Regulatory Information
HSA regulatory responsibility and product classification details
Regulatory Responsibility
Product Classification
Formulation Information
INJECTION, SOLUTION
**4.2 Posology and method of administration** Diagnosis and therapy with somatropin should be initiated and monitored by physicians who are appropriately qualified and experienced in the diagnosis and management of patients with the therapeutic indication of use. Posology _Paediatric population_ The posology and administration schedule should be individualized. Growth disturbance due to insufficient secretion of growth hormone in children: Generally a dose of 0.025–0.035 mg/kg body weight per day or 0.7–1.0 mg/m2 body surface area per day is recommended. Even higher doses have been used. Growth disturbance due to Turner syndrome: A dose of 0.045 – 0.050 mg/kg body weight per day or 1.4mg/m2 body surface area per day is recommended. Dosage recommendations for Paediatric Patients 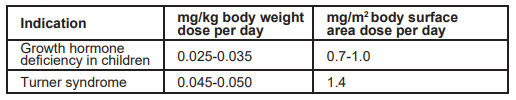 Treatment should not be used in children with a growth velocity less than 1 cm per year and near closure of epiphyses. _Growth hormone deficient adult patients_ Therapy should start with a low dose, 0.15 – 0.3 mg per day. The dose should be gradually increased according to individual patient requirements as determined by the IGF-I concentration. Treatment goal should be insulin-like growth factor (IGF-I) concentrations within 2 SDS from the age corrected mean of healthy adults. Patients with normal IGF-I concentrations at the start of the treatment should be administered growth hormone up to an IGF-I level into upper range of normal, not exceeding the 2 SDS. Clinical response and side effects may also be used as guidance for dose titration. The daily maintenance dose seldom exceeds 1.0 mg per day. Woman may require higher dose than men, while men showing an increasing IGF-I sensitivity over time. This means that there is a risk that women, especially those on oral oestrogen replacement are under-treated while men are over-treated. The accuracy of the growth hormone dose should therefore be controlled every 6 months. As normal physiological growth hormone production decreases with age, dose requirements may be reduced. The minimum effective dose should be used. Method of administration The injection should be given subcutaneously and the site varied to prevent lipoatrophy. For instructions for use and handling see section 6.6 – _please refer to the Product Insert/Patient Information Leaflet published on HSA for the full drug information_.
SUBCUTANEOUS
Medical Information
**4.1 Therapeutic indications** Children Growth disturbance due to insufficient secretion of growth hormone (growth hormone deficiency, GHD). Growth disturbance associated with Turner syndrome. Adults Replacement therapy in adults with pronounced growth hormone deficiency. Patients with severe growth hormone deficiency in adulthood are defined as patients with known hypothalamic pituitary pathology and at least one known deficiency of pituitary hormone not being prolactin. These patients should undergo a single dynamic test in order to diagnose or exclude a growth hormone deficiency. In patients with childhood onset isolated GH deficiency (no evidence of hypothalamic-pituitary disease or cranial irradiation), two dynamic tests should be recommended, except for those having low IGF-I concentrations (SDS < -2) who may be considered for one test. The cut-off point of the dynamic test should be strict.
**4.3 Contraindications** Hypersensitivity to the active substance or to any of the excipients listed in section 6.1 – _please refer to the Product Insert/Patient Information Leaflet published on HSA for the full drug information_. Somatropin must not be used when there is any evidence of activity of a tumour. Intracranial tumours must be inactive and anti-tumour therapy must be completed prior to starting GH therapy. Treatment should be discontinued if there is evidence of tumour growth. Somatropin must not be used for growth promotion in children with closed epiphyses. Somatropin should not be used in children with PWS and a corresponding severe respiratory disorder or severe obesity. Patients with acute critical illness suffering complications following open heart surgery, abdominal surgery, multiple accidental trauma, acute respiratory failure or similar conditions must not be treated with somatropin. In new-borns, SciTropin A 5mg/1.5mL Solution for Injection should not be used because of the presence of the preservative, benzyl alcohol.
H01AC01
somatropin
Manufacturer Information
SciGen Pte Ltd.
Sandoz GmbH (Shaftenau Plant)
