of the vials is cleaned with alcohol (70%) prior to insertion of the needle. Draw up the proper amount of diluent in the appropriate size syringe, and slowly inject the diluent into the vial. Since BOTOX® is denatured by bubbling or similar vigorous agitation, inject the diluent gently into the vial. Discard the vial if a vacuum does not pull the diluent into the vial. Gently mix BOTOX® with the saline by rotating the vial. Record the date and time of reconstitution on the space on the label. BOTOX® should be administered within twenty four hours after reconstitution. This product is for single use only and any unused solution should be discarded. During this time period, reconstituted BOTOX® should be stored in a refrigerator (2 to 8°C). Reconstituted BOTOX® should be clear, colourless and free of particulate matter. Parenteral drug products should be inspected visually for particulate matter and discoloration prior to administration and whenever the solution and the container permit. For safe disposal, unused vials should be reconstituted with a small amount of water and then autoclaved. Any used vials, syringes and spillages etc. should be autoclaved, or the residue BOTOX® inactivated using dilute hypochlorite solution (0.5%) for 5 minutes. **Dilution Tables:** 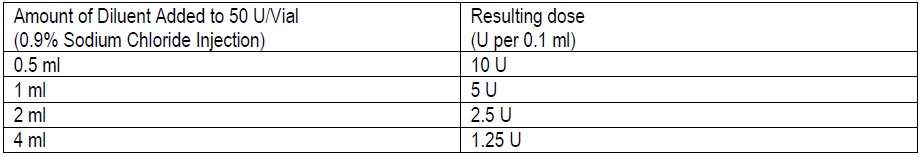 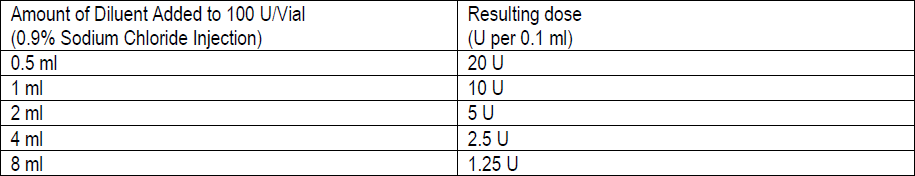 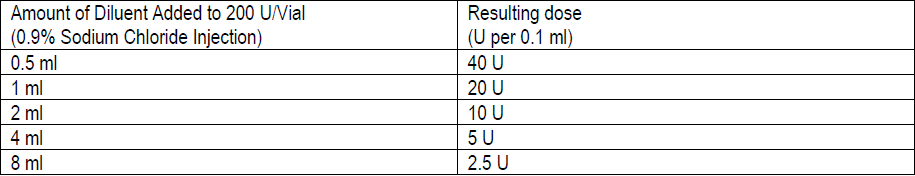 A decrease or increase in the BOTOX® dose is possible by administering a smaller or larger injection volume. **The “unit” by which the potency of preparations of BOTOX® is measured should be used to calculate dosages of BOTOX® only and is not transferable to other preparations of botulinum toxin.** **Doses recommended for BOTOX® are not interchangeable with other preparations of botulinum toxin.** **Blepharospasm:** For blepharospasm, reconstituted BOTOX® (see Dilution Table) is injected using a sterile, 27 – 30 gauge needle with or without electromyographic guidance. The initial recommended dose is 1.25 – 2.5 units in (0.05 – 0.1 mL volume at each site) injected into the medial and lateral orbicularis oculi of the upper lid and into the lateral orbicularis oculi of the lower lid. Injection placement may vary based on the patient’s presentation. Avoiding injection near the levator palpebrae superioris may reduce the complication of ptosis. Avoiding medial lower lid injections and thereby reducing diffusion into the inferior oblique, may reduce the complication of diplopia. Ecchymosis occurs easily in the soft eyelid tissues. This can be prevented by applying pressure at the injection site immediately after the injection. The hazard of ectropion may be reduced by avoiding injection into the lower lid area. In general, the initial effect of the injections is seen within three days and reaches a peak at one to two weeks post-treatment. Each treatment lasts approximately three months, following which the procedure can be repeated indefinitely. At repeat treatment sessions, the dose may be increased up to two-fold if the response from the initial treatment is considered insufficient – usually defined as an effect that does not last longer than two months. However, there appears to be little benefit obtainable from injecting more than 5.0 units per site. The initial dose should not exceed 25 units per eye. Normally no additional benefit is conferred by treating more frequently than every three months. It is rare for the effect to be permanent. In the management of blepharospasm total dosing should not exceed 100 units every 12 weeks. **Hemifacial spasm:** Patients with hemifacial spasm or VIIth nerve disorders should be treated as for unilateral blepharospasm, with other affected facial muscles each being injected as needed. Further injections may be necessary into the corrugator, zygomaticus major, orbicularis oris and/ or other facial muscles according to the extent of the spasm. Electromyographic control may be necessary to identify affected small circumoral muscles. The cumulative dose of BOTOX® for treatment of hemifacial spasm in a 2 month period should not exceed 200 units. **Strabismus:** BOTOX® is intended for injection into extraocular muscles utilizing the electrical activity recorded from the tip of the injection needle as a guide to placement within the target muscle. Injection without surgical exposure or electromyographic guidance should not be attempted. Physicians should be familiar with electromyographic techniques. BOTOX® is ineffective in chronic paralytic strabismus except to reduce antagonist contracture in conjunction with surgical repair. The efficacy of BOTOX® in deviations over 50 prism diopters, in restrictive strabismus, in Duane’s syndrome with lateral rectus weakness, and in secondary strabismus caused by prior surgical over-recession of the antagonist is doubtful. In order to enhance efficacy, multiple injections over time may be required. To prepare the eye for BOTOX® injection, it is recommended that several drops of a local anesthetic and an ocular decongestant be given several minutes prior to injection. Note: The recommended volume of BOTOX® injected for treatment of strabismus is 0.05 mL to 0.15 mL per muscle. 1. Initial doses in units (abbreviated as U). Use the lower listed doses for treatment of small deviations. Use the larger doses only for large deviations. 1. For vertical muscles, and for horizontal strabismus of less than 20 prism diopters: 1.25 units to 2.5 units in any one muscle. 2. For horizontal strabismus of 20 prism diopters to 50 prism diopters: 2.5 units to 5.0 units in any one muscle. 3. For persistent VIIth nerve palsy of one month or longer duration: 1.25 units to 2.5 units in the medial rectus muscle. 2. Subsequent doses for residual or recurrent strabismus. 1. It is recommended that patients be re-examined 7–14 days after each injection to assess the effect of that dose. 2. Patients experiencing adequate paralysis of the target muscle that require subsequent injections should receive a dose comparable to the initial dose. 3. Subsequent doses for patients experiencing incomplete paralysis of the target muscle may be increased up to two-fold compared to the previously administered dose. 4. Subsequent injections should not be administered until the effects of the previous dose have dissipated as evidenced by substantial function in the injected and adjacent muscles. 5. The maximum recommended dose as a single injection for any one muscle is 25 units. The initial listed doses of the reconstituted BOTOX® (see previous Dilution Table) typically create paralysis of injected muscles beginning one to two days after injection and increasing in intensity during the first week. The paralysis lasts for 2 to 6 weeks and gradually resolves over a similar time period. Over-corrections lasting over six months have been rare. About one-half of patients will require subsequent doses because of inadequate paralytic response of the muscle to the initial dose, or because of mechanical factors such as large deviations or restrictions, or because of the lack of binocular motor fusion to stabilize the alignment. **Spasmodic torticollis (cervical dystonia):** Dosing must be tailored to the individual patient based on the patient’s head and neck position, localization of pain, muscle hypertrophy, patient’s bodyweight, and patient response. A 25, 27 or 30 gauge needle may be used for superficial muscles, and a 22 gauge needle may be used for deeper musculature. For cervical dystonia, localization of the involved muscles with electromyographic guidance may be useful. In initial controlled clinical trials to establish safety and efficacy for cervical dystonia, doses of reconstituted BOTOX® ranged from 140 to 280 units. In more recent studies, the doses have ranged from 95 to 360 units (with an approximate mean of 240 units). As with any drug treatment, initial dosing in a naïve patient should begin at the lowest effective dose. The treatment of cervical dystonia typically may include, but is not limited to, injection of BOTOX® into the sternocleidomastoid, levator scapulae, scalene, splenius capitis, and/or the trapezius muscle(s). In general, a total dose of 6 units/kg every two months should not be exceeded for treatment of cervical dystonia. Diluted BOTOX® is injected using an appropriately sized needle (usually 25, 27 or 30 gauge). The table below is intended to give dosing guidelines for injection of BOTOX® in the treatment of cervical dystonia: 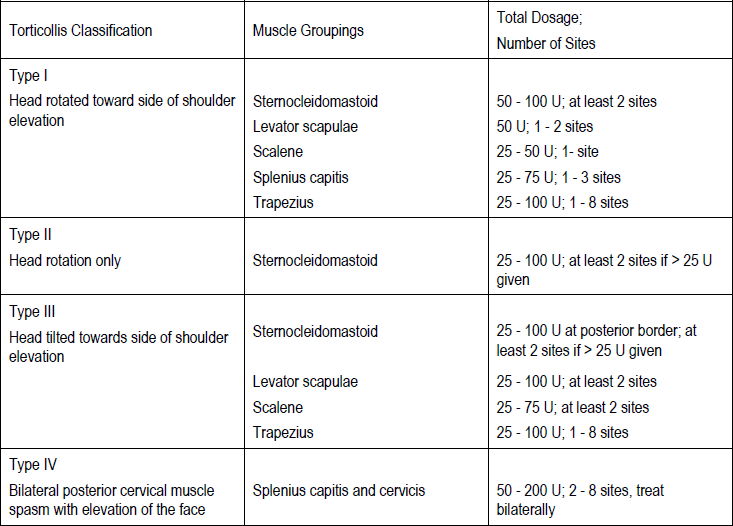 This information is provided as guidance for the initial injection. The extent of muscle hypertrophy and the muscle groups involved in the dystonic posture may change with time necessitating alterations in the dose of toxin and muscles to be injected. The exact dosage and sites injected must be individualised for each patient. In case of any difficulty in isolating the individual muscles, injections should be made under electromyographic assistance. No more than 50 units should be given at any one site. Limiting the dose injected into the sternocleidomastoid muscle to less than 100 units may decrease the occurrence of dysphagia. (See Precautions – _please refer to the Product Insert/Patient Information Leaflet published on HSA for the full drug information_.) To minimise the incidence of dysphagia, the sternocleidomastoid should not be injected bilaterally. The concentrations of reconstituted material needed are 5 units/ 0.1 mL and 10 units/ 0.1 mL to allow reasonable injection volumes. The table below shows the median dose of BOTOX® injected per muscle in a clinical study in which dose was determined by the practitioner based on the presentation of the individual cervical dystonia patient. 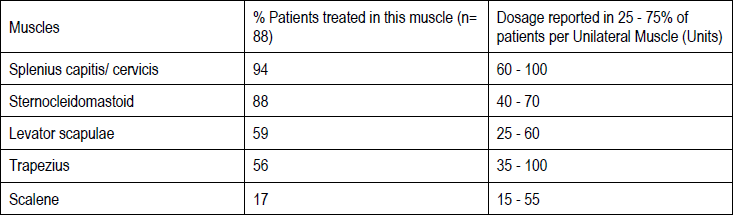 Multiple injection sites allow BOTOX® to have more uniform contact with the innervation areas of the dystonic muscle and are especially useful in larger muscles. The optimal number of injection sites is dependent upon the size of the muscle to be chemically denervated. Clinical improvement generally occurs within the first two weeks after injection. The maximum clinical benefit generally occurs approximately six weeks post-injection. Repeat doses should be administered when the clinical effect of a previous injection diminishes. The duration of therapeutic effect reported in the clinical trials showed substantial variation (from 2 to 32 weeks), with a typical duration of approximately 12 to 16 weeks, depending on the patient’s individual disease and response. “Booster” injections are not recommended. Dosing intervals should not be more often than every two months. **Paediatric cerebral palsy:** For the treatment of equinus due to spasticity in paediatric cerebral palsy, diluted BOTOX® is injected using a sterile 23–26 gauge needle. In clinical trials, doses of 4 units/kg were administered by injecting BOTOX® into each of two sites in the medial and lateral heads of the gastrocnemius muscle of the affected lower limb(s). Following initial injection to the gastrocnemius muscle, further involvement of the anterior or posterior tibialis may need to be considered for additional improvement in the foot position at heel strike and during standing. Clinical gait improvement generally begins within the first two weeks after injection, with further improvement over the next several weeks. Repeat doses should be administered when the clinical effect of a previous injection diminishes but not more frequently than every two months. The average duration of the therapeutic effect reported in an open-label clinical trial of 207 patients was 3.1 to 3.6 months. In this study, the dose was 4 units/kg, up to a maximum of 200 units at any single treatment session. **Focal Spasticity in Adults:** The exact dosage and number of injection sites should be tailored to the individual based on the size, number and location of muscles involved, the severity of spasticity, presence of local muscle weakness, and the patient response to previous treatment. The recommended dilution is 200 Units/4 mL or 100 Units/2 mL with preservative-free 0.9% Sodium Chloride Injection (see Dilution Tables). A 25, 27 or 30 gauge sterile needle may be used for superficial muscles, and a 22-gauge needle may be used for deeper musculature. For focal spasticity, localization of the involved muscles with electromyographic guidance or nerve stimulation techniques may be useful. Multiple injection sites allow BOTOX® to have more uniform contact with the innervation areas of the muscle and are especially useful in larger muscles. If it is deemed appropriate by the treating physician, repeat BOTOX® treatment may be administered when the effect of a previous injection has diminished, but generally no sooner than 12 weeks after the previous injection. The degree and pattern of muscle spasticity at the time of re-injection may necessitate alterations in the dose of BOTOX® and muscles to be injected. _**Upper Limb Spasticity**_ In clinical trials, the doses did not exceed 360 units divided among selected muscles (typically in the flexor muscles of the elbow, wrist and fingers) at any treatment session. Clinical improvement in muscle tone generally occurs within two weeks following treatment with the peak effect seen four to six weeks following treatment. In clinical studies, patients were reinjected at 12 to 16 week intervals. The table below is intended to give dosing guidelines for injection of BOTOX® in the treatment of upper limb spasticity associated with stroke. 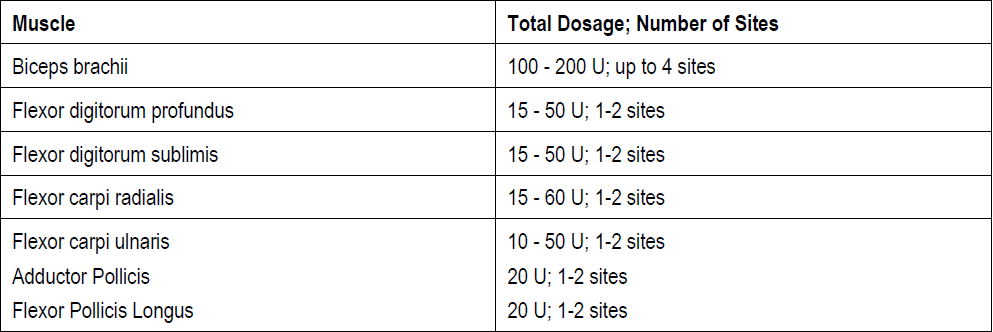 **_Lower Limb Spasticity_** The recommended dose for treating lower limb spasticity is 300 Units to 400 Units divided among affected muscles (see table and figure below). **BOTOX® Dosing by Muscle for Lower Limb Spasticity** 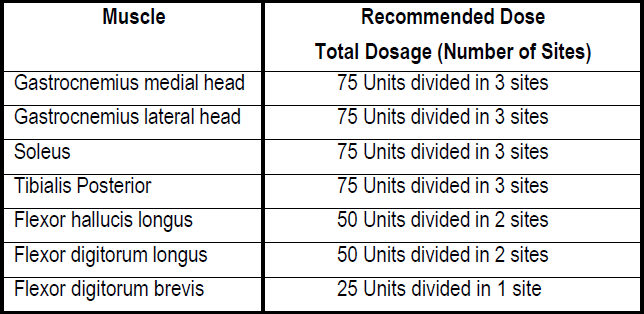 **Injection Sites for Lower Limb Spasticity** 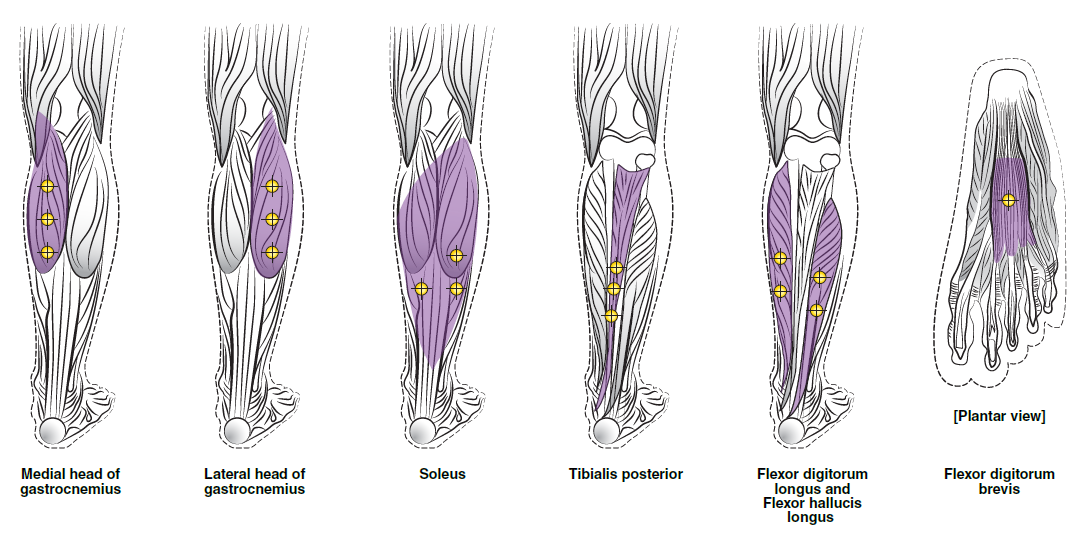 **Hyperhidrosis of the Axillae:** The hyperhidrotic area to be injected may be defined using standard staining techniques, e.g. Minor’s iodine-starch test. BOTOX® is reconstituted with 0.9% non-preserved sterile saline (100 units/4.0 mL). The recommended dose is 50units per axillae. Using a 30 gauge needle, 50 units (2.0 mL) is injected intradermally, in 0.1 to 0.2 mL aliquots to each axillae evenly distributed in multiple sites (10 to 15) approximately 1–2 cm apart. At week 1 BOTOX® treated patients demonstrated 95% treatment responder rate based on gravimetric assessment. At 16 weeks 82% of BOTOX® treated patients were responding to treatment. When patients received at least 2 consecutive treatments with BOTOX® the mean time to re-treatment following their first treatment was 33 weeks (range 15 to 51 weeks). Repeat injections for axillary hyperhidrosis should be administered when effects from previous injections subside but usually not more frequently than every four months. **Upper Facial Lines (Glabellar Lines, Crow’s Feet Lines, Forehead Lines):** As optimum dose levels and number of injection sites per muscle may vary among patients, individual dosing regimen should be drawn up. The recommended injection volume per injection site is 0.1 mL. **Dilution Instructions for BOTOX® Upper Facial Lines (100 Units and 50 Units)** 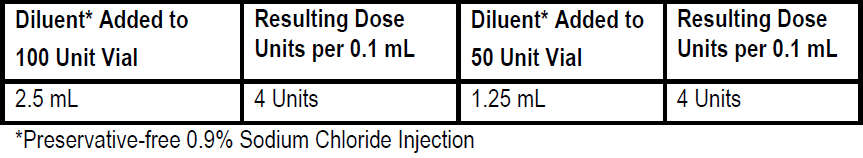 **_Glabellar Lines:_** BOTOX® is reconstituted with 0.9% sterile non-preserved saline (100 units in 2.5 mL or injected as 4 units/0.1 mL) and 0.1 mL is administered using a 30 gauge needle in each of 5 sites (see figure below), 2 in each corrugator muscle and 1 in the procerus muscle for a total dose of 20 units (see dilution table under _Upper Facial Lines (Glabellar Lines, Crow’s Feet, Forehead Lines)_). 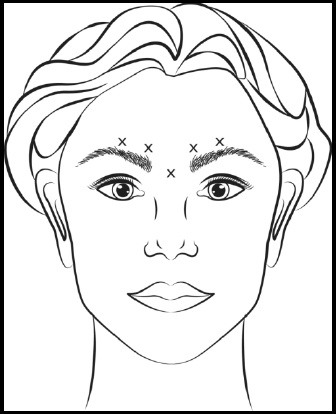 In order to reduce the complication of ptosis, avoid injection near the levator palpebrae superioris, particularly in patients with larger brow-depressor complexes. Medial corrugator injections should be placed at least 1 cm above the bony supraorbital ridge. In controlled clinical trials, improvement of severity of glabellar lines generally occurred within one week after treatment and the effect was demonstrated for up to 4 months. Typically the initial doses of reconstituted BOTOX® induce chemical denervation of the injected muscles one to two days after injection, increasing in intensity during the first week. Injection intervals should be no more frequent than every 3 months and should be performed using the lowest effective dose. Treatment with BOTOX® for cosmetic purposes may result in the formation of antibodies that may reduce the effectiveness of subsequent treatments with BOTOX® for glabellar lines or for other indications. **Crow’s Feet Lines:** BOTOX® should be injected bilaterally at 3 sites in the lateral aspect of the orbicularis oculi (i.e. total of 6 injections), where most lines are seen when a smile is forced. In general, 2–6 units is recommended per injection site at a 2–3 mm depth, for a total dose of 6–18 units per side. (see dilution table under _Upper Facial Lines (Glabellar Lines, Crow’s Feet, Forehead Lines)_). Injections should be at least 1 cm outside the bony orbit, not medial to the vertical line through the lateral canthus and not close to the inferior margin of the zygoma. **Forehead Lines:** Inject 4 Units (0.1mL) of reconstituted BOTOX® into 5 sites in the frontalis muscle, for a total of 20 Units (0.5mL). Treat forehead lines in conjunction with glabellar lines (see Glabellar Lines Administration) to minimize the potential for brow ptosis. The recommended total dose for treatment of forehead lines (20 Units \[0.5mL\]) in conjunction with glabellar lines (20 Units \[0.5mL\]) is 40 Units (1mL). When identifying the location of the appropriate injection sites in the frontalis muscle, assess the overall relationship between the size of the patient’s forehead, and the distribution of frontalis muscle activity. Locate the following horizontal treatment rows by light palpation of the forehead at rest and maximum eyebrow elevation: - Superior Margin of Frontalis Activity: approximately 1 cm above the most superior forehead crease - Lower Treatment Row: midway between the superior margin of frontalis activity and the eyebrow, at least 2 cm above the eyebrow - Upper Treatment Row: midway between the superior margin of frontalis activity and lower treatment row Place the 5 injections at the intersection of the horizontal treatment rows with the following vertical landmarks (see Figure below): - On the lower treatment row at the midline of the face, and 0.5 – 1.5 cm medial to the palpated temporal fusion line (temporal crest); repeat for the other side. - On the upper treatment row, midway between the lateral and medial sites on the lower treatment row; repeat for the other side. 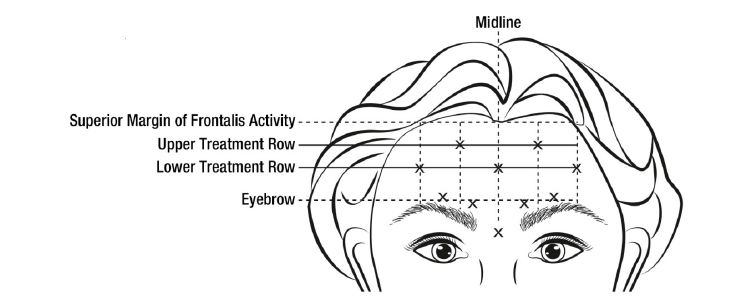 For simultaneous treatment with Crows’ Feet lines, the total dose is 64 Units, comprised of 20 Units for forehead lines, 20 Units for glabellar lines, and 24 Units for Crows’ Feet lines (see Crows’ Feet Lines Administration). Improvement in the severity of forehead lines seen at maximum eyebrow elevation occurred within one week of treatment. The time to retreatment of BOTOX® for forehead lines is approximately 4 months. The safety and effectiveness of dosing with BOTOX® more frequently than every 3 months have not been clinically evaluated. **Chronic Migraine:** The recommended dilution is 100 Units/2mL, with a final concentration of 5 Units per 0.1mL. The recommended dose for treating chronic migraine is 155 units to 195 units administered intramuscularly (IM) using a sterile 30-gauge, 0.5 inch needle as 0.1 ml (5 units) injections per each site. Injections should be divided across 7 specific head/neck muscle areas as specified in the diagrams and table below. A 1 inch needle may be needed in the neck region for patients with thick neck muscles. With the exception of the procerus muscle, which should be injected at 1 site (midline), all muscles should be injected bilaterally with the minimum dose per muscle as indicated below, with half the number of injection sites administered to the left, and half to the right side of the head and neck. The recommended re-treatment schedule is every 12 weeks. If there is a predominant pain location(s), additional injections to one or both sides may be administered in up to 3 specific muscle groups (occipitalis, temporalis, and trapezius), up to the maximum dose per muscle as indicated in the table below. The following diagrams indicate the **injection sites:** 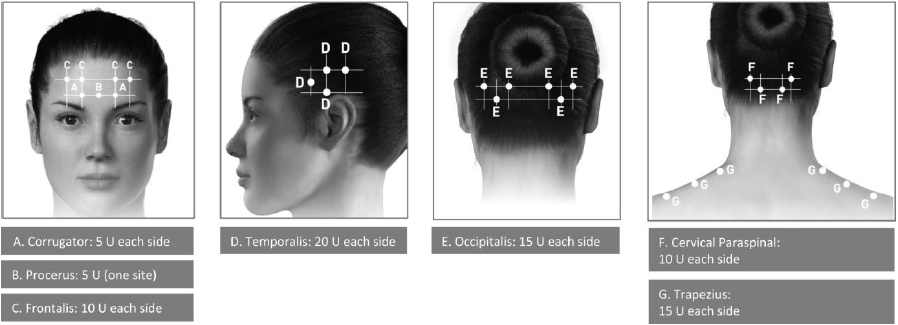 **BOTOX® Dosing By Muscle for Chronic Migraine** 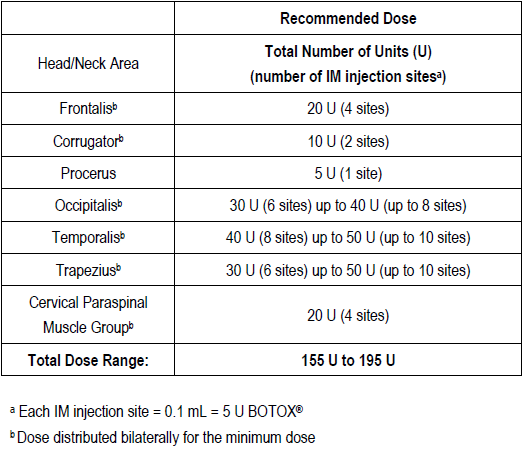 **Bladder Dysfunction (Overactive Bladder and Neurogenic Detrusor Overactivity):** Patients should not have a urinary tract infection prior to treatment. Prophylactic antibiotics (except aminoglycosides, see DRUG INTERACTIONS – _please refer to the Product Insert/Patient Information Leaflet published on HSA for the full drug information_) should be administered 1–3 days pre-treatment, on the treatment day, and 1–3 days post-treatment. It is generally recommended that patients discontinue anti-platelet therapy at least three days before the injection procedure. Patients on anti-coagulant therapy need to be managed appropriately to decrease the risk of bleeding. _Overactive Bladder_ An intravesical instillation of diluted local anesthetic with or without sedation may be used prior to injection, per local site practice. If a local anesthetic instillation is performed, the bladder should be drained and irrigated with sterile saline before injection. The recommended dose is 100 Units of BOTOX®. The recommended dilution is 100 Units/10 mL with 0.9% non-preserved saline solution (see dilution table). Dispose of any unused saline. Reconstituted BOTOX® (100 Units/10 mL) is injected into the detrusor muscle via a flexible or rigid cystoscope, avoiding the trigone. The bladder should be instilled with enough saline to achieve adequate visualization for the injections, but over-distension should be avoided. The injection needle should be filled (primed) with approximately 1 mL of reconstituted BOTOX® prior to the start of injections (depending on the needle length) to remove any air. The needle should be inserted approximately 2 mm into the detrusor, and 20 injections of 0.5 mL each (total volume of 10 mL) should be spaced approximately 1 cm apart (see figure below). For the final injection, approximately 1 mL of sterile normal saline should be injected so the full dose is delivered. After the injections are given, the saline used for bladder wall visualization should not be drained so that patients can demonstrate their ability to void prior to leaving the clinic. The patient should be observed for at least 30 minutes post-injection and until a spontaneous void has occurred. Clinical improvement may occur within 2 weeks. Patients should be considered for reinjection when the clinical effect of the previous injection has diminished (median duration in phase 3 clinical studies was 166 days \[~24 weeks\]), but no sooner than 3 months from the prior bladder injection. Based on patients who received treatments with only BOTOX® 100 Units from the pivotal studies through the open label extension study (N=438), the overall median duration of response was ~212 days (~30 weeks).195 **Injection Pattern for Overactive Bladder and Neurogenic Detrusor Overactivity** 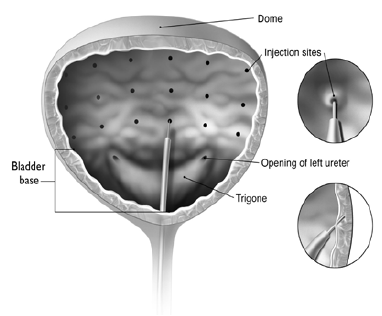 _Neurogenic Detrusor Overactivity_ An intravesical instillation of diluted local anesthetic with or without sedation, or general anesthesia may be used prior to injection, per local site practice. If a local anesthetic instillation is performed, the bladder should be drained and irrigated with sterile saline before injection. The recommended dose is 200 Units of BOTOX®. _Reconstitution of 200 Unit Vial_ Reconstitute a 200 Unit vial of BOTOX® with 6 mL of 0.9% non-preserved saline solution and mix the vial gently. Draw 2 mL from the vial into each of three 10 mL syringes. Complete the reconstitution by adding 8 mL of 0.9% non-preserved saline solution into each of the 10 mL syringes, and mix gently. This will result in three 10 mL syringes each containing 10 mL (~67 Units in each), for a total of 200 Units of reconstituted BOTOX®. Use immediately after reconstitution in the syringe. Dispose of any unused saline. _Reconstitution of 100 Unit Vial_ Reconstitute two 100 Unit vials of BOTOX®, each with 6 mL of 0.9% non-preserved saline solution and mix the vials gently. Draw 4 mL from each vial into each of two 10 mL syringes. Draw the remaining 2 mL from each vial into a third 10 mL syringe. Complete the reconstitution by adding 6 mL of 0.9% non-preserved saline solution into each of the 10 mL syringes, and mix gently. This will result in three 10 mL syringes each containing 10 mL (~67 Units in each), for a total of 200 Units of reconstituted BOTOX®. Use immediately after reconstitution in the syringe. Dispose of any unused saline. _Reconstitution of 50 Unit Vial_ **It is recommended that a 200 Unit vial or two 100 Unit vials are used for convenience of reconstitution.** Reconstitute four 50 Unit vials of BOTOX®, each with 3 mL of 0.9% non-preserved saline solution and mix the vials gently. Draw 3 mL from the first vial and 1 ml from the second vial into one 10 ml syringe. Draw 3 ml from the third vial and 1 ml from the fourth vial into a second 10 ml syringe. Draw the remaining 2 ml from the second and fourth vials into a third 10 ml syringe. Complete the reconstitution by adding 6 mL of 0.9% non-preserved saline solution into each of the three 10 mL syringes, and mix gently. This will result in three 10 mL syringes containing a total of 200 Units of reconstituted BOTOX®. Use immediately after reconstitution in the syringe. Dispose of any unused saline. _Administration_ Reconstituted BOTOX® (200 Units/30 mL) is injected into the detrusor muscle via a flexible or rigid cystoscope, avoiding the trigone. The bladder should be instilled with enough saline to achieve adequate visualization for the injections, but over-distension should be avoided. The injection needle should be filled (primed) with approximately 1 mL prior to the start of injections (depending on the needle length) to remove any air. The needle should be inserted approximately 2 mm into the detrusor, and 30 injections of 1mL each (total volume of 30 mL) should be spaced approximately 1 cm apart (see Figure above). For the final injection, approximately 1 mL of sterile normal saline should be injected so the full dose is delivered. After the injections are given, the saline used for bladder wall visualization should be drained. The patient should be observed for at least 30 minutes post-injection. **Clinical improvement may occur within 2 weeks. Patients should be considered for reinjection when the clinical effect of the previous injection diminished (median duration in phase 3 clinical studies was 256–295 days (36–42 weeks) for BOTOX® 200 Units), but no sooner than 3 months from the prior bladder injection. Based on patients who received treatments with only BOTOX® 200 Units from the pivotal studies through the open label extension study (N=174), the overall median duration of response was 253 days (~36 weeks). The safety and efficacy data beyond two intradetrusor treatments are limited.**
SUBCUTANEOUS, INTRAMUSCULAR, INTRADERMAL
Medical Information
**2\. USES** BOTOX® is indicated for the treatment of blepharospasm associated with dystonia, including benign essential blepharospasm, hemifacial spasm or VIIth nerve disorders in patients 12 years or older. BOTOX® is indicated for the correction of strabismus in patients 12 years of age or older. BOTOX® is indicated for the treatment of spasmodic torticollis (cervical dystonia) in adults. BOTOX® is indicated for the treatment of dynamic equinus foot deformity due to spasticity in paediatric cerebral palsy patients, two years of age or older. BOTOX® is indicated in the management of focal spasticity, of the upper limbs associated with stroke in adults. BOTOX® is indicated in the management of focal spasticity, of the lower limbs associated with stroke in adults. BOTOX® is indicated for the treatment of severe, primary axillary hyperhidrosis that is inadequately managed by topical agents. The objective of treatment is to reduce sweating to a physiologically normal level which patients find tolerable. Anhidrosis is not the target. BOTOX® is indicated for the temporary treatment of glabellar lines associated with corrugator and/or procerus muscle activity and crow’s feet associated with orbicularis oculi muscle activities in adult patients below 65 years of age. BOTOX® is indicated for the temporary improvement in the appearance of moderate to severe forehead lines in adults. BOTOX® is indicated for the prophylaxis of headaches in adults with chronic migraine (headaches on at least 15 days per month of which at least 8 days are with migraine). BOTOX® is indicated for the treatment of overactive bladder with symptoms of urinary incontinence, urgency, and frequency, in adults who have an inadequate response to or are intolerant of an anticholinergic medication. BOTOX® is indicated for the treatment of urinary incontinence due to neurogenic detrusor overactivity e.g., spinal cord injury (SCI) or multiple sclerosis (MS) in adults who have an inadequate response to or are intolerant of anticholinergic medications.
**Contra-indications:** BOTOX® is contra-indicated, a) in individuals with a known hypersensitivity to botulinum toxin type A or any constituent of the formulation; b) in patients with myasthenia gravis or Lambert-Eaton Syndrome. BOTOX® is contraindicated in the presence of infection at the proposed injection site(s). The recommended dosages and frequencies of administration of BOTOX® should not be exceeded. BOTOX® for treatment of bladder dysfunction is also contraindicated: - in patients who have a urinary tract infection - in patients with acute urinary retention who are not routinely performing clean intermittent self-catheterization (CIC).
M03AX01
botulinum toxin
Manufacturer Information
ABBVIE PTE. LTD.
Allergan Pharmaceuticals Ireland
Active Ingredients
Documents
Package Inserts
Botox Powder For Solution For Injection PI.pdf
Approved: January 27, 2023
